Unit 1
Business and its Environment
Meaning & Definition What Is a Business?
A business is defined as a corporation or enterprising entity engaged in commercial, industrial, or professional activities. Businesses are often for-profit entities or they can be non-profit organizations that operate to satisfy a charitable mission or further a social cause.
The term "business" also refers to the organized efforts and activities of people to produce and sell goods and services for profit. Businesses home in scale from a sole proprietorship to a global corporation. Several lines of theory are engaged with understanding business administration including organizational behavior, organization theory, and strategic management.
Nature of Business
The following are the important characteristics of a business:
1. Economicactivity:
Business is an economic activity of production and distribution of products and services. It provides employment opportunities in several sectors like banking, insurance, transport, industries, trade etc. it is an economic activity corned with creation of utilities for the satisfaction of human wants.
It provides a source of income to the society. Business results into generation of employment opportunities thereby resulting in growth of the economy. It bring about industrial and economic development of the country
2. Buying andSelling:
The basic activity of any business is trading. The business involves buying of material, plants and machinery, stationary, property etc. On the other hand, it sells the finished products to the consumers, wholesaler, retailer etc. Business makes available various goods and services to the various sections of the society.
3. Continuousprocess:
Business is not one-time activity. It is endless process of production and distribution of goods and services. One transaction of trade cannot be termed as a business. A business should be conducted regularly so as to grow and gain regular returns.
Business should continuously involve in research and developmental activities to achieve competitive advantage. a continuous improvement strategy helps to increase profitability of the firm.
4. ProfitMotive:
Profit is an indicator of success and failure of business. It is the difference between income and expenses of the business. The primary goal of a business is typically to get the highest possible level of profit through the production and sale of goods and services. It is a return on investment. Profit acts as a driving force behind all business activities.
Profit is required for survival, growth and expansion of the business. It is clear that each business operates to earn profit. Business has many goals but profit-making is that the primary goal of every business. It is required to develop economic growth.
5. Risk andUncertainties:
Risk is defined as the effect of uncertainty arising on the objectives of the business. Risk is related to every business. Business is exposed to two kinds of risk, Insurable and Non-insurable. Insurable risk is predictable.
6. Creative andDynamic:
Modern business is creative and dynamic in nature. Firm has to start with creative ideas, approaches and concepts for production and distribution of goods and services. It means to bring things in fresh, new and inventive way.
One has to be innovative because the business operates under constantly changing economic, social and technological environment. Business should also start with new products to satisfy the growing needs of the consumers.
7. Customersatisfaction:
The phase of business has changed from traditional concept to modern concept. Now a day, business adopts a consumer-oriented approach. Customer satisfaction is the ultimate aim of all economic activities.
Modern business believes in satisfying the customers by providing quality product at an inexpensive price. It emphasizes not only on profit but also on customer satisfaction. Consumers are satisfied only when they get real value for his or her purchase.
The purpose of the business is to make and retain the customers. The power to identify and satisfy the customers is the prime ingredient for the business success.
8. SocialActivity:
Business may be a socio-economic activity. Both business and society are interdependent. Modern business runs within the area of social responsibility.
Business has some responsibility towards the society and successively it needs the support of various social groups like investors, employees, customers, creditors etc. by making goods available to various sections of the society, business performs a crucial social event and meets social needs. Business needs support of various section of the society for its proper functioning.
9. Governmentcontrol:
Business organizations are subject to government control. They need to follow certain rules and regulations enacted by the government. Government ensures that the business is conducted for social good by keeping effective supervision and control by enacting and amending laws and rules from time to time.
Some important acts framed by the government include:
-The Competition Act, 2002
-Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999
-The Environment Act, 1986
-Indian Companies Act, 1956
-Consumer Protection Act
10. Optimum utilization ofresources:
Business facilitates optimum utilization of nation’s material and non-material resources and achieves economic progress. The scarce resources are delivered to its fullest use for concentrating economic wealth and satisfying the requirements and needs of the consumers.
For the smooth functioning of business, there is a need to perform the following functions:
1. Production function:
The Production function undertakes the activities necessary to produce the organization’s products or services. Its main responsibilities are: production planning and scheduling control and supervision of the production workforce managing product quality (including process control and monitoring
2. Research and Developmentfunction:
The Research and Development (R&D) function is concerned with developing new products or processes and improving existing products/processes. R&D activities must be closely coordinated with the organization's marketing activities to make sure that the organization is providing exactly what its customers want within the most efficient, effective and economical way.
3. Marketing function:
Marketing is concerned with identifying and satisfying customers' needs at the right price. Marketing involves researching what customers want and analyzing how the organization can satisfy these wants. Marketing activities is concerned with the selection of product markets, producing literature like product catalogues and brochures, placing advertisements within the appropriate media and so on. A fundamental activity in marketing is managing the Marketing Mix consisting of the ‘4Ps’: Product, Price, Promotion and Place.
Product: Having the right product in terms of advantages that customer’s value.
Price: Setting the right price which is in line with potential customers’
Perception of the worth offered by the product.
Promotion: Promoting the product in a way which creates maximum customer awareness and persuades potential customers to form the decision to purchase the product.
Place: Making the product available in the right place at the right time –
Including choosing appropriate distribution channels
4. Human Resourcesfunction:
The Human Resources function includes with the following:
- Recruitment andselection.
- Training anddevelopment.
- Employeerelations.
- Grievance procedures and disciplinarymatters.
- Health and Safetymatters
- Redundancy procedures
5. Financefunction:
The Accounting and Finance function is concerned with the following:
- Financial record keeping of transactions involving monetary inflowsor outflows.
- Preparing financial statements (the profit-and-loss statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement) for reporting to external parties likeshareholder the financial statements are the start line for calculating any tax due on business profits.
- Payroll administration Paying wages and salaries and maintaining appropriate tax and national insurancerecords.
- Preparing management accounting information and analysis toassist managers to plan, control and makedecisions.
6. Salesfunction:
In large firms the sales activities are performed by the sales division. The sales department works in close coordination with the marketing department. The sales department is concerned with the selling activities of the firm. It receives or book orders from dealers or customers, then distribute the products through the channel. The sales department may need to undertake follow up of sales, special in the case of durables or industrial goods.
7. Publicrelations:
There is a need to maintain good relation with the public. Therefore, it makes a good sense to maintain separate department to look after public relations, especially in big organizations. It is the work of the PR department to manage corporate image of the firm and to develop quality relations with the various section of the society.
8. Inventorymanagement:
Inventory management refers to the management of inventory such as raw materials, semi-finished goods, finished goods and other items of inventory. It involves the following activities:
-planning of materials
-acquiring material and other inputs
-store keeping, etc.
The scope of business is extremely broad. It covers a large number of activities which can be looked into from two perspectives, namely: Industry and Commerce.
(A) Industry: The activities of extraction, production, conversion, processing or fabrication of products are described as industry. These products of an industrymay fall into any one of thetypes:
Primary Industries: Primary industries include the followings as listed below:
-Extractive Industries
-Genetic Industries
-Extractive Industries: In extractive industries, the industries extract or draw their products from natural sources like earth, sea, air. The products of such industries are generally employed by other industries like manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished goods. Farming, mining, lumbering hunting, fishing, etc., are a number of the examples of extractive industries.
Genetic Industries: Genetic simply means parentage or heredity. Genetic industries are engaged in breeding plants, and animals for their use in further reproduction.
For breeding plants, the seeds and nursery are typical samples of genetic industries. Additionally, the activities of cattle-breeding farms, poultry farms and the hatchery come under the category of genetic industries.
Secondary Industries: Secondary industries include the followings as listed below:
-Manufacturing Industries
-Construction Industries
-Manufacturing Industries: These are engaged in producing goods through the creation of what is referred to as ‘form utility’ such industries are engaged in the conversion or transformation of raw materials or semi-finished products into finished products. The products of extractive industries generally become the raw-materials of producing industries. Factory production is the outcome of producing industry. Manufacturing industries may take any one of the subsequent forms: Analytical, Synthetic, Processing, and production line.
-Construction Industries: These sorts of industries are focused on the making of constructing of buildings, bridges, dams, roads, canals, etc. These industries use the products of producing industries like Iron and Steel, Cement, Lime, Mortar, etc., and also the products of extractive industry like stone, marble, granite, etc. one among the remarkable feature of these industries is that their products are not sold in the sense of being taken to the markets. They are constructed and fabricated at fixed sites.
(B) Commerce: it is an interchange of products or commodities, especially on a large scale between different countries (foreign commerce) or between different parts of an equivalent country (domestic commerce) trade; business. It can also refer to the method of buying and selling. It covers wholesale, retail, import, export trade and all those activities which facilitate or assist in such buying and selling like storing, grading, packaging, financing, transporting, insuring, communicating, warehousing, etc. the most functions of commerce is to get rid of the hindrance of
(i) Persons through trade;
(ii) place through transportation, insurance andpackaging;
(iii) Time through warehousing and storage; and
(iv) knowledge through salesmanship, advertising, etc., arising in reference to the distribution of products and services until they reach the ultimate consumers. The concept of commerce usually covers two important areas:
(i) Trade
(ii) Service business or Aids totrade
(i) Trade: The term trade refers the act or process of buying, selling, orexchanging commodities, at either wholesale or retail, within a rustic or between countries. It is also the process of transferring of products and services. It is the central activity around which the ancillary functions like banking, transportation, insurance, packaging, warehousing and advertising are surrounded. Trade are often categorized into twoclassifications:
(a) Domestic Trade: this is also referring to as internal trade. It's internal because, it only focuses on buying and selling of goods within the boundaries of a countryand the payment for the same is made in national or local currency either directly or through the banking system. Domestic trade is often further sub-dividedinto:
Wholesale trade - Buying of products in large quantities from producers and selling anequivalent in small quantities to retailers.
Retail trade - activities involved in the selling of commodities directly to consumers, i.e., an industry that sells primarily to individuals, not corporations.
(b) Foreign Trade: it is also referred to as international trade. It refers to the exchange of products and services between two or more countries. International trade involves the use of foreign currency ensuring the payment of the worth of the exported goods and services to the domestic exporters in domestic currency, and for making payment of the price of the imported goods and services to the foreign exporter therein country’s national currency. International trade allows expansion of markets for both goods and services that otherwise may not areavailable.
(ii) Service businesses: These are usually considered Aids to Trade. As already highlighted earlier, there are certain function like banking, transportation, insurance, ware-housing, advertising, communication, etc. which constitute themain auxiliary functions helping trade both internal and international. These auxiliary functions are discussedbelow.
(a) Banking: A financial organization licensed as a receiver of deposits. There are two kinds of banks: commercial/retail banks and investment banks. In most countries, banks are regulated by the national government or central bank. Banks provide a device through which payments for goods bought and sold are made thereby facilitating the acquisition and sale of products on credit. Commercialbanks are mainly concerned with managing withdrawals and deposits as well as supplying short-term loans to individuals and smallbusinesses.
(b) Transportation: it is any device used to move business item from one location to another. Common sorts of transportation include planes, trains, automobiles, and other two-wheel devices like bikes or motorcycles. It involved carrying goodsfrom producers to wholesalers, retailers, and final customers. It provides the wheels of business. It has linked all parts of the world together thereby enhancing internationaltrade.
(c) Warehousing: A warehouse may be a planned space for the storage and handling of goods and material. There is generally a delay between the production and consumption of products. This problem may be solved by storing the products in warehouse. Storage creates time utility and removes the hindrance of your time in trade. It performs the useful function of holding the products for the period they move from one location to another. Thus, warehousing assists in discharging the function of storing the products both for manufacturers and traders for such time till they plan to move the products from one point toanother.
(d) Insurance: In any economy, the insurance industry plays significant rolesin the helping smooth the business environment and shoring investors’ confidence. Insurance industry provides intangible products in the same way as banks, hotels, etc. therefore the firms within the industry are considered service companies.
(e) Insurance provides a canopy against the loss of products within the process oftransit and storage. An insurance firm performs a useful service of compensating for the loss arising from the damage caused to goods through fire, pilferage, thief and the hazards of sea, transportation and thus protects the traders form the fear of loss of products. It charges premium for the riskcovered.
(f) Advertising: Advertising is any paid sort of non-personal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods or services by an identified sponsor. When effectively advertising is better placed to satisfy the requirements of its customers, consumers and stakeholders. Advertising performs the function of bridging the knowledge gap about the availability and uses of products between traders and consumers. In the absence of advertising, goods produced by businessmen would not have been sold to a widely scattered market and customers would not be aware of the newproducts due to the paucity of time, physical-spatial distance,etc.
(g) Communication: this is another service area that aid business. It helps because up-to- date information is required. This information can be accessed through computers, satellite links and faxmachines.
(h) Salesmanship: It facilitates personal selling. Sales department is required to book orders from dealers or customers. Advantage of salesmanship is that, it provides information to the buyers and convinces or persuade them tobuy.
Following are the steps involved in formulating business Objectives.
1) Analyze InternalEnvironment:
An analysis of internal environment helps in fixing realistic Objectives. Internal environmental factors include human resources, financial resources, physical facilities, management structure, internal relationship etc. must be studied, and such an analysis helps in understanding strengths and weaknesses of the. The Organization has to make every possible effort to correct weaknesses and to boost the strengths of the organization.
2) Analyze ExternalEnvironment:
The Organization also has to analyses the external environment. It includes customers, suppliers, and competitors, political, economic, social, technological, and natural and so on. Such an analysis reveals the opportunities and threats created by the environment such analysis would help the organization to grab the opportunities and to attenuate or defuse thethreats.
3) Awareness of pastObjectives:
Past Objectives and achievements of the organization serve as guidelines for formulating future objectives. Normally an organization not to deviate excessive amount from the past objectives while setting objectives
4) Setting ofobjectives:
After analyzing the interior and external environment, the firm should set the objectives in all the areas. Long term and short-term objectives must be set. Further, these must be set on the basis of priority. Once the objectives are decided, it must be informed to the all personnel.
5) Implementation:
After setting objectives, the management must plan and implement the goals. Implementation involves:
-Organizing resources
-Directing subordinates
-Motivating subordinates.
6) Review:
There must be periodic review of activities. This might assist the firm to seek out whether the listed objectives are targeted or not, if any deviation takes place, corrective measures can be taken immediately including resetting of the objectives.
Business objectives are many and varied in nature. The success of any organizationdepends on how well these are balanced. Business objectives are broadly classified into five major categories:
- Organic Objective ofbusiness:
The organic objectives are also called as three-fold objectives of business.
Survival: Survival is the basic objective of each organization. Other objectives can be thought of as long as the organization survives. Due to globalization,liberalization and privatization, the business environment has become extremelycompetitive.
Further, technological advancements and changing consumer behavior has made the business environment complex. This has made survival extremely difficult.
Constant monitoring of the business situation and strategic planning are necessary for survival in the competitive business environment.
2) Growth: Growth is the second major organic business Objective. Business should grow in all directions over period of time. Growth takes place through expansion or diversification. Expansion involves increase in business by introducing a product which is similar to the prevailing line of products of the business. While diversification involves introducing a product which is completely different. Growth brings more profit, opportunities for advancement, better utilization of resources, reputation and goodwill etc. In fact, growth is required for survival ‘Grow or Perish’ is the requirement of the day which means if the organization is not able to grow it will be droop out from themarket.
3) Prestige: Every business enterprise desires to possess social recognition and prestige. This objective is partly economic and partly social. Prestige of an organization is due to standard quality of its products, regularity in their supply, reasonable prices and satisfactory service to customers. Recognition indicates public confidence on an organization. Such recognition is feasible only after a long period of useful service to thesociety.
B. Economic Objectives ofBusiness:
The main economic objective of business is profit. To earn profit, there are several other economic objectives, which are to be accomplished. The important-economic objectives of business are as follows:
1) Profit: The main economic objective of business is to earn profit. Commercial activity is primarily undertaken for earning profit. It enables a business to understand other objectives of business. Profit is the main motive of all business activities and is necessary for survival, growth and prestige of an enterprise. Profit is an indicator of business performance and a sign of efficiency. It is a reward for bearing risk and uncertainty in business. It is a lubricant which keeps the wheels of business moving.
2) Creation of Wealth: Creation of wealth is one of the important objectives of business. Creating wealth involves increasing the wealth of the shareholders. It happens as long as the business grows steadily whereby the shareholders get higher dividends and there is an appreciation in the market price of theshares.
3) Creation of Customer: the aim of business is to create a customer. Customer isthe foundation of a business. Business has a crucial human obligation. Profit can’t be earned only by producing the products. Every businessman has got to find customers for prime goods or services. Thus, the target of the business should be to identify the customer for their goods and services. This needs creation of customer in the market and distributes goods and services.
4) Innovation – Innovation refers to introduction of latest ideas or new methods of production. Innovation plays an important role in increasing the competitive strength and improving the image of business enterprise in the mind ofconsumers.
5) Optimum Utilization of Resources – Resources available with the business are generally limited. So, every business enterprise aims to make best possible use of physical, financial and human resources. This objective can be achieved through–
(a) Employing efficient and competent work force;
(b) Making full use of installed machinery;
(c) Minimizing wastage of materials.
C. Social objectives ofbusiness:
Business is an integral a part of society. Following are the social objectives of business:
1) Social Objectives towards Customers: The Survival and success of any business concern depends on its consumers. One universally accepted social objective of business is to satisfy consumers by providing goods and services as per their needs and expectations. Business activities are essential for meeting the requirements of consumers. Business needs to supply quality good at reasonable price to the customer.
2) Social Objectives towards Employees: The Social Objective of a business concern towards its employees is to treat them with respect and provide them with the right compensation and facilities. Business should provide better wages, working conditions, good treatment to the workers. It also provides monetary and non- monetary benefits for satisfaction of the workers. This also ensures industrial peace and harmony.
3) Social Objectives towards shareholders: Shareholders invest their money in the business in the form of shares, debentures bonds etc. the essential objective is that the shareholder should receive a good, return on their investment. The target of the business is to utilize efficiently the capital of the shareholder and provides them fair return on their investment in the form of dividend andinterest.
4) Social Objectives towards Government: A business can’t functionsmoothly without the support and co-operation of the government. Hence, it becomes necessary on the part of the organization to satisfy its social duties towards the government. These include payment of taxes and duties, following the principles and regulations framed by the government from time to time, contributing towards the welfare activities of the government and so on.
5) Social Objectives towards Suppliers: The suppliers can play a crucial role in the success of an organization by Supplying the right quality and quantity of material at the correct time. Therefore, a business concern needs to have social objectives towards supplier in respect of timely payment of dues. Helping the suppliers intheir financial requirements by making advancepayments.
6) Social objectives towards Dealers: Dealers assist firm by promoting andpushing goods and services within the market at the right time at the right place. It is one of the essential social objectives that goods of special quality be produced and supplied. If this basic demand of the society is met, the business may survive in the long run.
7) Social Objectives towards Society:Business gain profit due to the support of the society. Naturally, they are expected to supply support for various social, educational and cultural activities. This is also necessary for maintaining cordial relations with thesociety.
D. Human or IndividualObjectives
Human or individual objectives refer to the objectives related to the individual needs of the employees of an organization. As employees are one of the most valuable resources for an organization, satisfaction of their objectives is very important.
Individual objectives include the subsequent objectives:
(i) To provide healthy and safe workingconditions.
(ii) To pay fair and competitive salaries andperks.
(iii) To provide opportunities for private growth and development ofemployees.
(iv) To provide reasonable security ofservice.
(v) To provide various financial and non-financial incentives so as to motivate the workers.
(vi) To encourage employees to take initiative and participation inmanagement.
E. National Objectives of business:
National objectives are the more Specific objectives of business. These are aimed toward fulfillment of national needs and aspirations. The government has to implement the national plans and policies in accordance with the accepted priorities. Business organization should consider these priorities, policies and plans making business decisions. Following arethe important national objectives ofbusiness.
1) Social Justice: Social justice means providing equal opportunities to all,protecting the interest of neglected, unorganized and economically backward sections of the society and prevention of any kind of exploitation. For instance, a business concern should do social justice to its handicapped workers, and womenemployees.
2) Development of small-scale industries: Small scale industries are people who require less capital and generate more employment. In the present era of globalization, this sector is adversely affected; so as to spice up this industry, business organizations should assist the expansion of small-scale industries by purchasing raw material fromthem.
3) Self Sufficiency: Every business concern should make use of available natural resources and human resources for economic development. It should reduce the countries dependence on foreign countries by producing goods indigenously or by promoting exports and reducingimports.
4) Production as per National Priorities: Business organizations must make efforts to provide the essential requirement of life i.e., food, clothing and shelter atreasonable prices. In other words, every business concern should set its objectives after considering national priorities. Secondly, efforts should be made to reducethe nation’s dependence on foreign countries. This might be done by undertaking production indigenously, promoting exports and reducing imports.
5) Social welfare:Business concern may additionally support directly orindirectly welfare schemes in the society. The welfare schemes that business has to adopted i.e., adopting schools in backward areas, providing funds for rural development activities like construction of roads, irrigation etc. organizing health campsetc.
6) Development of Backward Areas:Business concern can contribute towards development of backward areas of the state. This will be done by fixing industries in such areas. Also, financial and technical assistance can be provided to units in such backward areas. The government too, encourages the event of backward areas by providing many incentives like tax holidays, low rates of taxation, tax exemptions thenon.
7) National Integration and communal Harmony:Business concern is referredas corporate citizens. Therefore, they should work for national integration and communal harmony. They should not support anti-social elements or communal forces who work against national integration. This is often one of the most important national objectives of business.
8) Creation of Employment opportunities: Business creates employment opportunities either directly or indirectly. In a country like India where unemployment and disguised employment are at a very high level, it is advisable for the industries to adopt wherever possible labor-intensive techniques so as to employ a greater number of individuals and thereby reduce the amount of people below the povertyline.
Business is a part of society and thus, it has to balance its economic and social objectives so as to satisfy the various groups i.e., consumers, employees, shareholders, Government, Suppliers, Competitors and society. The economic and social objectives can be reconciled as under:
1) Profit and consumer price:An important economic objective is to earn more profit. This might be done not by charging high price but by increasing efficiency, reducing wastages, putting the available resources to optimum use, innovations etc. such strategies on the part of the management would enable them to charge reasonable price for the products. This is often how a balance can be caused between the economic objectives of earning profit and therefore the social objective of charging a reasonableprice.
2) Profit and Research and Development: A business concern must earn profit. Apart of the profit must be invested in research and development. This would help the organization to enhance the standard. Improvement in quality would not only bring customer satisfaction but also higher sales to the businessconcern.
3) Business expansion and social Interest:Business concern should bring expansion of business activities not merely for profit maximization except for serving the customer better. However, expansion of business for securing the benefits of large- scale operations and passing on same portion of benefit to consumers is desirable. Expansion for generation of employment opportunities is also economically and socially desirable.
4) Profit and After-Sale-Service: business concern must focus on after sale service, especially in the case of durables. a part of the profit must be spent in training the after-sale-service work force. Additional after-sale-service work force could also be appointed by the firm to provide better service to thecustomers.
5) Profit and shareholders’ Interest: Shareholders expect higher dividend, which is feasible as long as the profit is high. When the organization earns higher profits, the employees may demand higher wages. Business concern needs to accept this fact and pay higher wages to the employees by correlating their performance with the pay. This would motivate the employees to put in their best efforts. Simultaneously, the organization should also pay higher dividend to the shareholders for thedanger undertaken by them by investing in the company. Thus, reconciliation between the two objectives could be broughtout.
6) Profit and Employees welfare: Business concern makes profits due to the efficiency of its manpower. Therefore, business must spend a part of its profits for the welfare of its employees by providing better facilities like improved working conditions, additional welfare facilities, and increase in salariesetc.
7) Profit and Social Development:Business organization spends some a part of profit for the social development activities. Like donations to colleges, colleges, trusts etc. contributions to government at the time of natural calamities, floods, famines etc., and for such other socialactivities.
8) Business expansion and Suppliers:Business concern needs support of suppliers for its business expansion plans. It shouldn't attempt to exploit the suppliers. There are a good number of cases, where large business concern exploits suppliers by delaying payment, demanding unreasonable higher discountetc.
Business environment consists of all the internal and external forces or factors that influence the working of a business firm.
The internal factors consist of firm’s strategy and policies, management-labor relations, resources like manpower, capital, machines, etc.
The internal forces consist of the micro factors like, economic, political, social, technical and other factors.
Features of Business Environment:
The main features of the Business Environment are as follows:
- Dynamic in Nature: Changes takes place in the external environment. For Instance, - Customers taste and preference may change any time.
- Competitors might introduce new product designs, may change pricing, etc.
- Government may introduce policy changes in respect to taxation, foreign trade, foreign investment, etc.
2. Direct & Indirect Impact: Business Environment may have direct and indirect impact in the cycle of business. For example,
- Micro external factors like competition, government policies, customer preference, etc., can have a direct and immediate effect on the working of a business firm.
- The macro external factors like social, economic and political factors may have indirect effect on the working of the business firm.
3. Internal and External Factors: Activities of business firms an influenced by internal and external factors. The internal factors are controllable in nature. It includes machinery, manpower, management-labor relations, etc. For instance, a company can replace old machinery with new, if so required. The external factors are beyond the control of a business firm. External factors include Government policies competitor’s strategies, customer preferences, etc. A business firm needs to adjust its strategies depending upon the changes in external factors.
4. Inseparable Part of Business: Environment is an integral part of business. Business firms cannot operate without environment. For instance, business firms cannot operate without customers, suppliers and dealers. Also, business firms depend upon natural environment for is resources such as raw materials. The technological and other factors also influence the working of the business.
5. Complex in Nature: Environment of modern business is more complex and unpredictable. In olden days, business environment was stable - customers' preferences were few, competition was limited, government policies were stable, and so on. Nowadays, the business environment is more complex due to heavy competition, growing customers' expectations, drastic changes in government policies, and so on.
6. Creates Opportunities and Obstacles: Environment provide opportunities and creates obstacles in the working of an Opportunities may be turned as favorable situations which facilitates higher profits and growth of the business. Obstacles are the unfavorable situations, which may adversely affect the organization’s profitability and organization growth.
7. Regulates Scope of Business: Environment regulates the scope of business activities. For instance, Government regulations such as restrictions on advertising of liquor and cigarettes, restricts advertising of socially undesirable products.
8. Reactive and Proactive Decisions: Due to environment, business firms take proactive and reactive decisions. Majority of the firms take reactive decisions, i.e., in reaction to decisions taken by others or competitors.
Few firms take proactive decisions to launch new models/ schemes, to introduce price changes, to restructure business, etc., before others do it. Such firms gain competitive advantage in the market. Examples: Hero Motorcycles, TCS (software), Ultra Tech Cements, etc.
9. Environment is Multi-dimensional: Changes in environment may have positive and negative impact on the working of business firms. Environmental changes may be favorable to some firms, and unfavorable to others.
For instance, Government of India has liberalized the entry of foreign companies into India. A majority of Indian domestic firms consider the Govt.'s move as a threat because they have to face competition from the foreign firms. However, few of the Indian firms consider it as an opportunity as they can have a tie-up with the foreign firms, and also they can learn techniques from the foreign firms.
10. Environment Analysis and Planning: The relationship between planning and environment analysis is inseparable. The main purpose is to set the goals or objectives. Environmental analysis indicates strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT. Depending on the SWOT analysis, a firm sets its objectives.
For instance, if the SWOT analysis indicates opportunities, the firm can set higher targets. However, if the threats are identified, the firm may lower down its targets.
- Internal Environment
The following are the factors on internal environment:
Value System:
The value system of an organization means the ethical beliefs that guide the organization in achieving its mission and objective. The value system of a business organization alsodetermines its behavior towards its employees, customers and society at large. The value system of the promoters of a business firm has an important bearing on the choice of business and the adoption of business policies and practices. Due to its value system a business firm may refuse to produce or distribute liquor for it may think morally wrong 8to promote the consumption of liquor.
Mission and Objectives:
The objective of all firms is assumed to be maximization of long-run profits. But mission is different from this narrow objective of profit maximization. Mission is defined as the overall purpose or reason for its existence which guides and influences its business decision and economic activities. The-choice of a business domain, direction of its development, choice of a business strategy and policies are all guided by the overall mission of the company. For example, “to become a world-class company and to achieve global dominance has been the mission of ‘Reliance Industries of India’. Similarly, “to become a research based international pharma company” has been stated as mission of Ranbaxy Laboratories of India.
Organisation Structure:
Organization structure means such things as composition of board of directors, the number of independent directors, the extent of professional management and share -holding pattern. The nature of organizational structure has a significant influence over decision making process in an organization. An efficient working of a business organization requires that its organization structure should be conducive to quick decision making. Delays in decision making can cost a good deal to a business firm.
The board of directors is the highest decision-making body in a business organization. It takes general policy decisions regarding direction of growth of business of the firm and supervises its overall functioning. Therefore, the managerial capability of the board of directors is of crucial importance for the functioning of a business firm and for achievement of its overall mission and objectives.
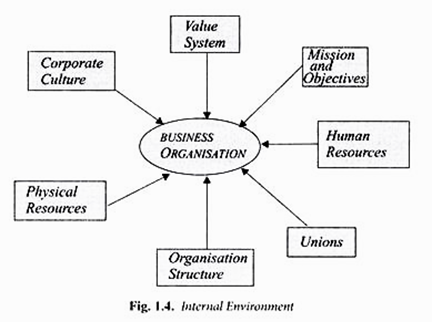
Corporate Culture and Style of Functioning of Top Management:
Corporate culture and style of functioning of top managers is important factor for determining the internal environment of a company. Corporate culture is generally considered as either closed and threatening or open and participatory.
In a closed and threatening type of corporate culture the business decisions are taken by top-level managers, while middle level and work-level managers have no say in business decision making. There is lack of trust and confidence in subordinate officials of the company and secrecy pervades throughout in the organization. As a result, among lower level managers and workers there is no sense of belongingness to the company.
On the contrary, in an open and participatory culture, business decisions are taken at lower levels of management, and top management has a high degree of trust and confidence in the subordinates. Free communication between the top-level management and lower-level managers is the rule in this open and participatory type of corporate culture. In this open and participatory system, the participation of workers in managerial tasks is encouraged.
Human Resources:
Human Resources of a firm is an important factor of internal environment of a firm. The success of a business organization depends to a great extent on the skills, capabilities, attitudes and commitment of its employees. Employees differ with regard to these characteristics.
It is difficult for the top management to deal directly with all the employees of the business firm. Therefore, for efficient management of human resources, employees are divided into different groups. The manager may pay little attention to the technical details of the job done by a group and encourage group cooperation in the interests of a company. Due to the importance of human resources for the success of a company these days there is a special course for managers how to select and manage efficiently human resources of a company.
Labour Unions:
Labor unions are another factor determining internal environment of a firm. Unions collectively bargain with top managers regarding wages, working conditions of different categories of employees. Smooth working of a business organization requires that there should be good relations between management and labor union.
Each side must implement the terms of agreement reached. Sometimes, a business organization requires restructuring and modernization. In this regard, the terms and conditions reached with the labor union must be implemented in both letter and spirit of cooperation of workers is to be ensured for the reconstruction and modernization of business.
Physical Resources and Technological Capabilities:
Physical resources such as plant and equipment, and technological capabilities of a firm determine its competitive strength which is an important factor determining its efficiency and unit cost of production. R and D capabilities of a company determine its ability to introduce innovations which enhance productivity of workers. The firm may take appropriate measures to correct weakness. For instance, the obsolete machines may be replaced.
Corporate Image:
A firm should develop and maintain good corporate image in the minds of the employees, investors, customers, and others. A firm should undertake analysis of its corporate image. If a firm finds problem in corporate image, then adequate measures need to be taken.
B. External Environment
The external environment consists of all the factors which provide opportunities or pose threats to an organization. In a wider sense, the external environment encompasses a variety of factors like international, national and local economy. Social changes, demographic variables, political system, technology, attitude towards business, energy sources, raw materials and other resources and many other macro level factors make up the external environment.
We could designate such wide perception of the environment as a general environment. All organizations, in some way or the other, are concerned about the general environment but the immediate concerns of any organization are confined just to a part of the general environment which could be termed as a highly relevant environment and enables the organization to focus its attention on those factors which are intimately related to its mission, purpose, objects and strategies.
Depending on its perception of the relevant environment, an organization takes into account those influences in its surroundings which have an immediate impact on its strategic management process.
i. Micro Environment:
Micro external factors have an important effect on business operations of a firm. However, all micro factors may not have the same effect on all firms in the industry. For example, suppliers, an important element of micro level environment, are often willing to provide the materials at relatively lower prices to big business firms. They do not have the same attitude towards relatively small business firms.
Some important micro elements of the business environment are described here:
a) Customer:
The prime task for any business is to attract and retain customers. This is to ensure its own long-term profitability and existence in the market. It therefore follows that the need and the desire of the customer should be monitored minutely to ensure customer delight, which will lead to the firm having an increasing number of loyal customers.
Changing tastes and preferences of the customer should not only be observed as they happen, but forecasted before, and necessary corrections should be made in the product/service profile by the company. Customers are the backbone of a company and the very reason for the company’s existence.
b) Products:
Product factors such as the demand, image, features, utility, function, design, life cycle, price, promotion, distribution, differentiation and availability of substitutes of products or services also form an intimate part of the business environment. The product/service features are the key to attract/retain customers.
c) Marketing Intermediary:
This includes all those who facilitate distribution of goods from the centres of production to the various centres of consumption. These are the middlemen who form part of the distribution channel and those who help reach the product/service to the ultimate consumer. They can be few or many in number, depending on the length of the distribution chain and type of distribution system that the company adopts. If this chain is hassle free and functions without many hurdles, it eventually helps the organisation.
d) Competitors:
The world has become a global market. There exists tremendous competition in each and every area. There are other business entities that manufacture similar products and compete with a company for market share and turnover. These have to be managed well and market intelligence is required to find out about their future plans. These can play a major role in making or marring the fortunes of any company.
e) Suppliers:
An important factor in the micro environment is the supplier, i.e., those who supply raw materials and components and machines to the company. The suppliers should be reliable and act as business partners, working in coordination to fulfil the ultimate consumer expectations. If the suppliers are reliable, there is no need to keep heavy inventory stocks that increases the risk of obsolescence and damage and also blocks to working capital of the company.
Ii. Macro Environment:
The macro environment is the larger, uncontrollable environment consisting of societal forces that affect all other environments. They offer tremendous opportunities for any business and also present threats that can harm a business in a major way. This environment becomes crucially important to understand and study for the purpose of strategic planning and decision-making.
It has broader dimensions than the micro environment. It consists of individuals, groups, agencies, events, conditions and forces with which the organisation comes into frequent contact in the course of its functioning. The macro environment is actually the real environmental factor that influences the growth and structure of any business to the greatest degree.
It is made up of following components:
a) Socio-Cultural Environment:
This consists of the society and culture of a place where the organisation is doing its business. It is a general entity and influences almost all firms in a similar manner. Some of the important factors and influences operating in the social environment are the buying and consumption habits of people, their languages, beliefs and values, customs and tradition, tastes and preferences, education and ail factors that affect the business.
b) Political Environment:
The political environment consists of factors related to the management of public affairs and their impact on the business of an organization. Political environment has a close relationship with the economic system and economic policies. For Example, communist countries have a centrally planned economic system. In most countries apart from those laws that control investment and related matters, there are a number of laws that regulate the conduct of the business. These laws cover such matters as standard of product, packaging, promotion, etc.
India is a democratic country having a stable political system where the Government plays an active role as a planner, promoter and regulator of economic activities. Businessmen therefore are conscious of the political environment that their organization faces. Most governmental decisions related to business are based on political considerations in line with the political philosophy followed by the ruling party at the centre and the state level.
c) Economic Environment:
The economic environment consists of macro level patterns related to the areas of production and distribution of wealth that have an impact on the business of an organization.
Some of the important factors and influences operating in economic environment are:
I. Economic stages existing at a given time in a country.
II. The economic structure adopted such as capitalistic, socialistic or mixed economy.
III. Economic planning, such as 5 — year plans, annual budgets, etc.
IV. Economic policies, such as industrial, monetary and fiscal policies.
d) Technological Environment:
The technological environment consists of those factors related to knowledge applied and the materials and machines used in the production of goods and services that have an impact on the business of an organization. For many enterprises, technology is the most dynamic of all environmental factors. An individual firm is concerned with its product and process technology. This environment consists of those factors that involve any type of technological advancement or lack of the same.
e) Demographic Environment:
This environment deals with the composition and characteristics of the population of a place. All the relevant descriptions of the population of a place with respect to its demographic profile will affect business decisions drastically. It would be in the interest of any firm to consider these aspects in detail before planning the strategy.
It includes factors such as:
I. Average family size
II. Size of population
III. Educational levels
IV. Economic stratification of the population, etc.
Business and environment are interdependent on each other for sustainable growth. The interrelationship between business and environment is explained as follows:
- Economic Environment: Economic environment includes all those forces which have an economic impact on business. Accordingly, total economic environment is consisting of agriculture, industrial production, infrastructure, planning, basic economic philosophy, stages of economic development, trade cycles, national income, per capita income, savings, money supply, price level and population. Business and economic environment is closely related. Business usually collects all its required inputs from the economic environment available and also absorbs the output of business units.
- Politico-legal Environment: It includes the activities of three political institutions, viz., legislature, executive and judiciary which usually play useful role in shaping, directing, developing and controlling business activities. The legislature takes decision on a particular course of action, the executive implements those decisions through government agencies and the judiciary serves as a watch-dog for ensuring public interest in all the activities of legislature and executive. In order to attain a meaningful business growth a stable and dynamic politico-legal environment is very important.
- Technological Environment: Technological environment is exercising considerable influence on business. Technology implies systematic application of scientific or other organized knowledge to practical tasks or activities. Business makes it possible for the technology to reach the people in proper format. As the technology is changing fast thus businessmen should keep a close look on those technological changes for its adaptation in their business activities.
- Global or International Environment: Global environment is also playing an important role in shaping the business activity. With the liberalization and globalization of the economy, business environment of an economy has become totally different when it has to bear all shocks and benefits arising out of global environment.
- Natural: Natural environment also influences business in a diverse way. Business of modern times is also dictated by nature. Natural calamities like floods, droughts, earthquake etc. affect the business activities in a worst manner.
- Socio-Cultural: Finally, social and cultural environment is also influencing the business environment indirectly. These includes people’s attitude to work and wealth, ethical issues, role of family, marriage, religion and education and also social responsiveness of business. Social and cultural environment also influences the demand for variety of goods and the type of employees the industry requires.
- Demographic Environment: Demographic environment influences business decisions. The business firms take business decision depending on demographic features of the population. For instance, business firms can provide fund to improve literacy in India.
- Primary Education:
In Maharashtra, primary education covers schooling up to 4th standard. (The Central Government considers primary education from 1st to 5th standard and upper primary education from 6th to 8th standard).
The government has taken several steps to spread primary education. The National Policy on Education had stated that children attaining 14 years would have free and compulsory education up to class V.
The Right to Education Act aims at providing free and compulsory education to children from 6 to 14 years. However, in spite of several efforts on the part to the government the dropout rate is very high.
2. Secondary Education:
In Maharashtra, it covers standards from Vth to TX. In a number of states education up to class X is free. In some state’s higher education for girls and for SCs and STs is free. However, the enrolment for secondary education is low and also there is high dropout ratio.
3. Higher Secondary Education:
Standards 11th and 12th constitute Higher Secondary Education. This stage is also known as +2 stage or Junior College as per 10+2+3 education system. In many states including Maharashtra, the Junior colleges are either attached to school or degree colleges.
Vocational courses are introduced at junior college level in order to make education more meaningful and gainful for employment. However, except a few isolated courses, and in few states, Vocationalist did not achieve the desired Objectives.
4. Higher Education:
The higher education system comprises both technical and general education. It is also known as university or degree level education and the normal duration is 3 to 5 years, depending upon the duration of the course. During the year 2017, in India, there were 819 universities and more than 40,000 affiliated colleges enrolling more than 20 million students. More than 85% of students are enrolled in bachelor s degree courses with majority enrolling in three-year B.A., B.Com. Or B.Sc. Degrees.
5. Professional Education:
Professional education is more specialized and is provided in the fields of management, accountancy, medicine, engineering technology, etc. It is very much required to create highly skilled manpower. As of 2017, in India, there are:
-23 leading Technical Institutes - Indian Institutes of Technology (ln)- Mumbai, Kanpur, Kharagpur, Chena, New Delhi. Goa and others.
-20 Indian Institutes of Management - Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Calcutta and Lucknow, Indore, Kozikhode and others.
-9 All India Institutes of Medical Sciences - Delhi, Bhopal Bhubaneshwar, Patna, Jodhpur, Raipur, Rishikesh, Guntur (AP) and Nagpur.
-There are also a number of other professional institutes imparting professional education.
Environmental analysis is a strategic tool. It’s a process to find all the external and internal elements, which affect the organization’s performance. The analysis entails assessing the extent of threat or opportunity the factors might present. These evaluations are later translated into the decision-making process. The analysis helps align strategies with the firm’s environment.
Our market is facing changes on a daily basis. Many new things develop over time and therefore the whole scenario can alter in just some seconds. There are some factors that are beyond your control. But, you'll control plenty of these things.
Businesses are greatly influenced by their environment. All the situational factors which determine day to day circumstances impact firms. So, businesses must constantly analyse the trade environment and therefore the market.
There are many strategic analysis tools that a firm can use, but some are more common. The foremost used detailed analysis of the environment is that the PESTLE analysis. This is a bird’s eye view of the business conduct. Managers and strategy builders use this analysis to seek out where their market currently. It also helps foresee where the organizations are going to be in the future.
PESTLE analysis consists of varied factors that affect the business environment. Each letter in the acronym signifies a group of factors. These factors can affect every industry directly or indirectly.
The letters in PESTLE, also called PESTEL, denote the subsequent things:
Political factors
Economic factors
Social factors
Technological factors
Legal factors
Environmental factor
Often, managers prefer to study political, economic, social and technological factors only. Therein case, they conduct the PEST analysis. PEST is additionally an environmental analysis. It's a shorter version of PESTLE analysis. STEP, STEEP, STEEPLE, STEEPLED, STEPJE and LEPEST: All of those are acronyms for an equivalent set of things . a number of them gauge additional factors like ethical and demographical factors.
I will discuss the 6 most typically assessed factors in environmental analysis.
P for Political factors
The political factors take the country’s current political situation. It also reads the worldwide political condition’s effect on the country and business. When conducting this step, ask questions like “What quite government leadership is impacting decisions of the firm?”
Some political factors that you simply can study are:
Government policies
Taxes laws and tariff
Stability of state
Entry mode regulations
E for Economic factors
Economic factors involve all the determinants of the economy and its state. These are factors which will conclude the direction during which the economy might move. So, businesses analyse this factor supported the environment. It helps to line up strategies in line with changes.
I have listed some determinants you'll assess to understand how economic factors are affecting your business below:
The rate of inflation
The rate of interest
Disposable income of buyers
Credit accessibility
Unemployment rates
The monetary or fiscal policies
The foreign exchange rate
S for Social factors
Countries vary from one another. Every country features a distinctive mindset. These attitudes have an impression on the companies. The social factors might ultimately affect the sales of products and services.
Some of the social factors you ought to study are:
The cultural implications
The gender and connected demographics
The social lifestyles
The domestic structures
Educational levels
Distribution of Wealth
T for Technological factors
Technology is advancing continuously. The advancement is greatly influencing businesses. Performing environmental analysis on these factors will assist you stay up to date with the changes. Technology alters every minute. This is often why companies must stay connected all the time. Firms should integrate when needed. Technological factors will assist your skills the consumers react to varied trends.
Firms can use these factors for his or her benefit:
New discoveries
Rate of technological obsolescence
Rate of technological advances
Innovative technological platforms
L for Legal factors
Legislative changes happen from time to time. Many of those changes affect the business environment. If a regulatory body sets up a regulation for industries, for instance , that law would impact industries and business therein economy. So, businesses should also analyse the legal developments in respective environments.
I have mentioned some legal factors you would like to remember of:
Product regulations
Employment regulations
Competitive regulations
Patent infringements
Health and safety regulations
E for Environmental factors
The location influences business trades. Changes in climatic changes can affect the trade. The buyer reactions to particular offering also can be a problem . This most frequently affects agri-businesses.
Some environmental factors you'll study are:
Geographical location
The climate and weather
Waste disposal laws
Energy consumption regulation
People’s attitude towards the environment
There are many external factors aside from those mentioned above. None of those factors are independent. They believe one another.
If you're wondering how you'll conduct environmental analysis, here are 5 simple steps you'll follow:
1. Understand all the environmental factors before moving to subsequent step.
2. Collect all the relevant information.
3. Identify the opportunities for your organization.
4. Recognize the threats your company faces.
5. The ultimate step is to take action.
It is true that industry factors have an impression on the corporate performance. Environmental analysis is important to see what role certain factors play in your business. PEST or PESTLE analysis allows businesses to take a glance at the external factors. Many organizations use these tools to project the expansion of their company effectively.
The analyses provide a decent look at factors like revenue, profitability, and company success. If you would like to require the proper decisions for your firm, employ environmental analysis.
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, then a SWOT Analysis is a technique for assessing these four aspects of your business.
You can use SWOT Analysis to form the most of what you've , to your organization's best advantage. And you'll reduce the probabilities of failure, by understanding what you're lacking, and eliminating hazards that might otherwise catch you unawares.
Better still, you'll start to craft a technique that distinguishes you from your competitors, and then compete successfully in your market.
How to Do a SWOT Analysis
First, draw up a SWOT Analysis matrix, or use our free downloadable template. This is often a 2x2 grid, with one square for every of the four aspects of SWOT. Figure 1 shows what it should appear as if (click on the image to ascertain a larger version).
Figure 1 A SWOT Analysis Matrix
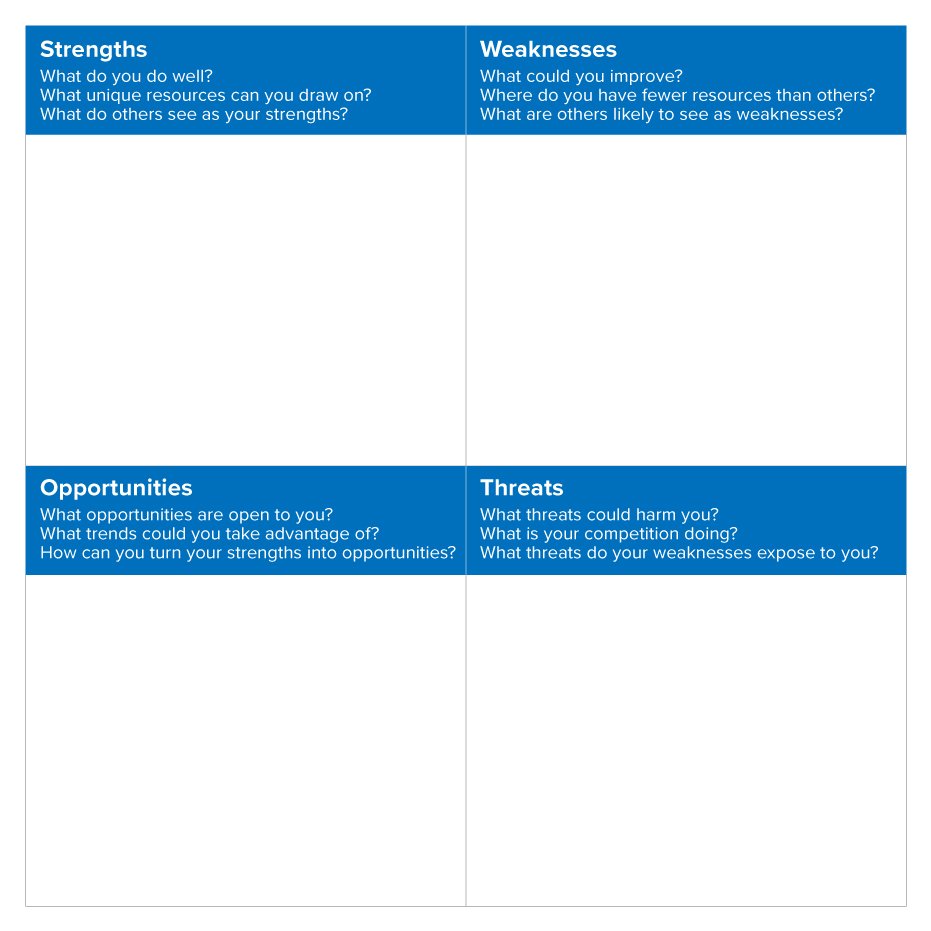
You can approach a SWOT Analysis in two ways: to urge people together to "kick off" strategy formulation informally, or as a more sophisticated and formal tool.
In either case, gather a team from a variety of functions and levels in your organization. Use Brainstorming techniques to create a list of ideas about where your organization currently stands. Whenever you identify a Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, or Threat, write it down in the relevant a part of the grid.
To clarify which section an idea belongs to, it's going to be useful to consider Strengths and Weaknesses as internal factors – that’s, to try to with the organization, its assets, processes, and people. Think about Opportunities and Threats as external factors, arising from your market, your competition, and therefore the wider economy.
Let's check out each area in more detail and consider what questions you'll ask as a part of your analysis.
Strengths
Strengths are things that your organization does particularly well, or in a way that distinguishes you from your competitors. Think about the benefits your organization has over other organizations. These could be the motivation of your staff, access to certain materials, or a strong set of producing processes.
Your strengths are an integral a part of your organization, so think about what makes it "tick." What does one do better than anyone else? What values drive your business? What unique or lowest-cost resources can you draw upon that others can't? Identify and analyse your organization's Unique Selling Proposition (USP), and add this to the Strengths section.
Then turn your perspective around and ask yourself what your competitors might see as your strengths. What factors mean that you get the sale before them?
Remember, any aspect of your organization is merely strength if it brings you a clear advantage. For instance, if all of your competitors provide high-quality products, then a high-quality production process isn't a strength in your market: it is a necessity.
Weaknesses
Now it is time to consider your organization's weaknesses. Be honest! A SWOT Analysis will only be valuable if you gather all the knowledge you need. So, it is best to be realistic now, and face any unpleasant truths as soon as possible.
Weaknesses, like strengths, are inherent features of your organization, so specialise in your people, resources, systems, and procedures. Think about what you'll improve, and the kinds of practices you should avoid.
Once again, imagine (or find out) how other people in your market see you. Do they notice weaknesses that you simply tend to be blind to? Take time to look at how and why your competitors do better than you. What are you lacking?
Opportunities
Opportunities are openings or chances for something positive to happen, but you will need to claim them for yourself!
They usually arise from situations outside your organization, and require a watch to what might happen in the future. They could arise as developments in the market you serve, or in the technology you employ. Being able to identify and exploit opportunities can make an enormous difference to your organization's ability to compete and take the lead in your market.
Think about good opportunities you'll spot immediately. These don't got to be game-changers: even small advantages can increase your organization's competitiveness. What interesting market trends are you conscious of , large or small, which could have an impact?
You should also be careful for changes in government policy associated with your field. And changes in social patterns, population profiles, and lifestyles can all present interesting opportunities.
Threats
Threats include anything which will negatively affect your business from the outside, like supply chain problems, shifts in market requirements, or a shortage of recruits. It is vital to anticipate threats and to take action against them before you become a victim of them and your growth stalls.
Think about the obstacles you face in getting your product to market and selling. You'll notice that quality standards or specifications for your products are changing, and that you will need to alter those products if you're to remain in the lead. Evolving technology is an ever-present threat, also as an opportunity!
Always consider what your competitors do , and whether you ought to be changing your organization's emphasis to satisfy the challenge. But remember that what they're doing might not be the right thing for you to do, and avoid copying them without knowing how it'll improve your position.