UNIT 4
Brand building and special purpose advertising
Brand Building is generating awareness, establishing and promoting company using strategies and tactics. In other words brand building is enhancing brand equity using advertising campaigns and promotional strategies. Branding is crucial aspect of company because it is the visual voice of the company. Goal of brand building is creating a unique image about the company.
Importance of Brand Building
Brand building can be initiated with a well thought brand identity which can help create a strong brand image which goes a long way in consolidating the brand.
Brand Building comprises of creating value to consumers that how consumers feel, think and know about your brand. There are three popular brands known-
• Product brand: A physical product or items or goods are a product brand. Brand building is ensuring a good quality product is given to the customer along with good brand visibility, packaging, warranty etc. All these cumulatively help in brand building. Example of product brands are Adidas, Rolex etc
• Service Brand: A non-tangible offering is a service brand like telecom service, ecommerce etc. In this case, brand building is most dependent on the experience that a customer gets. Example of service brands are McDonald’s, Starbucks etc
• Retail Brand: Retail brands are a combination of service & product i.e. products are sold through a service offering. Hence brand building has to ensure good customer experience as well as high quality products. Example of retail brands are Tesco, Walmart etc.
Process of brand building
There is no definite way of brand building. Brand building requires innovation, creativity, correct value proposition, constant monitoring & ensuring good customer experience.
Steps involved in brand building are-
• Describe your brand: The first step of brand building is to describe the brand. This can be done through product description, packaging, logos etc. The way a brand is defined builds the brand equity and forms the foundation of the customer perception.
• Brand Differentiation & Positioning: Once a product or service is created, it is critical that the brand is differentiated from its competition with some unique value. Also, positioning the brand correctly is an essential element of brand building.
• Brand Promotion: Advertising & promoting the brand using TVCs, social media, print ads, online advertising etc is one of the most important pillars of brand building as it helps in creating brand awareness. Correct communication and effective media channels can help build a strong brand and helps increase brand recall.
• Personalise the Brand: Brand building can be effective is a customer feels connected to it. Hence giving a personal touch to the customer, through innovation and customization can help building a stronger perception in the mind of the customer.
• Evaluate the Brand: It is important that a company keeps on monitoring and reviewing the performance of its products, services and brands. Hence evaluation & review of a brand is an essential element of brand building.
The communication process
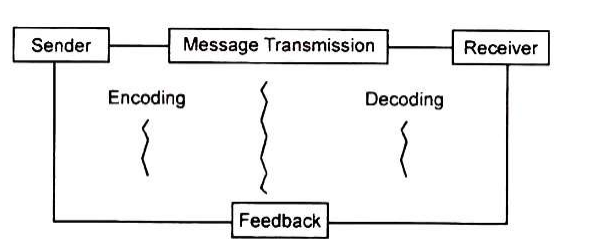
Communication process is a sequence of activities where message sent is understood by the receiver in its intended meaning. Communication is a process that connects the sender with the receiver of the message. A process is “a systematic series of actions, operations or series of changes directed to some end.”
These elements are discussed below:
1. Sender:
Sender is the person who initiates, generates and sends the message. He represents the source of message. The communication process begins when the sender develops an idea or message he wants to transmit. He must arrange the ideas in a manner that can be understood by the receiver. A lecturer delivering a lecture in the classroom is the sender of the message or a manager addressing his team in a meeting is sender of the message.
2. Message:
Message is the idea or information that the sender wants to convey. He may convey it verbally (by writing or speaking) or non-verbally (through gestures or body language). Whatever the form, the message should be clearly formed so that desired objective is accomplished.
3. Encoding:
Once the sender is clear of what message to transmit, he decides the code through which the message shall be transmitted. The message is abstract and intangible and, therefore, has to be converted into some form (words, gestures, pictures etc.) to make it meaningful. Encoding means converting the message into symbols.
4. Transmission:
Transmission involves selecting the medium or channel of communication. Once decided that the message has to be sent in writing, the sender may select the electronic channel and the medium of e-mail or fax. Short messages can be transmitted through telephone but lengthy messages can be sent through letters or circulars.
5. Receiver:
Receiver is the person or a group of persons to whom the message is conveyed. In case of telephonic conversation, the sender can send message to one receiver but in case of group discussions, seminars and conferences, receivers can be more than one. The message must be designed, encoded and transmitted in a manner that receiver can understand it easily. Use of technical words, jargons and complicated symbols should be avoided. Depending on the channel selected, receiver may be a listener, viewer or a reader.
6. Decoding:
Decoding means giving meaningful interpretation to the message. On receiving the message, the receiver translates the symbols into meaningful information to the best of his ability. Communication is effective if receiver understands the message in the same way as intended by the sender. The receiver must, therefore, be familiar with the codes and symbols used by the sender.
7. Noise:
It represents the disturbing factor in the process of communication. It interferes with effective communication and reduces clarity of the message. The message may be interpreted differently than intended by the sender. Conversing near a machine making sounds, disturbance in telephone line, physical ailment or mental distress of sender or receiver, psychological barriers (degree of trust, fear, perception etc.) are the common forms of noise that obstruct the quality of message transmitted from sender to the receiver.
8. Feedback:
Feedback is receiver’s response to sender’s message. The receiver communicates his reaction to the sender through words, symbols or gestures. It is the reversal of communication process where receiver becomes the sender and sender becomes the receiver. Unless the receiver responds to the message, communication process is incomplete.
AIDA Model
AIDA Model is a selling concept presented by Elmo Lewis to explain how personal selling works. AIDA Model identifies the processes for achieving promotional goals in terms of stages of consumer involvement with the message. The Stages are Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action.
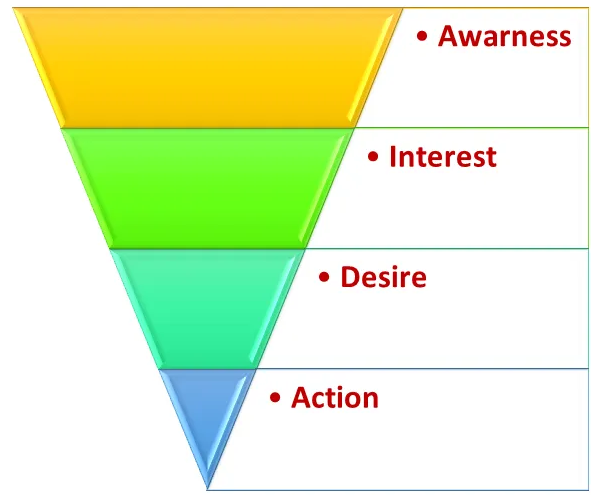
Attention
The attention stage occurs in beginning of the marketing message and is designed to give the prospects a reason to take notice. The advertisers need to be quick and direct to grab audience attention. Ads are required to be eye catchy which can make audience stop and read or watch what advertiser have to say next. To make the ads attractive powerful words and pictures are used.
Interest
After getting attention of a chunk of the targeted audience, under this stage it is required to keep them engaged with the ad to make them understand the message in more detail. Gaining the audience interest is more difficult process than grabbing their attention. The advertisers must stay focused on audience needs to gain audience interest
An advertisement is designed to create interest for the goods or services of the advertiser, interest is closely related to attention. An advertiser has to take note of these two aspects while developing an advertisement. A good advertisement starts with a point of interest to the reader and proceeds to a point of interest to the advertiser.
Advertising aims at stimulating primary demands for a new product. It is used for existing product to bring a greater bit of the marketing share. It is also used to remind the consumers about their needs. A good advertisement should arouse interest of the prospects in the advertised product.
Desire
In this stage, the objective is to show the prospects how the product can solve the problem. Under this the prospects are explained the features of the products or services and demonstrate how the benefits fulfill their need. A good advertisement should be able to create desire in the minds of the readers about the product. It is not enough for a good advertisement to attract attention create interest but also arouse desire in the heart of the prospect to have the product. The advertiser should make use of proper appeals and selling points while creating desire for the product. Making use of proper appeal will depend on the seasonal consumption of the product. For example, the sale of rain-coats in monsoon will emphasise selfprotection against rains. It is through the sales appeal that the advertiser creates a desire for the product.
Action
Finally, advertiser need to be very clear about what action he want the audience to take- trial, purchase, repurchase, or other. This is an important stage where the advertiser can study the impact of his advertisement. If the advertisement has attracted attention, aroused interest, created desire, then the advertisement should appeal the prospect to act i.e., to come forward for making purchases.
The advertiser should tell the prospect about the product, their main features, how they can be consumed and where they are available. For example, the prospect who wants to book new scooter should get such information in the advertisement as: place of display, place and date of booking. Every advertisement normally carries such basic information to guide the prospective buyers. It is this stage which plays a decisive role in generating the sale of the advertiser‟s product.
Role of advertising in developing Brand Image and Brand Equity,
Role of advertising in developing brand image
Advertising has a central role to play in developing brand image. It informs consumers of the functional capabilities of the brand while simultaneously inspiring the brand with symbolic values and meanings relevant to the consumer. Advertising people in an advertising agency looking for unique emotional values to add to the brand. They look for ways to create emotional involvement because this represents the stronger bonding between the brand and target customer.
Businesses use advertising to spread their brand among the masses as well as to directly sell products and services to the public at large. Repetition of the company’s message creates a familiarity with the brand. Advertising is important for companies trying to direct consumer behavior because it is an effective method for mass selling and communications.
What is Brand Image?
Brand image is a mental picture or perception of a band in the mind of the consumers.
Creates Awareness
The major roles of advertising are to create awareness of the product or services such as brand name and price. By highlighting the unique features of the brand the awareness of the product or services can be created. Nowadays, due to intense competition, awareness is extremely required.
Persuasion
The marketers try to provide reasons regarding the superiority of their products as compared to competitors available in the market through persuasive messages. Persuasion can be done through creative advertising messages, product demonstration at trade fairs, offering free gifts, premium offers and organizing contests.
Reminder
The reminder objective may be necessary if target customers already have a positive approach towards a firm’s product or service, because the satisfied customers can be targets for competitors’ appeals. They should keep on reminding them about their presence in the market.
Brand Image
Advertising helps in building a good image of the brand in the minds of the target audience. There are several factors that can help to develop the brand image in the minds of the target audience, such as the character of the personality that endorses the brand, the content of the advertising message, nature, and type of packaging and the type of programmes or events sponsored.
Brand Loyalty
Advertising helps in developing brand loyalty, which results in repeat purchases and favourable recommendations to others by existing customers. Sales promotion, effective personal selling, timely and efficient direct marketing, and other techniques also help to develop brand loyalty.
Ways of developing brand image
Marketer can develop brand image of the product through several ways. The various factors that play an important role in building brand image are as follows:
I. ADVERTISING RELATED FACTORS:
1. Creativity in Advertising: The advertiser must come up with creative ads to develop a good brand image. Therefore, the advertiser or the ad agency must be selective in respect of various element of an ad such as headline, copy text, slogan, colour combination, etc.
2. Brand Ambassadors: The personality of the person endorsing the brand must match with the personality of the brand. Therefore, the advertiser must be selective to choose the right personality to endorse the brand. Also, a sports star of a short stature may not be used to promote luxury products.
3. Media Selection: The quality of media or programmes sponsored may influence the brand image. Raymond Suitings may advertise in Business Magazines, but not in cheap local magazines. Advertising in cheap media or by sponsoring cheap or silly programmes may adversely affect the rich image of a brand.
4. Media Scheduling Strategy: Advertiser needs to adopt appropriate media scheduling strategy. At the product launch stage, the advertiser may adopt bursting, flighting or pulsing strategy. However, over repetition of ads must be avoided. Too much repetition of ads irritate the audience and they may ignore such ads and may even develop a negative image.
5. Symbols:
The Symbols / logos should be so designed to create a distinct image of the brand. The symbols or logos also facilitate instant brand recognition and recall.
Some of the famous logos include:
McDonalds –two golden arches which signify warm welcome or hospitality.
Mercedes – three-pointed star which signifies sign of luxury.
MRF Tyres – muscled man which signifies strength or durability
6. Sponsoring of Events: The events sponsored by the brand / company can affect its image. Therefore, brands having rich image sponsor prestigious events. For instance, top tennis tournaments are sponsored by reputed brands such as Mercedes and Rolex Watches.
7. Size / Length of Ad: The full page in the magazine or newspaper can create better impact. However, in case of newspaper, it may be advisable to insert half page ad alongside the matter of interest to the readers. This will create more impact in terms of noticeability of the ad. While reading the interesting matter, the reader may also glance at the ad.
8. Humour in Advertising: Humour may be used in advertising depending upon the nature of the product:
If the product is a FMCG, and if popular brand image needs to be developed, the advertiser may use good or witty humour but not cheap humour.
If the product is luxury one, and if premium brand imageis to be developed, the advertiser may not use humour, but instead the ad must be highly creative.
II. NON-ADVERTISING RELATED FACTORS:
- Distribution: The type of distribution undertaken by a company can affect the image of the brand. For instance, Tanishq Jewellery is available at select stores in India, so that the brand get rich image. Also, Rolex Watches are marketed through a couple of stores in Metro cities to convey a distinct image.
- After-Sale-Service: Prompt and effective after sale service helps to develop a good image of the brand in the market. For instance, Suzuki Motors enjoys a good image in India because of its after-sale-service network, and other factors. Due to its image Suzuki Motors still commands about 50% of market share of the Indian car industry
- Product Performance: The product itself is an important factor for developing brand image. The brand should perform well. It must generate customer satisfaction.
- Price: The price factor can generate image for the brand. For example, the premium pricing by Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Volkswagen, etc., has developed a rich image not only for the company but also for its brands.
- Company: The image of the company can influence the image of the brand. For instance, companies like Tata Group, P&G etc., which enjoy goodwill in the market can generate favourable image for their brands.
- Packaging: The package is the face of the product. Therefore, it must be properly designed in order to give a rich image to the brand. He material, colour, shape, size, etc., of the package can affect the image of the brand.
Brand equity
Meaning:
Every brand has a value, and the value of a brand is brand equity. Brand equity must not be confused with brand personality or image. Edward Tauber defines brand equity as “The incremental value of a business above the value of its physical assets due to the market position achieved by its brand and the extension potential of the brand.”
Factors Influencing Brand Equity:
The factors influencing brand equity are as follows:
1. Brand Loyalty:
Customer’s brand loyalty is the vital base of a brand’s equity. It is true that it is expensive to gain new customers and relatively inexpensive to keep existing ones – provided the existing customers are satisfied with the brand. Satisfaction of customers results in brand loyalty. Satisfied customers continue to use the brand, even though competitors make enough efforts to win them over.
2. Brand Name Awareness:
Brand awareness is the ability of a potential buyer to recognise or recall that a brand belongs to a certain product category. In other words, it is a process of linking product class and brand.
Buyers often buy a known brand. Familiarity of a brand makes it more reliable in the minds of the buyers.
3. Perceived Quality of the Brand:
Perceived quality is the customer’s perception of the overall quality or superiority of a product as compared to other competing brands.
Perceived quality directly influences purchase decisions and brand loyalty, especially when a buyer is not motivated or able to conduct a detailed analysis of the product’s actual or manufacturing quality.
4. Brand Associations:
A brand association is anything “linked” to a brand. The underlying value of a brand name often is based upon associations linked to it. Like perceived quality, brand associations do influence purchase decisions and brand loyalty. Nike brand is associated with sports. Goa is associated with beautiful beaches.
5. After-sale-service:
The after sale-service provided by the company can make a difference in brand equity. Nowadays, most of the durable products are more or less standardised.
To provide effect after-sale-service, firms need to:
- Select the competent and committed after-sale-service staff.
- Train the service staff to improve their knowledge, attitudes, skills and social behaviour.
- Motivate the service staff with monetary and non-monetary incentives.
Brand Ambassadors:
Some marketing experts claim that brand ambassadors can enhance brand equity. For instance, the Lux soap is associated with female film stars and positioned as the beauty soap of film stars.
Some marketing experts do not agree that brand ambassadors enhance brand equity. Creative advertising does the trick such as that of Zoo zoos of Vodafone.
7. Brand Patent:
Companies can obtain brand patents for new and innovative products. They need to register under the Patent Act of respective countries where they want to patent it.
Patenting the product gives exclusive marketing rights for certain number of years. Other companies cannot sell similar product in the market without the permission of patent holder. For instance, pharma companies get exclusive marketing rights for at least 15 to 20 years.
8. Brand Logo:
Brand logo can enhance brand equity. The brand logo like brand names facilitates instant identity of the brand. Some of the brands that have unique logo include Apple, Nike, McDonalds, Mercedes, Audi (4 rings), Reebok, Pepsi, and soon.
Managing Brand Crises
Brand crisis takes place when certain negative event centers on one particular brand or a set of brands belonging to the same company. When a brand crisis breaks out, consumers and other stakeholders (employees, shareholders, customers, the media, regulators and the Society) are likely to raise questions about the affected brand and why the crisis happened.
Questions may be raised such as:
- Who is to blame?
- What would be the effect on company’s corporate image?
- What would be the effect on the company’s stock prices?
- What would be the future of the company?
- What would be the penalty or loss to the company?
Short-term effects of a crisis are lost sales and the costs associated with product recalls. In the long term, the incident can severely damage the affected brand’s reputation. The key challenge for companies faced with a crisis is to restore consumer trust in the brand. For competitors, the crisis is often a great opportunity to steal consumers away from the affected brand.
- Assess the situation – Firstly we need to gather a full picture of the brand crisis. Speak to employees who may be able to shed light on the situation. Understand what actually happened and how the general public are interpreting it. Media monitoring tools can help you to gather a quick overview of how the public is responding on social media.
- Assign duties and communicate – as soon as the situation is understood. The public facing employee should be briefed about it. At this time also decide who will manage the press, keep the executive team informed, serve as liaison to other key stakeholders (including partners, customers, members, etc.), and record every detail, action taken, external response, and resolution.
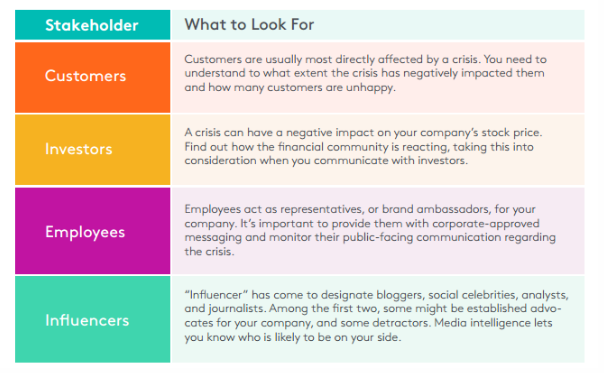
- Understand the audience – under this we need to understand how the crisis going to impact the concerned audiences. The chart below goes into more depth about identifying audiences and how they’re likely to react.
4. Decide how to respond - Based on how the crisis is likely to affect your stakeholders and what the most common concerns of the public are, decide what the best medium of response is. You response can be communicate through social media, a press release, blog post, or a combination. If there are a lot of people discussing the crisis on social media, then you have some form of response on there.
5. Get your message heard - Reach out to media with whom you have relationships with and respond to those who have been writing about the crisis. If the crisis has been picked up on social media post a response on there too.
6. Measure the impact of your statements and posts as you go - Media monitoring enables us to track how people are responding and how sentiment is shifting. A press release sends through a comprehensive PR distribution tool, you can also track how many people opened the release, as well as the amount of time they spent reading it.
7. Know when to stop - When PR and social media mentions begin to dramatically drop, it’s time for you stop reminding everyone of what happened and start to rebuild value.
8. Prevention –
- To prevent loss of data ensure all data is backed up securely.
- Create social media guidelines for employees to prevent them from putting you in a sticky situation.
- To spot any developing negative discussions set up alerts for spikes in social media mentions.
- Double check any marketing and PR campaigns with focus groups or employees not in your team to spot any wording that could cause offense or be misinterpreted.
- Develop relationships with key PR and social media influencers, as they will help to shape public opinion if a crisis hits again.
Key takeaways-
- Communication is a process that connects the sender with the receiver of the message.
- AIDA Model stands for Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action.
- Brand image is a mental picture or perception of a band in the mind of the consumers.
- Every brand has a value, and the value of a brand is brand equity
- Brand crisis takes place when certain negative event centers on one particular brand or a set of brands belonging to the same company.
Rural advertising
Advertising in rural markets is a quite a challenge because of lack of standard opportunities; there exists a sense of unanimity and complexity in the rural markets. Hence, its often considered a tough responsibility creating an advertising campaign for rural India. Rural marketing is a different field that drives marketing gurus to unlearn the traditional concepts. When the focus is shifted to rural marketing every facet and feature of marketing demands a refashion.
Definitions
Thomsen defined Rural marketing as,” The study of Rural marketing comprises of all the operations, and the agencies conducting them, involved in the movement of farm produced food, raw materials and their derivatives, such as textiles, from the farms to the final consumers, and the effects of such operations on producers, middlemen and consumers.”
According to G.N. Murthy – “Rural marketing is the study of all the activity, agency and policy involved in the procurement of farm inputs by the farmers and the movement of rural products from farmers to consumers”.
Features
- Large and scattered population - 740 million Indians forming 70 per cent of India’s population live in rural areas, according to the 2001 census. The rate of increase in rural population is greater than that of urban population. The rural population is scattered in over 6 lakhs villages. The rural population is highly scattered, but holds a big promise for the marketers.
- Higher purchasing capacity - Purchasing power of the rural people is increasing. The potential of rural markets are realized by the marketers, and thus are expanding their operations in rural India. In recent years, in countries like China and India rural markets have acquired significance, as the overall growth of the economy has resulted into substantial increase in purchasing power of rural communities.
- Market growth – Over the years the rural market is growing steadily. Demand for traditional products such as bicycles, mopeds and agricultural inputs; branded products such as toothpaste, tea, soaps and other FMCGs; and consumer durables such as refrigerators, TV and washing machines has also grown over the years.
- Development of infrastructure - There is development of infrastructure facilities such as construction of roads and transportation, communication network, rural electrification and public service projects in rural India. The growth in infrastructure has increased the scope of rural marketing.
- Low standard of living - The standard of living of rural areas is low and rural consumers have diverse socio-economic backwardness. A consumer in a village area has a low standard of living because of low literacy, low per capita income, social backwardness and low savings.
- Traditional outlook - The rural consumer values are old customs and traditions. Resist to changes. Gradually, the rural population is changing its demand pattern, and there is demand for branded products in villages.
- Marketing mix - The urban products cannot be used on rural population; separate sets of products are designed for rural consumers to suit the rural demands. According to the requirements of the rural consumers the marketing mix elements are to be adjusted.
Strategies for Rural Advertising:
The marketers may use the following strategies to advertise in the rural areas:
1. Influencer Strategy:
Advertising under this strategy actually depend on the convincing power of influential people and / or events in the villages to communicate the commercial messages to the rural customers. The marketers may utilise the services of influential people in the village such as the local Panchayat leaders, local priests or poojaris, influential landlords, and even the school teachers.
2. Participatory Strategy:
Events like different festivals and different games and sports competitions actually have a high participation level in the rural India. The local events and shows offer great opportunity to effectively reach to rural masses. Firms can sponsor different events and shows in rural villages which is usually a cost-effective way to advertise with the participatory strategy.
3. Show-N-Tell Strategy:
Several firms are venturing into different ways to educate the rural consumers about their brands and their usage through different shows and events. This kind of initiatives actually creates huge awareness about the brand among the interested people in the rural India.
4. Product Demonstration Strategy:
Marketers may also use product demonstration strategy to communicate the merits and features of the product. The product is demonstrated by trained and tactful persons conversant with the local language. The promotion team members demonstrate the process of using / operating the product and highlight special benefits of using the product. The promoters may also provide free samples to the villagers.
Political advertising
Political advertising includes advertising about a political party, representative or candidate, advertising about political issues or issues of public interest, and advertising in relation to government policies
Political advertising includes but is not limited to election advertising. During election periods the number of complaints received about political advertising often increases.
Political advertising refers to advertising on the part of political parties, local Govt. Bodies, Statement Governments, and Central Government
Definition
Political advertising includes any advertising displays, newspaper ads, billboards, signs, brochures, articles, tabloids, flyers, letters, radio or television presentations, digital or social media advertising, or other means of mass communication, used for the purpose of appealing, directly or indirectly, for votes or for financial or other support in any election campaign.
Political advertising does not include letters to the editor, news or feature articles, editorial comment or replies to editorials in a regularly published newspaper, periodical, or on a radio or television broadcast where payment for the printed space or broadcast time is not normally required.
Contents:
Political advertising may include the following contents:
- Achievements in terms of educational levels and health standards of a particular local area, state or even nation.
- Developments in the field of infrastructure such as irrigation projects, roads, power generation, water supply etc.
- Special schemes introduced specially to uplift weaker sections.
- International agreements signed and implemented (in case of Central Government)
- Increase in economic growth.
- Number of jobs created during certain period.
Purpose: The main purpose of political advertising is to create a favourable image on the minds of public by highlighting their achievements – past, present and potential. At the time of election, the political parties urge the voters to vote for their candidate.
Media Used: Generally, the media used include newspapers and outdoor. But sometimes, some political parties may also use radio and magazines. Nowadays, SMS (cell phones) is also used especially at the time of elections.
Timing of Advertising: Normally, a bulk of political ads appears during the time of elections. The political ads may also appear after completion of 1 year or so by the Government at the Centre or at the State Level. The political ads may be also displayed during important festivals or such other cultural activities.
Code for Political Advertising: Political advertising is subject to a code laid down by Govt. Authorities with respect t the content of advertising, and also the amount of funds to be spent on advertising especially during elections.
Advantages of Political Advertising-
1. Political advertising influences the voters to vote for a particular candidate or the party at the time of elections.
2. Political advertising helps to enhance the image of the political party, as it may highlight special achievements, and the promises that may fulfilled after coming to power.
3. It helps to create awareness among the masses regarding the problems or defects of the opposition parties or candidates at the time of elections.
Advocacy advertisement
It is a kind of corporate advertising, which is presented in an aggressive manner. This type of advertising is usually argumentative and controversial in nature. A company can advocate its arguments on several issues ranging from government policies to employee related issues such as strikes.
Reasons for Advocacy Advertising
At times, a company may not get favourable reporting in the media due to poor public relations. In order to counter such unfavourable reporting, a company may resort to advocacy advertising. For instance, during employees’ strike, media may report negatively against the company and in support of the employees. In such situation, the affected company may present its viewpoint through the ads.
Media Used
Generally, the media used for advocacy advertising is newspapers. This is because; the wrong reporting or rumours mostly originate through the press. Secondly, the firm can provide detailed facts and arguments. In media like radio, TV, outdoor, and magazines, it is difficult to present the advertisement with details. Secondly, newspaper advertising gives the benefit to highlight current topics.
Undertaken by:
This type of advertising can be undertaken by person or party or organisation. It can be undertaken by organisations to present their point of view. Individuals may also resort to such ads to present their views on certain issues such as lack of empathy on the part of Government authorities towards social problems. The Government may also undertake such advocacy such as advertisement condemning bandh by opposition parties.
Advantages of Advocacy Advertising:
- Advocacy advertising helps to correct negative attitudes of the general public towards the firm and its policies.
- It helps to maintain or improve the image of the firm in the minds of stakeholders.
- It helps to develop good relations with the members of the public.
- It develops a sense of security and confidence in the minds of employees and shareholders.
Corporate image advertising
Meaning and Purpose
It is also known as institutional advertising. It is undertaken to build, maintain and improve good image of the firm in the minds of general public. The emphasis in the ads is placed on the company rather than its products or services.
Who Undertakes?
Normally, large firms undertake institutional advertising. Small firms may not be able to afford the cost of institutional advertising. Normally, newspapers or magazines are used to advertise institutional ads. At times, television may be used.
Nature of Corporate Image Advertising
This type of advertising is non-controversial and non-argumentative in nature. Through institutional ads, a firm seeks to communicate positive attributes about itself and presents itself in a favourable way.
Aspects
- The following aspects are normally included in institutional ads:
- Research & Development of the firm.
- Number of factories or branches of the firm.
- The number of employees and facilities provided to them.
- Foreign collaborations, if any.
- Distribution network of the firm.
- Market position of the firm.
- Products or services offered by the firm.
- Social welfare programmes undertaken by the firm, etc.
Green advertising
The concept of green advertising has come into existence on account of green marketing initiatives. Green marketing refers to marketing of eco-friendly products. Thus, green advertising refers to promotional campaigns relating to eco-friendly products. It also includes the green initiatives undertaken by business and non-business organizations to protect the environment.
According to green environmentalists, a green advertising campaign has to inspire a movement among buyers. Firms that produce green (eco-friendly) products need to highlight the same in their promotional campaigns. They should make people aware of the benefits of eco-friendly products. They need to highlight the fact that they invest a good amount of money on R&D to design eco-friendly products.
Common Green Marketing / Advertising Claims:
The following are some of the common green marketing / advertising claims made by sellers, especially in developed countries like USA, UK, Japan and so on:
1. “Free Of” Claim:
Companies may make a point to let the consumers know that their products are “free of” any harmless chemical or other ingredient that poses a risk to their health or lives.
2. VOC-Free:
Some products are labelled and “low-VOC” or “VOC-free”. VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) which are found in paint, household cleaning products, floor polishes, charcoal lighter fluid, windshield wiper fluid, and some hair styling products, among other products. VOCs are emitted as gases, and may cause smog by contributing to ground-level ozone formation, or have negative effects on the health of users.
3. Non-Toxic:
Marketers may state that their products is “non-toxic” – safe for both humans and environment.
4. Ozone-Friendly:
The Ozone layer in the upper atmosphere prevents harmful radiation from the sun from reaching the earth. But ozone at ground level forms smog and can cause serious breathing problems for some people.
A company may state that its products are “Ozone-friendly” or “Ozonesafe” – its products do not harm the upper ozone layer and the air at ground level.
5. Biodegradable:
A company may state that its product or packaging is biodegradable Something that’s biodegradable, like food or leaves, breaks down and decomposes into elements found in nature when it’s exposed to light, air, moisture, certain bacteria, or other organisms.
6. Recyclable and Recycled Products:
A company may say that its products is recyclable or recycled. Recyclable products are those which people can recycle the package or product after use. Recycled products are made with content that was kept out of – or delivered from – the trash either during the manufacturing process or after people used a product.
7. Carbon Offset Claims:
A company can make claims that it takes action to reduce greenhouse gasses, like planting trees, or using green technology and can get credits for those “carbon offset” activities.
8. Renewable Claims:
A company make claims that it uses Renewable Materials and Renewable Energy.
Key takeaways-
- Advertising in rural markets is a quite a challenge because of lack of standard opportunities; there exists a sense of unanimity and complexity in the rural markets.
- Political advertising refers to advertising on the part of political parties, local Govt. Bodies, Statement Governments, and Central Government
- Advocacy advertisement is a kind of corporate advertising, which is presented in an aggressive manner.
- Corporate image advertising is undertaken to build, maintain and improve good image of the firm in the minds of general public.
Trends in media
1. Convergence of Media:
Advertising industry is witnessing convergence of media. In advertising convergence, and more appropriately digital convergence, refers to a growing trend for using computer technology to deliver media programming and information.
Convergence allows one media outlet to take advantage of features and benefits offered through other media outlets. For instance, there is convergence of television and internet. In the case of some television programmes, one see the same programme on the television, and another person can see it on the internet.
2. Interactivity:
Interactivity means that audience can send messages back and forth to the media and vice versa. This is a significant change, until recently, most advertising was a one-way media, where the audience only viewed or listened or read. Now the audience can respond, ask questions, or even place orders for products and services.
3. Trends towards Non-traditional Media:
Nowadays, firms are making use of non-traditional media to support the traditional media campaign for a brand. In 2003, an interesting use of a new medium employed by Reebok was the tattoos on the forehead of college students. Reebok hired 500 college students to wear temporary tattoos containing the Reebok logo and the slogan ‘The plain train is coming’ on their foreheads. These students were strategically placed around the 26.2 mile course of the Boston marathon in an attempt to take away attention from the official sponsor of the event – Adidas.
4. Audience Tracking:
Now-a-days, technology has made it possible for audience tracking. Downloading entertainment from the Internet, such as games, video and software, may contain a hidden surprise – internet spy-ware. Spyware is a special program that runs in the background of a user’s computer and regularly forwards information over the Internet to the spyware’s company operating the spyware. In some cases spyware keeps track of websites the user has visited. The information is then used to gain an understanding of the user’s interests, which then results in delivery of special ads when a user visits a certain site.
5. New Media Options:
Today, the media options available to supplement an advertiser’s primary vehicles have grown dramatically. The introduction of vehicles such as the internet, video catalogues, mobile and interactive television has brought major changes to the job of the advertising and media professionals.
For instance, the media planners have created new ways to view the media function and media buyer. Media planners are forced to go beyond costs in developing plans.
6. Unbuilding of Media Services:
The split between creative agencies and media agencies is often referred to as ‘unbundling’. The idea of breaking away the media function (From the ad agency) as a separate business has become an important reality in the last two decades. Upto the late 1990’s, media buying was generally carried out by the media department of an advertising agency.
The unbundling of media independents has opened the doors of to the outside clients as well i.e. clients other than own agency affiliation are now pitched for as new business.
7. Trends Towards Internet Advertising:
There is a growing trend towards internet advertising. Internet advertising includes banner ads, online classified advertising, etc. Advertising through social networking sites like Facebook, Twitter, and many others have also started gaining importance in India.
Trends in Ad spends
The Indian advertising market is expected to grow by 13.5 percent to Rs. 56,152 crore in 2017 from RS. 49,480 crore in 2016 says Madison Media Group in its report titled. Pitch Madison Advertising Report 2017, which was published in February 2017. As expected, the growth for the ad industry came mainly from digital, which grew by 40 percent to Rs. 7,315 crore from Rs. 5,120 crore in 2015, and now claims 15 percent of the total market. The growth for all other media – television, print outdoor, radio and cinema slowed down to 8.5 percent.
Share of Media in Ad Expenditure:
Digital media share in ad expenditure grew by over 40% in 2106. IT generated Rs. 7,315 crore with a total media expenditure share of 15%.
Category Wise Ad Expenditure (AdEx):
Close to 50 percent of print’s growth of RS. 1,216 crore is accounted by only four categories, namely FMCG, auto, education and BFSI.
Trends in ad agencies
1. Trends towards Global Joint Ventures:
In India, there is a growing trend of Indian ad agencies having a tie up with global agencies. Due to globalisation of business, it gives a big advantage for Indian ad agencies to have a tie-up with foreign ad agencies. At present, most of the top 20 agencies in India have a global partner or owner, which provides an immediate link to global markets.
2. Media Buying Agencies:
There is a growing trend to set up media buying agency. A number of ad agencies have set up subsidiary media buying agencies, and several other agencies will do so in the near future.
The media buying agency perform certain functions:
- Buys space / time slots from media owners and sells the same to advertisers.
- Schedules slots at different television channels and radio stations.
3. Smaller Niche Ad Agencies:
Clients (Advertisers) in developed countries like USA have also started moving away from agency giants, instead opting to bring work in-house or use a raft of smaller agencies. P&G has reduced the number of PR and advertising agencies it works with by around 50% over the past three years.
4. Less Investment by Ad Agencies:
Ad agencies are investment less in people, marketing and sales. Recruitment in ad agencies has slowed down especially in advanced countries. This may be due to the shift towards inhouse agencies and small creative boutiques.
Trends in execution of advertisements
1. Live streaming of Ads:
The user base of all the big social networks (Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Twitter) have grown considerably in the past few years. The live streaming services of all the big social networks grow further their user base and the concept of live streaming has gained acceptance among consumers. Facebook went in hard with a multimedia advertising campaign to promote its Facebook Live Service in December 2016, while its sister company Instagram added live video functionality in November 2016.
2. Participatory Strategy:
Events like different festivals and different games and sports competitions actually have a high participation level in the rural India. The local events and shows offer great opportunity to effectively reach to rural masses. Firms can sponsor different events and shows in rural villages which is actually a cost-effective way to advertise with the participatory strategy.
3. Show-N-Tell Strategy:
Several firms are venturing into different ways to educate the rural consumers about their brands and their usage through different shows and events. This kind of initiatives actually creates huge awareness about the brand among the interested people in the rural India.
4. Influencer Strategy on Social Media:
Influencer strategy on social media has become a buzzword among advertisers. The concept of influencer marketing is straightforward – to reach new audiences on social media, brands pay “influencers” (social media personalities and celebrities with massive follower counts) to post about the products, which they use.
5. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality:
A trend that may emerge in 2017 is augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). The launch of Pokémon Go was a wakeup call to many businesses who haven’t explored this option. The mainstream shift toward AR and VR provides new ways to connect with customers and offer unique, memorable interactions.
Key takeaways –
- Advertising industry is witnessing convergence of media.
- In India, there is a growing trend of Indian ad agencies having a tie up with global agencies.
- The user base of all the big social networks (Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Twitter) have grown considerably in the past few years.
News

Sources-
- The advertising concept book by Pete Berry
- Tested advertising methods by Jon Steel
- Scientific advertising by Claude C Hopkins
- Truth, lies and advertising by Jon Steel