Unit III
Formulation of strategy
Strategy is the basis for all decisions that must be made within an organization. If the strategy is not properly selected and formulated by top management, it will have a significant impact on the effectiveness of employees in almost every department within the organization. In article on "What is Strategy," I tried to define and explain what a business strategy refers to and what is not considered part of the strategy. In this article, we will analyze your strategy in three different components or at the "strategy level". These three levels are enterprise-level strategy, business-level strategy, and functional-level strategy. These three levels of strategy can be combined and described in the so-called “strategic pyramid” (Figure 1). Corporate strategy is not same from business and effective strategy. Corporate-level strategy is at the top of the pyramid, but this article starts by discussing business-level strategy.
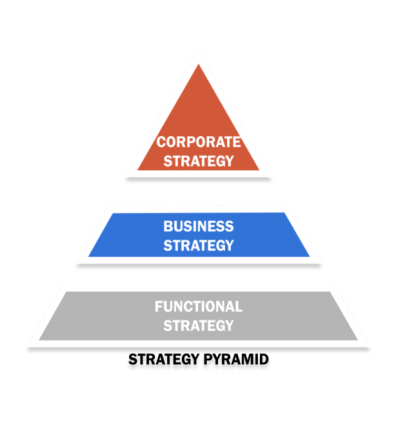
Figure 1. Strategic Pyramid
Business-level strategy
Business-level strategies are familiar to most people and are "how to compete" and "how to gain a (sustainable) competitive advantage over rivals." Is about the question. To answer these questions, it is important to first have a good understanding of your business and its external environment. At this level, you can use internal analysis frameworks such as value chain analysis and VRIO models, and external analysis frameworks such as Porter's Five Forces analysis and PESTEL analysis. A good strategic analysis allows top management to proceed with strategy development by using the framework as a general strategy for value areas, blue ocean strategies, and porters. After all, business-level strategies aim to gain a competitive advantage by providing real value to customers while being a unique and difficult-to-mimic player in a competitive environment.
Functional level strategy
Functional-level strategies relate to the question, "How do you support business-level strategies within functional departments such as marketing, human resources, production, and R & D?" Within these departments, workers often refer to "marketing strategies," "personnel strategies," or "R & D strategies." The goal is to align these strategies with larger business strategies as closely as possible. For example, if your business strategy is aimed at delivering products to students and young adults, the marketing department will make these people as accurate as possible through marketing campaigns by choosing the right (social) media channels. Must be targeted. Technically, these decisions are so functional in nature that they are not part of the strategy. As a result, it's better to call them tactics rather than strategies.
Corporate level strategy
However, corporate-level strategies require management to consider not only how to gain a competitive advantage in each business area in which the company operates, but also which business it should participate in in the first place. It's about choosing the best set of businesses and deciding how to integrate them into your entire enterprise, your portfolio. Key investment and sale decisions are typically made at this level by top management. M & A (M & A) is also an important part of corporate strategy. This level of strategy allows a company to operate in more than one business area through different business units with different business level strategies that need to be coordinated to form a consistent company-level strategy within the company. Only needed if you are doing. As a result, corporate strategies are often found in multinational corporations (MNEs) or conglomerates rather than small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Samsung example
Let's use Samsung as an example. Samsung is a conglomerate of multiple Strategic Business Units (SBUs) with diverse product sets. Samsung sells smartphones, cameras, TVs, microwave ovens, refrigerators, washing machines, as well as chemicals and insurance. Each product or strategic business unit requires a business strategy to succeed within its own industry. But at the corporate level, Samsung needs to decide on more fundamental questions, such as "Are you pursuing the camera business in the first place?" Or, "Should we invest more in the smartphone business or should we focus on the TV screen business?" Both the BCG Matrix and the GE McKinsey Matrix are portfolio analysis frameworks that you can use as a tool to understand this.
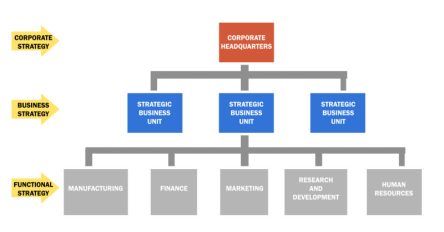
Figure 2: Hierarchy of Strategy
Total strategy level
The most common level of strategy is business strategy, which exists within a strategic business unit with the goal of gaining a competitive advantage in a particular market. If your company has multiple SBUs, you need a comprehensive corporate strategy that connects all the SBUs through your enterprise structure. Here, top management must do decide where to allocate resources, invest in, and sell. Finally, functional strategies exist within departments such as marketing, HR, and production. Ideally, due to the operational nature of the decisions made within these departments, we should refer to tactics rather than strategies.
Key takeaways:
Concept of business environment
You can start a business, but you need financial resources, such as finance, that you have to rely on financial institutions to succeed. Acceptance of social norms that must depend on society. Appropriate market conditions that must depend on the market. Sale of products / services that must be customer dependent. Labor that must depend on society.
Then there are natural resources and raw materials, which must depend on nature. Also, government legal support that must depend on the government. There are many factors and aspects that affect the business environment. These factors are many different components of a single concept called the business environment.
These business-dependent factors aren't stopped, they're very dynamic and constantly changing. For example, the trend, the Fidget Spinner trend, has provided the greatest impetus for the silicone mold industry to date.
The changing needs of customers and new innovations in the market are part of the business environment. The challenge for companies in this tech era is not to enter the market, but to survive in the market. Surviving the market means adapting to change as soon as possible. Adapting to change means being aware of the business environment.
Meaning of business environment
The power to compose a business environment is its suppliers, competitors, consumer groups, media, governments, customers, economic conditions, market conditions, investors, technologies, trends, and several other institutions operating outside the business. Makes up the business environment. These forces affect your business, even when it's outside the boundaries of your business.
For example, government tax changes can reduce customer purchases. Here, businesses need to reestablish prices to survive change. The business was not involved in initiating the change, but had to adapt to the change in order to survive or take advantage of profitable opportunities. Now let's talk about the importance of the business environment.
Components of Business Environment
Andrews also correctly defines the company's environment as a pattern of all external influences that affect the life and development of the company. Keith Davis also states that the business environment is a collection of all the conditions, events and impacts that surround and influence it.
The business environment is constantly changing and uncertain. For this reason, the business environment is said to be the sum of all factors outside the control of the company's management. These factors are constantly changing and involve both opportunities and risks, or uncertainties. Undermine the future of business.
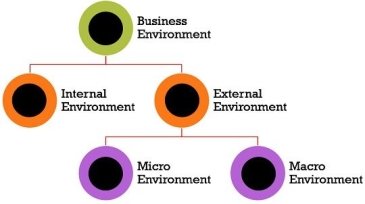
Some of the components of the business environment are: ---
A. Internal environment – 1. Financial ability 2. Marketing ability 3. Operational ability 4. Human resources ability 5. General management ability
B. External environment – 1. Micro environment 2. Macro environment.
In addition, you will learn about other components of the business environment:
1. Economic environment 2. Technical environment 3. Social environment 4. Demographic environment 5. Political and legal environment 6. Global environment.
Business environment components: internal and external environment
Business Environment Components – Two Key Components: Internal and External
Component # 1. Internal environment:
This refers to all factors within an organization that affect the functioning of the organization. These factors are generally considered controllable. That is, the organization can change or change such factors.
Some of the important internal factors are:
I. Financial capacity:
Financial capacity factors relate to all relevant aspects related to the availability of funds, usage, management, and the capacity of an organization and its ability to implement its strategy.
Some of the key factors that affect an organization's financial strength are:
(A) Related to funding sources such as capital structure, capital raising, financing patterns, working capital availability, borrowing, capital and credit availability, reserves and surpluses, relationships with banks and financial institutions Factor.
(B) Factors related to the use of funds such as capital investment, acquisition of fixed assets, current assets, loans, distribution of dividends and relationships with shareholders.
(C) Factors related to cash management such as financial accounting and budgeting, business management systems, financial position, cash, inflation, credit, returns and risk management, cost reduction and management, tax planning and management.
II. Marketing ability:
Marketing capability factors relate to the ability to price, promote, distribute, and implement organizational strategies for a product or service and all relevant aspects related to that capability.
Some of these key factors that influence this marketing ability of an organization are:
(A) Product-related factors such as variety, differentiation, mixed quality, and positioning package.
(B) Price-related factors such as pricing objectives, policies, changes and protection benefits.
(C) Promotion-related elements such as sales promotion tools, sales promotion, advertising, and public relations.
(D) Integrated and systematic elements such as marketing mix, distribution system, market position, corporate image, marketing organization, marketing system, marketing management, information system.
III. Operational capacity:
Operational capacity factors relate to all relevant aspects related to the production of a product or service, the use of critical resources, and the ability of an organization to implement its capabilities and strategies.
Some of these key factors that influence this marketing ability of an organization are:
(A) Product-related factors such as variety, differentiation, mixed quality, and positioning package.
(B) Price-related factors such as pricing objectives, policies, changes and protection benefits.
c) Promotional elements such as promotional tools, promotions, advertising and public relations.
(D) Integrated and systematic elements such as marketing mix, distribution system, market position, corporate image, marketing organization, marketing system, marketing management, information system.
IV. Personnel ability:
The HR capacity factor is related to the existence and use of human resources and skills, and all relevant aspects related to the ability and ability to implement an organization's strategy.
Some of the key factors that affect an organization's human capabilities are:
(A) Factors related to the HR system, such as systems for selection, development, compensation, communication and evaluation of personnel plans, the location of HR departments within the organization, procedures and standards.
(B) Factors related to organizational and employee characteristics, such as corporate image, quality of managers, staff and workers, awareness of the employer's organizational image, availability of employee development opportunities, and working conditions.
(C) Factors related to labor relations such as trade unions – management relations, collective bargaining, safety, welfare and safety, employee satisfaction and morale, etc.
General management functions:
V. General management functions relate to the integration, coordination, and direction of functional functions towards a common goal and all relevant aspects related to the ability of an organization to implement its strategy.
Some of the key factors that affect an organization's general management capabilities are:
(A) General such as strategic management system, mission-related process, purpose and purpose setting, strategy formulation and implementation mechanism, strategic evaluation system, management information system, corporate planning system, top manager compensation and incentive system, etc. Elements related to the management system, etc.
(B) Factors related to general managers such as orientation and risk — trends, values, norms, personal goals, abilities, work abilities, achievements, balance of functional experience, etc.
Component # 2. External environment:
The external environment consists of all the factors that provide an opportunity or pose a threat to an organization. In a broad sense, the external environment includes various factors such as the international economy, the domestic economy, and the regional economy. Social change, demographic variables, political systems, technology, business attitudes, energy sources, raw materials, other resources, and many other macro-level factors make up the external environment.
Such a wide range of environmental awareness can be called a general environment. All organizations are somehow interested in the general environment, but their immediate concerns are limited to some of the common environments that may be referred to as relevant environments. , Organizations can focus their attention. About those factors that are closely related to their mission, purpose, purpose and strategy.
I. Micro environment: Micro external factors have a significant impact on a company's business operations. However, not all microfactors have the same impact on all companies in the industry. For example, suppliers, a key component of the micro-level environment, are often willing to offer materials to large companies at relatively low prices. They do not have the same attitude towards small businesses relatively.
Here are some important micro elements of the business environment.
a) Customers:
The main task of any business is to attract and retain customers. This is to ensure unique long-term profitability and market presence. Therefore, it is necessary to closely monitor the needs and desires of customers to ensure their joy. This will increase the number of loyal customers in the company.
Customer preferences and changes in preferences need to be predicted in advance, not just observed when they occur. The company also needs to make the necessary modifications to the product / service profile. Customers are the backbone of the company and that's exactly why the company exists.
b) Product:
Product elements such as demand, image, function, utility, function, design, life cycle, price, promotion, distribution, differentiation, and availability of alternatives to products and services also form a close part of the business environment. I will. Product / service functionality is the key to attracting / retaining customers.
c) Marketing broker:
This includes all people who promote the distribution of goods from production bases to various consumption bases. These are the intermediaries that form part of the distribution channel and those who help deliver the product / service to the ultimate consumer. The number can be small or large, depending on the length of the distribution chain and the type of distribution system your company employs. If this chain is hassle-free and works without many hurdles, it ultimately helps the organization.
d) Competitors:
The world has become a global market. There is fierce competition in every field. There are other entities that manufacture similar products and compete with the company for market share and sales. These need to be managed properly and market intelligence is needed to find future plans. These can play a major role in building or damaging the property of any company.
e) Supplier:
A key element in the microenvironment is the supplier, the supplier that supplies the company with raw materials, components, and machinery. Supplier must be reliable, act as a business partner, and work together to meet the ultimate consumer expectations. If the supplier is reliable, there is no need to hold large inventories that increase the risk of obsolescence or damage and block the company's working capital.
II. Macro environment:
A macro environment is a larger, uncontrollable environment composed of social forces that affect all other environments. They offer tremendous opportunities for any business and present threats that can be of great harm to the business. This environment is very important for understanding and studying for strategic planning and decision-making purposes.
It has a wider dimension than the micro environment. It consists of individuals, groups, institutions, events, conditions, and forces that the organization frequently contacts in the course of its functioning. The macro environment is, in fact, a real environmental factor that has the greatest impact on the growth and structure of any business.
It consists of the following components:
a) Sociocultural environment:
It consists of the society and culture of the place where the organization operates. This is a common entity and affects almost every enterprise in a similar way. Some of the key factors and impacts of working in the social environment are all factors that influence people's buying and consuming habits, their language, beliefs and values, habits and traditions, tastes and preferences, education and business.
These factors are:
b) Political environment:
The political environment consists of factors related to the management of public relations and the impact of the organization on its business. The political environment is closely related to the economic system and economic policy. For example, communist countries have a centrally planned economic system. Apart from the laws governing investment and related matters, most countries have many laws that regulate the conduct of their businesses. These laws cover matters such as product standards, packaging and promotions.
India is a democratic country with a stable political system, and the government plays an active role as a planner, promoter and regulator of economic activities. Therefore, businessmen are aware of the political environment facing the organization. Most business-related government decisions are based on political considerations in line with the political philosophy followed by the central and state-level ruling parties.
Some aspects of the political environment are:
I. General state of political development
II. Degree of politicization of business and economic issues
III. Political moral level
IV. Situation of law and order
V. Political stability
VI. Ruling party political ideology and practices
c) Economic environment:
The economic environment consists of macro-level patterns related to the areas of wealth production and distribution that affect an organization's business.
Some of the key factors and implications that work in the economic environment are:
I. An economic stage that exists at a particular time in a country.
II. Adopted economic structures such as capitalism, socialism and mixed economy.
III. Economic plan such as 5-year plan and annual budget.
IV. Economic policies such as industry, finance and fiscal policy.
V. Economic indicators such as national income, income distribution, GNP growth and growth rate, per capita income, disposable personal income, savings rate, investment, import / export value, balance of payments.
VI. Infrastructure factors such as financial institutions, banks, transportation, telecommunications equipment, and energy sources.
Below are some examples that emphasize the role of the economic environment.
1) Economic liberalization since the last 20 years has had various impacts on Indian industry. While most companies have the advantage of being able to freely change the composition and capacity of their products, they have also had some negative impacts in the areas of capacity overcapacity and intensifying competition.
With the partial deregulation of cement in 1982, production capacity and the resulting supply increased rapidly, and market conditions changed from severe shortage to a comfortable surplus. The liberalization of imports led to intensified competition in the capital goods industry, reducing profits and, as a result, many companies were unable to sustain their businesses.
2) India's public savings have traditionally been invested in fixed assets and precious metals. Shares of savings invested in the government have been carried through post offices and banks. But lately, investors are increasingly looking at other means such as stock markets and company deposits.
Recent changes in economic and fiscal policy have made many important developments. Entry into equity trading by leasing and finance companies, bonds, mutual funds, venture capital businesses, new financial products, banks and financial institutions is part of the development that provides resources for capital markets and project finance.
d) Regulatory environment:
The regulatory environment consists of factors related to the planning, promotion and regulation of government economic activities that affect an organization's business.
Some of the key factors and implications of operating in a regulated environment are:
I. Constitutional framework, principles of directive, basic rights, and distribution of legislative rights between the central and state governments.
II. Policies related to license monopoly, foreign investment and industrial finance.
III. Policies related to distribution and pricing and their management.
IV. Policies related to imports and exports.
V. Public sector, small industry, disease industry, rear area development, pollution control, and other policies related to customer protection.
Business and industry operate in a regulated environment. The relationship between the industry and the regulatory environment exists as a two-way process. The government has established policies, procedures, and rules for the industry to function.
There are many administrative controls over the business that are exercised through regulatory mechanisms.
Some of the important areas of management are:
1) Industrial policy and licenses;
2) Monopoly and restrictive trade practices.
3) Laws related to the operation of the company.
4) Import / export control and foreign exchange control.
5) Management of foreign investment and cooperation.
6) Management by consumer protection. And
7) Management of environmental pollution
e) Technical environment:
The technical environment consists of applied knowledge and elements related to the materials and machines used to produce goods and services that affect an organization's business. For many companies, technology is the most dynamic of all environmental factors. Individual companies are interested in their products and process technologies. This environment is made up of factors that accompany all sorts of technological advances or their lack.
Some of the specific factors that can be explained are:
I. Technology sources such as corporate sources, external sources, foreign sources.
II. Technology development, stage of change in development, rate of change in technology, research and development.
III. The impact of technology on the environment of humans, human mechanical systems, and technology.
IV. Communication and infrastructure technology and management technology.
V. Technical obsolescence.
In the Indian context, we can see that the state of technological development varies between different sectors of the industry. It is generally believed that the technical aspects of competition depend on customer needs and government policies.
f) Demographic environment:
This environment deals with the composition and characteristics of the place's population. All relevant descriptions of the location's population with respect to its demographic profile have a dramatic impact on business decisions. It is beneficial for any company to consider these aspects in detail before planning a strategy.
It includes elements such as:
Business Environment Components – Economic, Technical, Social, Demographic and Minority
The general environment of an organization is made up of key factors such as economic, technical, social, demographic, political, legal, and global power. These have positive, neutral and negative impacts on your business. Professor Alex Miller and Professor Gregory Dess describe this well under the title "Strategic Management."
Component # 1. Economic environment:
It is macroeconomic indicators that strategists study to influence their decisions. These indicators shape the health and well-being of the economy. These are determinants of a company's ability to make a profit and generate wealth. More important is the maximization of wealth, as it means maximizing profits and returning them to investments that generate more income.
The components of the economic environment are:
I. General economic situation:
The general economic situation that prevails in the economy is a determinant of economic prosperity and community well-being. These economic conditions are variables in which the amount of national income, per capita income, economic resources, income and wealth distribution, and economic development determine people's economic prosperity.
Revenue and its distribution determine the business outlook and therefore the business strategy. In an economy where it is low and per capita is relatively low, demand will decline. This pessimistic situation does not attract business people who invest in and execute manufacturing and marketing activities.
On the other hand, in an economy where the income of the economy is increasing, it leads to more and more investment and entry into industrial and marketing activities. In India, the backbone of the Indian economy, the Middle, is ready to increase income and invest in business.
Even NRI considers it beneficial to invest surplus income in this way, helping the Indian economy to become stronger and thus benefit from profits.
II. Economic system:
The economy is an arrangement that encourages the use of free resources to generate and distribute income, based on some accepted economic philosophies. Economy around the world is widely linked to Kabbalism, socialism, and communism as a hybrid economy called a pure variety or mixed economy.
India is the best example of a mixed economy, with the benefits of capitalism and socialism in one focus, eliminating the disadvantages of pure socialism or capitalism.
Capitalism gives maximum economic freedom in the management of economic activity, socialism talks about maximum domination by the state, mixed economy is freedom and the role of the state in which both the public and private sectors support each other. I have.
The collapse of the mighty nation formed in the early 20th century had to kick a bucket for a period of 100 years. Today, the Soviet Union is divided into small nations that were one of the greatest forces in the world linked to socialist ideology.
III. Economic policy:
It is the appropriate and timely economic policies adopted and implemented by the government that determine the fate of the state and its citizens. Think about India before 1991 and now. The Indian economy is on the verge of collapse and foreign exchange reserves were enough to pull another eight days.
It was a change in personality as a political leader and the brain behind them, together they freed India from control and opened the Indian economy to the whole world.
Private and public sector businesses that worked under the umbrella of protection were set up and faced the challenge of changing competition. Which foreign companies couldn't replace them as Indian players became global players?
IV. Economic growth:
Economic growth or development is the rise and maintenance of per capita income for all individuals who are members of the economy. It is economic growth, which represents increased consumer spending and lower pressure in the industrial sector, that provides more opportunities and enables businesses to withstand the severity of the threat. Other methods also apply. Declining economic growth and lower consumer spending will increase pressure and reduce profitability.
V. Interest rate:
Interest rates affect the demand for goods and services in the economy when they are purchased through borrowing. If interest rates are low, the demand for the product may be durable or non-durable. This gives Philip to a growing industry.
The opposite is true if the rate is high. Today, R.B.I is emerging at lowest interest rates to increase demand for durable and non-durable consumer goods, which will bring the Indian economy out of pessimism and tomorrow's rut.
The cost of capital also depends on interest rates. When they are getting capital at the lowest rates, the companies will encourage all companies to have ambitious plans and strategies in the case of borrowed funds.
VI. Exchange rate:
Exchange rates represent currency conversions to other currencies. It may be hard or soft. In 1991, the Indian Rupee was devalued to make Indian products cheaper in the global market to boost Indian exports. This was a great opportunity for all Indian exporters to export more commodities and reserves and earn forex.
Today, foreign exchange reserves are at a record high of Rs 200 billion, at least costly to boost quality production. Indian exporters do so only if they regularly understand and implement three strategies for export cost, export quality, and export volume. Therefore, it is the exchange rate that determines the fate of a country.
Component # 2. Technical environment:
The rapid development of technology has a strong impact on all organizations, not just those operating in high-tech environments such as microprocessor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and fiber optic technology. The combined impact of computers, digital technology, and telecommunications affects most private and public sector businesses.
As J. Shunpeter, as rightly called by everyone else, it is the "permanent gate of creative destruction." Technology change is a creative and destructive process in that it is responsible for building new things by destroying old ones. Therefore, the core of progress is destruction.
This means that destruction and construction are not contradictory and provide complementary opportunities and threats. In an era of rapidly changing technology, the secret to success is triangular strategy. That is, managers need to anticipate, innovate, and excel to be successful.
Companies that do not do so will be thrown away. When an American boxer took over Muhammad Ali, he said: Ali, you are the best, but I am the latest. We have to learn from Japanese. Before the war, "Made in Japan" was a sign that no one bought it because the product was the cheapest but the quality was the lowest.
However, today, Japanese products are completely quality conscious, "zero defects", "automobiles" or "zips", "made in Japan", so there is a great demand. It talks about their ability to predict, innovate and excel. The Japanese are the best copy cuts and can innovate and excel others. Today, of the 2000 Toyota cars, 700 land daily on the soil of America, the great power of the United States.
The strategic impact of technology changes was successfully brought about in the fall of 1982, in the article "The Emergence of Technology Portfolios" by Russian thinker Basis Petrov.
(I) It may change the relative competitive cost position within the business.
(II) Can create new markets and new business segments
(III) By reducing or eliminating segment barriers, previously independent businesses can be disrupted or consolidated.
New ideas, new products, new processes New methodologies are the result of technological change. That means that changing the order offers many opportunities for threats. That's why it pays off when strategists are constantly monitoring the technology kingdom and its impact on the company and its activities.
Component # 3. Social environment:
The social environment is the socio-cultural environment. The socio-cultural environment is made up of a system of values, and the attitudes, beliefs, desires, expectations, aspirations, customs and customs of society change accordingly, and there are many opportunities and threats to the business operated for society. This socio-cultural environment covers aspects of society and its components.
For a business house, it means:
(I) Expectations from the business community for society.
(II) Social attitudes towards business and its management.
(III) View on job achievement.
(Iv) Perspectives on authority structure, responsibilities and organizational position.
(V) Views on customs, traditions and customs.
(VI) Class structure and labor movement.
(VII) Level of education.
These socio-cultural environmental factors affect organizations in three ways:
(I) Organizational goal setting,
(II) Organizational processes and
(III) Products and services provided by the organization.
The changes that occur in society due to the changes in accepted values are right for the members of society. Therefore, what a particular age group wears, eats and entertains is determined by cultural values. Today, everyone is aware of a particular lifestyle based on social norms. The outlook on life is that life is short — enjoy it at any cost.
As a result, more and more people are thinking about traveling to faraway places. Another thing is to get rich with simple money and storms. This has led the community to rely on lottery tickets, horse racing, betting and more. This also led to antisocial activity.
Today, kidnapping and hijacking are very common for getting loot. These activities have created a demand for products and services that facilitate these activities. Countering these has also provided services and products that provide self-defense.
Women's whereabouts are no longer limited to the kitchen. They are more educated and occupy reserved positions for men because they have an equal share. This meant that they didn't have time to prepare meals to care for their children. In this way, fast food habits are revealed, the services of domestic servants are increasing, and more and more families are seeking washing machines and entertainment on small screens.
The younger generation has the freedom of video surfing, nightclub participation, expensive and high quality clothing, shoes, deodorants and toiletries. Mobile, mobike and car are the needs of these young people. Similarly, older people look younger and want to be younger, which helps maintain their hair color and health. Nowadays, people are becoming more health conscious.
With this special attention and caution, they seek mineral water, preventative medications, preventive health checks, and dietary changes. Therefore, high cholesterol is a major cause of coronary artery disease. That's why people are looking for double or table refined cooking oils that consume too little. They avoid lean meat and choose white meat, that is, chicken and fish such as beef, mutton and pork.
Recently, social awareness has been increasing. Social issues such as pollution, social responsibility of businesses, and worker safety and welfare are becoming more prominent. The social demands placed on the business community as a social responsibility are increasing. Did this affect what the business house produces? What kind of process do you adopt? How will the product be packed? And so on.
Fully effective consumerism is responsible (responsible for the enactment of MRTP and consumer protection laws. Consumerism has influenced standards of technology, product quality, marketing activities and after-sales service. This is all about the business community producing and selling products and services that are determined by socio-cultural values.
Component # 4. Demographic environment:
Demographic characteristics deal with populations such as family size, fertility rate, growth rate, age structure, family size, education level, language, caste, income level, earners and non-earners. The demand for goods and services depends on those demands, the demand is the potential or real market, and the market means the real and potential consumers.
There is a positive relationship between population growth and demand for goods and services. Lower fertility has a direct or indirect impact on products and services for infants.
If the population is made up of older people than young people, they are in high demand for preventative and therapeutic medical services, medicines, awakening sticks, hair color, etc. If you have a lot of young people, you will need everything from convenience goods, specialty goods, and shopping goods by consumer segment.
Dislikes, style movements, fashion, and their part-time or full-time income.
These changes in population offer many opportunities and pose challenging threats as well. The availability of skilled and cheap workforce, and the increasing demand for consumer goods and services, may allow multinationals to invest in new activities.
Consumers in different countries may prefer "Made in India" products, where Indian companies have a cost advantage. It attracts foreign investment, which leads to optimal use of national resources and increased imports and exports.
Population change cannot be underestimated in many ways that provide good opportunities to pose a threat on the same path. It is up to the business house to form strategies for success and implement them to embrace these opportunities by effectively handling threats.
Component # 5. Political and legal environment:
The political and legal environment is, of course, called the regulatory environment. National, state and local governments play a constructive role as citizen administrators. To protect and promote the interests of citizens, they rely on regulatory activities that can be undertaken through constitutional provisions, government policy and industrial law.
As for the constitutional provisions of India, the Constitution of India was passed by the Constituent Assembly in 1949. Constitutional provisions provide guidelines for central and state governments to control and regulate socio-economic policies.
The provisions of the Constitution are divided into "basic rights" and "directive principles." Basic rights are set out in Articles 15, 16, 19, 23, and 24. Article 15 prohibits discrimination against citizens on the grounds of religion, race, caste, gender, or place of birth. Article 16 describes equal opportunity for all citizens in public employment, savings and the provision of settlements by the state.
Article 19 states that all citizens have the right to practice any profession, profession, trade or business. Article 23 describes the right to human exploitation and transportation. Article 24 provides for the prohibition of child labor under the age of 14 in factories, mines or dangerous work. Directive principles are principles and laws that can be enforced by a court.
These serve as guidelines for these governments and businesses. The main ones are:
(I) Promotion of people's welfare.
(Ii) Minimize income inequality and eliminate inequality in status facilities and citizens' opportunities.
(Iii) Secure appropriate means of livelihood for citizens.
(Iv) Equal amount of money paid to both men and women for equal work
(V) Providing fair and human working conditions and relieving childbirth
(Vi) Ensuring wages and working conditions to provide an appropriate standard of living.
(Vii) Participation in worker management.
(Viii) Proper distribution of ownership and management of natural resources to prevent the concentration of a small number of wealth and instead serve the public interest of the community.
When it comes to government policy, these are based on industrial resolutions. Industrial resolutions embody government policy in power. Government policy is both positive and negative in the approach. Policy frameworks and implementations provide four roles: regulation, publicity, entrepreneurship, and planners.
The "regulatory role" consists of:
(I) Restrictions on private sector participation in areas such as defense, industry and nuclear power.
(II) Management of plant capacity and location.
(III) Set an upper limit on expenses, ……… Lower limits on wages and bonuses, and provisions for legal welfare measures.
(IV) Regulations on equity participation and foreign investment.
(V) Corporate tax, professional tax, taxes such as entertainment expenses,
(VI) Import / export rules, tariffs, tariffs, etc.
"Promotional roles" include:
(I) Development of infrastructure for industrial and commercial activities such as roads, industrial parks, telecommunications equipment, electricity.
(II) Support for subsidies, investment subsidies, tax incentives, tax exemption periods, subsidized water or electricity charges, etc.
(III) Provide financial and financial incentives.
The "entrepreneurial role" has something to do with:
(I) Participation in businesses and industries where private sector participation is inadequate, that is, power generation and distribution.
(II) Ownership and management of reserved industries such as defense production, nuclear power, oil and gas.
(III) Management of industry in the public sector.
The role of planning covers the following areas:
(I) 5-year plan.
(II) Industry prioritization.
(III) Foreign participation and bilateral agreements with other states or countries.
(IV) Greenfield area development plan.
(V) Regional development plans and programs.
Focusing on "industrial law", many laws have been passed from time to time to regulate industry and commerce.
Activities, protection of employee interests.
The most important things that the business community should take into account are the Indian Contract Act of 1872, the Trade Union Act of 1926, the Employee (Industry) Permanent Order Act of 1946, the Industrial Dispute Act of 1947, and Exports of 1947. Immigration law, capital issues. 1947, 1948 Factory Law, 1948 Employee National Insurance Law, 1951 Industrial Development and Regulation Law, 1952 Employee Reserve Fund Law, 1955 Mandatory Commodity Law, 1956 Indian Enterprise Law, 1956 Securities Contract (Regulation) ) Law, Trade Marking Act 1958, Weight and Measurement Act 1958, Income Tax Act 1961, Borm Act 1965, Exclusive and Restricted Trade Practices Act 1969, Water (Contaminated and Contaminated) Control) Act, Household Electrical Appliances (1976 Quality Control Act, 1981 Air (Pollution Prevention and Control) Act, 1986 Consumer Protection Act, 1986 Environmental Protection Act, 1992 Indian Securities Trading Committee law.
There is a tax law that is revised every year. The same applies to price control regulations.
These laws and sets are very important to administrators. Because his policies and strategies can't hate local law.
Component # 6. Global environment:
The global or international environment is especially important in the face of strong globalization turmoil. Changes in the global environment create a range of opportunities and threats to a company's domestic and international share. Thus, the collapse of national communism in Eastern Europe has created enormous growth opportunities for American multinationals, Western European countries, and the emerging "Tiger of Asia."
The removal of trade barriers between community members of the European Community in 1992 provided them with free trade opportunities. The case of the Eurodollar as a new currency in 1999 poses many opportunities and threats to the various currencies of member countries.
In 1991, the Government of India announced a new Indian policy to meet the needs of liberalization and globalization of the Indian economy. This meant a thorough overhaul of the government's monetary and fiscal policies, under which artificial trade barriers were dismantled and the "license and management large" was rejected.
Bold policy initiatives were in the areas of industrial licensing, foreign investment, foreign technology agreements, changes in MRTP legislation, reform of the public sector, promotion of the small-scale sales industry, and reform of trade policy. The price of globalization has influenced global events.
Therefore, the oil crisis of the 1980s, the formation of the European Union and other economic groups, the dismantling of the Soviet Union, and the recession. This strengthens the retention of MNC and TNC. As a result, new strategic concepts such as international value chains, networking and relationship marketing cannot be revealed. Today's managers are global players, so we need to analyze the international environment from both focus and distance.
Industry environment:
An industry is a group of companies that manufacture or provide services for the same product. Therefore, the steel industry means all units engaged in the production of steel or steel products. Similarly, we can talk about the automobile industry. Here, it means in a specific context. For example, a four-wheeled vehicle.
However, it can include two-wheeled vehicles, three-wheeled vehicles, six-wheeled vehicles, and eight-wheeled vehicles. Even when we talk about it, it consists of Scotty, or mopeds, scooters and motorcycles. Convenience is the basis for calculating costs and prices.
That is, each unit in the industry is a competitor to the other units. The industry environment has components such as competitors, customers, suppliers, and alternatives. Each is a competing force. Perhaps the best model of competition in the industry environment was developed by Michael Porter, who is considered a leader in strategy.
This pentaforce model is widely accepted and explains how competitiveness works within the industry. The following is a model of competitiveness described in Harvard Business Review, March-April 79, "How Competitiveness Shapes Strategy."
Every strategist or manager needs to study the impact of this pentaforce, which is constantly working in the industry.
Key takeaways:
Environmental Analysis
Definition: Environmental analysis is described as the process of inspecting all internal or external components that affect an organization's performance. Internal components show the strengths and weaknesses of business entities, and external components show opportunities and threats outside the organization.
Performing an environmental analysis requires a constant flow of relevant information in order to find the best course of action. Strategic planners use the information gathered from environmental analysis to anticipate future trends. This information can also be used to evaluate your production environment and set your organization's goals.
Check if your current strategy can achieve the goals defined by your organization. If your existing strategy does not meet these goals. Then a new strategy is devised or the old strategy is modified accordingly.
Check if your current strategy can achieve the goals defined by your organization. If the existing strategy fails to meet these goals, a new strategy will be devised or the old strategy will be modified accordingly.
Benefits of environmental analysis
The internal insights provided by environmental analysis are used to assess employee performance, customer satisfaction, maintenance costs, and take corrective action as necessary. In addition, external metrics help you be positive about your environment and tailor your strategy to your organization's goals.
Environmental analysis helps detect threats early and helps organizations develop strategies for survival. In addition, identify opportunities to take the largest share of the market over competitors, such as prospects, new products, segments, and technologies.
Environmental analysis is a continuous process that continuously scans for forces affecting the business environment and follows a holistic approach that covers 360 degrees of the horizon rather than specific segments.
Business environment Analysis process
The business environment analysis process involves many steps, including:
1. Gathering the necessary information.
2. Scan and search for information.
3. Obtaining information by spies.
4. Predict the situation.
5. Observe the environment.
6. Evaluation.
1. Gathering the necessary information
Gathering the information, you need is the first step in the business environment analysis process. It also includes observing various factors that are prevalent in a particular area. When you analyze and create an environment, you must first collect verbal information from various sources about the environmental elements of that particular business.
2. Scan and search for information
Scanning and searching are important techniques for business environment analysis. Once the required information has been collected, it should be scanned. What's more, you can continue to search for other relevant information. This technique gives results on already established hypotheses. This allows analysts to know what the general conditions are at one time in a particular business.
3. Obtaining information by spies
Spies are also a method of business environment analysis. If you need to analyze the activity of a particular business and cannot collect such information in the traditional way, rely on espionage techniques. This happens especially when there is business competition. In most cases, this technique is used to collect conflict information.
4. Situation forecast
Scan provides images about the past and present. However, strategic decision-making requires a future direction. Predictions are scientific guesses based on some serious research. Therefore, it is especially useful to know how the situation of business and society as a whole is shaped.
5. Observation of the environment
You can analyze the business environment just by observing. Observations reveal a variety of conditions that are prevalent at any given time. This will help you understand the entire existing environment and make the right decisions.
6. Evaluation
The assessment is done to determine the impact on your organization's current and potential strategies. Assessment involves identifying and assessing how and why current and anticipated environmental changes affect the strategic management of an organization. It aims to answer questions such as what are the key issues posed by the environment. What is the impact of such issues on the organization?
Environmental scanning:
Scanning is the process of analyzing your environment to identify factors that can affect your business. Its purpose is to identify new trends or early warning signals. These trends may have evolved or suddenly appeared over time. Environmental scans alert organizations to potentially significant forces in the external environment and enable them to take appropriate strategic initiatives before they become important to the organization. Scans are basically exploratory. There are many environmental factors that affect business operations. Not all of these factors are relevant to the enterprise.
Therefore, it is necessary to identify important and high-priority factors. Several factors influence the choice of relevant environmental factors, such as business philosophy, age, size, power, geographic aspects, and the industry of the organization.
Environmental Scan: Scanning and searching are important techniques for business environmental analysis. Once the required information is collected, it should be scanned. What's more, you can continue to search for other relevant information. This technique gives results on already established hypotheses. This allows analysts to know what the general conditions are at one time in a particular business.
Environmental monitoring: At this stage, information from the relevant environment is collected. Once the environment-related factors are identified, appropriate data about these factors is collected to identify new patterns and trends in them.
The four stages given above are intertwined as can be seen below:
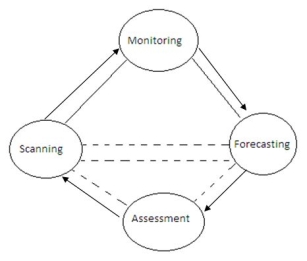
Definition: Environmental Scan
Environmental scanning is the process of analysing internal and external factors in the environment. Environmental scanning is the process by which an organization conducts research to identify opportunities and threats in the industry.
Environmental scans are part of the SWOT analysis. The information gained through the environmental scan can be used by leaders to design new goals and strategies or modify existing goals and strategies. Organizations need to be agile in responding to environmental challenges while maximizing the opportunities available.
Importance and necessity of environmental scanning
Environmental scanning is an important aspect of predicting the future and preparing for a volatile business environment. The frequency of environmental scans depends on your organization's needs. Organizations operating in industries that are heavily impacted by innovation must constantly monitor their environment and use the results to design their processes. On the other hand, some organizations may need to perform environmental scans on an ad hoc basis.
The following are the necessity and importance of Environmental Scanning.
1] SWOT Analysis:
As we saw earlier in the sense of environmental scanning, it's a complex process. A closer look at an organization's internal and external environment reveals invaluable information: the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a company. Let's take a quick look.
Strengths: As a result of analysing the internal environment of a company, it is possible to identify the strengths that give the company a competitive advantage. Entrepreneurs can use this information to maximize these strengths and benefit more.
Weaknesses: Internal environment surveys have also pointed out weaknesses in the company.
Opportunities: Analysing the external environment helps identify possible opportunities. Entrepreneurs can be prepared to take advantage of these.
Threats: Analysing the external environment can also help identify business threats and other factors from competitors. The company can come up with strategies to spread or minimize its impact.
2. Optimal use of resources:
Proper environmental assessment helps to make the best use of terrifying human, natural and capital resources. A systematic analysis of the business environment helps companies reduce waste and make the best use of available resources without realizing that they cannot effectively use internal and external environmental resources.
3. Survival and growth:
A systematic analysis of the business environment helps companies maximize their strengths, minimize their weaknesses, seize opportunities, and spread threats. This allows companies to survive and grow in a highly competitive business world.
4. To plan a long-term business strategy:
Business organizations have short-term and long-term goals. Appropriate analysis of environmental factors helps companies develop plans and policies that may help them easily achieve their organizational goals. Without an environmental scan, companies cannot develop strategies for business success.
5. Environmental scans help you make decisions.
Decision making is the process of choosing the best option from the various options available. Environmental analysis is a very important tool for understanding and making decisions in every aspect of the business. The success of a company depends on its ability to make accurate decisions. Environmental analysis research allows businesses to choose the best options for their success and growth.
Area to be scanned for environment-
a) Economic situation.
b) Competition.
c) Global opportunities.
d) Employment trends.
e) Technological progress.
f) industry.
g) Geopolitical climate.
Analysis of internal capabilities using different approaches
What is internal analysis?
Internal analysis examines an organization's internal environment to assess its resources, capabilities, and competitive advantage. you'll perform internal analysis to spot the strengths and weaknesses of your organization. this data helps management make strategic decisions in implementing the strategy development and execution process.
In this article, we'll see why internal analysis may be a key component in creating effective strategies and explain the tools you'll use to perform internal analysis.
These include:
Why does one do an indoor analysis?
As mentioned earlier, internal analysis reveals the strengths and weaknesses of a corporation within the areas of its capabilities, resources, and competitive advantage. Once complete, organizations got to have a transparent idea of where they're good, where they're okay, and where their current deficits and gaps are. Analysis gives management the knowledge to require advantage of its strengths and opportunities. Management also can develop strategies to mitigate threats and structure for identified weaknesses.
By starting strategy development after this analysis, you'll make certain that you simply have developed a strategic decide to leverage your strengths and opportunities to offset or ameliorate your weaknesses and threats. That way, you'll be confident that your organization is effectively and efficiently investing resources, time, and concentration.
Internal analysis tool
Before you'll perform an indoor analysis, you would like to make a decision which tool to use to perform the analysis. There are many tools and frameworks, each of which is effective for a specific purpose. We've put together an inventory of popular and effective internal analysis tools and an outline of what each tool can assist you achieve so you'll choose the proper tool.
What is SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis may be a thanks to assess these four aspects of your business, as SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
You can use SWOT analysis to require full advantage of your organization and obtain the foremost out of what you gain. you'll also reduce your chances of failure by understanding what's missing and eliminating risks that you simply wouldn't otherwise notice.
Even better, you'll start to differentiate yourself from your competitors and develop strategies to win the competition within the market.
Features of SWOT analysis
SWOT analysis focuses on four elements of acronyms, helping companies identify the forces that influence their strategies, actions, or initiatives. Knowing these positive and negative factors can assist you more effectively communicate which parts of your plan your company must recognize.
When creating a SWOT analysis, a private typically creates a table divided into four columns, listing each of the influential element’s side by side for comparison. The strengths and weaknesses are ultimately interrelated and must be interrelated, but they typically don't match the listed opportunities and threats verbatim.
Billy Bauer, director of Royce Leather, said the mixture of external threats and internal weaknesses can highlight the foremost serious problems companies face.
“Once you've identified the risks, it's appropriate to allocate company resources to resolve the difficulty to eliminate internal weaknesses, or by abandoning and strengthening areas exposed to business threats. you'll determine if it is best to scale back external threat, “said Bauer.
SWOT analysis example
Bryan Weaver, a partner at Scholefield Construction Law, was deeply involved in creating the SWOT analysis for his company. He provided a sample SWOT analysis template and example for news daily. This template and example were utilized in the company's decision to expand its operations to incorporate dispute mediation services.
Key issues in SWOT analysis:
Strengths
1) Unique ability?
2) Sufficient financial resources?
3) Do buyers think twice?
4) Recognized market leader?
5) Well-thought-out functional area strategy?
6) Access to economies of scale?
7) Is it (at least to some extent) isolated from strong competitive pressure?
8) Unique technology
9) What are the cost benefits?
Weaknesses
1) Is there a clear strategic direction?
2) Loss of competitiveness?
3) Abandoned facility?
4) Depth of management and lack of talent?
5) Are you lacking important skills or abilities?
6) Is the implementation record of the strategy insufficient?
7) Are you suffering from internal operational issues?
8) Are you vulnerable to competitive pressure?
9) Are you behind in R & D?
Conducting SWOT analysis
A company's success is usually associated with a specific critical success factor (CSF). These are related to the factors that market suppliers must meet in order to win the competition. When performing a SWOT, you need to clearly identify the key CSFs in the market segment, and each factor should be weighted from 100, depending on its importance to the customer. The total weight should be 100 in total. You can score each major competitor on a scale of 10 for performance against each CSF. Multiplayer each score with its weight allows you to quantitatively assess the relative strength of each competitor in the segment.
Key takeaways:
References: