Unit 3
Marketing Decisions
Case study
Snowman Logistics partners with Dr Reddy's for Sputnik Covid-19 vaccine in India
Snowman Logistics has entered in a strategic partnership with Hyderabad based Dr Reddy's to provide temperature-controlled end-to-end logistics solutions for the delivery of the two-dose Sputnik Covid-19 vaccine across India, the company said in a filing on Thursday. Snowman will manage the delivery through five of its high-capacity temperature-controlled warehouses in Mumbai, Delhi-NCR, Kolkata, Chennai, and Bengaluru. The company will offer storage, order processing, shipper packing and secondary transportation from these locations. ''The locations are strategically located to take care of not just the state distribution, but the whole of the regional requirements. The temperature, throughout, will be maintained between -20 degrees Celsius and -25 degrees Celsius. With this, Snowman will be the largest 3PL service provider for vaccines in the country offering national reach to Dr. Reddy's Lab,'' Snowman Logistics said. The company said that it has the capability to readily store 650 million doses at any given time, which can be increased to 1.05 billion doses with a short notice for Pan-India distribution. It also has the ability to store at upto -80 degrees Celsius, and provides real time temperature monitoring to ensure the correct conditions for vaccine distribution during the entire supply chain. In addition, the company has a capex plan of roughly ₹425 crores for capacity expansion, with a focus on the Pharma and E-commerce sector where the company has seen huge increases in demand since the onset of the pandemic, especially as there is a dearth of capacities in the organised sector, Snowman said.
Concept
Physical distribution is that the group of activities associated with the availability of finished product from the production line to the consumers. The physical distribution considers many sales distribution channels, like wholesale and retail, and includes critical decision areas like customer service, inventory, materials, packaging, order processing, and transportation and logistics you frequently will hear these processes be stated as distribution, which is used to clarify the marketing and movement of products.
Philip Kotler has defined physical distribution as, “Physical distribution involves planning, implementing and controlling the physical flow of materials and final goods from the aim of origin of use to satisfy consumer needs at a profit.”
As per William J. Stanton, “Physical distribution involves the management of physical flow of products and establishment and operation of flow systems.”

Factors influencing Physical Distribution
Physical distribution is crucial to provide time utility and place utility to the customers. The factors influencing the physical distribution are discussed below-
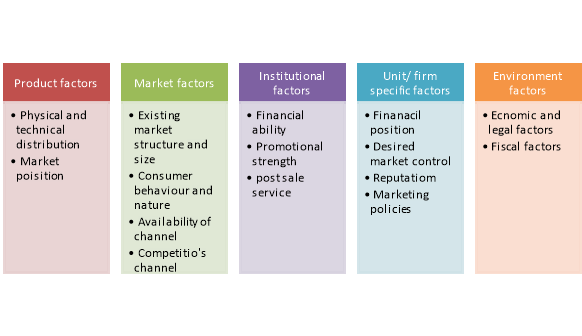
Figure 1: Factors influencing physical distribution
1. Product Factors/Considerations:
The first and most significant factor that influences on the choice of the channel of distribution is that the nature of goods. Perishable goods like cakes and breads that are required to be sold quickly are sold directly by the manufacturers to the consumers through stores. Goods that last longer are often handled by more intermediaries to insure a bigger market.
i. Physical and Technical Nature:
- Products which are of low unit value and have common use amongst consumers are generally sold through middle men; whereas, the sale of pricy and elite commodity and industrial products is conducted directly by the producer himself.
- Products that are perishable, i.e., products which are subjected to frequent changes in fashion or style or trend, also as those products which are heavy and bulky, undergo relatively shorter routes and, are often distributed directly so on minimize costs and damage.
- Industrial products that need demonstration, installation and after sale-services are often sold on to the consumers; while, retailers generally sell consumer products which are of technical nature.
- Certain technical or complex products need installation and advice of product use including demonstration, service visits, etc. For this, having exclusive trained personnel is important. Some companies prefer exclusive dealership in such cases.
- In case of an entrepreneur who produces a large number of products, he may find it economical to line up his own shops and sell his products on to the consumers. At an equivalent time, companies which have a narrow range of products may make their sale through wholesalers and retailers.
Ii. The Market Position:
A product promoted by an established and reputed manufacturer features a higher degree of market acceptance and, therefore, are often sold through various channels with little effort a brand new product, thus, has quick sales based on the producer’s reputation. This may, however, have long-term risks.
2. Market Factors/Considerations:
i. The existing market structure and size:
Producers may need to study the existing market structure. It is often geographically concentrated or wide spread. For instance, industrial markets are usually concentrated during a few large cities involving only large customers. Producers or channel commanders can have difficulty in changing that. However, consumer goods market features a different structure, as; it's directly related to, the masses. Consumer preferences dictate channel selection. For instance, baby food manufacturers changed their channel of distribution to supermarkets, as; research revealed that mothers preferred super markets over drug stores.
Ii. Consumer behaviour and nature of the purchase deliberation:
Purchase decisions are made differently for various products. Consumers spend more time and effort on durables like washing machine and mobile phone than on a pack of biscuits or toothpaste. The frequency of purchase influences purchase deliberations. Products, which are purchased frequently by consumers, have more buyer-seller contacts and middlemen are suggested.
Iii. Availability of the Channel:
Availability of a channel refers to the willingness of channel members to accept a brand. For this, the channel commander or the producer has the task of winning over the cooperation of the channel members. The producer may adopt push or pull strategy. In push strategy, the producer resorts to regular activities of convincing the prevailing channel members to simply accept the product and passes it through various points to reach the retailer then the final consumer.
In the pull strategy, the producer resorts to aggressive promotional activities on the final consumer, relying on the fact that strong consumer demand will force middlemen to simply accept the product so as to cater to the buyer satisfaction.
Iv. Competitor’s Channels:
A new firm always studies the prevailing distribution pattern and this, necessarily, includes identifying the distribution channels employed by competitors. Every business has certain established norms and practices and this might, even, apply to channels of distribution. If the existing pattern has given success to the competitors, a new firm may adopt the same channel as long because it is suitable and logical. As a matter of fact, finding new avenues may prove to be costlier and cumbersome.
3. Institutional Factors/Considerations:
The channel members also influence the choice of the channel to be selected.
i. Financial Ability of Channel Members:
In the process of sending the goods through the channels of distribution, it's found that manufacturers got to aid the retail dealers financially, either through, interest free loans, or other credit terms. Credit terms being competitive the willingness to increase credit may be a determinant in channel acceptance. Retailers also sometimes finance their suppliers either directly or by investing within the company. Usually, government agencies are restricted from making advance payments.
Ii. The Promotional Strengths of Channel Members:
Every producer, i.e., the channel commander, wants his product to be promoted. For national brands, producers themselves take up the responsibility. However, for others, distributors promote jointly with the producer. Just in case of certain private brands, the job is taken up by wholesalers or retailers who establish the name.
Iii. The Post-Sale Service Ability:
Many products carry a warranty and this is often employed by the consumer post purchase. The responsibility of serving the warranty has got to be established. It are often the manufacturer himself or a channel member. Since the retailer-distributor is that the closest up-to-date with the buyer, the buyer may expect this service from them itself. In certain cases, the product could also be returned to the manufacturer for servicing or services could also be performed by an independent service outlet established for this purpose.
4. Unit or Firm Specific Factors/Considerations:
Every firm has its own strengths and weaknesses, which influence channel decisions. Among them, important ones are discussed below:
i. The Company’s Financial Position:
Huge companies, which have the financial and human resource capability might not only produce the goods but also may have the ability to line up their own retail outlets thereby creating tons of visibility for themselves. On the other hand, smaller companies which don't have either the financial capability or manpower resources might just consider production and leave the marketing of products to others.
Ii. The Extent of Market Control Desired:
Market control refers to the power of a firm to influence the behaviour of channel members according to the will of the management. Here, the whole distribution network is served by factors like resale price maintenance, territorial restrictions, quotas and therefore the like. The channel commander, i.e., the producer or the manufacturer, may desire to exercise such command from time to time. The extent to which they need the control is that the question to be answered, as, higher the control, higher will be the channel directness.
Iii. The Company’s Reputation:
Popular companies, known for his or her products or services, have little or no problem in settling with a particular channel. This is often because reputed companies don't enter search of intermediaries. Instead, the intermediaries come in search of them. Reputation is reflected through higher sales, timely and quick replenishment of stocks, low levels of inventory, easy settlement of claims; competitive margins granted etc. the chosen channel seems to be cheaper and dependable due to the willingness and cooperation extended by channel members.
Iv. The Company’s Marketing Policies:
A company’s marketing strategy lays down the tactic of distribution. Important factors like advertising, advertisement, pricing, delivery and after sale services influence the channel selection the foremost. For instance, a corporation that invests heavily in advertising and sales promotion makes the selected channel direct, as, little effort is required to push the product through the chosen line. Alternatively, a company adopting a price penetration policy, [comes with a low margin], chooses a longer channel.
5. Environmental Factors/Considerations:
i. Economic and Legal Factors:
Due to the economic disparity prevalent within the economy, the govt. Promotes public distribution system through fair price shops to succeed in out to the economically weak sector. This constitutes the general public distribution system, which primarily focuses on the distribution of necessities. The private distribution system also needs a particular amount of regulation. Much legislation has been passed from time to time to manage the functioning of the varied channels of distribution. One such important legislation is that the MRTP Act of 1969. The provisions of this Act aim at preventing exclusive dealership, regulating territorial restrictions, reselling price maintenance, full line forcing, etc. the companies Act, 1956, forbids sole selling agency arrangements in industries like paper, cement, vanaspati, etc. Such provisions prevent cut throat competition; prevent creation of monopoly and therefore the like which are objectionable to public interests.
Ii. Fiscal Factors:
Sales tax rates vary from state to state because it may be a state fiscal matter. Although such sales tax is a component of the retail price set for a product, it's actually borne by the final consumer; it's its role to play in channel arrangements. For example, allow us to say, sales tax rate in Karnataka is higher when compared to Kerala, a producer may, therefore, take advantage of this benefit, like better to open his office in Kerala and expire the reduced tax benefit within the sort of reduced price. This will also become a competitive advantage to the product.
Marketing Channels (Traditional & Contemporary Channels)
A marketing channel consists of the people, organizations, and activities necessary to transfer the ownership of goods from the point of production to the point of consumption. It is the way products get to the end-user, the consumer; and is also known as a distribution channel.
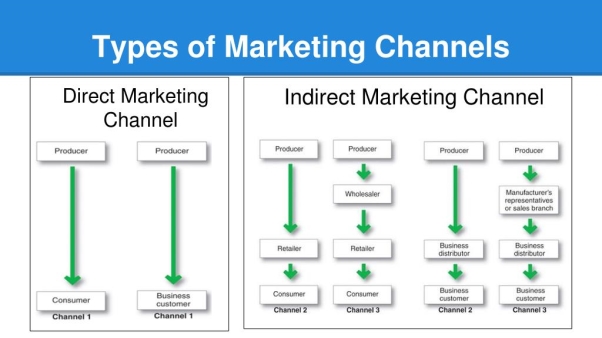
Figure 2: Marketing channels
Traditional marketing is an umbrella term that covers the wide array of advertising channels we see daily. These may include print media, billboard and TV advertising, flyer and poster campaigns and radio broadcast advertising. Modern marketing refers to theories that stress the importance of customer orientation versus the traditional market orientation. The differences between them are-
Sl no. | Traditional marketing channel | Modern marketing Channel |
1. | It needs to interrupt the customers to get their attention | They engage with the customer when and how they want. |
2. | It pushes a consistent message. | It joins conversation with them. |
3. | IT has limited marketing channels. | It has wide range of marketing channels. |
4. | It is mostly right brained creative and art. | It is mostly left brained science and math. |
5. | It has less customer base. | It has large customer base. |
Supply Chain Management-Concept
Supply chain management (SCM) is that the broad range of activities required to plan, control and execute a product's be due materials to production to distribution within the most economical way possible. SCM encompasses the integrated planning and execution of processes required to optimize the flow of materials, information and capital in functions that broadly include demand planning, sourcing, production, inventory management and logistics -- or storage and transportation. Companies use both business strategy and specialized software in these endeavours to make a competitive advantage. Supply chain management is an expansive and sophisticated undertaking that relies on each partner from suppliers to manufacturers and beyond -- to run well. Due to this, effective supply chain management also requires change management, collaboration and risk management to make alignment and communication between all the participants.
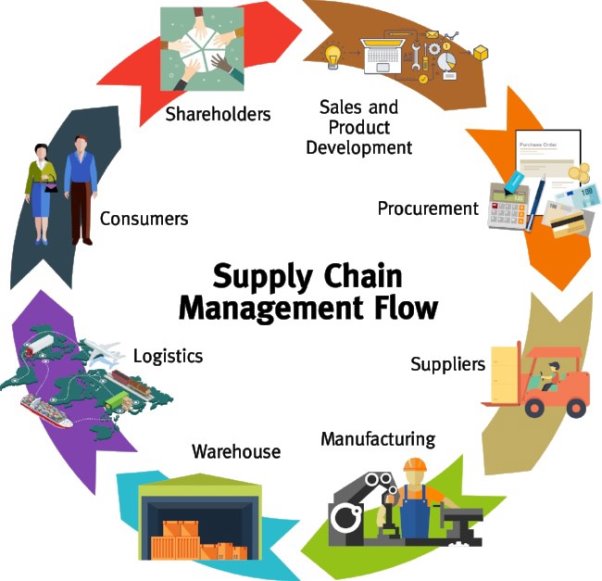
Figure 3: Supply chain management concept

Components of SCM
The supply chain management is designed by organisation depending on the nature of product, location of production, distribution area etc. The effective supply chain management provides time and place utility to customers. The components of supply chain management are discussed below-
1. Planning
This is one among the most important stages. Before the start of the whole supply chain, it's essential to finalise the strategies and put them into place. Checking the demand for the product or service, checking the viability, costing, profit, and manpower etc., are vital. Without a correct plan or strategy in place, it'll be well-nigh impossible for the business to realize effective and future benefits. Therefore, enough time has got to be dedicated to this phase. Only after the finalisation of the plans and consideration of all pros and cons, can one proceed further. Every business needs an idea or blueprint or a roadmap supported which the strategies are made. Planning helps to spot the demand and provide trends within the market and this, in turn, helps to make a successful supply chain management system.
2. Information
The world today is dominated by endless flow of data. Do as to achieve success, it's essential that a business stays abreast with all the newest information about the varied aspects of its production. The market trends of supply and demand for a specific product are often best understood if the data is correctly and timely disseminated through the various levels of the business. Information is crucial during a knowledge-based world economy, and ignorance about any aspect of business may very well spell doom for the prospects of the business.
3. Source
Suppliers play a really crucial role in supply chain management systems. Products and services sold to the top user are created with the assistance of various sets of raw materials. It's therefore necessary that suitable quality raw materials are procured at cost effective rates. If a supplier is unable to provide on time, and within the stipulated budget, the business is sure to suffer losses and gain a negative reputation. It is crucial that a company procures good quality resources so it can create good quality products and maintain its reputation within the market. This necessitates a strong role for suppliers within the supply chain management system.
4. Inventory
For a highly effective supply chain management system it's essential that a listing is kept and thoroughly maintained. A listing means the ready list of things, raw materials and other essentials required for the product or service. This list has got to be regularly updated to demarcate available stock and required stock. Inventory management is critical to the function of supply chain management, because without proper inventory management the assembly, also as sale of the product, isn't possible. Businesses have now begun to pay more attention to the present component just because of its impact on the availability chain.
5. Production
Production is one of the foremost important aspects of this technique. It's only possible when all the other components of the availability chain are in tandem with one another. For the method of production to start out it's essential that proper planning and provide of goods, also because the inventory, are well maintained. The assembly of goods is followed by testing, packaging and therefore the final preparation for delivery of the finished product.
6. Location
Any business, that desires to survive also as flourish, needs a location which is profitable for the business. As a example, a carbonated drink factory is about up in an area where water system is scarce. Water may be a basic necessity of such business. The shortage of water could hamper the assembly also as affect the goodwill of the company. A business cannot survive if it's to share an already scarce material with the community. Hence, an appropriate location which is well connected, and really on the brink of the source of essential resources for production is significant to a business’ prosperity. The need and availability of manpower must even be considered while fixing a business unit.
7. Transportation
Transportation is significant in terms of carrying raw materials to the manufacturing unit and delivering the ultimate product to the market. At each stage, timely transportation of goods is mandatory to sustain a smooth business process. Any business which pays attention to the present component, and takes good care of it, will enjoy the assembly and transportation of its goods on time. It is essential that a company works towards a secure and secure transportation process. Be it in-house or a third-party vendor, the transportation management system must ensure zero damage and minimal loss in transit. A well-managed logistic system alongside flawles invoicing are the 2 pillars of secure transportation.
8. Return of goods
Among the varied components that make a robust supply chain is that the facility for the return of faulty/malfunctioning goods, alongside a highly responsive consumer grievance redress unit. No one is infallible. Even a machine may malfunction once during a million times if less. As an area of a strong business process, one may expect the return of products under various circumstances. Even the simplest internal control processes may have unavoidable momentary lapses. Within the case of such lapses, inevitably followed by consumer complaints, a business must, instinctively, recall the product/s and issue an apology. This not only creates a good customer bonding, but also maintains goodwill within the end of the day.
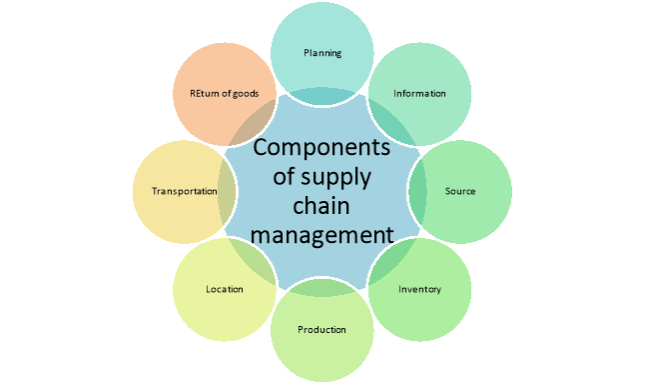
Figure 3: Components of supply chain
Key takeaways-
- Physical distribution is that the group of activities associated with the availability of finished product from the production line to the consumers.
- A marketing channel consists of the people, organizations, and activities necessary to transfer the ownership of goods from the point of production to the point of consumption. It is the way products get to the end-user, the consumer; and is also known as a distribution channel.
Concept
Promotion is one of the elements of marketing mix which indicates any sort of marketing communication want to inform or persuade target audiences of the relative merits of a product, service, brand or issue. It helps marketers to make a particular place in customers' mind. The aim of promotion is to extend awareness, create interest, generate sales or create brand loyalty. It's one among the essential elements of the market mix, which incorporates the four Ps, i.e., product, price, place, and promotion. Promotion covers the methods of communication that a marketer uses to supply information about its product. Information is often both verbal and visual. Different classification of promotion are personal selling, advertising, sales promotion, direct marketing publicity and should also include event marketing, exhibitions, and trade shows.
Importance of promotion
Promotion is crucial to make people aware about the product and convenience to purchase the product or service.
1) Increasing brand awareness
Promotions help in creating brand awareness. With the help of varied media just like the television, billboards, radio or local newspaper news, you'll spread across information about your brand and company, which helps people to seek out more about you and look into your products and make purchases.
2) Segment Identification
If your promotional and marketing strategy is loosely structured, it'd not achieve success in targeting the “right” audiences. Having a full-proof and well-thought-out promotional strategy and marketing plan can assist you identify different segments of consumers within the market and offer suitable solutions for your clients.
3) Increasing customer traffic
Promotion also helps in increasing customer traffic. The more you promote your brand, the more will the purchasers realize you and your company and thus the more will they need an interest in your products. Promotion are often done even by giving out free samples which work wonders for purchasers they fight your product and ultimately, come to you and make purchases.
4) Benefits for customers
Customers are able to recognise a product in the market and fell confident to purchase them. Frequent advertisements about a product occupy a place in the mind of the customers. They also able to know about the use, price, benefit etc. about the product.
5. Increases customer base
It helps the company to go for mass campaign and make aware about their product/service to target groups located in different geographical areas.
Elements of Promotion mix
Elements of promotional mix are also called as tools, means, or components. Basically, there are five elements involved in promotional mix. Elements of market promotion mix are
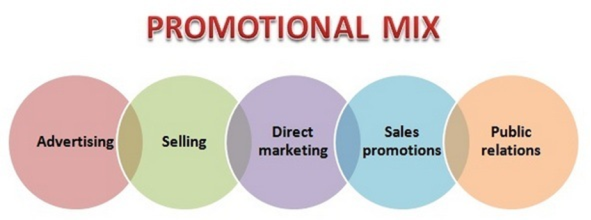
Figure 4: Promotional mix
1. Advertising:
Advertising is defined as any paid sort of non-personal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, and services by an identified sponsor. It is the preferred and widely practiced tool of market promotion. Major a part of promotional budget is consumed for advertising alone. Various advertising media – television, radio, newspapers, magazines, and outdoor means then forth – are used for advertising the product. Characteristics of advertising are as follow:
i. Adverting is non-personal or mass communication. Personal contact isn't possible.
Ii. It is a paid kind of communication.
Iii. It is a one-way communication.
Iv. Identifiable entity/sponsor-company or person gives advertising.
v. It's costly choice to promote the sales.
Vi. It's often reproduced frequently as per need.
Vii. Per contact cost is that the lowest.
Viii. Various audio-visual, print, and outdoor media are often used for advertising purpose.
Ix. It is a widely used and highly popular tool of market promotion.
2. Sales promotion:
Sales promotion covers those marketing activities apart from advertising, publicity, and personal selling that stimulate consumer purchasing and dealer effectiveness. Sales promotion mainly involves short-term and non-routine incentives, offered to dealers also consumers the favoured methods used for sales promotion are demonstration, fair, exhibition, exchange offer, seasonal discount, free service, gifts, contests, etc.
Characteristics of sales promotion are as follows:
i. The primary purpose of sales promotion is to induce customers for immediate buying or dealer effectiveness or both.
Ii. Excessive use of sale promotion may affect sales and reputation of an organization adversely.
Iii. It's taken as supplementary to advertising and personal selling efforts.
Iv. It involves all the promotional efforts aside from advertising, personal selling, and publicity.
v. It consists of short-term incentives, schemes, or plans offered to buyers, salesmen, and/ or dealers.
Vi. It involves non-routine selling efforts.
3. Personal Selling:
Personal selling includes face-to-face personal communication and presentation with prospects (potential and actual customers) for the aim of selling the products. It involves personal conversation and presentation of products with customers. It’s considered as a highly effective and dear tool of market promotion.
Characteristics of personal are listed below:
i. Personal selling is an oral, face-to-face, and personal presentation with consumers.
Ii. Basic purpose is to market products or increase sales.
Iii. It involves two-way communication.
Iv. Immediate feedback is usually measured.
v. It's a capability of salesmen to influence or influence buyers.
Vi. It's more flexible way of market communication.
Vii. Per contact cost is above advertising.
Viii. It involves teaching, educating, and assisting people to shop for.
4. Publicity:
Publicity is additionally how of mass communication. It is a non-paid sort of mass communication that involves getting favourable response of buyers by placing commercially significant news in mass media. Publicity isn't purchased by the organization. Publicity comes from reporters, columnists, and journalists. It are often considered as an area of PR. Publicity involves giving public speeches, giving interviews, conducting seminars, charitable donations, inauguration by film actor, cricketer, politician or popular personalities, stage show, etc., that attract mass media to publish the news about them.
Main characteristic of publicity include:
i. Publicity involves obtaining favourable presentation about company or company’s offers upon radio, television, or stage that's not acquired by the sponsor.
Ii. It is a non-paid kind of market promotion. However, several indirect costs are involved in publicity.
Iii. It should include promotion of latest product, pollution control efforts, special achievements of employees, publicizing new policies, etc., for increasing sales. It’s primarily concerns with publishing or highlighting company’s activities and products. It’s targeted to make company’s image.
Iv. Mostly, publicity is usually carried via newspapers, magazines, radio or television.
v. Company has no control over publicity in terms of message, time, frequency, information, and medium.
Vi. It is a high degree of credibility. Publicity message is more likely to be read and reacted by audience.
Vii. Publicity is usually done at how lower cost than advertising. Company must spend a bit amount to urge the event or activity publicized.
Viii. Frequency or repetition of publicity in mass media depends upon its social significance or the values for news. Mostly, it appears just once.
5. Public Relations:
The PR is comprehensive term that has maintaining constructive relations not only with customers, suppliers, and middlemen, but also with an outsized set of interested publics. Note that PR include publicity, i.e., publicity is that the part of PR.
Main characteristic of publicity are as under:
i. PR could also be a paid sort of market promotion. Company possesses to incur expenses.
Ii. PR activities are designed to create and maintain a favourable image for an organization and a favourable relationship with the organization’s various publics.
Iii. It's an integral a region of managerial function. Many companies operate a special department for the aim, referred to as the general public relations department.
Iv. It involves kind of interactions, like contacting, inviting, informing, clarifying, responding, interpreting, dealing, transacting, then forth.
v. PR covers variety of publics – formal and informal groups. These publics could even be customers, stockholders, employees, unions, environmentalists, the govt. People of area people, or another groups in society.
Vi. PR activities are undertaken continuously. It is a part of routine activities.
Vii. All the officials, from top level to supervisory level, perform PR activities.
Viii. In reference to modern management practices, the overall PR is treated because the profession.
Thus, there are five major elements or promotion mix. Each tool/element has its advantages, limitations, and applicability. Depending upon company’s internal and external situations, one or more tools are used. Mostly, company’s promotional programme involves more elements, each element supplements others.
Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
Concept
Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) could also be an idea under which a company carefully integrates and coordinates its many communications channels to deliver a transparent and consistent message. It aims to form sure the consistency of the message and thus the complementary use of media. IMC is an integration of all marketing tools, approaches and resources within a corporation which maximizes impact on the buyer mind leading to maximum profit at minimum cost. For example,
- OYO helps in hotel booking,
- Zomato helps in ordering of food,
- Amazon helps in online shopping, recharge, ticket booking,
- Facebook, LinkedIn helps work as social networking platform. Etc.
Integrated Marketing Communication tools
Integrated marketing communication refers to integrating all the methods of brand name promotion to market a specific product or service among target customers. In integrated marketing communication, all aspects of selling communication work together for increased sales and maximum cost effectiveness. The integrated marketing tools are-
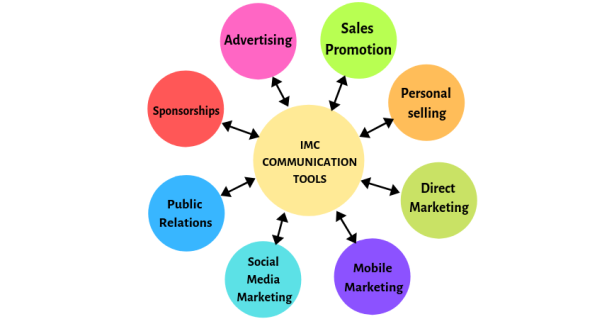
Figure 4: IMC tools
- Advertising
Advertising is defined as any paid sort of non-personal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods, and services by an identified sponsor. It is the preferred and widely practiced tool of market promotion. Major a part of promotional budget is consumed for advertising alone. Various advertising media – television, radio, newspapers, magazines, and outdoor means then forth – are used for advertising the product.
2. Sales Promotion
Sales promotion covers those marketing activities apart from advertising, publicity, and personal selling that stimulate consumer purchasing and dealer effectiveness. Sales promotion mainly involves short-term and non-routine incentives, offered to dealers also consumers the favoured methods used for sales promotion are demonstration, fair, exhibition, exchange offer, seasonal discount, free service, gifts, contests, etc.
3. Public Relation
Public relations (PR) involves communication designed to help improve and promote an organization’s image and products. PR is often perceived as more neutral and objective than other forms of promotion because much of the information is tailored to sound as if it has been created by an organization independent of the seller. Public relations materials include press releases, publicity, and news conferences. While other techniques such as product placement and sponsorships, especially of events and experiences, tend to generate a lot of PR, the growth of expenditures and importance of sponsorships are so critical for so many companies that it is often considered a separate component in the communication mix.
4. Direct marketing
Direct marketing involves the delivery of personalized and often interactive promotional materials to individual consumers via channels such as mail, catalogues, Internet, e-mail, telephone, and direct-response advertising. By targeting consumers individually, organizations hope to get consumers to take action.
5. Personal Selling
Personal selling includes face-to-face personal communication and presentation with prospects (potential and actual customers) for the aim of selling the products. It involves personal conversation and presentation of products with customers. It’s considered as a highly effective and dear tool of market promotion.
5. Social media
Changes in communication technology and instant access to information through tools such as the Internet and social media (online communication among interdependent and interconnected networks of organizations, people, and communities) explain one of the reasons why integrated marketing communications have become so important. Many consumers and business professionals seek information and connect with other people and businesses from their computers and phones. The work and social environments are changing, with more people having virtual offices and texting on their cell phones or communicating through social media sites such as Facebook, LinkedIn, Pinterest, and Twitter.
7. Sponsorship
Sponsorships typically refer to financial support for events, venues, or experiences and provide the opportunity to target specific groups. Sponsorships enhance a company’s image and usually generate public relations. With an increasing amount of money being spent on sponsorships, they have become an important component of the promotion mix.
8. Mobile marketing
Many college students are part of the millennial generation, and it is consumers from this generation (people like you perhaps) who are driving the change toward new communication technologies. You might opt to get promotions via mobile marketing—say, from stores on your cell phone as you walk by them or via a mobile gaming device that allows you to connect to the Web.
Scope
In integrated marketing communication, all aspects of marketing communication work together for increased sales and maximum cost effectiveness. The scope of activities of integrated marketing communication are-
- The Foundation
As the name suggests, foundation stage involves detailed analysis of both the product as well as target market. It is essential for marketers to understand the brand, its offerings and end-users. You need to know the needs, attitudes and expectations of the target customers. Keep a close watch on competitor’s activities.
2. The Corporate Culture
The features of products and services ought to be in line with the work culture of the organization. Every organization has a vision and it’s important for the marketers to keep in mind the same before designing products and services. Let us understand it with the help of an example.
3. Brand Focus
Brand Focus represents the corporate identity of the brand.
4. Consumer Experience
Marketers need to focus on consumer experience which refers to what the customers feel about the product. A consumer is likely to pick up a product which has good packaging and looks attractive. Products need to meet and exceed customer expectations.
5. Communication Tools
Communication tools include various modes of promoting a particular brand such as advertising, direct selling, promoting through social media such as facebook, twitter, instagram and so on.
6. Promotional Tools
Brands are promoted through various promotional tools such as trade promotions, personal selling and so on. Organizations need to strengthen their relationship with customers and external clients.
7. Integration Tools
Organizations need to keep a regular track on customer feedbacks and reviews. You need to have specific software like customer relationship management (CRM) which helps in measuring the effectiveness of various integrated marketing communications tools.
Importance of integrated market communication
Integrated marketing communication plays an integral role in communicating brand message to a bigger audience. Some the significance of integrated marketing communication are discussed below-
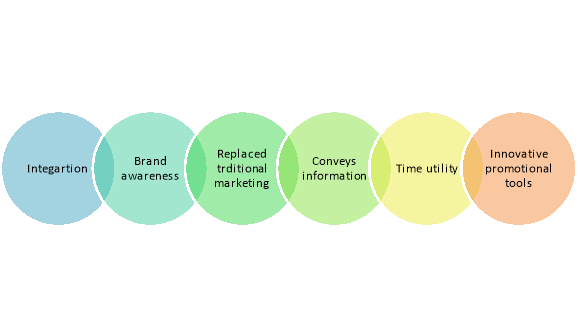
Figure 5: Importance of integrated marketing communication
- Integration:
Integrated Marketing communication helps in integrating all essential components of promoting to communicate similar message to potential and existing end-users.
2. Brand awareness:
Integrated marketing communication goes an extended way in creating brand awareness among customers at a minimal cost. Integrated marketing communication is vital not just for business to business marketing but also for direct interaction with customers. Organizations implementing integrated marketing communication not only successfully promote their brands among audience but also develop trust among them who would always stick with their brands, no matter what. Through integrated marketing communication, similar message goes to customers simultaneously, eventually creating a much better impact on them. Believe me; the end-user doesn't even consider buying Brand B, if features and benefits of brand name A are communicated well to the end-users. Integrated marketing communication is easier because it carefully blends various marketing tools like advertising, PR, direct marketing then on.
3. Replaced traditional marketing:
Integrated marketing communication scores over traditional ways of selling because it focuses on not only winning new customers but also maintaining future healthy relationship with them. Integrated marketing communication ensures two way dialogues with customers - a requirement altogether business. Customer feedbacks need to be monitored well if you'd prefer to survive within the end of the day. Remember, their feedbacks are valuable and want to be evaluated carefully.
4. Conveys information:
Integrated marketing communication plays a crucial role in delivering a unified message to end-users through various channels and thus has better chances of attracting customers one message goes to customers across all marketing channels be it TV, Radio, Banners, hoardings then on. Integrated marketing communication ensures the brand (product or service) may be a moment hit among end-users. It also develops how of attachment and loyalty among end-users.
5. Provides time utility:
Integrated marketing communication saves time which is typically lost choose the only marketing tool. Through integrated marketing communication, marketers can smartly blend and integrate all marketing tools for better response during a layman’s language integrated marketing communication provides a decent range of options which help marketers connect easily with their target customers. Integrated marketing communication ensures that the customer gets the right message at the right place and right time.
6. Innovative promotional tools:
Integrated marketing communication uses several innovative ways to promote brands among customers like newspaper inserts, hoardings and banners at the most strategic locations, pamphlets, brochures, radio or television advertisements, press releases, discount coupons, loyalty clubs, membership clubs, public relation activities, sales promotional activities, direct marketing initiatives, social networking sites.
Key takeaways-
- Promotion is one of the elements of marketing mix which indicates any sort of marketing communication want to inform or persuade target audiences of the relative merits of a product, service, brand or issue.
- Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) could also be an idea under which a company carefully integrates and coordinates its many communications channels to deliver a transparent and consistent message.
Concept
Sales management is the process of developing a sales force, coordinating sales operations, and implementing sales techniques that allow a business to consistently hit, and even surpass, its sales targets. Sales management is also defined because the planning, direction, and control of private selling including recruiting, selecting, equipping, assigning, routing, supervising, paying, and motivating as these tasks apply to non-public sales department. Sales management originally referred exclusively to the direction of the sales force. Later the term took on broader significance additionally to the management of private selling. Sales management specifically contributes to understand the marketing objectives of a firm. In fact, sales managers set their personal selling objectives and formulate the private selling policies and methods. For example,
3. Training and development of employees,
4. Free foreign trip on fulfilment of target,
5. Advertisement through social media.
6. Bonus on festive season etc.

Figure 6: Concept of sales management

Components
The components of sales management are discussed below-
- Leadership
• The organization takes on the personality of the leader, sets the culture of the business.
• Establish culture – disciplined, ethics, values, etc.
• Establish the strategic direction – set the course and commitment to attain.
• Establish expectations, parameters and standards of performance & excellence.
2. Sales management
• Oversee the right activity and related appropriate actions needed to enhance day-to-day results.
• Maintain high level of involvement.
• Insure the right people are within the right place.
• Be adaptive to alter.
3. Sales development
• Institute and practice sound territory and account management.
• Profile and understand who the optimum client is and replicate the link and success.
• Retain and grow existing clients.
• Acquire new accounts
• Fire unprofitable accounts.
• Develop skills of individual salespeople.
4. Performance management
• Establish and monitor sound performance metrics.
• Improve productivity and performance.
• Conduct consistent developmental activity with reps.
5. Channel management
• Align & assign the proper accounts with correct right people doing the proper job.
• Understand all potential revenue streams and have interaction each for optimum results.
6. Information management
• Track, report and monitor performance using technology and every one available data sources.
• Streamline for operational efficiency.
7. Time management
• Evaluate urgent vs. Important activities.
• Plan and prepare for effectiveness and efficiencies.
• Evaluate urgent vs. Important activities.
• Plan and steel oneself against effectiveness and efficiencies.
• Set and communicate expectations.
8. Resource management
• Insure support staff is aligned with objectives.
• Engage appropriate technical resources.
• Create materials in line with objectives.
• Identify and acquire needed additional resources.
• Establish and monitor realistic budget.
Emerging trends in selling
The marketing concept evolves over a period of time depending on the change of customer priority, increase competition, globalisation, variety of choice etc. The producers/service providers adopt changes in tools and techniques to increase the sale. Some of the emerging trends in selling are-
- Investing in Future Growth
Thinking three moves ahead is significant in any game, and is vital to sales growth. But this skill doesn't come automatically the simplest sales leaders make analysis a proper a part of the sales-planning process, and make forward planning an area of someone’s description this suggests they're perfectly poised to capture the opportunities created by sudden changes within the environment. Knowledge is simply one a part of the equation, though. Top-performing sales organizations have the will and thus the means to translate macro shifts into real top-line impact fast. The first-mover advantage created by forward-looking sales plans drives sales in areas where competitors have yet to arrive. Many sales executives explicitly account for investment in new growth opportunities in their annual capacity-planning processes quite half the fast-growing companies we interviewed inspect least one year out, and 10% look quite three years out. Thinking ahead isn't almost resource planning: 45% of fast-growing companies invest quite 6% of their sales budget on activities supporting goals that are a minimum of a year out.
2. Finding the expansion in Micro markets
Averages lie within the follow sales growth, averages can mask where growth truly lies, and thus the hidden pockets of growth in your industry could even be in your own backyard. The most successful sales leaders I speak to are extremely proactive at mining the expansion that lies beneath their feet in what can appear — on the average — to be mature markets. They take a geological hammer to all or any or any their market and customer data; they break larger markets down into much smaller units, where the opportunities — prospects, new customer segments, or micro segments — are often assessed intimately. This disaggregation makes it apparent very quickly that a broad-brush approach leads to resources being wasted where growth is significantly below average. Micro market strategies are heavy on the analytics, so it’s important that sales teams on the bottom don’t get trapped by the small print, and should use the information within the simplest way.
3. Capturing Value from Big Data and Advanced Analytics
Sales forces have a fantastic amount of data at their fingertips today compared with even four or five years ago, but getting insights from it and making those actionable is way harder. Sales leaders that catch on right make better decisions, uncover insights into sales and deal opportunities, and refine sales growth strategies. The big shift we see today is from the analysis of historical data to using data to be more predictive. Sales forces use sophisticated analytics to make a decision not only what the simplest opportunities are, but also which of them will help minimize risk. In fact, in these areas, three-quarters of fast-growing companies believe themselves to be above average, while 53%–61% of slow-growing companies hold an equivalent view. But even among fast-growing companies, barely over half those— 53% — claim to be moderately or extremely effective in using analytics to form decisions. For slow-growing companies, it drops to a touch over a third this suggests that there remains significant untapped potential in sales analytics To start with, you'd prefer to possess tons of very smart data scientists to help you mine the data, then you'd like people with the business expertise to translate that into something that salespeople can influence. Then, subsequent time a rep goes to determine a customer, he or she knows exactly who to ascertain, when to ascertain them, what to mention, and precisely what to supply.
4. Outsourcing the Sales Function
One of the sales trends that we began to ascertain while doing the research for sales growth is that the outsourcing of parts of (and sometimes lots of) the sales value chain. What’s new today is that the automation we mentioned has enabled third-party vendors to run a company’s entire end-to-end sales process. I’m talking all the way from demand generation to customer acquisition and fulfillment. These companies understand your target segments, they use big data to identify leads, they market to different segments with different offers and using different platforms, then they match their own sales reps to individual customers based on the likelihood of converting that specific sort of person. For the sales organization, it means moving to a model where your pay is predicated not on the service, but on the new customers being acquired.
5. Understanding Social Selling
An effective sales organization must explore every avenue in its quest to actually understand the customer. It’s important for sellers to understand who the individual customer is, who the buyers are, who the decision-makers are, who the influencers are, and who owns the budget — and what their perception of their organization is a lot of which can be learned through what they share online on different platforms and in several ways: expressing opinions, asking for help, and general discussions.
6. Collaborating More Closely with Marketing
Marketing and sales could seem inextricably linked, but often when I’m working with commercial functions at large organizations; I find their relationship is usually contentious and lopsided: Sales dominates in B2B sectors, while marketing dominates in B2C. Our own research for Sales Growth revealed a striking trend in sales and marketing: 61% of companies that have both functions deliver above-market revenue growth and enjoy high profitability. It’s important to align sales with marketing in order that both understand precisely whom they're targeting and thus the journey those buyers are making. This might sound obvious, but the 2 functions often add a vacuum, each with different views of which customers to pursue. Both functions also generate enormous volumes of valuable data on customer segments and preferences, but the flow of those insights tends to be one-way: from marketing to sales. At the outperforming companies I see, the front line reports back to assist marketing refine its offerings, and datasets are integrated to form more accurate pictures of selling opportunities. At the foremost basic level, chief marketing officers and heads of sales got to engage with one another on an equal footing. In my experience, failure to collaborate is outmoded at the best and dangerous to a company’s performance at the worst.
7. Adopting automation
Even with CRM systems in place, we see companies where 75% of leads aren’t followed informed. Those are leads that have already had time and money spent on them, but is then left to wither away. When variety of the organizations we work with began to use AI (AI) for his or her lead generation qualification, the results are a 100% touch rate, and thus the AI can keep these leads warm for months, sometimes even making the primary introduction this is often just one aspect of sales that AI can help with, which we see no reason why automation and AI can’t be utilized in additional complex elements of the sales process.
8. Value-based Selling
Although it sounds counterintuitive, the best tip for boosting your sales in 2021 is to stop trying to sell! Gone are the days when you could shove an offer into a prospect’s face and expect them to accept it just because it’s ‘an offer they can’t refuse’. In 2021, customers are sick and tired of being treated like cash cows, especially in the B2B world. The only way to attract your customers’ attention and push them towards making a purchasing decision is to convince them you prioritise their satisfaction over your profit. The most sincere way to prove that is to lower the price of your product, but let’s be real here… Every for-profit business’s goal is to generate as much revenue as possible. Giving out discounts like there’s no tomorrow is likely to make you go bankrupt before anything else. Instead of changing the price, you should change your leads’ perception of your offers. One way to do that is to implement a value-based selling strategy.
9. Social Selling is essential
The rise in popularity of social selling further proves that the concept of ‘obvious selling’ is dying out. The idea of social selling has been in heavy rotation for a couple of years now. However, if in the previous couple of years it was merely advisable to wrap your head around the concept, in 2021 social selling is a must-practice for your business to stay afloat. Instead of trying to sell your product right here and now, you should plant an idea into your prospects’ heads and keep developing it. Move into their heads by always being there for them, answering their questions, and showcasing your expertise online. When they’re looking for a product to buy, you should be the first business to come to their mind.
10. Customer success over customer support
Another way to provide value to your customers and convince them to make a purchasing decision is by ensuring them that you’re genuinely interested in their business success. Instead of just focusing on ensuring outstanding customer support, you should prioritise providing a more positive, holistic customer experience. Shifting your focus towards customer success lays the foundation for it. This trend emerged in early 2020, and was predicted to reach its full potential by the end of the year. However, the importance of implementing a strong customer success strategy has been multiplied by the change of customer priorities caused by the pandemic.
11. The emergence of multi-channel, personalised experiences
One of the biggest recent changes that brought is the speeding up of the transition of buying and selling into the world of digital. Because of such vast accessibility of information, a large percentage of the buyer’s journey is independent. Businesses can’t predict when exactly a buyer will enter the funnel as it can happen at any stage. On top of that, buyers are no longer tied to a single channel.
12. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is taking over
The importance of AI is increasing day by day to improve the sales management. Some of the sales tasks that can be improved through the use of AI include.
- Clients’ buying trends data collection and interpretation;
- Dissemination of suggestions to customers based on their recent purchases;
- Buying and selling trends forecasting and planning.
Personal Selling- Concept
Personal selling could also be a face-to-face selling technique by which a salesman uses his or her interpersonal skills to influence a customer in buying a selected product. The salesperson tries to spotlight various features of the product to convince the customer that it will only add value. However, getting a customer to buy for a product is not the motive behind personal selling whenever often companies plan to follow this approach with customers to make them aware of a replacement product. For example, sales person in retail outlets, BPO, medical representatives etc.
Process of personal selling
The steps involved in the process of personal selling are-
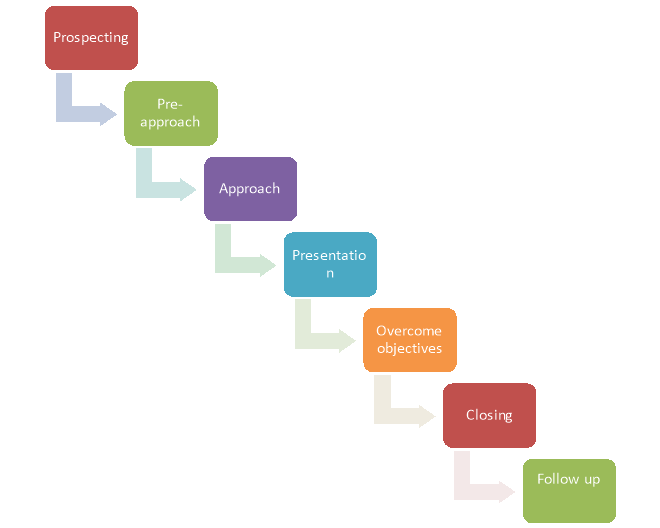
Figure 7: Personal selling process
- Prospecting
The first step within the method involves prospecting. With this step within the process, sales representatives look for new customers that they're going to potentially sell their products to the present are going to be done by cold calling or by going out into the market and lecture people. This a part of the tactic could also be a numbers game, and thus the sales representative has got to contact many people.
2. Pre-Approach
The pre-approach is that the second step within the personal selling process. At this point, the sales representative prepares for the first contact with the potential customer. During this stage, the sales representative looks at any information that he may have about the customer. He may practice his sales presentation and do anything necessary to arrange for it.
3. Approach
The approach is that subsequent step within the method and it is also one of the foremost important. During this step, the sales representative takes a moment or two to undertake to urge to understand the prospect. This phase usually involves some chitchat to warm up the prospect and help them open up.
4. Presentation
During this stage of the method, the sales representative makes a presentation. This may involve demonstrating the product or service and showing the customer why they need it. The sales rep should specialise in the features and benefits of the product or service during this a part of the method.
5. Overcome Objections
In some cases, the sales representative will need to overcome objections by the customer. Many purchasers have questions and concerns at now of the sales process. If the sales representative can answer the questions and overcome any objections successfully, the barriers for a successful sale are going to be removed.
6. Closing
After the objections are removed, the sole thing left to undertake to shut the sale. This may involve writing up an invoice and providing any final information to the customer. At this stage of the method, you will get to negotiate the ultimate sales price and any payment terms.
7. Follow Up
The follow up is that the last stage within the private sales process. After the product or service has been delivered, the sales representative follows up with the customer to seek out if they're pleased. If there are any issues with the product, the sales rep can work with the customer to urge them resolved. If the customer is happy, the sales rep can also plan to obtain additional referrals from the customer.
Skill Sets required for Effective Selling
The personal selling demands some skills of sales person to attract and convenience customers to make purchase decision. The skills required for effective selling are-
1. Product Knowledge
Sales person should have deep understanding of the product they’re selling. Product knowledge enables them to explain the customers confidently and answer all the queries of the customer.
2. Strategic Prospecting Skills
The sales person should possess the capability to identify the prospective buyers by using networks and accordingly contact them to aware about the availability of products/service.
3. Buyer-Seller Agreement
In order to line mutual expectations and to make the prospects easier , sales man should determine the way to make a Buyer-Seller Agreement, , to line the tone for all calls and meetings. These are verbal agreements at the start of the sales process that outline expectations for each side.
4. Active Listening
Most sales person feel comfortable lecture prospects, but listening is another story. They need to become proficient in active listening, or listening with a strict focus and asking intelligent follow-up questions.
5. Communication
On the phone, the tone of voice, volume and pace of a sales person’s speech are surprisingly important sales skills. In sales, how they communicate influences the sale of the firm/company.
6. Qualification Questioning
The salesperson should have minimum qualification to understand and communicate with the local language, understanding capability of product, communication skills etc.
7. Time Management
. The key to being highly productive is using blast management skills the sales person wish to train each of them to sort through leads to find the most promising ones, and not waste an excessive amount of time on a deal that isn’t going anywhere.
8. Objection Prevention
Great sales person practice the art of proactive “Objection Prevention” and not merely “Objection Handling” and should thus reduce variety of the foremost basic objections by way of how they approach a purchase.
9. Objection Handling
Even the simplest sales person can’t prevent every objection, so it’s important to help them prepare for objection handling once they are doing hear one. They need to get on their toes in order that the sales process doesn’t end abruptly which they lose the chance at the deal. They need to learn to sincerely understand the prospect’s problem, invite more information, and offer clarity to help the prospect overcome their objections.
10. Demo skills
For many B2B products, the demo is critical to starting a sales process. Sales person need to not only understand the merchandise, but must be able to boast it’s capabilities to an opportunity effectively through a demo. Demos are challenging therein they need to first discover what benefits are getting to be most vital to solving a prospect’s pain, and highlight the business value of those features during the demo.
11. Gaining Commitment
The key's ensuring the proper people with the proper approval power are bought in to the method because the sale progresses. Sales person must continually ask questions, assess the prospect’s needs and reinforce what the prospect is curious about buying.
12. Closing Techniques
Managers got to train reps to push prospects, invite the order and acquire it signed fast. Plenty of prospects will attempt to push the closing date back a number of weeks or a couple of months, and the sales person could even be trying to achieve a monthly or quarterly goal for the team during this case.
Key takeaways-
- Sales management is the process of developing a sales force, coordinating sales operations, and implementing sales techniques that allow a business to consistently hit, and even surpass, its sales targets. Sales management is also defined because the planning, direction, and control of private selling including recruiting, selecting, equipping, assigning, routing, supervising, paying, and motivating as these tasks apply to non-public sales department.
References-
1. Philip Kotler (1987) Marketing: An Introduction. Prentice-Hall; International Editions.
2. Ramaswamy, V.S., 2002, Marketing Management, Macmilan India, New Delhi.
3. Kotler P, Armstrong G,2008, Principles of Marketing, 9th Edition, Prentice Hall, New Delhi.
4. Https://g8m6s4b5.rocketcdn.