Unit 1
Introduction to Marketing
Case studies (Zomato: Redefining Digital Marketing)
In April 2020, with the whole world in the grip of the Covid-19 pandemic, India imposed a total lockdown that forced businesses to shut down or allow their employees to work from home. While essential services were allowed, online food service aggregators (FSA) like Zomato were also disrupted as the government sometimes allowed them to operate and sometimes put restrictions. A Twitter handle decided to have some fun at Zomato’s expense: “My parents think I am as useless as Zomato in our phones during this lockdown. My parents are wise,” Though Zomato wasn’t even tagged on the tweet, its social media team noticed it and retorted: “We’re actually delivering groceries now, aap apna dekh lo,” Analysts credited Zomato with redefining digital marketing over the last decade. This was just one of the instances that Zomato had won over the netizens with its witty replies and posts on social media.
The Growth Story
Zomato was co-founded by two Gurgaon-based employees of Bain & Co. – Deepinder Goyal and Pankaj Chaddah (Chaddah) – in 2008, under the name Foodiebay.com. The sight of their colleagues queuing up at the office cafeteria every day to go through a file of restaurant menu cards to order food resulted in Goyal coming up with the idea of an online restaurant information service. He scanned the menu cards and listed them on an intranet website. Many employees soon started using the service. Seeing the huge traffic to the site, Goyal and Chaddah launched their site publicly in 2008. The website foodiebay.com listed restaurants in Delhi NCR. By the end of 2008, it had become the biggest restaurant directory in the region. In 2010, Foodiebay was renamed Zomato. ..
Competition and Stakeholder Tension
While Zomato had been able to grow at a brisk pace, it had to also contend with aggressive and well-funded rivals in a cut throat market. The food service sector in India was valued at around Rs 4,238 billion as of March 2019, according to a report by the National Restaurant Association of India (NRAI) . And much of this growth was attributed to the rise of food delivery platforms. According to consulting firm Redseer, the number of orders placed on such ordering apps had increased from around 1.7 million a day in 2018 to about 2.2 million in 2019...
Digital Marketing Strategy of Zomato
With the tagline “Discover great places to eat around you”, Zomato targeted the age group of 18-35 years who had access to smartphones and were comfortable using apps. The company’s target segment was the working professional, who wanted to dine out, wanted to refer to ratings and reviews of the restaurants they wished to visit, and also wanted to get food delivered at their doorstep. Zomato positioned itself as a platform that brought restaurants, suppliers, consumers, food suppliers, and logistics partners together. It also positioned itself as the app consumers should look for when it came to authentic reviews and recommendations before visiting or ordering from a restaurant. ..
The Road Ahead
In the first half of FY2020 (i.e. April-September 2019), Zomato reported revenue of US$205 million compared to US$63 million in the first half of FY19 – an increase of 225%. The company also reported that its monthly burn rate, which measures the rate at which a company is losing money, was down by 60%. In the segment of ‘Dining Out’, globally the number of restaurant listings on Zomato was increased from 1.2 million in September 2018 to 1.5 million in September 2019. In table reservations, Zomato had reported 800 thousand booked covers in January 2019 to over 1.3 million booked covers in September 2019. The revenue from Hyperpure for April-September 2019 was USD 6.5 million. “We achieved tremendous results in optimizing our costs, without affecting new product launches or innovation,” commented Goyal.
Marketing refers to activities a company undertakes to promote the buying or selling of a product or service. Marketing includes advertising, selling, and delivering products to consumers or other businesses. Philip Kotler defines marketing as “the science and art of exploring, creating, and delivering value to satisfy the needs of a target market at a profit. Some marketing is done by affiliates on behalf of a company. Marketing includes activities like PR, sales promotion, advertising, social media, pricing, distribution and much of other functions. For example, advertisement in print and electronic media, discount on purchase etc.
Here is also a short overview of the evolution of marketing concepts-
- Production concept
An operations-based concept where the buyer expects products that are easily available and affordable. Here the business focuses on production efficiency, lowering costs and mass distribution. This concept works in developing economies where the requirement is more for the product than the features it offers.
2. Product concept
A consumer oriented concept where consumers expect products that are superior, high-performance and with unique features. This idea assumes that customers are likelier to be loyal when the product meets all their expectations then , the business strives to offer innovative products consistently.
3. Selling concept
Where the business believes that its products will sell only through active promotion and selling and therefore the customer won't respond until pushed. In short, it's a matter of the business trying to sell what it makes rather than make products to fulfill the market’s needs.
4. Marketing concept
This idea is radical, compared to the above and focuses on the target market, its needs and needs and a desire to be better than the competition while delivering value to its market. Unlike the earlier concepts that believe push marketing, it believes in pull marketing by creating brand loyalty. While the sales concept is seller-oriented, the marketing concept is buyer-oriented.
5. The societal marketing concept
It is that the ideal situation where, along with the focus on the target market’s wants and needs and delivering better value than its competition, the business also strives to preserve the well-being of its target market and therefore the society as an entire . This takes into consideration environmental and natural resources preservation and minimizing the carbon footprint.
Features of marketing Some of the features of marketing are- 
Features 1: features of marketing
1. Customer focus: The marketing function of a business is customer-centred. It makes an attempt to check the customer needs, and goods are produced accordingly. The business existence depends on human needs. During a competitive market, the goods that are best suited to the customer are the ones that are well-accepted. Hence, every activity of a business is customer-oriented. 2. Customer satisfaction: A customer expects some services or benefits from the product that payment is made. If this benefit is quite the amount paid, then the customer is satisfied. Within the long run, customer satisfaction helps to retain market demand. It helps achieve organizational objectives. Customer satisfaction is often enhanced by providing value-added services, which includes providing additional facilities at little or no extra cost. 3. Objective-oriented: All marketing activities are objective-oriented. Different objectives are fixed at different levels, but the main objective is to earn profit from business alongside the satisfaction of human wants. Marketing activities undertaken by sellers make an effort to seek out the weaknesses within the existing system, and measures are taken to improve the shortfalls in order that the objectives are achieved. 4. Marketing is both art and science: Art refers to a specific skill that's required in marketing activities of any type of business. Science refers to a scientific body of knowledge, based on facts and principles. The concept of marketing includes a bunch of social sciences like economics, sociology, psychology and law. It indicates market operations based on some principles. Hence, marketing is an art also as a science. 5. Continuous and regular activity: Marketing is an activity designed to plan, price, promote and distribute products. At the same time, it also addresses both the current and future consumers. Thus, it's endless process. A marketer has got to consistently monitor environment. This helps in arising with new products. 6. Exchange process: Marketing involves exchange of products, services and ideas with the medium of money. Exchange takes place between sellers and buyers. Most of marketing activities are concerned with the exchange of products. Functions like distribution, after-sale services and packaging help within the exchange process. Channels of distribution and physical distribution play an important role within the exchange process by creating place utility. 7. Marketing environment: Economic policies, market conditions, and environmental factors, like political, technological, demographic and international, influence marketing activities. Marketing activities are inseparable from such environmental factors. A successful marketer must adapt to those changing factors and adjust marketing strategies to suit new market developments. 8. Marketing mix: A combination of 4 inputs constitutes the core of a company’s marketing system—product, price, place, and promotion. Marketing mix may be a flexible combination of variables. They’re influenced by consumer behaviour, trade factors, competition and government regulatory measures. 9. Integrated approach: The marketing activities must be co-ordinated with other functional areas of an organization. Functions like production, finance, research; purchasing, storekeeping and PR (PR) are to be integrated with marketing. This may help in achieving organizational objectives. Otherwise, it'll end in organizational conflicts. 10. Commercial and non-commercial organizations: With the societal marketing concept gaining importance, social marketers are finding useful new ways of applying marketing principles. Commercial organizations also are adopting cause-related marketing to strike long-term relations with consumers. Business organizations like educational institutions, hospitals, religious institutions and charitable trusts have also found meaningful applications of marketing. Thus, marketing is applicable to both business and non-business organizations. 11. Precedes and follows production: Identifying consumer needs and needs is that the primary task of a marketing manager. Production activities are adapted to those consumer needs. Thus, marketing precedes production. Marketing helps within the distribution of the goods which follows production. Hence, production and marketing activities are closely related to each other.
Importance of marketing

The importance of marketing are-
(1) Marketing Helps in Transfer, Exchange and Movement of Goods:
Marketing is extremely helpful in transfer, exchange and movement of goods. Goods and services are made available to customers through various intermediaries’ viz., wholesalers and retailers etc. Marketing is helpful to both producers and consumers. To the former, it tells about the precise needs and preferences of consumers and to the latter about the products that manufacturers offer. According to Prof. Haney Hansen “Marketing involves the design of the products acceptable to the consumers and also the conduct of these activities which facilitate the transfer of ownership between seller and buyer.”
(2) Marketing is useful In Raising and maintaining the standard Of Living of The Community: Marketing is specifically the giving of a typical of living to the community. Paul Mazur states, “Marketing is that the delivery of ordinary of living”. Professor Malcolm McNair has further added that “Marketing is that the creation and delivery of ordinary of living to the society”. By making available the uninterrupted supply of goods and services to consumers at an affordable price, marketing has played a vital role in raising and maintaining living standards of the community. Community comprises of three classes of people i.e., rich, middle and poor. Everything which is used by these different classes of people is supplied by marketing. In the times, with the emergence of latest marketing techniques even the poorer sections of society have attained an affordable level of living standard. This is often basically thanks to large scale production and lesser prices of commodities and services. Marketing has indeed, revolutionized and modernized the living standard of individuals in times.
(3) Marketing Creates Employment: Marketing is complex mechanism involving many of us in one form or the other. The main marketing functions are buying, selling, financing, transport, warehousing, risk bearing and standardization, etc. In each such function different activities are performed by a large number of individuals and bodies. Thus, marketing gives employment to many people. It's estimated that about 40% of total population is directly or indirectly dependent upon marketing. Within the time of big scale production and industrialization, role of selling has widened. This enlarged role of marketing has created many employment opportunities for people. Converse, Huegy and Mitchell have rightly observed that “In order to have continuous production, there must be continuous marketing, only then employment are often sustained and high level of commercial activity are often continued”.
(4) Marketing as a Source of Income and Revenue: The performance of marketing function is all important, because it is the only way through which the priority could generate revenue or income and convey in profits. However, someone must actually enter the market place and acquire dollars from society so on sustain the activities of the company, because without these funds the organization will perish. Marketing does provide many opportunities to earn profits within the method of buying and selling the goods, by creating time, place and possession utilities. This income and profit are reinvested within the priority, thereby earning more profits in future. Marketing should tend the best importance, since the very survival of the firm depends on the effectiveness of the marketing function.
(5) Marketing Acts as a Basis for making Decisions: A businessman is confronted with many problems within the type of what, how, when, what proportion and for whom to produce? Within the past problems was less on account of local markets. There was an instantaneous link between producer and consumer. In times marketing has become a very complex and tedious task. Marketing has emerged as new specialised activity beside production. As a result, producers are depending largely on the mechanism of marketing, to make a decision what to produce and sell. With the assistance of marketing techniques a producer can regulate his production accordingly.
(6) Marketing Acts as a Source of latest Ideas: The concept of selling could also be a dynamic concept. It's changed altogether with the passage of some time. Such changes have far reaching effects on production and distribution. With the rapid change in tastes and preference of people, marketing has got to come up with a similar. Marketing as an instrument of measurement, gives scope for understanding this new demand pattern and thereby produce and make available the goods accordingly.
(7) Marketing is beneficial in development of an economy: Adam Smith has remarked that “nothing happens in our country until somebody sells something”. Marketing is that the kingpin that sets the economy revolving. The marketing organisation, more scientifically organised, makes the economy strong and stable, the lesser the strain on the marketing function, the weaker are getting to be the economy.
Functions of marketing
The seven functions of marketing are distribution, market research, setting prices, finance, product management, promotional channels and matching products to consumers. 
Distribution is about deciding how you'll get the products or services you'd prefer to sell to the people who want to shop for them. Having an idea for a product is great, but if you're not able to get that product to the purchasers you're not going to make money. Distribution are often as easy as fixing shop within the a part of a city where your target customers are – but in an increasingly interconnected world, distribution more often than not now means you will need to require your products or services to the customers. 2. Financing an Enterprise It takes money to form money. As a business owner, an important function of marketing a product is finding the money through investments, loans, or your personal capital to finance the creation and advertising of your goods or services. 3. Deep market research Market research is about gathering information concerning your target customers. Who are the people you'd prefer to sell to? Why should they buy from you as against a rival business? Answering these questions requires that you simply do some on-the-ground observation of the market trends and competing products. 4. Setting Prices Setting the right price for your product or service is usually a challenge. If you price it too high, you'd possibly lose customers – but if you price it too low you'd possibly be robbing yourself of profits. The "right" price normally comes through trial and error and performing some market research. 5. Product and service Management Once you've determined the target market and set the price of your product or service, the goal becomes to effectively manage the merchandise or service. This involves paying attention of consumers, responding to their wants and needs, and keeping your products and services fresh and up so far. 6. Promotional Channels Most business owners are familiar with the thought of promotion. Advertising your products and services is vital to attracting new customers and keeping existing customers coming. Because the marketplace changes, you will be eager to reply appropriately by tailoring your promotion messages to social media, by sticking with more conventional outlets, or by employing a combination of the old and new. 7. Matching Products to Customers While we tend to think about selling and marketing as being closely linked, selling is last on the list of the seven functions of marketing. This is often actually because selling can happen only after you've determined the requirements and needs of your customer base and are able to respond with the correct products at the correct price point and time-frame.
Evolution Marketing has changed over the centuries, decades and years. The assembly centred system systematically become relationship era of today and over the period; the specializations have emerged like sales versus marketing and advertising versus retailing. The general evolution of selling has given rise to the concept of business development. Marketing has taken the fashionable shape after browsing various stages since last the top of 19th century. The production oriented practice of marketing before the 20 th century was conservative and hidebound by rules-of-thumb and lack of information. Science & technology developments and specially the event of knowledge technology have now changed the way people live, the way people do business and thus the way people sell and buy. Following could also be a brief summary of the varied stages of evolution of marketing are-

• Production Orientation Era: The prevailing attitude and approach of the production orientation era was -“consumers favor products that are available and highly affordable”. The mantra for marketing success was to “Improve production and distribution”. The rule was “availability and affordability is what the customer wants”. The age was marked by narrow product-lines; system based on the prices of production and distribution, limited research, primary aim of the packaging was to shield the product, minimum promotion. Advertising meant, “Promoting products with a lesser quality”. • Product Orientation Era: The attitude changed slowly and approach shifted from production to product and from the quantity to quality. The prevailing attitude of this era was that buyers favor products that provide the foremost quality, performance and innovative features and thus the mantra for marketers was ‘A good product will sell itself’, so doesn't need promotion. • Sales Orientation Era: The increased competition and kind of choices / options available to customers changed the marketing approach and now the attitude was “Consumers will buy products as long because the company promotes/ sells these products”. This era indicates rise of advertising and thus the mantra for marketers was “Creative advertising and selling will overcome consumers’ resistance and convince them to buy”. • Marketing Orientation Era: The shift from production to product and from product to customers later manifested within the Marketing Era which focused on the “needs and desires of the customers” and thus the mantra of marketers was” ‘The consumer is king! Find a requirement and fill it’. The approach is shifted to delivering satisfaction better than competitors are. • Relationship Marketing Orientation Era: This can be the modern approach of marketing. Today’s marketer focuses on needs/ wants of target markets and aims at delivering superior value. The mantra of a successful marketer is ‘Long-term relationships with customers and other partners cause successes
Strategic v/s Traditional Marketing
The differences between strategic and traditional marketing are-
Key takeaways- 1) Marketing refers to activities a company undertakes to promote the buying or selling of a product or service. 2) Marketing has changed over the centuries, decades and years. The assembly centered system systematically become relationship era of today and over the period. |
Concept
Market research is defined because the process of gathering data on goods and services to determine whether the merchandise or service will satisfy customers' needs. Market research can identify market trends, demographics, economic shifts, customer's buying habits, and important information on competition. You’ll utilize this information to define your target markets and establish a competitive advantage within the marketplace. For market research to be useful, the information must be timely and relevant to your business. A successful new venture sells customers goods and services they need or need and continually grows a base of satisfied customers. The following image shows marketing research of an online shopping site-
![33 Online Shopping Questionnaire + [Template Examples]](https://glossaread-contain.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/epub/1642870818_3670313.png)

Functions of market research
The features of market research are-
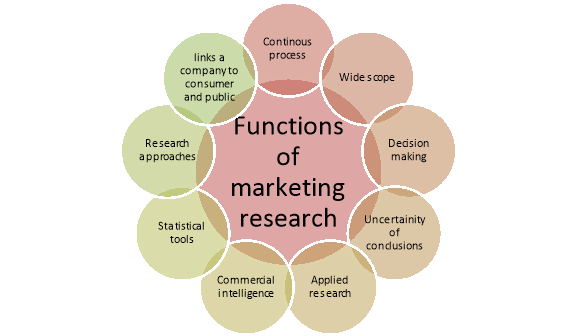
Figure: Functions of marketing research
1. Continuous process:
Marketing research isn't only continuous but also a scientific and systematic process. It’s scientific and systematic because it's well-defined procedures. It’s a process of generating and evaluating data, then refining it. It’s professionally organized. It’s a continuous process because every firm is faced with problems and opportunities.
2. Wide scope:
Marketing may be a specialized activity. It encompasses several functions. Thus, marketing research features a wide scope. It includes marketing research, market research, consumer research, promotion research, international market research, price research and distribution research.
3. Aid to decision-making:
It helps the managers take practical decisions. Decisions supported experience and research is best than decisions supported intuition. Functions like description, evaluation, explanation and prediction by the marketing researcher help in practical decision-making. Thus, it an essential tool not just for marketing managers but also for other functional managers.
4. Uncertainty of conclusions:
Consumer is that the focus of marketing research. However, consumer behaviour is difficult to gauge precisely. It’s not a physical science, but science due to this inherent nature; it suffers from certain levels of inaccuracy.
5. Applied research:
Marketing research isn't a fundamental research because it doesn't reveal conceptual aspects. It’s an applied research, because it begins with defining or identifying a drag or opportunity, and ends with a follow-up of recommendations made up of research. Moreover, it's related to the commercial aspects.
6. Commercial intelligence:
Marketing research is equivalent of military intelligence. It provides vital insights and information of product, price, place and promotional aspects. It’s the soul of modem marketing management.
7. Statistical tools:
Various mathematical and statistical tools are used for data analysis and interpretation. Percentages, ratios, averages, z-test, t-test, chi-square tests, etc. are used for presentation and interpretation of findings. The utilization of computer software has made it more convenient for in-depth analysis, cross-sectional studies, detection of errors in sampling and questionnaires.
8. Research approaches:
A researcher has several options of research methodology. Methods include the field survey method, the observation method and therefore the experimental research. The choice depends on factors like time availability, funds, number of respondents to be covered, location of respondents and literacy levels.
9. Links a company to the consumers and public:
Marketing research may be a function that links a company to the consumers, customers and public, through information. It evaluates marketing actions, marketing performances and marketing processes. This evaluation leads to collection of information that brings company closer to its customer and society.
Process of marketing research
The steps involved in marketing process are-
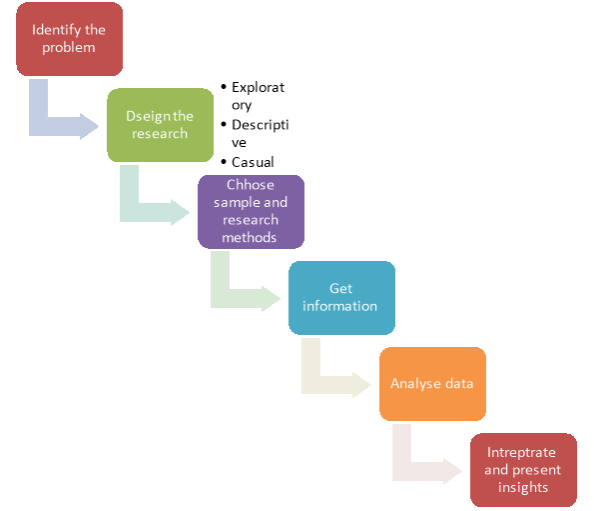
Figure: Market research process
1. Identify the problem
Identifying the matter is the most vital step in market research processes. It’s going to determine every step you're taking within the future—of market research anyways.
2. Design the research
There are three types of research designs-
- Exploratory research - If you don’t know the key variables or factors at play, your research is ambiguous. Exploratory research can assist you develop a hypothesis or ask a more precise question.
- Descriptive research - Descriptive research is useful for parsing out market segments and measuring performance. Consequently, you would like a pretty good idea of what you’re measuring and the way it'll be measured. If you would like to know how cause and effect are linked, you need:
- Causal research - Market researchers conduct causal research once they want to know the relationships between two or more variables. Simply, causal research helps you understand cause and effect.
3. Choose your sample and research method
Data is that the essence of market research. At the end of those market research processes, data is analyzed, interpreted, and became information and actionable insights. Data are often qualitative or quantitative. Simply, qualitative data can take many forms, from descriptions to audio and video. Quantitative data is usually presented in values and figures.
4. Get the info
Depending on your research design, you'll want to see internally for secondary data. For instance, let’s say you’re trying to know the annual purchase cycle for your business. You’d gather sales and reports and company records—that is secondary data. There are two ways to collect primary data: directly or indirectly. Direct data collection is simply that—you are speaking to your participants directly which will be through surveys, interviews, focus groups, and so on. Indirect data collection typically means observation. Think in-store observation, shelf experiments, or website heat maps.
5. Analyse the data
Data analysis may be a process of trying to find patterns in data and trying to know why those patterns exist. Data are often analysed quantitatively or qualitatively. Quantitative data analysis may be a process more complicated than are often described here. Unless you’re a math whiz, you’ll probably just use data analysis software like SPSS or StatCrunch. Qualitative data analysis typically involves coding—but not the computer programming kind, don’t you are worried. This type of coding is often done by hand or using software like NVIVO. It involves trying to find themes, concepts, and words that repeated throughout the data.
6. Interpret and present the insights
That’s where themes and patterns are available. You’ll describe trends and present those using figures or descriptions drawn from your participants.
Part of interpretation is using what you know about customers, businesses, or markets to provide recommendations for a way to move forward. These data-driven suggestions should offer an answer to the initial problem. The results of the research also can bring back light a drag you weren’t even aware you
Marketing Information System-Concept
The Marketing data system refers to the systematic collection, analysis, interpretation, storage and dissemination of the market information, from both the interior and external sources, to the marketers on a daily, continuous basis. The marketing data system distributes the relevant information to the marketers who can make the efficient decisions related to the marketing operations viz. Pricing, packaging, new product development, distribution, media, promotion, etc. Every marketing operation works in unison with the conditions prevailing both inside and outside the organization, and, therefore, there are several sources ( viz. Internal, Marketing Intelligence, Marketing Research) through which the relevant information about the market are often obtained.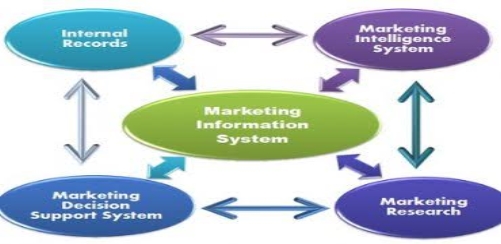
Figure: The market information system
- Internal Records:
The company can collect information through its internal records comprising of sales data, customer database, product database, financial data, operations data, etc. The detailed explanation of the internal sources of data is given below:
• The information are often collected from the documents like invoices, transmit copies, billing documents prepared by the firms once they receive the order for the goods and services from the customers, dealers or the sales representatives.
• The current sales data should be maintained on a daily basis that is an aide to a Marketing data system. The reports on current sales and therefore the inventory levels help the management to decide on its objectives, and therefore the marketers can make use of this information to style their future sales strategy.
• The Companies maintain several databases such as*Customer Database- wherein the entire information about the customer’s name, address, phone number, the frequency of purchase, financial position, etc. is saved.
a) Product Database- wherein the complete information about the product’s price, features, variants, is stored.
b) Salesperson database, wherein the complete information about the salesperson, his name, address, telephone number, sales target, etc. is saved.
• The companies store their data within the data warehouse from where the info is often retrieved anytime the need arises. Once the info is stored, the statistical experts mine it by applying several computer software and techniques to convert it into meaningful information that gives facts and figures.
2. Marketing Intelligence System:
The marketing intelligence system provides the info about the happenings within the market, i.e. data associated with the marketing environment which is external to the organization. It includes the knowledge about the changing market trends; competitor’s pricing strategy, change within the customer’s tastes and preferences, new products launched within the market, promotion strategy of the competitor, etc.
In order to possess an efficient marketing information system, the companies should work aggressively to enhance the marketing intelligence system by taking the following steps:
• Providing the right training and motivating the sales force to stay a check on the market trends, i.e. the change within the tastes and preferences of customers and provides suggestions on the improvements, if any.
• Motivating the channel partners viz. Dealer, distributors, retailers who are within the actual market to supply the relevant and necessary information about the purchasers and therefore the competitors.
• The companies also can improve their marketing intelligence system by getting more and more information about the competitors. This will be done either by purchasing the competitor’s product, attending the trade shows, reading the competitor’s published articles in magazines, journals, financial reports.
• The companies can have an efficient marketing information system by involving the loyal customers within the customer advisory panel who can share their experiences and provides advice to the new potential customers.
• The companies can make use of the govt data to enhance its marketing data system. The info are often associated with the population trends, demographic characteristics, agricultural production, etc. that help a corporation to plan its marketing operations accordingly.
• Also, the companies can buy the information about the marketing environment from the research companies who perform the researches on all the players within the market.
• The Marketing Intelligence system are often further improved by asking the customers directly about their experience with the product or service via feedback forms which will be filled online.
3. Marketing research:
The Marketing Research is that the systematic collection, organization, analysis and interpretation of the first or the secondary data to seek out the solutions to the marketing problems. Several Companies conduct market research to analyze the marketing environment comprising of changes within the customer’s tastes and preferences, competitor’s strategies, the scope of latest product launch, etc. by applying several statistical tools. So as to conduct the marketing research , the data is to be collected which will be either primary data (the first-hand data) or the secondary data (second-hand data, available in books, magazines, research reports, journals, etc.) The secondary data are publicly available, but the first data is to be collected by the researcher through certain methods like questionnaires, personal interviews, surveys, seminars, etc. A marketing research contributes a lot within the marketing information system because it provides the factual data that has been tested several times by the researchers.
4. Marketing Decision Support System:
It includes several software programs which will be employed by the marketers to analyze the data, collected thus far , to require better marketing decisions. With the use of computers, the marking managers can save the large data during a tabular form and may apply statistical programs to research the info and make the decisions in line with the findings. Thus, the marketers need to keep a check on the marketing environment, i.e. both the internal (within the organization) and therefore the external (outside the organization, in order that marketing policies, procedures, strategies are often designed accordingly.
Key takeaways-
1) Market research is defined because the process of gathering data on goods and services to determine whether the merchandise or service will satisfy customers' needs. Market research can identify market trends, demographics, economic shifts, customer's buying habits, and important information on competition.
2) The marketing data system distributes the relevant information to the marketers who can make the efficient decisions related to the marketing operations viz. Pricing, packaging, new product development, distribution, media, promotion, etc.
Concept
Data mining is a process used by companies to turn raw data into useful information. By using software to look for patterns in large batches of data, businesses can learn more about their customers to develop more effective marketing strategies, increase sales and decrease costs. We can simply define data processing as a process that involves searching, collecting, filtering and analysing the info. It’s important to know that this is often not the quality or accepted definition. But the above definition caters to the entire process. A large amount of knowledge is often retrieved from various websites and databases. It is often retrieved in form of data relationships, co-relations, and patterns. With the arrival of computers, internet, and large databases it's possible to gather large amounts of data. The data collected could also be analysed steadily and help identify relationships and find solutions to the existing problems. Governments, private companies, large organizations and all businesses are after a large volume of data collection for the needs of business and research development. The data collected are often stored for future use. Storage of data is quite important whenever it's required. It's important to notice that it's going to take an extended time for finding and searching for information from websites, databases and other internet sources. Data mining is an interactive process.

The steps involved in data mining are-
1. Requirement gathering
Data mining project starts with the need gathering and understanding. Data processing analysts or users define the need scope with the vendor business perspective. Once, the scope is defined we move to subsequent phase.
2. Data exploration
Here, during this step data mining experts gather, evaluate and explore the need or project. Experts understand the problems, challenges and convert them to metadata. During this step, data mining statistics are wont to identify and convert the info patterns.
3. Data preparations
Data mining experts convert the info into meaningful information for the modelling step. They use ETL process – extract, transform and load. They’re also liable for creating new data attributes. Here various tools are wont to present data during a structural format without changing the meaning of data sets.
4. Modeling
Data experts put their best tools in place for this step as this plays an important role within the complete processing of data. All modeling methods are applied to filter the info in an appropriate manner. Modeling and evaluation are correlated steps and are followed same time to see the parameters. Once the ultimate modeling is done the ultimate outcome is quality proven.
5. Evaluation
This is the filtering process after the successful modeling. If the result isn't satisfied then it's transferred to the model again. Upon final outcome, the need is checked again with the seller so no point is missed. Data mining experts judge the entire result at the top.
6. Deployment
This is the final stage of the entire process. Experts present the info to vendors within the kind of spreadsheets or graphs. Have a glance at the below diagram for CRISP DM- Cross Industry standard process for data mining.
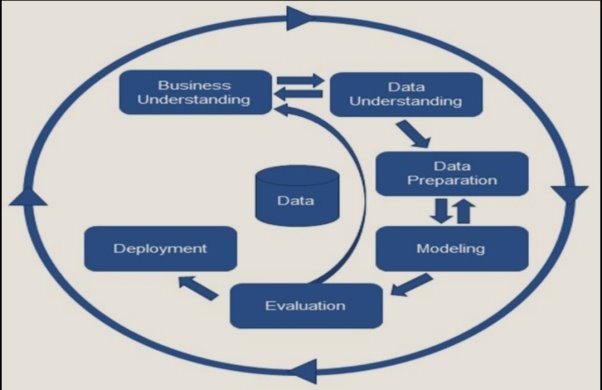
Figure: Data mining process
Importance of data mining
Some of the importance of data mining are-
- With the help of data mining-
Marketing companies build data models and prediction based on historical data. They run campaigns, marketing strategy etc. This results in success and rapid climb.
2. The retail industry is additionally on an equivalent page with marketing companies-
With data processing they believe predictive based models for his or her goods and services. Retail stores can have better production and customer insights. Discounts and redemption are based on historical data.
3. Benefits for banks:
Data mining suggest banks regarding their financial benefits and updates. They build a model based on customer data then inspect the loan process which is actually based on data mining. In other ways also data mining serves tons to the banking industry.
4. Benefits for manufacturers:
Manufacturing obtains benefits from data processing in engineering data and detecting the faulty devices and products. This helps them to chop off the defected items from the list then they will occupy the simplest services and products in place.
5. Assist Government:
It helps government bodies to analyse the financial data and transaction to model them to useful information.
6. Improves decision making:
Data mining organization can improve planning and decision makings. New revenue streams are generated with the assistance of knowledge mining which ends up in organization growth. Data mining not only helps in predictions but also helps within the development of latest services and products.
Meaning of consumer behaviour
Consumer behaviour is that the study of how individual customers, groups or organizations select, buy, use, and dispose ideas, goods, and services to satisfy their needs and needs . It refers to the actions of the consumers within the marketplace and therefore the underlying motives for those actions. Marketers expect that by understanding what causes the consumers to buy particular goods and services, they're going to be ready to determine which products are needed in the marketplace, which are obsolete, and the way best to present the goods to the consumers. The study of consumer behaviour assumes that the consumers are actors within the marketplace. The perspective of role theory assumes that consumers play various roles within the marketplace ranging from the information provider, from the user to the payer and to the disposer consumers play these roles within the decision process. The roles also vary in several consumption situations; for instance, a mother plays the role of an influencer during a child’s purchase process, whereas she plays the role of a disposer for the products consumed by the family.
According to Engel, Blackwell, and Mansard, ‘consumer behaviour is that the actions and decision processes of people who purchase goods and services for personal consumption’.
Consistent with Louden and Bitta, ‘consumer behavior is that the decision process and physical activity, which individuals engage in when evaluating, acquiring, using or disposing of goods and services’.

Factors influencing Consumer Behaviour
Consumer behaviour is influenced by many different factors. A marketer should try to understand the factors that influence consumer behaviour. Here are 5 major factors that influence consumer behaviour:
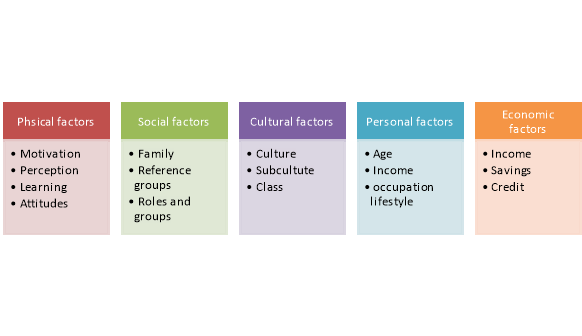
Figure : Determinants of consumer behaviour
1. Psychological Factors
Human psychology may be a major determinant of consumer behaviour. These factors are difficult to live but are powerful enough to influence a buying decision. Some of the important psychological factors are:
i. Motivation
When an individual is motivated enough, it influences the buying behaviour of the person. A person has many needs like the social needs, basic needs, security needs, esteem needs and self-actualization needs. Out of these needs, the basic needs and security needs take a position in particular other needs. Hence basic needs and security needs have the power to motivate a consumer to buy products and services.
Ii. Perception
Consumer perception may be a major factor that influences consumer behaviour. Customer perception may be a process where a customer collects information a few products and interprets the information to make a meaningful image a few particular products. When a customer sees advertisements, promotions, customer reviews, social media feedback, etc. concerning a product, they develop an impact about the product. Hence consumer perception becomes a great influence buying decision of consumers. Learning is often either conditional or cognitive.
Iii. Learning
When a person buys a product, he/she gets to find out something more about the product. Learning comes over a period of your time through experience. A consumer’s learning depends on skills and knowledge. While a skill is often gained through practice, knowledge is often acquired only through experience. In conditional learning the consumer is exposed to a situation repeatedly, thereby making a consumer to develop a response towards it. Whereas in cognitive learning, the consumer will apply his knowledge and skills to seek out satisfaction and an answer from the product that he buys.
Iv. Attitudes and Beliefs
Consumers have certain attitude and beliefs which influence the buying decisions of a consumer based on this attitude, the consumer behaves during a particular way towards a product. This attitude plays a big role in defining the brand image of a product. Hence, the marketers try hard to know the attitude of a consumer to style their marketing campaigns.
2. Social Factors
Humans are social beings and that they live around many of us who influence their buying behaviour. Human attempts to imitate other humans and also wish to be socially accepted within the society. Hence their buying behaviour is influenced by people around them. These factors are considered as social factors. A number of the social factors are:
i. Family
Family plays a big role in shaping the buying behaviour of a person. A person develops preferences from his childhood by watching family buy products and continues to shop for the same products even when they grow up.
Ii. Reference Groups
Reference group may be a group of people with whom a person associates himself. Generally, all the people within the reference group have common buying behaviour and influence one another.
Iii. Roles and standing
A person is influenced by the role that he holds within the society. If a person is during a high position, his buying behaviour is going to be influenced largely by his status. a person who may be a Chief military officer during a company will buy consistent with his status while a staff or an employee of the same company will have different buying pattern.
3. Cultural factors
A group of people are related to a set of values and ideologies that belong to a particular community. When an individual comes from a specific community, his/her behaviour is very influenced by the culture concerning that particular community. A number of the cultural factors are:
i. Culture
Cultural Factors have strong influence on consumer buyer behaviour. Cultural Factors include the basic values, needs, wants, preferences, perceptions, and behaviours that are observed and learned by a consumer from their near family members and other important people around them.
Ii. Subculture
Within a cultural group, there exist many subcultures. These subcultural groups share an equivalent set of beliefs and values. Subcultures can contains people from different religion, caste, geographies and nationalities. These subcultures by itself form a customer segment.
Iii. Class
Each and each society across the globe has form of class. The class isn't just determined by the income, but also other factors like the occupation, family background, and education and residence location. Class is important to predict the buyer behaviour.
4. Personal Factors
Factors that are personal to the consumers influence their buying behaviour. These personal factors differ from person to person, thereby producing different perceptions and consumer behaviour.
Personal factors
i. Age
Age may be a major factor that influences buying behaviour. The buying choices of youth differ from that of middle-aged people. Elderly people have a completely different buying behaviour. Teenagers are going to be more interested in buying colourful clothes and beauty products. Middle-aged are focused on house, property and vehicle for the family.
Ii. Income
Income has the power to influence the buying behaviour of a person. Higher income gives higher purchasing power to consumers. When a consumer has higher disposable income, it gives more opportunity for the buyer to spend on luxurious products. Whereas low-income or middle-income group consumers spend most of their income on basic needs like groceries and clothes.
Iii. Occupation
Occupation of a consumer influences the buying behaviour. A person tends to buy things that are appropriate to this/her profession. For instance, a doctor would buy clothes consistent with this profession while a professor will have different buying pattern.
Iv. Lifestyle
Lifestyle is an attitude, and how during which an individual stay in the society. The buying behaviour is very influenced by the life-style of a consumer. For instance when a consumer leads a healthy lifestyle, then the products he buys will relate to healthy alternatives to food.
5. Economic Factors
The consumer buying habits and decisions greatly depend upon the economic situation of a rustic or a market. When a nation is prosperous, the economy is robust , which leads to the greater money supply within the market and better purchasing power for consumers. When consumers experience a positive economic environment, they're more confident to spend on buying products. Whereas, a weak economy reflects a struggling market that's impacted by unemployment and lower purchasing power.
i. Income
When a person has a higher disposable income, the purchasing power increases simultaneously. Disposable income refers to the cash that's left after spending towards the basic needs of a person. When there's a rise in income, it results in higher expenditure on various items but when the disposable income reduces, parallel the spending on multiple items also reduced.
Ii. Family Income
Family income is that the total income from all the members of a family. When more people are earning within the family, there's more income available for shopping basic needs and luxuries. Higher family income influences the people within the family to shop for more. When there's a surplus income available for the family, the tendency is to shop for more luxury items which otherwise an individual won't are ready to buy.
Iii. Credit line
When a consumer is obtainable easy credit to get goods, it promotes higher spending. Sellers are making it easy for the consumers to avail credit within the form of credit cards, easy installments, bank loans, hire purchase, and many such other credit options. When there's higher credit available to consumers, the purchase of comfort and luxury items increases.
Iv. Liquid assets
Consumers who have liquid assets tend to spend more on comfort and luxuries. Liquid assets are those assets, which may be converted into cash very easily. Take advantage hand, bank savings and securities are some examples of liquid assets. When a consumer has higher liquid assets, it gives him more confidence to buy luxury goods.
v. Savings
A consumer is very influenced by the amount of savings he/she wishes to set apart from his income. If a consumer decided to save more, then his expenditure on buying reduces whereas if a consumer is interested in saving more, then most of his income will go towards buying products.
Market Segmentation- Concept
Market segmentation is one among the most efficient tools for marketers to cater to their target group. It makes it easier for them to personalize their campaigns, focus on what’s necessary, and to group similar consumers to focus on a specific audience during a cost-effective manner. Market segmentation is getting used by marketers since the late 1900s. Simple though it's going to be, it's of important use to forming any marketing plan. Market Segmentation may be a process of dividing the market of potential customers into different groups and segments on the idea of certain characteristics. The member of those groups share similar characteristics and typically has one or quite one aspect common among them. There are many reasons on why market segmentation is completed. One among the main reasons marketers segment market is because they will create a custom marketing mix for every segment and cater them accordingly. The concept of market segmentation was coined by Wendell R. Smith who in his article “Product Differentiation and Market Segmentation as Alternative Marketing Strategies” observed “many samples of segmentation” in 1956. Present-day market segmentation exists basically to solve one major problem of marketers; more conversions. More conversion is possible through personalized marketing campaigns which require marketers to segment market and draft better product and communication strategies according to the needs of the segment.
Benefits of market segmentation
Market segmentation makes it easier for marketing teams to develop highly targeted and effective marketing campaigns and plans. Below several benefits are outlined which exist with understanding and defining market segments.
- Greater company focus
When a company has identified specific market segments, it helps them to focus on what segments they need to focus on with specific products/ services/ content/ blogs and campaigns. When a company features specialize in specific segments, they ensure they're targeting the proper segment with the proper product which can see the greatest ROI.
2. Better serve a customer’s needs and wants
Having defined segments enables companies to satisfy a variety of customer needs by offering different bundles and incentives. Different forms and promotional activities are going to be used for various segments based on that segments needs/ wants and characteristics.
3. Market competitiveness
When a company is focusing on a specific segment, their market competitiveness increases. Which successively will cause a better ROI. The company is focused on specific segments and learns everything they have to understand that segment, to market their products to them.
4. Market expansion
With geographic segmentation as discussed earlier, market expansion is feasible immediately. When a company understands their segments and the way to market to a segment during a particular location, they will expand immediately into another nearby location. If segmentation is based on demographics, then once the corporate knows their demographic segment they will expand therein segment with similar products.
5. Targeted communication
Even when product features and benefits are an equivalent, it's important for companies to target segments with specific communication. For instance , if your segment was senior engineers, they'll respond better to technical information a few product within the kind of white papers or info graphics, but a project manager might respond better to information regarding cost savings, efficiencies etc. within the form of a blog, case study or video. Messaging will be different for various segments. Platforms which are wont to target different segments will be different also. The key's to know your segments and target communication relevant to them on the relevant platforms.
Bases of market segmentation
The firms can segment the market on the following bases:
- Geographical Segmentation:
Here, the segmentation is completed on the idea of the geographical location of the customers. The geographical segmentation is predicated on the premise that people living in one area have different purchasing or buying habits than those living in other areas of the country. For example, the banking needs of people living in rural and urban areas are different and. Therefore, different banking products and services are designed keeping in mind the various preferences of every customer group. Also, the factors like climatic zone, state, region, constitutes geographic segmentation.
2. Demographic Segmentation:
The demographic segmentation means dividing the customer market on the basis of several variables like age, sex, gender, occupation, income, education, marital status, family size, community, social station , etc. Such segmentation is based on the premise, that customer’s buying behaviour is very much influenced by his demographics, and moreover, these variables are often measured easily as compared to the other factors.
3. Psychographic Segmentation:
The psychographic segmentation relates to the personality, lifestyle, and attitude of the individual. It's believed that the consumer buying behaviours are often determined by his personality and lifestyle. The personality refers to the traits, attitudes and habits of an individual and therefore the market is segmented according to the personal traits like introvert, extrovert, ambitious, aggressiveness, etc. The lifestyle means the way an individual lives his life and does the expenditures. Here the companies segment the market on the idea of interest, activities, beliefs and opinions of the individuals.
4. Behavioural Segmentation:
Here, the marketer segments the market on the idea of the individual’s knowledge about the product and his attitude towards the usage of the product. Several behavioral variables are occasions, benefits, user status, usage rate, buyer readiness stage, loyalty status and therefore the attitude.
Thus, market segmentation helps the companies to divide the potential customers into small groups who have similar needs and plan the marketing strategies accordingly. This enables a firm to concentrate more on a specific group and earn more profits instead of catering to the needs of the whole market that have different needs and desires.
Customer Relationship Management- Concept
Customer relationship management (CRM) is that the combination of practices, strategies and technologies that companies use to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle, with the goal of improving customer service relationships and assisting in customer retention and driving sales growth. CRM systems compile customer data across different channels, or points of contact between the customer and therefore the company, which could include the company's website, telephone, live chat, direct mail, marketing materials and social media. CRM systems also can give customer-facing staff detailed information on customers' personal information, purchase history, buying preferences and concerns. The art of managing the organization’s relationship with the customers and prospective clients ask customer relationship management. Customer relationship management includes various strategies and techniques to take care of healthy relationship with the organization’s existing also as potential customers. Organizations must ensure customers are satisfied with their products and services for higher customer retention. Remember one satisfied customer brings ten new customers with him where as one dissatisfied customer takes away ten customers alongside him. In simpler words, customer relationship management refers to the study of needs and expectations of the customers and providing them the proper solution.
Techniques
Firms use a number of techniques to build, maintain and enhance CRM. The techniques include the software programmes, promotional techniques, pricing strategies, MVC programmes, and so on. Some of the techniques are discussed in detail.
1. Data Warehousing and Data Mining:
CRM analysts develop data warehouses and use data-mining techniques to develop and maintain long- lasting relationships with the precious customers.
a) A data warehouse may be a company-wide electronic database of detailed customer information. The aim of data warehouse isn't just to collect information, but to put it into a central location for easy access.
b) Once the info warehouse locates the info at a central place, the info analysts use data mining techniques to look at the mounds of data to find out interesting facts of the customers.
The mined data are often utilized for various marketing decisions like the following:
1. Product design and modification,
2. Product pricing,
3. Promotion mix,
4. Selection of channels of distribution,
5. Maintaining dealer relationships.
2. One-to-one Marketing:
Some firms adopt one-to-one marketing strategy. Such firms treat their customers as partners; especially within the case of B2B markets firms solicit the assistance of consumers to style new products or to enhance their services. If the customer gets involved the firm, then they're more likely to stay with the firm.
3. Loyalty Programmes:
Firms may use sort of loyalty programmes to retain customers. For instance , airlines may offer special discount for frequent fliers. Firms can also provide gifts and other benefits to the loyal customers. But it's to be noted that each one loyal customers needn't be profitable, and every one profitable customers needn't be loyal. Therefore, the firm must be selective. So as to enhance marketing efficiency, a firm has got to determine which of its customers are worth retaining and which aren't and which customers should tend extra care and attention. In other words, the firm has got to determine the value of its customers, and focus on MVCs accordingly.
4. Priority Customer Programs:
Some firms introduce priority customer programs. The priority customers are the MVCs. They're given priority in after-sales service, delivery and resolving complaints. The priority customer programs are followed by several organizations, especially within the banking industry. For example, Citibank maintains a list of priority customers and provides them with additional facilities special offers like free ticket to concerts, movies, and so on. Some banks, like Syrian Catholic Hank provide personalized services to the important customers.
5. CRM a social savvy Tool:
CRM software is now social friendly and it's a further advantage for Marketers. They will now track customer interactions across various social media platforms. We are already conscious of People based marketing techniques followed on Facebook. Integrated CRM software can make this strategy even better. This system can convince be a great help to review customer behavior for marketers. CRM software has come a long way. CRM is not any more limited to managing client relationships, it's now evolved into technology that permits Sales Automation, simpler customer engagement and people based marketing.
6. Advent of Beacons has created opportunities for CRM’s:
The biggest challenge for marketers nowadays is to create seamless experience for his or her customers who are quickly changing devices and are moving from digital to in-store environment frequently throughout shopping journeys. Here comes the role of beacons, which helps in communication, collects data and sends push notifications to customers. They're a good source of information for brands as they will easily capture customer signals both in-store and online. According to some researches, Beacons were expected to get $138 million in 2015 in retail sales. CRM systems provide opportunity to Marketers to integrate this data with CRM software for improved customer engagements.
7. CRM Predictive Analytics:
Advance CRM technology solutions are now equipped with predictive analysis qualities that help the marketers to focus on real customers. This prediction is formed on the idea of their past purchases and behaviors. Marketers can easily switch to those technology solutions which allow them to act on their customer data and predictive insights across channels through different mediums.
Market Targeting- Concept
A company cannot consider all the segments of the market. The company can satisfy only limited segments. The segments the company wants to serve are called the target market, and therefore the process of selecting the target market is referred as market targeting. Market segmentation results into dividing total market into various segments or parts. Such segments could also be on the idea of consumer characteristics or product characteristics or both. Once the market is split into various segments, the company has got to evaluate various segments and decide how many and which of them to focus on. It’s simply an act or process of selecting a target market.

Five patterns of Target market Selection
After evaluating the segments on the idea of segment potential, competitor’s position and potential goal and objective achievement, the firm can select the segment which can be the target market(s). The firm can consider five patterns of target market selection. They’re as follows:
1. Single segment concentration
Through single segment concentration strategy, the firm achieves a robust market position within the segment thanks to its greater knowledge of the segment’s needs and thus the special reputation it gains. Furthermore, the firm enjoys operating economies through specializing its production, distribution and promotion. Because it captures leadership within the segment, the firm can earn a high return on its investment. At a similar time, concentrated marketing involves above normal risks. The actual market segment can turn bitter.
3. Selective specialization:
During this strategy, the firm selects kind of segments (see following figure), each objectively attractive and appropriate, given the firm’s objectives and resources. There could even be little or no synergy between segments but each segment promises to be a money maker.
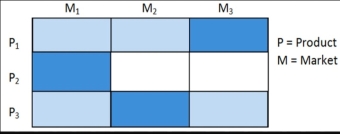
Selective Specialization
This strategy has the advantage of diversifying the firm’s risk even though one segment becomes unattractive, the firm can still earn money in other segments.
4. Product specialization:
The firm makes a particular product that it sells to several segments (see following figure). An example would be a microscope manufacturer who sells to university, government, and commercial laboratories. The firm makes different microscopes for the various customer groups and builds a powerful reputation within the precise product area. The downside risk is that the product could even be supplanted by a totally new technology.
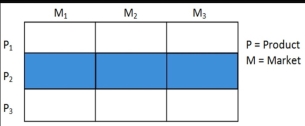
5. Market specialization:
The firm concentrates on serving many needs of particular customer group (see following figure). An example would be a firm that sells an assortment of products only to college laboratories. The firm gains a powerful reputation in serving this customer group and becomes a channel for addition products the customer group can use. The downside risk is that the customer group may suffer budget cuts.
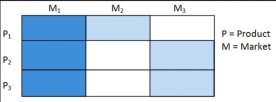
6. Full market coverage:
When a company decides to enter all or a minimum of most segments, full coverage market segmentations is used. This is often a high sales strategy, since greater penetration into each segment is combined with broad coverage of a complete market (see following figure).
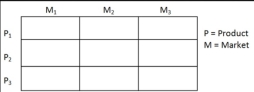
Extensive resources are required to implement the strategy because it affords limited opportunity for economies of scale. Full coverage market segmentation is therefore possibly to be adopted by a large organization.
7. Niche marketing:
The niches are the market segment that has been neglected by large organizations. Market niches are identified by dividing the market segments into sub-segments or by identifying customer groups whose needs haven't been met by the big organizations.

Many companies succeed by producing a specialized product aimed toward a way focused segment of market (or ‘niche’). During this pattern a company concentrates on niche market segments to use market opportunities.
Key takeaways-
1) Data mining is a process used by companies to turn raw data into useful information.
2) Consumer behaviour is that the study of how individual customers, groups or organizations select, buy, use, and dispose ideas, goods, and services to satisfy their needs and needs.
References-
- Philip Kotler (1987) Marketing: An Introduction. Prentice-Hall; International Editions.
- Ramaswamy, V.S., 2002, Marketing Management, Macmilan India, New Delhi.
- Kotler P, Armstrong G,2008, Principles of Marketing, 9th Edition, Prentice Hall, New Delhi.