Unit 3
Project Planning
Business Planning Process Concept
Planning is the basic function of management which involves thinking before doing. It bridges the gap from where we are & where we want to be by making decisions regarding –
• What to do?
• When to do? &
• How to do?
In the words of Koontz and O’Donnell, “Planning is deciding in advance what to do, how to do it, when to do it, and who is to do it.”
James Stoner defines “Planning is the process of establishing goals and a suitable course of action for achieving those goals”
Business planning process
Planning process involves some steps to be followed in a chronological order. The figure1 highlights the steps involved in planning process-
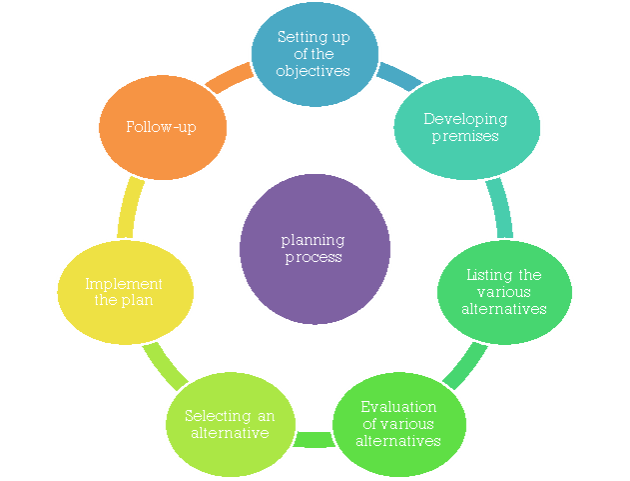
Figure 1: Planning process
1. Setting up of the objectives:
In planning function manager begins with setting up of objectives because all the policies, procedures and methods are framed for achieving objectives only. The managers found out very clearly the objectives of the company keeping in mind the goals of the company and therefore the physical and financial resources of the company. Managers prefer to set up goals which may be achieved quickly and in specific limit of your time. After fixing the goals, the clearly defined goals are communicated to all the employees.
2. Developing premises:
Premises refer to making assumptions regarding future. Premises are the base on which plans are made. It's a sort of forecast made keeping in sight existing plans and any past information about various policies. There should be total agreement on all the assumptions. The assumptions are made on the basis of forecasting. Forecast is that the technique of gathering information. Common forecast are made to seek out the demand for a product, change in government or competitor policy, tax rate, etc.
3. Listing the various alternatives for achieving the objectives:
After fixing of objectives the managers make a list of alternatives through which the organisation can achieve its objectives as there are often many ways to attain the target and managers must know all the ways to succeed in the objectives.
For example, if the target is to extend in sale by 10% then the sale are often increased:
(a) By adding more line of products;
(b) By offering discount;
(c) By increasing expenditure on advertisements;
(d) By increasing the share within the market;
(e) By appointing salesmen for door-to-door sale etc.
So, managers list out all the alternatives.
4. Evaluation of various alternatives:
After making the list of varied alternatives alongside the assumptions supporting them, the manager starts evaluating each and each alternative and notes down the positive and negative aspects of each alternative. After this the manager starts eliminating the alternatives with more of negative aspect and therefore the one with the most positive aspect and with most feasible assumption is chosen as best alternative. Alternatives are evaluated within the light of their feasibility.
5. Selecting an alternative:
The best alternative is chosen but as such there's no mathematical formula to pick the most effective alternative. After preparing the main plan, the organisation has got to make number of small plans to support the main plan. These plans are associated with performance of routine jobs in the organisation. These are derived from the major plan. So, they're also called derivative plans.
6. Implement the plan:
The managers prepare or draft the main and supportive plans on paper but there's no use of those plans unless and until these are put in action. For implementing the plans or putting the plans into action, the managers start communicating the plans to all or any the workers very clearly because the workers actually have to carry on the activities according to specification of plans.
7. Follow-up:
Planning is a continuous process therefore the manager’s job doesn't get over just by putting the plan into action. The managers monitor the plan carefully while it's implemented. The monitoring of plan is extremely important because it helps to verify whether the conditions and predictions assumed in plan are holding true in present situation or not. If these aren't coming true then immediately changes are made within the plan.
Concept and Importance of Project Planning
Project planning is a procedural step in project management, where required documentation is created to ensure successful project completion. Documentation includes all actions required to define, prepare, integrate and coordinate additional plans. The project plan clearly defines how the project is executed, monitored, controlled and closed. The project planning stage requires several inputs, including conceptual proposals, project schedules, resource requirements/limitations and success metrics. Project planning begins by setting the scope of a project and eventually working through each level of dependent actions, tasks, checkpoints and deadlines. Project planning requires an in-depth analysis and structuring of the following activities:
- Setting project goals.
- Identifying project deliverables.
- Creating project schedules.
- Creating supporting plans.
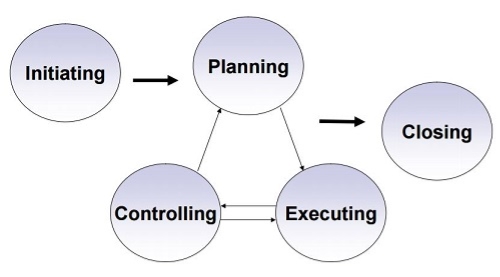
Figure 2: Project planning
The basic processes of project planning are:
- Scope planning – It specifies the in-scope requirements for the project to facilitate creating the work breakdown structure.
- Preparation of the work breakdown structure – It spells out the breakdown of the project into tasks and sub-tasks.
- Project schedule development – It involves in listing the entire schedule of the activities and detailing their sequence of implementation.
- Resource planning – It involves indicating who will do what work, at which time, and if any special skills are needed to accomplish the project tasks.
- Budget planning – It specifies the budgeted cost to be incurred at the completion of the project.
- Procurement planning – It is focusing on vendors outside your company and subcontracting.
- Risk management – It involves planning for possible risks and considering optional contingency plans and mitigation strategies
- Quality planning – It involves in assessing quality criteria to be used for the project.
- Communication planning – It involves designing the communication strategy with all project stakeholders.
Importance of project planning
Project planning plays an essential role in helping guide stakeholders, sponsors, teams, and the project manager through other project phases. Planning is needed to identify desired goals, reduce risks, avoid missed deadlines, and ultimately deliver the agreed product, service or result. Some of the significance of project planning are-
- It boosts project performance and success rates
Project planning involves comprehensive mapping and organizing of project goals, tasks, schedules, and resources before anyone assigns roles for the project and the team begins to execute the plan. You can avoid almost all of the problems that lead to project failure with proper project planning.
2. It saves money
A poorly planned project can easily run into delays, unexpected glitches, and loss of money. Project planning provides structure and foresight for the execution stage, helping to eliminate wasteful activities and patterns.
3. It improves team communication
Good communication is essential for smooth project execution. When a project involves multiple employees or teams, outsourced suppliers, and perhaps even staff members in other locations or time zones, then planning how project leads and team members will manage communications becomes vital.
4. It ensures the best use of resources
One of the key components of project planning is resource planning. Every project is based on resource use, including staffing, equipment, budget, office space, and time. Without proper planning, it’s nearly impossible to make sure an organization allocates and uses resources in the most cost-effective and appropriate way.
5. It makes it easy to track project goals and outcomes
Another key part of the project planning process is defining the project’s goals and objectives. Clearly defined and specific project goals are easier for team leads to translate into quantitative measures of success.
6. It helps keep all collaborators aligned
Teamwork is a critical factor in any group activity — especially in project management. Good teamwork exists only when all collaborators know their roles and responsibilities, how their part fits in with the whole, what impact their actions have on other team members’ productivity, and what expectations project leads have for them as individuals and as a team.
7. It improves employee retention
Project planning not only benefits the project’s performance and outcome but also plays a role in employee retention. Involving employees in project planning encourages them to contribute their perspective and skill, rather than simply telling them what they need to do. This ensures more effective execution and makes team members feel like a valued part of the company.
8. Ideation
The project planning is an important step to collate ideas from the customer, vendors, your team, top management, and your thoughts and put them in learning. This entails us to research further and know the gaps if there any.
9. Document the Project Plan
Document everything necessary such as risks, previous project failures and work around, the resources needed, time frame, cost and budget, contingency plan, etc. This ultimately helps the project for the successful completion.
10. Risk identification
It helps to identifies risk to be arising in near future for implementation of project. Risk identification allows to take prevention measures earlier.
Project Report
A Project Report is a document which provides details on the overall picture of the proposed business. The project report gives an account of the project proposal to ascertain the prospects of the proposed plan/activity. A project report consist of following information-
- General Information
A project report must provide information about the details of the industry to which the project belongs to. It must give information about the past experience, present status, problems and future prospects of the industry. It must give information about the product to be manufactured and the reasons for selecting the product if the proposed business is a manufacturing unit. It must spell out the demand for the product in the local, national and the global market.
2. Organisation summary
The project report should indicate the organization structure and pattern proposed for the unit. It must state whether the ownership is based on sole proprietorship, partnership or joint stock company. It must provide information about the bio data of the promoters including financial soundness. The name, address, age qualification and experience of the proprietors or promoters of the proposed business must be stated in the project report.
3. Project Description
A brief description of the project must be stated and must give details about the following:
- Location of the site,
- Raw material requirements,
- Target of production,
- Area required for the work shed,
- Power requirements,
- Fuel requirements,
- Water requirements,
- Employment requirements of skilled and unskilled labour,
- Technology selected for the project,
- Production process,
- Projected production volumes, unit prices,
4. Marketing Plan
The project report must clearly state the total expected demand for the product. It must state the price at which the product can be sold in the market. It must also mention the strategies to be employed to capture the market. If any, after sale service is provided that must also be stated in the project. It must describe the mode of distribution of the product from the production unit to the market. Project report must state the following:
- Type of customers,
- Target markets,
- Nature of market,
- Market segmentation,
- Future prospects of the market,
- Sales objectives,
- Marketing Cost of the project,
- Market share of proposed venture,
5. Capital Structure and operating cost
The project report must describe the total capital requirements of the project. It must state the sources of finance, it must also indicate the extent of owner’s funds and borrowed funds. Working capital requirements must be stated and the source of supply should also be indicated in the project. Estimate of total project cost, must be broken down into land, construction of buildings and civil works, plant and machinery, miscellaneous fixed assets etc.
6. Management Plan
The project report should state the following.
- Business experience of the promoters of the business,
- Details about the management team,
- Duties and responsibilities of team members,
- Current personnel needs of the organization,
- Methods of managing the business,
- Plans for hiring and training personnel,
7. Financial Aspects
In order to judge the profitability of the business a projected profit and loss account and balance sheet must be presented in the project report. It must show the estimated sales revenue, cost of production, gross profit and net profit likely to be earned by the proposed unit. In addition to the above, a projected balance sheet, cash flow statement and funds flow statement must be prepared every year and at least for a period of 3 to 5 years. The income statement and cash flow projections should include a three-year summary, detail by month for the first year, and detail by quarter for the second and third years. Break-even point and rate of return on investment must be stated in the project report.
8. Technical Aspects
Project report provides information about the technology and technical aspects of a project. It covers information on Technology selected for the project, Production process, capacity of machinery, pollution control plants etc.
Feasibility Study types and its importance
A feasibility study is an analysis that takes all of a project's relevant factors into account—including economic, technical, legal, and scheduling considerations—to ascertain the likelihood of completing the project successfully. Project managers use feasibility studies to identify the pros and cons of undertaking a project before they invest a lot of time and money into it. Feasibility studies also can provide a company's management with crucial information that could prevent the company from entering carelessly into risky businesses. The goals of feasibility studies are:
- To understand thoroughly all aspects of a project, concept, or plan.
- To become aware of any potential problems that could occur while implementing the project.
- To determine if, after considering all significant factors, the project is viable—that is, worth undertaking.
Different types of feasibility study are-
1. Technical Feasibility
This assessment focuses on the technical resources available to the organization. It helps organizations determine whether the technical resources meet capacity and whether the technical team is capable of converting the ideas into working systems. Technical feasibility also involves the evaluation of the hardware, software, and other technical requirements of the proposed system. As an exaggerated example, an organization wouldn’t want to try to put Star Trek’s transporters in their building—currently, this project is not technically feasible.
2. Economic Feasibility
This assessment typically involves a cost/ benefits analysis of the project, helping organizations determine the viability, cost, and benefits associated with a project before financial resources are allocated. It also serves as an independent project assessment and enhances project credibility—helping decision-makers determine the positive economic benefits to the organization that the proposed project will provide.
3. Legal Feasibility
This assessment investigates whether any aspect of the proposed project conflicts with legal requirements like zoning laws, data protection acts or social media laws. Let’s say an organization wants to construct a new office building in a specific location. A feasibility study might reveal the organization’s ideal location isn’t zoned for that type of business. That organization has just saved considerable time and effort by learning that their project was not feasible right from the beginning.
4. Operational Feasibility
This assessment involves undertaking a study to analyze and determine whether—and how well—the organization’s needs can be met by completing the project. Operational feasibility studies also examine how a project plan satisfies the requirements identified in the requirements analysis phase of system development.
5. Scheduling Feasibility
This assessment is the most important for project success; after all, a project will fail if not completed on time. In scheduling feasibility, an organization estimates how much time the project will take to complete. When these areas have all been examined, the feasibility analysis helps identify any constraints the proposed project may face, including:
- Internal Project Constraints: Technical, Technology, Budget, Resource, etc.
- Internal Corporate Constraints: Financial, Marketing, Export, etc.
- External Constraints: Logistics, Environment, Laws, and Regulations, etc.
Importance of feasibility study
1. Get a broader view
Executing a project is not a simple task. It is a huge responsibility of everyone in the project. Specially the chief responsibility of a project manager. Having said that, it is important to understand the opportunity and threat in starting and completing a project. One must take a broader look considering every single factor in mind and thus it goes without saying the importance of feasibility study.
2. Easy to make a plan
It helps to list down all risks and prospects at the beginning of the project. Thus planning becomes simple. In case you fail to make the study, then you may have to rework your plan. Planning is crucial and a fool proof plan will help all the team members to stick to it and work with a flow. Thus understand the importance of feasibility study and do not skip.
3. Execution becomes straight forward
Devising a proper plan is one part of the project but the execution is the key to successful project completion. When you finish the feasibility study, in the beginning, you can make a proper plan and that is pave way for execution. Execution will involve cost, time, and resources so it becomes feasible to utilize all after a proper study of the project viability and complete the project economically surpassing client expectation.
4. Get ready with an alternative
In the event of something goes wrong due to any uncertainty then a detailed feasibility study done will spontaneously allow the PM to make an alternate plan. This will save cost and time. If there is no awareness of the possibilities, then everyone must get on to the board to start from scratch. That is why the importance of feasibility study is greatly emphasized in every PMP certification online course to train all PMs in one platform.
5. Help to define goals and objectives
A feasibility study will help clarify what goals need to put in place to be successful by providing benchmarks for a project’s viability. For example, if your community would like to build an indoor/outdoor sports facility, you may not have a clear picture of the construction costs. A feasibility study helps you understand your facility’s costs as well as its revenue earning potential. With this information in hand you can either obtain the resources needed to complete your project or “right-size” your project based on available resources.
6. Help to develop a plan
Like ideas, goals are only useful when you start the work. As you define your goals, with the help of your feasibility study, you will have a better understanding of the next steps in the development cycle. From there, a program plan for a “right-sized” facility can be developed and combined with a financial forecast and economic impact study to attract funding partners.
7. Help execute the plan
Arguably the greatest benefit of a feasibility study is that they give you specific information about what a project requires for it to be sustainable. By understanding development costs, the competitive landscape, where potential customers will come from, and revenue potential, you’ll have a feel for the sources of capital, partners, and business model needed to achieve success. The components of the feasibility study will serve as a roadmap, describing the most optimal path to creating a new complex.
8. Feasibility studies provides an identity
When planning a new sports, recreation, or entertainment facility, you’ll have a general idea of who you are targeting. However, to attract this valued audience, you must understand their needs as well as the competitive landscape. A feasibility study will help you understand what they have to offer.

Key takeaways-
- Planning is thinking before doing.
- Project planning is a procedural step in project management, where required documentation is created to ensure successful project completion.
Concept and steps of business unit promotion
Promotion of business unit refers to establishment and starting of business venture either individually or jointly by the owner/owners of business. The owners of business are promoters of business. It is the first stage in the formation of a business unit. It involves conceiving a business opportunity and taking and initiative to form a company so the particular shape can be given to exploiting the available business opportunity. The promoter/promoters of a business undertakes activities for
- Identification of business opportunity.
- Feasibility study.
- Approval of name of the business unit.
- Fixing up signatories to the MOA.
- Appointment of professionals.
- Preparation of necessary documents.
The business unit promotion involves the following steps-
(1) Discovery of an Idea:
At first the promoters will find out what shall be the purpose of forming the company. Such an idea can be formulated out of experience of their own or of others. The purpose must be meaningful having a practical basis otherwise all the efforts will be futile.
(2) Investigation:
They have to make enquiries in the market about the potentiality of the proposed business. Various facts, data and information shall have to be collected and the market has to be studied.
(3) Planning:
After proper deliberation and computation of the facts, information, etc., a plan for the proposed business has to be prepared with details. Opinions of management consultants may be sought and a Project Report may be obtained. In advanced industrial countries there are professional promoters who do the promotional job.
(4) Financing:
Finance is necessary from the early stage till formation of the company is complete. The initial money comes from the promoters themselves and also from underwriters, if any, to be reimbursed by the company out of its capital. Expenses relate to legal obligations, stationery, conveyance and communication with the Government, the financial institutions (if any), the share brokers, etc.
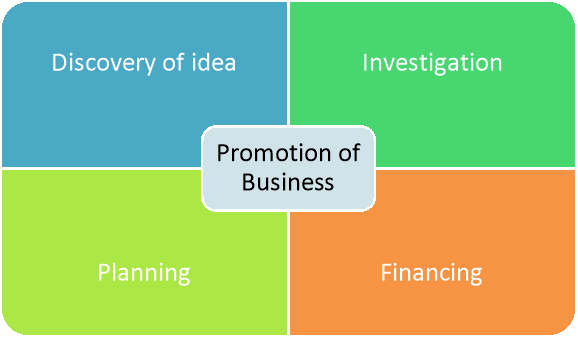
Figure 3: Stages of business unit promotion
Factors determining location
Location of business is the place where the business set up its outlet/manufacturing unit/office etc. Location of business is crucial for business unit to get the advantage of customer access, market access, transport facility etc. The factors that determine the location of business are-
- Proximity to the Market
The promoter will choose the location that will at the centre of the market or nearby market place. It facilitates them to get advantage of large customer attraction due to frequent visit of customers in the market. For example, Retail outlets, Shopping mall etc. were considers this element.
2. Rent Price
The rent price is another determining factor for location of business. The promoters will hire a place of business depending on the cost involved in it. The small business organisations generally consider the rent price.
3. Analyse the Demographics
The demographic factors like composition gender, income, living standard, literacy rate, religion, values and beliefs etc. also influence on the location of business. For example, A seller can sell AC, LED TV etc. where the high income level people are residing.
4. Infrastructure and Accessibility
Power and water supply, good road connections are just a few factors to consider when choosing your business location. Lack of enough parking spaces for your employees, or accessibility for people with disabilities, can be an issue in some locations. For example, manufacturing units, retail outlets etc.
5. Distribution Network
Manufacturing units require a good location for a business start-up. Nobody likes to spend more money on transportation than they have to. Think twice before choosing a business location, good proximity to suppliers is key in minimizing logistics costs.
6. Security
The location of business unit should be secured enough for peaceful business. The promoters never prefer to locate in the areas disturbed by insurgency, terrorism, political instability, civil war etc. The areas like Sriya, Gaza etc. will not preferred by promoters for investment.
7. Business Rates
It is important to research the average business rates including rent, utility bills and taxes in the area to ensure you can afford the premises. Simple hidden costs such as deposits and whether you need to pay to park need to be snuffed out before committing to a location.
8. Competition
By knowing where your competitors are, you can find a business location that allows you to establish your own base. It can also allow you to better gauge demand for your product or service compared to other companies.
9. Workforce
It is good to be based where suitable staff can easily get to work. Assessing this can range from crude categorisation (younger staff for local bars) to more sophisticated categories, such as academic background and subject expertise among a skilled workforce. Data visualisation will help location planning by showing where your talent pool is deepest.
10. Foot traffic
For most retail businesses, foot traffic is extremely important. It helps them to attract the customers by displaying the products, offering discount and rebate, conducting contests etc.
Role of Government in Promotion
The Government plays an important role in promoting business operations. The promotional role encompasses government efforts to provide adequate infrastructure and an environment conducive for business.

Some of the major functions performed by the government in promoting business operations are as follows:
- Maintenance of public utilities
The government maintains the public utility services like transportation, logistic, power, internet, banks, minerals, ecology etc. which are used by business units in production, distribution and sale of their products/services.
2. Promote private and foreign investment
Government formulate plans and policies to promote private and foreign investment in different areas of the economy, import and export etc. The LPG policy, industrial policy, fiscal policy, monetary policy etc. are some of such measures adopted by government regarding this.
3. Provide trade incentives for promoting foreign trade
Government of India formulates foreign trade policy and other schemes for promotion of export and reduction of unnecessary import. Promotion of foreign trade allows more inflow of foreign exchange.
4. Match and control money supply with development requirements
Central government control the money supply in the economy through the monetary policies. Bank rate, open market operation, repo rate, variable reserve ratio and qualitative measures are adapted to control the money supply in the economy. Moreover, the financial market is regulated by the regulatory bodies for fair trading of financial assets.
5. To enable effective utilization of various resources
For effective utilisation of local resources government promotes local industries, MSMEs, entrepreneurship by implementing different schemes.
6. Encourage developmental attitude among various sectors
7. The Government work as motivator for industrial sectors by providing them support for financial, marketing, opportunity to start a business venture etc. to develop the attitude among various sectors.
8. Ensure equitable income distribution
To ensure equitable distribution of income wealth between large scale and MSME sector, the Government use the tools of monetary and fiscal policy. Subsidised loan, tax relief, marketing assistance, other incentives etc. are provided to MSME sector and large scale business houses are charged market rate of interest on loan, tax etc.
9. Research and Development
The government provides grants to academic institutions working to develop new technologies that will benefit industry with the caveat that the institutions share the technologies with industry. In some instances, the government provides grants to private companies making a new product or service that will improve a vital area of an economy, such as transportation, energy, agriculture or communications. Some states also fund research and development projects and work with private investors and the federal government to raise funds.
10. Education and Training Programs
Government establishes technical and vocational institutes to develop the skills and provide training and education for establishment, development and expansion of business units.
11. Regulatory role:
Government regulates the business activities for fair trade and business. It formulates different laws, establishes regulatory institutions etc. For example, SEBI, RBI, FEMA, Environment act, Consumer protection act, labour laws, industrial dispute act, Patent act, IT act etc.
Key takeaways-
- Promotion of business unit refers to establishment and starting of business venture either individually or jointly by the owner/owners of business. The owners of business are promoters of business.
- Location of business is crucial for business unit to get the advantage of customer access, market access, transport facility etc.
Licensing and Registration procedure
Registration of company is done either before starting a business or after commencement of business. The procedure for registration of business are-
- Choose a Business Structure
It is the first step where promoter have to decide which business structure want to register. The choices are sole proprietorship, corporation, partnership or limited liability company (LLC). The business structure you choose correlates with the type of documentation you have to file with the state secretary’s office where the business operates in order to register the business.
2. Pick a Business Name
In order to register any type of business, the promoter has to choose a business name which cannot be identical with other existing business. It is a requirement for the business name to carry one of the following designations: Incorporated, Corporation, Company, Inc., Corp. Or Co.
3. Register with the State
One can obtain the application that pertains to the business structure from the office of the Secretary of the State for the state where you are registering your business. Depending on the business structure, you may have to supply supplemental documentation with the application. For example, a corporation requires the Articles of Incorporation and a partnership requires a Partnership Agreement.
4. Register with the revenue service
The Revenue Service requires business enterprises to obtain an employer identification number, which is the business equivalent of a Social Security number. This is the number you use to file all of your business tax return forms. IRS Form 2553.
5. Obtain Business Licenses
Some businesses need one or more licenses to operate. The types of business licenses one need depend on the type of business is opening and the city, county and state. While some states do require you to obtain a business license, other states, such as Texas, do not require a business to obtain a state license.
Licensing for business
The process of obtaining license changes from one type of business to the other, based on various determining factors like the number of employees, sector, the type of business, the place of business etc.
- Company or LLP Registration
Most businesses in India are started as proprietorships or partnership firms, without any registration from the Central Government. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs regulates the registration of a company and LLP. It is advisable for Entrepreneurs who have plans for operating a business with an annual turnover of more than Rs.20 lakhs to obtain a LLP or Company registration. Once, a company or LLP is registered, the entity would have a separate legal identity and the promoters would enjoy limited liability protection. Further, the business would also become easily transferable and the entity would have perpetual existence. Hence, before starting a business, its best to consult and expert and register a company or LLP.
2. GST Registration
All types of entities and individuals who have an aggregate annual turnover of more than Rs.20 lakhs in most State and Rs.10 lakhs in Special Category States are required to obtain GST Registration. Further, any person supplying goods involved in intra-state supply is required to obtain GST Registration, irrespective of turnover. In addition to the above criteria, various other criteria has been provided under the GST Act, establishing the criteria’s for GST registration. It is important for all Entrepreneurs to understand the criteria’s and obtain GST registration within 30 days of starting a business.
3. Udyog Aadhar Registration
This is a registration available for entrepreneurs who want to start and operate a small business – micro, small and medium enterprises. The eligibility criteria for obtaining Udyog Aadhaar registration is based on the investment in plant & machinery made by a manufacturing concern or investment in equipment made by a service provider. Once, Udyog Aadhaar registration is obtained for a business, it can enjoy various subsidies and schemes specially provided by the Government for helping small businesses in India.
4. FSSAI License or Registration
“Food safety and standard authority of India”(FSSAI), is responsible to verify the safety and standardization of food products nationwide. Retail stores, restaurants, modern trade outlets, kiosks and consumers alike look for this five letter word in their food packets or containers.
Under FSSAI, the license or registration is divided into three categories namely:
- FSSAI Central License,
- FSSAI State License,
- FSSAI State Registration,
5. Import Export Code
Any person involved in import or export of goods/services from India must obtain Import Export Code from the DGFT Department. To obtain Import Export Code, it is mandatory for the business to have a PAN and a Current Account in a bank.
6. Shop and Establishment Act License
“The Shop and Establishments Act”, was created for regulating the conduct of business like the hours of work, child labor, payment of wages, safety and general health of the employees. Shop and Establishment Act license or registration is issued by the State Governments and varies from States. Hence, based on the State in which the business is situated, the concerned State Government authority must be approached for obtaining Shop and Establishment Act License.
7. Gumastha licence
If you are planning to start a business in the state of Maharashtra, you must obtain a Gumastha licence. To procure it, one needs to posses the following documents;
- PAN Card,
- An Address proof or a no-objection certificate from the landlord,
- Application letter in the prescribed format to the Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai,
- Authority Letter for Business,
- Government Prescribed Fees for a partnership Firm,
- Memorandum and Article Of association,
- Certificate Of incorporation of the Company,
- Director’s ID and Address proof.
8. Other Licenses and Registrations
Certain types of business that involve aspects of dealing or providing insurance, financial services, broadcasting services, defence related services, etc., would require approval from regulatory bodies like Reserve Bank of India, IRDAI, etc., Further, a business may also have to obtain permits from the fire department, or the pollution control board, or maybe the local healthcare system. It all depends on the type of business you are willing to operate. Hence, prior to starting a business, make sure you discuss your business with a Professional to determine and understand the legal and regulatory requirements.
Filling returns and other documents
A business tax return is basically an income tax return. The return is a statement of income and expenditure of the business. Also, any tax to be paid on the profits made by you is declared in this return. The return also contains details of the assets and liabilities held by the business. Items like fixed assets, debtors and creditors of business, loans taken and loans were given are declared here. Filing business tax returns will depend on the kind of business you are whether a proprietorship, partnership firm, limited liability partnership or a private limited company.
All the taxpayers that may vary from manufacturers & suppliers to retailer & consumers, have to file GST returns every year. In the digital era, the government is also pressing pedals towards innovation & automation and has started facilities for e-filing or online filing of GST returns on common GST portal. The returns can be filed online through applications & software introduced by Goods and Service Tax Network (GSTN). These innovative facilities by government automate the fling process and auto-populates the details in GSTR forms. The steps involved in online GST filing are-
Step 1: Go to GST portal – www.gst.gov.in
Step 2: Obtain a 15-digit GSTIN (GST identification number) which will be issued based on your state code and PAN.
Step 3: Upload the relevant invoices on the software or the GST portal. An invoice reference no. Against each invoice will be allotted to you.
Step 4: Once all the invoices, inward, outward return and cumulative monthly return are uploaded, check all the errors and file the returns.
Points to ponder before filing the returns
- GSTR-1 is an outward supply return which has to be furnished via information section on the GST Common Portal (GSTN) by the 10th of the following month.
- The supplier may or may not accept modifications of the details of inward supplies given by the recipient in GSTR-1A.
- The supplier has to furnish & made available the details of outward supplies in GSTR-2A to the recipient.
- The details of outward supplies have to be verified, validated and modified by the recipient, followed by filing the details of credit or debit notes.
- The details of inward supplies of taxable goods and services have to be furnished by the recipient in GSTR-2 form.
Key takeaways-
- The process of obtaining license changes from one type of business to the other, based on various determining factors like the number of employees, sector, the type of business, the place of business etc.
References-
- Www.india.fillings.com.
- Www.gst.gov.in.
- Www.mca.gov.in.
- Principles & Practices of Management: L. M. Prasad.
- Principles of Management: P. C. Tripathy & P.N. Reddy.