Unit 3
SYBAF
Subject matter of public finance:
The economics of public finance is fundamentally concerned with the technique of rising and dispersion of dollars for the functioning of the government. Thus, the find out about of public revenue and public expenditure constitutes the principal division in the find out about of public finance.
But with these two symmetrical branches of public finance, the hassle of business enterprise of elevating and disbursing of assets additionally arises.
It has also to resolve the query of what is to be performed in case public expenditure exceeds the revenues of the state. In solving the first problem, “financial administration” Comes into the picture. In the latter problem, obviously, the technique of public borrowings or the mechanism of public debt is to be studied.
Since both public debt as well as financial administration offers upward jab to a variety of distinctive problems, these are conventionally handled as a separate branch of the subject.
As such, we have four major divisions (traditionally set) in the find out about of public finance:
1. Public revenue, which offers with the approach of elevating funds and the principles of taxation. Thus, within the purview of public revenue, we take up the classification of public revenue, canons and justification of taxation, the hassle of incidence and transferring of taxes, consequences of taxation, etc.
2. Public expenditure, which offers with the ideas and problems bearing on to the allocation of public spending’s. Here we find out about the vital concepts governing the glide of public dollars into exclusive channels; classification and justification of public expenditure; expenditure insurance policies of the authorities and the measures adopted for accepted welfare.
3. Public debt, which offers with the study of the motives and strategies of public loans as nicely as public debt management.
4. Financial administration, under this the trouble of how the financial equipment is organized and administered is dealt with.
The scope of public finance is not just to find out about the composition of public income and public expenditure. It covers a full discussion of the have an impact on of government fiscal operations on the stage of typical activity, employment, costs and increase system of the financial device as a whole.
According to Musgrave, the scope of public finance embraces the following three functions of the government’s budgetary coverage limited to the fiscal department:
(i) the allocation branch,
(ii) the distribution branch, and
(iii) the stabilization branch.
These refer to three goals of finances policy, i. E., the use of fiscal instruments:
(i) to impenetrable adjustments in the allocation of resources,
(ii) to impenetrable changes in the distribution of income and wealth, and
(iii) to achieve financial stabilization.
Thus, the function of the allocation department of the fiscal branch is to decide what changes in allocation are needed, who shall endure the cost, what income and expenditure policies to be formulated to fulfill the desired objectives.
The characteristic of the distribution department is to decide what steps are needed to carry about the favored or equitable nation of distribution in the economy and the stabilization branch shall confine itself to the choices as to what ought to be carried out to tightly closed charge steadiness and to keep full employment level.
Further, modern public finance has two aspects:
(i) positive aspect and (ii) normative aspect.
In its advantageous aspect, the study of public finance is concerned with what are sources of public revenue, gadgets of public expenditure, constituents of budget, and formal as nicely as tremendous incidence of the fiscal operations.
In its normative aspect, norms or standards of the government’s monetary operations are laid down, investigated, and appraised. The simple norm of modern finance is normal economic welfare. On normative consideration, public finance turns into a skillful art, whereas in its nice aspect, it remains a fiscal science.
1. Allocation function:
The provision for social goods, or the manner by way of which complete aid use is divided between private and social goods and via which the mix of social goods is chosen.
This provision can also be termed as the allocation function of price range policy. Social goods, as distinct from private goods, can't be provided for via the market system.
The fundamental motives for the market failure in the provision of social items are:
Firstly, consumption of such is non-rival, in the sense that one person’s engaging of benefits does not minimize the benefits handy to others.
The advantages of social items are externalized. Secondly,
The exclusion precept is no longer possible in the case of social goods.
The application of exclusion is often impossible or prohibitively expensive. So, the social goods are to be supplied through the government.
2. Distribution function:
Adjustment of the distribution of profits and wealth to assure conformance with what society considers a ‘fair’ or ‘just’ nation of distribution.
The distribution of earnings and wealth determined by means of the market forces and laws of inheritance contain a big diploma of inequality. Tax transfer insurance policies of the authorities play a vital role in decreasing the inequalities in earnings and wealth in the economy.
3. Stabilization function:
Fiscal policy is wished for stabilization, in view that full employment and fee stage steadiness do no longer come about robotically in a market economy. Without it the financial system tends to be difficulty to good sized fluctuations, and it may additionally go through from sustained periods of unemployment or inflation.
Unemployment and inflation can also exist at the identical time. Such a state of affairs is recognized as stagflation.
The ordinary stage of employment and prices in the economy depends upon the stage of mixture demand, relative to the attainable or ability output valued at prevailing prices. Government fees add to total demand, while taxes limit it. This suggests that budgetary consequences on demand increase as the degree of expenditure will increase and as the degree of tax income decreases.
4. Economic growth:
Moreover, the trouble is not only one of maintaining excessive employment or of curtailing inflation inside a given stage of ability output. The results of fiscal coverage upon the charge of growth of attainable output should also be allowed for. Fiscal policy might also have an effect on the charge of saving and the willingness to make investments and may thereby impact the price of capital formation.
Capital formation in turn impacts productiveness growth, so that fiscal coverage is a great factor in financial growth.
Introduction
the precept of most social advantage is one o0f the core objectives of public economics. Public economics deal about of administration of assets of an economy.
It consists of many things like public revenue, public expenditure, public debt and so on.
Taxation and public charges are the sizable matters of public finance.
The precept of maximum social advantage is associated with the names of two economists like professor Dalton’s and Pigou.
By this principle, it is aimed to analyze the welfare of a society. It additionally suggests the ways which can be accompanied to acquire most social advantage.
The principle of maximum social advantage
Broadly public finance has two aspects like public expenditure and public revenue. Public revenue are these which collects from the public to government treasury. It may additionally be in the varieties of taxation, fees, fines, expenses etc. Public expenditure is those which incurred from the section of government.
It can also be in different forms like social welfare programs, defense, infrastructural traits etc.
Public expenditure creates many benefits in the society.
It will make bigger the income of the humans and which will assist the growth of the economy. So in fact, increasing of public expenditure will extend utility and benefits in the society. On contrary, public revenue or imposition of taxes creates dis-utility. This may additionally badly have an effect on t6he economy. So, there will be social sacrifice.
Suppose authorities raised revenue by means of increasing company tax and profits tax, human beings will be discouraged. Because, higher charge of tax will limit the proposal for similarly production this may also carry the economic system in to backwardness. In short, increasing of utility by way of expanding expenditure, the financial system can revel in most social benefits. Similarly, decreasing of dis-utility by means of reducing tax will lead to minimal social sacrifice.
Public expenditure and maximum social benefits
Public expenditure is very imperative for bettering economic activities. Because, public expenditure will assist to inject money in to the economy Therefore, higher the public expenditure ensures maximum social benefits. It can be representing graphically as showing below.
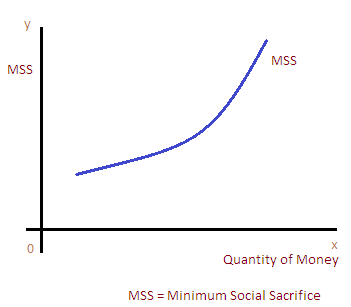
In the graph, the extent of money in government is represented on ‘x’ axis and most social benefits on ‘y’ axis. There is a bad relationship exists in between maximum social advantages and the quantity of money.
When the quantity of money in the government is brief due to the fact of higher public expenditure, there will be higher degree of social benefits. Similarly, if authorities elevated its cash in the treasury by lowering public expenditure, there will be decrease degree of social benefits.
Public revenue (taxation) and minimum social sacrifice
Public income is generally accumulated in the shape of taxation. Higher taxation will minimize the quantity of cash in the economy. Therefore, greater stage of taxes will lead to higher level of social sacrifice. But, higher level of social sacrifice will discourage the economic activities and its growth. At the equal time government can impose greater taxes on luxurious products. It can be representing graphically as follows.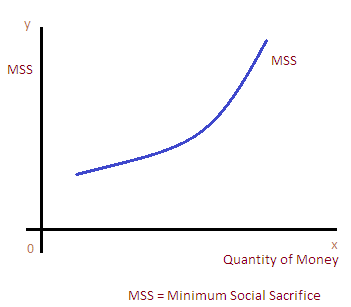
In the above graph, the extent of money is represented on ‘x’ axis and level of social sacrifice on the ‘y’ axis. When the government extend volume of cash by means of charging greater taxes, it will create greater level of social sacrifice. On the different side, the social sacrifice will be decrease if authorities lowers taxes.
Maximum social advantage
the ultimate intention of public finance is to obtain most social gain by way of adjusting minimum social sacrifice and most social benefits. That is in alternative sense, the repute of public finance is connected to the equilibrium of public expenditure and public revenue. It can be represented in a design as showing below.
The principle of maximum social benefit says that, there should be an equalization between maximum social advantages and minimal social sacrifice as depicted in the above figure (point ‘e’).
Where the condition (maximum social benefits = minimum social sacrifice) is satisfied. The equilibrium is reached at the volume of money equaled to ‘om’. When the quantity of cash diminished (between ‘o’ to ‘m’), the advantages or expenditure will be greater than the sacrifice or taxation.
On the different side, if the extent of cash in the government elevated above ‘om’ level, taxation or sacrifice will be greater than the expenditure or benefits.
In short, maximum social benefit can be attained at a factor the place social sacrifice and social advantages are equal. This circumstance can be known as as “optimum public finance”.
Musgrave’s view on maximum social advantage
Musgrave used to be another renowned economist who elaborated the identical precept with some alterations.
He emphasized the same principle by connecting to benefit.
Musgrave says that, thee expenditure spend by way of authorities flows in to a number fields such as defense, education, healthcare etc. So there will be exclusive benefit for every field.
Similarly the sacrifice additionally impacts specific fields or outlays. Therefore, Musgrave conclude that, maximum social benefits from each fields or outlays need to be equal to the most social sacrifice of every outlay.
Criticisms
the principle of maximum social advantage is no longer free from criticisms. Some of them are listed below.
I) the precept assumes that, sacrifice and advantages are measurable. But in sensible level it has limited scope.
Ii) Equalizing marginal utility or advantage for every outlay is difficult.
Iii) Now, the cutting-edge view is based totally on purposeful finance. That is taxes and expenditure can be adjusted according to the circumstances to reap maximum social advantage.
Musgrave’s approach to maximum social advantage:
Prof. R.a. Musgrave states that the principle of maximum social ad-vantage is a logical extension of the Pigouvian welfare method to taxation integrated in the idea of minimal combination sacrifice.
Musgrave is of the opinion that ultimate measurement of the finances be determined at a point where the marginal net advantage is zero.
Fundamentally there is no longer a lot distinction between the strategy of prof. Dalton’s and Musgrave.
Musgrave re-designate Dalton’s’s principles of maximum social benefit as the maximum welfare principles of finances determination.
Even although Musgrave pursued the line of reasoning endorsed by means of Dalton’s and Pigou, his therapy is based totally on valuation of character preferences.
Musgrave’s approach is illustrated in the following diagram:
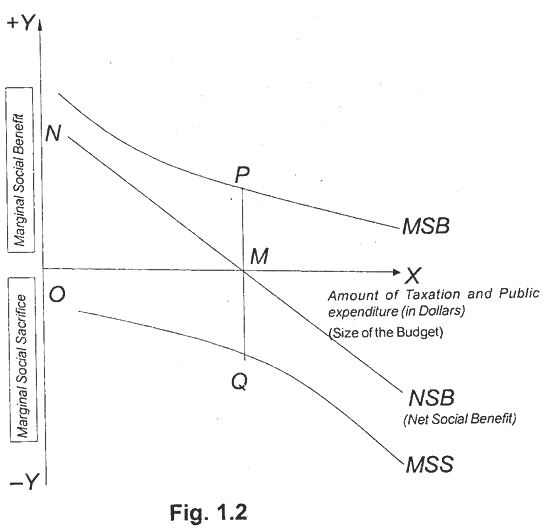
In the above parent the dimension of the price range is measured on the horizontal axis. The marginal social sacrifice and the marginal social benefits are proven one at a time on the vertical axis. The marginal utility of successive dollars of public expenditure allotted optimally between public makes use of is shown by means of the line MSB in the figure.
MSS point out the marginal disutility of taxes, imposed so as to cause least total sacrifice.
The line NSB suggests the internet social benefit curve. It is derived through deducting MSS from MSB. Hence it suggests the net social advantages derived from successive growth of the budget.
We locate that the ultimate size of the finances is decided at Om where marginal net gain is zero. When a quantity Om is raised through taxation and spend with the aid of the state, then the marginal social gain and the marginal social sacrifice are equated (MP = MQ).
Till then they give to the society is more than the loss. The net gain to the society is equal to the location on.
It is right here that the nation should give up expanding its activities.
If the country stops its finances operation at a figure much less than OM, the society will be forgoing a viable gain; on the contrary, if operations are increased beyond OM, the complete internet benefit will once more begin falling.
The difficulty to determine the choice on which the values of MSB and MSS schedules are to be primarily based and the hassle of selecting between alternate options are the simple barriers of this approach, admitted through Musgrave himself.
The fundamental hassle is that of planning the price range efficiently.
The following
Three imperative concepts of finances operations help the kingdom to obtain the precept of maximum social advantage:
1. The marginal social advantage of public expenditure and the marginal social sacrifice of taxation need to be equal.
2. The sources of the kingdom have to be so allotted on different heads of expenditure in such a way that the marginal return of satisfaction from every of them is the same
3. The tax burden have to be so disbursed that the marginal social sacrifice of taxation to each tax payer ought to be equal.
3.5 MARKET EFFICIENCY AND GOVERNMENT INTERVENTION
Government intervention in market things to do occurs in response to certain circumstances. Government can intervene in market operation in the course of cases of market failure, in limiting abuse of market strength and to amplify market efficiency.
Government intervention generally includes coverage changes and implementation of specific market policies which can also restriction opposition between markets and/or calibrate affectivity of the market to favor public interest (“government intervention”).
Accordingly, John Maynard Keynes supported the notion of government intervention to bring in market efficiency.
Keynes believed that the market cannot stand on its own, and is especially inclined to instability due to deflation.
Consequently, government intervention in the market things to do can be of applicable assist in stabilizing the economy.
The authorities should actively take part in economic activities by means of controlling pastime rates at a secure charge to make sure that monetary prosperity will be performed and the enterprise will be stabilized (francis).
Consequently, a secure monetary situation with low inflation stage can assist in generating jobs for the public.
Thus, government intervention in the market approaches can be of amazing assist in responding to the employment problems of the state. Stabilizing the wage fee for the employees via authorities intervention can lead to rise in the employment rate.
Thus, in contrast to the laissez faire economics, which proposed that the economy alone can modify itself, keynesian economics argue that authorities intervention is a critical must in making sure market efficiency as market cannot operate on its very own while providing advantages for the majority of the citizens.
The government can and need to intervene in imposing rules and insurance policies that shall make the economic system less susceptible to deflation, hence, creating a more efficient market procedure that will stabilize the economic system and advantage the majority of the people.
3.6 THE CONCEPT OF PUBLIC GOODS
Public utility
One cannot exclude folks from enjoying its advantages when the properly is provided. A suitable is non depletable if one individual’s enjoyment of the desirable does not scale back the quantity of the appropriate accessible to others.
For example, smooth air is (for all realistic purposes) a public good, due to the fact its use through one character does no longer
(for all practical purposes) expend the inventory reachable to different individuals, and there is no way to exclude an person from consuming it, if it exists.
Another frequent instance is country wide defense, because it is assumed that a nation-state cannot choose to protect just some of its residents from foreign aggression whilst aside from others from that protection; so too, imparting one resident
With countrywide defense does not curb the protection being furnished to other residents. A public bad is in a similar way described to be a “bad” That is non-excludable and nondepletable. For example, polluted air is a public bad,
For the same reasons that easy air is a public good Public item are socially beneficial but are almost never produced by free markets.…
Public items contrast with personal goods, which are both excludable and depletable. Food is a straightforward instance of a personal good:
One person’s consumption of a piece of food deprives others of eating it (hence, it is depletable), and it is feasible to rule out some humans from ingesting it (by assigning enforceable private property rights to food items, for example).
Some goods fit neatly into neither category, due to the fact they are excludable however nondepletable (such as a music concert) or are non-excludable however depletable (such as a public beach, which may additionally emerge as much less attractive, or “depleted,” As greater folks make use of it).
Public items (and bads) are textbook examples of goods that the market generally undersupplies (or oversupplies in the case of public bads).
For example, profit-maximizing firms and self-interested persons can be anticipated to pick ranges of manufacturing and consumption such that the aggregate stage of air pollution resulting from their activities leaves anyone worse off (according to their very own preferences) than if each have been someway averted from producing or eating as a lot as is in my opinion optimal. Commonly suggested options to such “market failures” Include taxes and subsidies or government intervention
A necessary similarity exists between troubles involving the provision of public goods and collective motion problems—such as voting, public protest, or output restriction in the case of oligopolists—where a man or woman commonly can't be averted from benefiting from the fulfillment of the intention of the collective action, if it is achieved. In such cases, the success of the goal can be thinking of as a non-excludable good. Consequently, it is often concept that humans can also have little incentive to make contributions to its achievement—by turning out to vote or taking part in a protest—if they view the act of contribution as in itself steeply-priced and not going to have a massive have an effect on on whether or not the collective purpose is achieved.