Unit 3
Social and Cultural Environment
The cultural environment consists of the influence of religious, family, educational, and social systems within the marketing system. Marketers who intend to market their products overseas could also be very sensitive to foreign cultures. While the differences between our cultural background within the India and people of foreign nations could seem small, marketers who ignore these differences risk failure in implementing marketing programs. Failure to consider cultural differences is one among the first reasons for marketing failures overseas.
A number of cultural differences can cause marketers problems in attempting to promote their products overseas. These include:
(a) Language,
(b) Colour,
(c) Customs and taboos,
(d) Values,
(e) Aesthetics,
(f) Time,
(g) Business norms,
(h) Religion, and
(i) Social structures.
Impact of Foreign Culture on Business Culture is formed based on beliefs, attitudes, assumptions, values and a number of other social factors. Every culture is different, and has different types of etiquette. Every day deals are lost through misunderstandings, even between relatively similar cultures. Culture varies from nation to nation. it's necessary to review the cultural variables
Impacts
• Changing attitude of employees towards work and goal
• Workforce diversity
• Changing attitude of managers
• Change in consumption pattern
• Change in saving habits
• Changing attitude of managers
• More labour mobility
Culture impacts many things in business, including
• The pace of business;
• Business protocol—how to physically and verbally meet and interact;
• Decision making and negotiating;
• Managing employees and projects;
• Propensity for risk taking; and
• Marketing, sales, and distribution.
Impact of culture and traditional values on business
• Culture creates people it determines ethos of individuals
• Culture determines goods and services for people
• Language makes important contribution in making business a hit
• Attitude – that determines people’s objectives
• Role of family in protection, inheritance, support, affection, and transmission of cultural values
• Culture makes person ambitious.
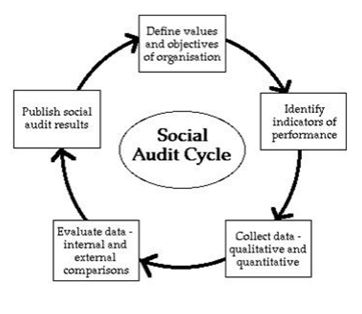
‘Social Audit’ is “a public assembly where all the details of a project are scrutinized”. it's “a way of measuring, understanding, reporting and ultimately improving an organization’s/programme’s social and ethical performance”.
Social Audit (SA):
*Social Audit is a process within which details of the resources, both financial and non-financial, is used by public agencies for development initiatives and is shared with the people often through public platforms.
*It includes in-depth scrutiny and analysis of the working of an entity within which the general public is involved is-à-vis. its social relevance.
Origin of social audit in India:
*In India, the initiative of conducting social audits was taken by Tata Iron and steel company Limited (TISCO), Jamshedpur within the year 1979.
*Social audit gained significance after the 73rd amendment. The approach paper to the 9th FYP (2002-07) emphasized upon social audit for effective functioning of Panchayat Raj institutions (PRIs) and empowered gram sabhas to conduct SAs additionally to its other functions.
*National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005 provides for normal “Social Audits” so as to ensure transparency and accountability within the scheme.
*The state government shall identify or establish, under the NREGS, an independent organization, Social Audit Unit (SAU), at the state level, to facilitate conduct of social audit by Gram Sabhas.
|
Features of social audit
- Voluntary process
- Evaluates social performance
- Helps to meet corporate social responsibility
- Subjective process it varies from one company to other
- It is an analytical study of business
BENEFIT OF SOCIAL AUDIT:
The main reason for the push for social audit is that the huge disconnect between what people want and what people get. As soon as social audit kicks in, it exercises its control over the policy developers and implementers within the following manner:
- Reduces corruption: SA uncovers irregularities and malpractices within the public sector and maintains oversight on government functioning, thus reducing leakages and corruption.
- Monitoring and feedback: It monitors social and ethical impact of an organisation’s performance and provides feedback on the work.
- Accountability and transparency: SA ensures accountability and transparency in working of government bodies and reduces trust gap between people and native governments.
- Participative and democratic: SA promotes participation of individuals in implementation of programmes and makes people more forthcoming for social development activities.
- Strengthens the Gram Sabha: SA gives voice and influencing power to the Gram Sabha, the lynchpin of rural governance structure.
- Generates demand: Serves because the basis for framing the management’s policies by rising demands during a socially responsible and accountable manner by highlighting the important problems.
- Improves professionalism: SA boosts professionalism in public bodies by forcing Panchayats to maintain proper records and accounts of the spending made against the grants received from the govt. and other sources.
- Collective platform: SA provides a collective platform like a social audit Gram Sabha, for people to precise their common needs, resulting into social cohesion.
Corporate governance is also defined as follows:
Corporate governance refers to the accountability of the Board of Directors to all stakeholders of the corporation i.e. shareholders, employees, suppliers, customers and society in general; towards giving the corporation a good, efficient and transparent administration.
Following are cited some popular definitions of corporate governance:
(1) “Corporate governance means company managers its business in a manner that's accountable and responsible to the shareholders. in a wider interpretation, corporate governance includes company’s accountability to shareholders and other stakeholders like employees, suppliers, customers and native community.” – Catherwood.
(2) “Corporate governance is that the system by which companies are directed and controlled.” – The Cadbury Committee (U.K.)
Certain useful comments on the concept of corporate governance are given below:
(i) Corporate governance is more than company administration. It refers to a good, efficient and transparent functioning of the company management system.
(ii)Corporate governance refers to a code of conduct; the Board of Directors must abide by; while running the company enterprise.
(iii)Corporate governance refers to a group of systems, procedures and practices which make sure that the corporate is managed in the best interest of all corporate stakeholders.
Need for Corporate Governance:
The need for corporate governance is highlighted by the subsequent factors:
(i) Wide Spread of Shareholders:
Today a company features a very large number of shareholders spread everywhere the state and even the world; and a majority of shareholders being unorganised and having an indifferent attitude towards corporate affairs. the thought of shareholders’ democracy remains confined only to the law and therefore the Articles of Association; which needs a practical implementation through a code of conduct of corporate governance.
(ii) Changing Ownership Structure:
The pattern of corporate ownership has changed considerably, in the present-day-times; with institutional investors (foreign also Indian) and mutual funds becoming largest shareholders in large corporate private sector. These investors became the greatest challenge to corporate managements, forcing the latter to abide by some established code of corporate governance to create up its image in society.
(iii) Corporate Scams or Scandals:
Corporate scams (or frauds) within the recent years of the past have shaken public confidence in corporate management. The event of Harshad Mehta scandal, which is probably, one biggest scandal, is within the heart and mind of all, connected with corporate shareholding or otherwise being educated and socially conscious.
The need for corporate governance is, then, imperative for reviving investors’ confidence within the corporate sector towards the economic development of society.
(iv) Greater Expectations of Society of the corporate Sector:
Society of today holds greater expectations of the corporate sector in terms of reasonable price, better quality, pollution control; best utilisation of resources etc. to satisfy social expectations, there's a requirement for a code of corporate governance, for the simplest management of company in economic and social terms.
(v) Hostile Take-Overs:
Hostile take-overs of corporations witnessed in several countries, put a question mark on the efficiency of managements of take-over companies. This factors also points bent the necessity for corporate governance, within the sort of an efficient code of conduct for corporate managements.
(vi) Huge Increase in Top Management Compensation:
It has been observed in both developing and developed economies that there has been a good increase within the monetary payments (compensation) packages of top level corporate executives. There’s no justification for exorbitant payments to top ranking managers, out of corporate funds, which are a property of shareholders and society.
This factor necessitates corporate governance to contain the ill-practices of top managements of companies.
(vii) Globalisation:
Desire of more and more Indian companies to urge listed on international stock exchanges also focuses on a requirement for corporate governance. In fact, corporate governance has become a buzzword within the corporate sector. there's no doubt that international capital market recognises only companies well-managed consistent with standard codes of corporate governance.
Important Objectives of corporate governance:
1. A properly structured board capable of taking independent and objective decisions is in place at the helm of affairs
2. The board is balance as regards the representation of adequate number of non-executive and independent directors who will look out of their interests and well-being of all the stakeholders
3. The board adopts transparent procedures and practices and arrives at decisions on the strength of adequate information
4. The board has an efficient machinery to take care and manage the concerns of stakeholders
5. The board keeps the shareholders informed of relevant developments impacting the corporate
6. The board effectively and frequently monitors the functioning of the management team
7. The board remains in effective control of the affairs of the corporate at all times
The overall endeavour of the board should be to require the organisation forward so on maximize future value and shareholders’ wealth.
Regulatory framework on corporate governance
The Indian statutory framework has, by and large, been in consonance with the international best practices of corporate governance. Broadly, the company governance mechanism for companies in India is enumerated within the following enactments/ regulations/ guidelines/ listing agreement:
1. the companies Act, 2013 inter alia contains provisions concerning board constitution, board meetings, board processes, independent directors, general meetings, audit committees, related party transactions, disclosure requirements in financial statements, etc.
2. Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Guidelines: SEBI may be a regulatory agency having jurisdiction over listed companies and which issues regulations, rules and guidelines to companies to make sure protection of investors.
3. Standard Listing Agreement of Stock Exchanges: For companies whose shares are listed on the stock exchanges.
4. Accounting Standards issued by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI): ICAI is an autonomous body, which issues accounting standards providing guidelines for disclosures of monetary information. Section 129 of the New Companies Act inter alia provides that the financial statements shall provide a true and fair view of the state of affairs of the corporate or companies, suits the accounting standards notified under s 133 of the New Companies Act. it's further as long as items contained in such financial statements shall be in accordance with the accounting standards.
5. Secretarial Standards issued by the Institute of Company Secretaries of India (ICSI): ICSI is an autonomous body, which issues secretarial standards in terms of the provisions of the New Companies Act. So far, the ICSI has issued Secretarial Standard on "Meetings of the Board of Directors" (SS-1) and Secretarial Standards on "General Meetings" (SS-2). These Secretarial Standards have come into force w.e.f. July 1, 2015. Section 118(10) of the New Companies Act provide that each company (other than one-person company) shall observe Secretarial Standards specified intrinsically by the ICSI with reference to general and board meetings.
Profit maximisation was viewed as the sole business objective; putting this view no more holds good. Business Managers have begun to understand that they owe responsibility to society as they owe to business enterprises.
Some of views of experts on the social responsibility and industry are:
i. Social responsibility is an organisation’s obligation to profit society in ways in which transcend the primary business objective of maximising profit.
ii. Social responsibility refers to obligation of an organisation to hunt actions that protect and improve the welfare of society alongside its owners.
iii. Social responsibility is implying, enforced or felt obligation of managers, acting in their official capacities to serve or protect the interest of groups aside from themselves.
iv. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is that the continuing commitment by the business to behave ethically and contribute to economic development, while improving the standard of life of the workforce and their families also as of the area people and society at large.
v. CSR is about capacity building for sustainable livelihoods. It respects cultural differences and finds the business opportunities in building the talents of employees, the community and therefore the Government. CSR is about business giving back to society.
vi. Companies should make all efforts to market CSR throughout the value-creation chain that they're a part of. they ought to take responsibility for the social, economic and ecological consequences of their actions and also engage in dialogues with all those that are involved in these dimensions.
vii. Developing and advocating socially responsible business practices, which benefit not only the company social responsibility (SRO) and its employees, but also the greater community, the economy and therefore the world environment. SRO seek to reshape the way business is done in both for profit and not for profit arena.
SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY OF BUSINESS
Introduction:
As we are member of family, we are also part of society. Society and family do several things for our benefit and also expect certain obligations from us. As a student, as an individual, you have certain responsibilities such as completing your assignment in time, taking care of your parents, eating healthy food and keep yourself fit and keeping promises.
It is true for business also business operates within a society. It uses resources of society. It depends on various factors of society for its function. Land, water and others resources i.e. factors of production required by business units are owned by society. Requirements of capital and financial needs are supported by investors who are members of society. Without employees and customers, business unit cannot function.
So all the activities of business should be performed in such a manner that they will not harm any part of society rather they will protect and contribute to the interest of society. Social responsibility refers to all such duties, obligations of business towards welfare of society. Profit making is not the sole function.
Definition:
The international seminar on the social responsibility of business held on New Delhi in 1965 defined – “Social responsibility of business has responsibility to the customers, workers, shareholders and the community.”
In ancient literature, we found a concept of helping poor and disadvantaged through profits made by the traders and emperors. So it was philanthropic concept. It was developed as the business was growing. We found charitable foundations, education and health care institutions and trust of community. Activities of charity such as developing gardens, parks, motivation of research, sponsoring games and sports at national and international level are examples of social responsibility. Modern concept has wider idea, it includes ethical, legal and economic aspects.
Traditional Help i.e. poor people disadvantaged section of society
Ethical - avoid questionable practices Modern Concept Legal - obeying all laws – consumers/environment law Economic - minimizing cost and maximize sales revenue |
Observe recent trends of business, we find globalization and pressing ecological issues. That is why role of business is redefined. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is the newest management strategy where we try to create a positive impact on society while doing business.
International organization for standardization (ISO) has developed an international standard to provide guidelines for adopting and disseminating social responsibilities ISO 26000 for social responsibility. It was published in 2010. These standards are encouraging voluntary commitment for social responsibility and also its methods of evaluation. The standards describe itself as a guide of dialogue for business.
Recent Trends (CSR):
- Improved relations with investors and community
- Better access to capital
- Stronger financial performance
- Profitability through operational efficiency
- Enhance employment relation
- Innovation and Productivity
Needs for social Responsibilities: -
(1) Expectation of society: Business should change as per the market conditions, if it wants to survive and grow. The expectation of the public (society) too has changed. They now expect business to fulfil responsibilities their social obligations. Business now must adopt the motto of ‘profit through service’.
(2) Creating Favourable Public Image: Society now expects business to contribute towards social welfare. Hence if a company fulfils its social obligations, people regard such businesses favourably. It thus builds the company’s public image.
(3) Long term Self Interest: By fulfilling its social obligations, the business is indirectly serving its own long term self-interest. By providing quality goods at fair prices, paying fair wages etc. The company is ensuring not only its immediate survival but also is ensuring its future its growth as it gets the support of its shareholders, consumers etc.
(4) Minimizing Government Control: Government interferes through various regulations and control over such businesses which do not function as per the laws. Hence to avoid too much government control, businesses should not only follow all rules and laws but also fulfil their social duties.
(5) Pressure of Trade Unions: Trade Unions protect and promote the interest of the workers. These days they have a major role in maintaining industrial peace and stability. Hence businesses should conduct activities in such a manner that is fair to the employees.
(6) Pressure of Consumer Movement: Consumers to become more aware of their rights and now expect the businessman to be just and fair with them. It is due to the consumer movement that businessmen consider consumer satisfaction as one of their main goals next to profit making.
(7) Maximum utilization of Resources: Resources are scarce. It is said that only business has the ability to ensure that these scarce resources are used in a manner that will ensure maximum satisfaction of wants. Business should use resources in such a manner that will benefit the entire society.
(8) Protection of Environment: Business use natural resources for undertaking their commercial activities. In doing so, they may misuse these resources. Either they may waste the resources or may wrong use the resources, which directly or indirectly affects the environment. They are the ones who cause all kinds of pollution in the environment. Hence these days, business is supposed to take necessary steps to protect the environment.
(9) Principle of Trusteeship: Mahatma Gandhi said that businessmen should consider themselves as trustee of the society. The profits that they earn are not entirely their own. A part of it belongs to the society. Hence by fulfilling their social obligations they are giving back something to the society.
(10) Help to government: Government alone cannot tackle all the social, economic and political problems existing in a country. This is because it does not have enough resources or skills to handle all the problems. Hence the business community is supposed to help the government in solving the various problems faced by the society. It may either undertake social projects of its own or sponsor some government projects.
SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITIES TOWARDS DIFFERENT SOCIAL GROUPS:
A) Social Responsibilities towards Employees: Without the help and cooperation of the employees, no business can survive. Hence to keep their employees happy, business should fulfil the following duties towards employees.
(1) Job security: The Company should provide job security to its employees. The workers should not be kept temporarily for a long time. They must be given permanent jobs.
(2) Monetary factors: Workers should be paid proper wages and other incentives like bonus, medical allowance, etc. Prompt payment often results in higher motivation to the workforce. There should be increment and revision in wages.
(3) Working conditions: The workers should be provided with good working conditions. There should be adequate lighting and ventilations. Noise, dirt and dust pollution should be avoided. There should be proper working hours with rest pauses.
(4) Health and safety measures: The Company should take proper measures to protect health of the employees. They should be provided with canteen facilities, and medical facilities. Proper maintenance of machines and building must be done to prevent accidents.
(5) Proper personnel policies: There must be proper personnel policies in respect of transfers, promotions, recruitment, training, etc. There should be no partiality in promotions and transfers of employees.
(6) Workers participation in management: The workers must have been courage to take part in management. There are different ways of worker’s participation in management, such as quality circles, Works committee, suggestion schemes, profit sharing and so on.
(7) Grievance Procedure: There should be a proper grievance procedure to handle employee’s complaints. Any complaint of the employee must be immediately sorted by suitable grievance procedure.
(8) Recognition of worker’s union: To maintain industrial peace is the responsibility of management. Therefore, the management should recognition the rightful trade union, representing majority of the workers.
B) Social Responsibilities towards Shareholders (Owners): The main motive of a business is to earn profit and this profit is utilized for growth and prosperity of the owners. If the business fails to satisfy its responsibility towards owners, it may not too able to perform its responsibility towards any other social group. Following are the responsibilities of business towards it owners.
1.] Opportunities: In business usually an organization which innovates and starts something new has a big advantage over than organizations. It is important that they keep looking for opportunities and exploit it as soon as it is available. This leads to success of the business.
2.] Wastage of reduced: Organization need to work efficiently any kinds of wastage. No financial loss should be allowed. If an organization Is not working in an efficient manner, it may require more funds than necessary.
3.] Need to keep updated: Business should keep its owner’s updates about its financial position and performance. Owners should be always knowing how well is a company performing. This information can be given by way of annual reports, newspapers, internet etc.
4.] Efficiency and Effectiveness: Business should be efficient as well as effective. This will help in increasing sales as well as profits if company. Efficiency is to do the things in right manner so that cost can reduce. Effectiveness means to do right things and thereby increase sales.
5.] Return: Business should generate sufficient returns. Reasonable returns shall keep the owners / shareholders interested in the business. Further, shareholder’s funds must be utilized in the best possible manner.
6.] Standard practice on stock exchange: The price of the share of the company in the stock exchange is an indicating of the performance of the company for a shareholder. Therefore, business should follow standard and fair practice related to stock exchange. It should declare all material information and not provide any wrong information to stock exchange.
7.] Goodwill: A company cans great goodwill by manufacturing world class products, following standards practices, giving sufficient returns, performing its social responsibility etc. It helps to create a respectable stand in market. Owners feel proud to be associated with such companies.
8.] Growth: Business should undertake various plans which result in expansion of company. They should keep innovating which will help them to stay ahead of their competitors. Business must also concentrate on research and development. As results, it will lead to the growth of the business and higher returns to shareholders.
9.] Safety of Capital: Business should use the capital carefully. The management should take calculated risks. It should analyse the risk factor in every decision. Shareholders prefer safety of their funds over a high return.
C] The responsibilities of business towards its investors
Investors are basically those who provide fiancé to the company. They are ones who provide capital for the functioning of business. Following are the duties of business towards investors:
1.] Image: A company can crate goodwill by manufacturing world class products, following standard practice, giving sufficient returns, performing its social responsibility etc. It helps to create a respectable stand in market. Investors feel proud to be associated with such companies.
2.] Need to maintain transparency: Investors are the true owners of a business. They invest their money with a possibility of losing the amount of invested. Since, an organization runs on the funds received from other people, it should maintain transparency in their operations. The organization should not hide any information from the investors.
3.] Effective procedure to handle grievances: At time, investors have queries or complaints there should be proper procedure to handle such complaints. Investors grievance should be resolved at the earliest. Investors are satisfied if an organization listens to their problems and provides a quick solution.
4.] Safety of Capital: Safety of capital and return on investment are the two most important objectives of investors. Safety of capital also includes no reduction in value of amount invested. Business should be ensuring that the funds of investor are invested properly and efficiently.
5.] Trust: Business should develop trust among its investors. This can be done by disclosing information completely, timely and correctly. The information can be disclosed by way of statement, reports, circulars etc.
6.] Organize periodic meetings: Meetings with the investors should be conducted at periodic intervals. Investors should be sent notice as well as agenda for the meeting in advance. They should be informed about the usage of funds the future plans, profits, important decision etc.
7.] Return: Investors invest in a business with an objective of earning satisfactory returns. Business should generate sufficient returns in form of interest/ dividends. Reasonable returns, appreciation of the amount invested and safety of the amount invested shall keep the investors interested in the business.
D) Social Responsibilities of business towards Customers: No business can survive if can’t satisfy its customers. Besides good quality products, customers have various other expectations from business. Following are the Social Responsibilities towards customers.
(1) Quality: The Company should produce quality goods. The company should always be giving importance to improve its quality. At no time quality can be 100%, and as such there is always a room for improvement.
(2) Fair price: The consumers will not like if they are being cheated. After all, the company will not be able to fool the consumers all the time.
(3) Consumer welfare: The firm should assist government and consumer associations in promoting consumer welfare.
(4) Market Research: The firm should conduct proper market research so that it produces the right kind of goods required by the consumers.
(5) Honest Advertising: The consumers expect true facts of the product, its uses, merits, side-effects and so on. The company should also alert from vulgar and unethical advertisements.
(6) After-sale-service: The consumers expect efficient and effective after-sale-service, especially in the case of consumer durables.
(7) Availability of goods: The consumers should be made available the goods regularly as and when they need it. The company should not create artificial shortage and hoard the goods in cooperation with unethical dealers.
(8) Redressal of complaints: The complaints of the consumers must be immediately solved by the Company. Valid suggestions of the consumers must be taken into consideration.
(9) Consumer safety: The consumers expect the company to produce goods which are customer-health oriented and environment friendly products. Unsafe products must not be marketed by the company. Consumers should be warned of any such unsafe goods.
E) Social Responsibilities of business towards Society: Business taken all factors of production from the society. Business survives only because of the society in which it operates. Hence Business should satisfy the need of the society to ensure its existence. Following are the Social Responsibilities towards society.
(1) Protection of Environment: The organization should take all possible measures to prevent air and water pollution. Business firms should not misuse or over-exploit natural resources.
(2) Optimum use of resources: The business firms make use of scarce natural resources such as raw material of iron, steel, fuel, and so on. The business firm should not make wrong use of scarce resources in the interest of the society.
(3) Upliftment of Backward regions: The society expects that the companies should start industries in backward areas. This will generate employment facilities and increase in purchasing power of the rural public.
(4) Help to weaker sections of the society: The business Organization should also uplift the weaker sections of the society. Certain jobs may be reserved for economically weaker sections of the society.
(5) Financial Assistance: The society also expects donations and financial assistance to various social causes, such as eradication of poverty, illiteracy, etc. They expect the company to take part in anti- drug campaigns, anti-noise campaigns, and so on.
(6) Prevent congestion in cities: The companies should also work to avoid congestion in cities by spending their industries in different places or locations.
(7) Least participation in anti-social activities: The society expects that the companies should not take part in anti-social activities. They should not support and provide financial assistance to anti-social elements.
(8) Expansion: The society expects expansion and diversification of industries so as to generate employment opportunities and at the same time to enhance standard of living of the society.
(9) Employment Generation: Business firms should make all possible efforts to generate employment. Such efforts will help to solve problems caused to unemployment in the society.
F) Social Responsibilities of business towards Government: Government is the authority, which governs the working of all business enterprises. Having a cordial relationship with government helps a business to function smoothly. Following are the Social Responsibilities towards government.
(1) Assistance in implementing socio-economic policies: The government expect cooperation and Assistance from the business sector to assist it in implementing socio-economic programmes.
(2) Payment Taxes: The government expects the corporate sector to pay taxes and duties regularly. If the corporate sector does not pay taxes and duties on time, then it would be difficult for the government to undertake its plans.
(3) Observance of Government rules and regulations: The government expects strict observance of its rules and regulations on the part of the corporate sector. If the corporate has any valid suggestions to modify the rules and regulations, then it should do so in the interest of the society.
(4) Political stability: The corporate sector should work towards the political stability of the country. A stable government often brings more returns and peace in a democratic society. Therefore, corporate sector should not support those elements who are inducing in political instability.
(5) No seeking of unfair favours: The companies should not seek unfair favours from government officials by bribing or influencing them.
(6) Earning of Foreign Exchange: Companies, especially the large ones should enter in export trade to earn valuable foreign exchange for the country. This foreign exchange is necessary to pay for vital imports.
(7) Advising the Government: Corporate sector should provide timely advice to the government in respect of framing various policies, such export-import policy, licensing policy, industrial policy, and so on.
(8) Contribution to Government Treasury: The corporate sector should contribute funds during the times of emergencies or natural calamities, such as floods, earthquakes, etc.
G) Social Responsibilities of business towards Debenture holder: The debenture holders are the creditors of the company. They provide medium term or long term funds by subscribing to the debentures issued by the company. The company has certain social obligations towards the debenture holders:
1) Proper Disclosure of information: A company must provide proper financial information at the time of issue of debentures. The financial performance of the company must be provided correctly so that the prospective investors can take the right decision whether to invest in the debentures or not.
2) Payment of interest: A company should make regular payment of interest to the debenture holders. As far as possible, delay in payment of interest to be avoided.
3) Handling Grievances: A company should handle the grievances of the debenture holders effectively. Also all queries of the debenture holders must be effectively answered.
4) Redemption of Debentures: A company must redeem the debentures as stated in the debenture certificate. If, due to certain reasons, the company cannot redeem the debentures on the due date, then proper explanation must be given to the debenture holders.
5) Conversion of Debentures: A company may issue convertible debentures. It must convert the debentures into equity shares, and send proper notice to that effect to the debenture holders.
6) Meetings: A company may call meetings of debenture holders affecting their rights and interests. Proper notice of meetings must be sent to debenture holders.
Key Take Away SOCIAL AND CULTURAL ENVIRONMENT The cultural environment consists of the influence of religious, family, educational, and social systems within the marketing system. Marketers who intend to market their products overseas could also be very sensitive to foreign cultures. While the differences between our cultural background within the India and people of foreign nations could seem small, marketers who ignore these differences risk failure in implementing marketing programs. Failure to consider cultural differences is one among the first reasons for marketing failures overseas.
IMPACT OF FOREIGN CULTURE ON BUSINESS
Impact of Foreign Culture on Business Culture is formed based on beliefs, attitudes, assumptions, values and a number of other social factors. Every culture is different, and has different types of etiquette. Every day deals are lost through misunderstandings, even between relatively similar cultures. Culture varies from nation to nation. it's necessary to review the cultural variables
SOCIAL AUDIT *Social Audit is a process within which details of the resources, both financial and non-financial, is used by public agencies for development initiatives and is shared with the people often through public platforms. CORPORATE GOVERNANCE Corporate governance refers to the accountability of the Board of Directors to all stakeholders of the corporation i.e. shareholders, employees, suppliers, customers and society in general; towards giving the corporation a good, efficient and transparent administration.
CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY Profit maximisation was viewed as the sole business objective; putting this view no more holds good. Business Managers have begun to understand that they owe responsibility to society as they owe to business enterprises.
Some of views of experts on the social responsibility and industry are: i. Social responsibility is an organisation’s obligation to profit society in ways in which transcend the primary business objective of maximising profit. ii. Social responsibility refers to obligation of an organisation to hunt actions that protect and improve the welfare of society alongside its owners. iii. Social responsibility is implying, enforced or felt obligation of managers, acting in their official capacities to serve or protect the interest of groups aside from themselves Social Responsibilities towards Employees:
Social Responsibilities towards Shareholders (Owners):
What are the responsibilities of business towards its investors?
Social Responsibilities of business towards Customers:
Social Responsibilities of business towards Society:
Social Responsibilities of business towards Government:
|
Technological environment refers to the state of science and technology within the country and related aspects like rate of technological progress, institutional arrangements for development and application of latest technology, etc.
According to the well-known economist J.K. Galbraith, technology means, “systematic application of scientific or other organised knowledge to practical tasks”.
Technology comprises of both machines (hard technology) and scientific thinking (soft technology) used to solve problems and promote progress. It consists of not only knowledge and methods required to hold on and improve production and distribution of products and services but also entrepreneurial expertise and professional skills. Technology includes inventions and innovations.
The main features of technological environment are as follows:
- Technological environment is a component of macro or indirect action environment.
- Technological environment changes in no time
- Technological environment affects the way in which the resources of the economy are converted into output.
- Technological environment is self-reinforcing. An invention in one place results in a sequence of inventions in other places.
Technology has transformed the modern economy and world deeply. From changing the preferences of consumers to reshaping the assembly and marketing of products, technology manifests itself in small details of daily business operations. It’s increased the productivity of investments and workers, accelerated economic activities, promoted interdependence between the modern industries and allowed the deployment of latest technologies. Here are a number of the impacts of technology on business process operations.
Productivity
By improving business processes, product development and developing worker skills technology is increasing productivity in most business operations. Even though the exact size of improvement is debatable, some technologies like emails make communication faster and easier. Practice management software and online customer services reduce personal attention additionally to increasing the productivity of every investment in the areas without sacrificing the customer experience. Practice management software is employed by various professional industries like legal software, accounting software and medical software.
Acceleration
Whether it’s through fast online data transfers or through airplanes, technology has accelerated business operations. A process that took several weeks some years ago through face-to-face interactions and mail can now take a few seconds with computer keystrokes. Web purchasing, editing of photos with services like Fix the photo, online money transfers and sharing of files through the internet has accelerated the production cycle and has made the production, capitalization and therefore the sale and distribution of products faster. From the production standpoint, acceleration of technologies has forced companies to meet the demands of their customers faster and provided the required tools for the processes.
Global communication
Companies can now communicate with others easily and transfer resources globally and are therefore ready to conduct businesses with clients and suppliers from all parts of the globe. Availability of worldwide economic data and internet video conferencing make the conduction of companies feasible and opening a business on another continent is more like opening one within the neighbouring town. Technology has facilitated integration and interdependence through the improvement of transport, communications, and logistics.
Product development
Technological innovations make consumers demand new products. Therefore, businesses need to keep adjusting their operations to match the market demands. Businesses are integrating new technologies including software packages and computers into their production cycle and daily operations. They will now produce new products like new electronics. Businesses driven by the desires of consumers for brand spanking new technological goods and convenient technological services are ready to compete supported the pace of innovation and new technologies adoption.
Risks
Even though the adoption of the new technology comes with many benefits for businesses, the technology presents numerous risks. If your employees don’t have the skills to use the new systems, technology will decrease productivity and reduce the satisfaction of your employees. The fast migration of corporate and personal operations data to the online databases makes companies prone to cyber-attacks, which may affect the operations adversely or maybe, shut the business down.
The business world has witnessed a rise in new technology adoption and as a result, things have improved rapidly and transformed business operations for better growth. Almost every business process has seen a major transformation. With increased automation, some things have changed and technological advancements have affected the production processes.
Impact of technology on business
- Technology and society
- Technology reaches to people through business
- Faster and better services than human
- Creates new jobs and develops new skills
- Creation of new social system – new food, new dressing style, changed food habits.
2. Technology and economy
- Increased productivity at lower cost
- Job becomes more intellectual
- Problem of employ retention
- Demand for multi professional managers
- Increased capital investments on new ideas, training, educating managers
- Impact on product life
- Allocation of more funds to R&D.
3. Technology and plant level changes
- Influence on organization structure
- Increase in risk
- New set of problems
- Resistance to change
- Growth of E – Business
- Huge impact on marketing
A competitive environment is the dynamic external system in which a business competes and functions. The more sellers of a similar product or service, the more competitive the environment in which you compete. look at nutriment restaurants - there are numerous to choose from; the competition is high. However, if you look at airlines servicing Hawaii, very few actually fly to the islands.
Direct competitors are businesses that are selling the same kind of product or service as you. For instance, McDonalds is a direct competitor with Burger King. Indirect competitors are businesses that still compete even though they sell a different service or product. The products or services offered by indirect competitors tend to be those that can be substituted for each other. Again, considering travel, you've got the choice to travel by plane, train, or car. Therefore, airlines are competing with train lines and buses (assuming the travel doesn't go overseas).
Advantages and disadvantages
Without competition, businesses don't last very long, if at all. There are advantages and drawbacks to having competition. The disadvantages are probably the most pronounced, as nobody likes competition!
- More competition means fewer sales because the other companies take some market share.
- Competitors can become allies with other competitors and become more powerful within the market.
- Competitors can take away potential investors or buyers. An investor isn't likely to invest in two companies that compete; they're going to choose the one to invest in.
- Competitors are fierce! Some companies may try to convince consumers why your brand or product is inferior to theirs, potentially damaging your reputation.
- Despite the laundry list of disadvantages, there are some significant advantages to competition.
Nothing motivates a company more than having competition! Look at smart phones - every company tries to outdo the last released model. It spurs innovation and creativity on the way to better your product or service.
Marketing efforts from competition can increase your sales also. Check out the car industry advertising the advantages of hybrid vehicles. Ford's hybrid commercial can potentially benefit Toyota's sales of hybrids because it's spreading the word of how great hybrid cars can be.
Drucker believed that managers should, above all else, be leaders. Instead of setting strict hours and discouraging innovation, he opted for a more flexible, collaborative approach. He placed high importance on decentralization, knowledge work, and management by objectives (MBO) and a process called SMART.
Management by Objectives
In the changing economic environment old techniques of management don't give better results. The expansion of business in size and changes in technology has necessitated replacement thinking in managerial approach. a number of latest techniques of management are developed within the recent past and Management by Objectives (MBO) is one among them. Though MBO is now practiced round the world yet there's no unanimity about its meaning. Some consider it as an appraisal tool, others see it as a motivational technique, and still others consider it as an impact device.
MBO is one among the techniques by which executives can improve organizational performance and effectiveness. The thought of MBO was contributed by Donaldson Brown and Alfred Sloan in 1920s and Edward Hagenin in 1930s. Peter Drucker, referred to as father of MBO technique, coined this term in 1954. Other authorities on the topic are Charles L. Hughes, Goal Setting (American Management Association, 1965); Dale D. Mc Conkey, the way to manage by Results (American Management Association, 1967); George S. Ordiorne, Management by Objectives (Pitman, 1965); W.J. Reddin, Effective Management by Objectives (Mc Graw-Hill, 1971).
In order to know the concept of MBO some definitions are given:
According to George S. Ordiorue, “The system of management by objectives are often described as a process whereby the superior and subordinate managers of a corporation jointly identify its common goals, define each individual’s major areas of responsibility in terms of results expected of him, and use these measures as guides for operating the unit and assessing the contribution of each of its members.”
According to Koontz and Weihrich, “Management by objectives may be a comprehensive managerial system that integrates many key managerial activities during a systematic manner which is consciously directed toward the effective and efficient achievement of organizational and individual objectives.”
S.K. Chakravarty defines it as, “MBO may be a result-centered, non-specialist, operational managerial process for the effective utilization of material, physical, and human resources of the organization by integrating the individual with the organization and organization with the environment.”
The characteristics of MBO system:
(i) Some sort of corporate or unit plan by which objectives are laid down;
(ii) Measurable and time bound objectives for every managerial position;
(iii) Objectives for every position are established by the job holder and therefore the boss together;
(iv) Mutually agreed job improvement plans to facilitate the accomplishment of objectives;
(v) Periodic reviews and updating, wherever necessary, of the mutually agreed objectives by the boss and subordinates together;
(vi) Such mutually agreed objectives form the premise of performance evaluation;
(vii) Sharp definition of responsibilities and authorities for positions, which brings in clarity within the organizations; and
(viii) Aligning and linking of objectives up, down and across.
Management Theory of Michael Porter
Michael Porter theory focuses on several major models. the foremost practical are Expectancy Theory and Value Chain Analysis.
Through Expectancy Theory, Porter codified the main factors that impact an employee's motivation to perform. He stated that numerous factors fuel an employee's efforts to reach an organizational goal, including the expectation that performance will yield positive rewards which rewards will match effort. Through Value Chain Analysis, Porter defined effective supply chain management, presenting a model which categorizes the activities that form a company's product-delivery system as either Primary or Support activities and showing how they work together to make profit. Both models, alongside Porter's more complex Five Forces model, form the centre of Michael Porter's Strategic Management Theory.
In order to properly understand Porter's Leadership Theory, you need to focus on the subsequent information:
1. You need to achieve as much knowledge as possible on Porter management theory.
2. You'll need to hire a business consultant who is thoroughly comfortable with management theories.
3. You must find tools that allow you to place Porter's theory into action.
Value chain model of Michael Porter
The Value chain model by Michael Porter offers a summary of the components that can make up an organization. The model is therefore ideal for stopping a new strategy for a while to see whether you have not overlooked a business unit. the value chain comes from the book Competitive Advantage: creating and sustaining superior performance from 1985.
5 forces model of Michael Porter
The 5 forces model by Michael Porter is that the leading management model to analyse an industry and determine how competitive this industry is. From this analysis you'll determine how attractive the market is that a corporation enters (or wants to enter). Michael Porter's five forces model relies on five forces which will play a role within a branch or industry. Michael Porter's famous five-force model was developed in 1979.
Generic strategies of Michael Porter
The Generic strategies by Michael Porter mean that you can select from four strategies as a corporation. As a corporation, consistent with Michael Porter, you have to make sure that you concentrate on one of these strategies and that you do not get stuck within the middle of anything. The four Generic strategies of Michael Porter are:
• Cost leadership
• Differentiation
• Cost focus
• Differentiation focus
Competitive strategy is a long-term action plan of a company which is directed to achieve competitive advantage over its rivals after evaluating their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats in the industry and compare it with your own. Michael Porter, a professor at Harvard presented competitive strategy concept. According to him there are four sorts of competitive strategies that are implemented by businesses globally. It’s necessary for businesses to know the core principles of this idea that will help them to make a well-informed business decision in the course of action.
Competitive Strategy
Michael Porter divided competitive strategy in four differing types of strategies.
Cost Leadership Strategy
Cost leadership strategy is difficult to implement for small scale businesses because it involves making long term commitment for offering products and services at lower prices within the market. For this purpose, firms got to produce products at low cost otherwise it'll not make profit.
Since the cost leadership means to become low cost producer or provider in the industry, any large-scale business which may provide and manufacture products at low cost by attaining economies of scale. There are many cost leadership factors such efficient operation, large distribution channels, technological advancement and bargaining power. Here Walmart could be a good example.
Differentiation Leadership Strategy
Identifying attribute of a product which are unique from competitors in the industry is that the driving factor in the differentiation leadership strategy. When a product is able to differentiate itself from other similar products or services within the market through superior brand quality and value added features it'll be able to charge premium prices to cover the high cost.
Cost Focus Strategy
This strategy is sort of a resemblance to the cost leadership strategy; however, a major difference is that the value focus strategy businesses target a particular segment within the market which segment is offered the lowest price of the product or service. this sort of strategy is extremely useful to satisfy your consumer and increase brand awareness.
Differentiation Focus Strategy
Similar to the cost focus strategy, differentiation focus strategy targets a specific segment within the market; however, rather than offering lower prices to consumer; firms differentiate itself from its competitors. Differentiation strategy offers unique features and attributes to appeal its target segment.
Market Leader Strategies
Almost every company follow a market leader who has the biggest market share. Usually, the leader leads the opposite firms in new product developments, price changes. Distribution systems & promotion event However, the leader might not be respected by others. But others may concede its dominance. Companies only follow the leader, take a challenge, imitate or avoid. The best-known market leader is-
- Walmart
- McDonald’s
- Verizon
- Coca-Cola
- Caterpillar
- Nike
Obviously, a market leader life isn't very easy. It needs to careful every time. Others company always tries to require the benefits of leader weaknesses.
To keep the primary position in the market, the leading brand can take any of the three actions.
- Expanding total demand
- Protect market share
- Expand market share
- Expanding total demand
Comparatively, the leader firms get the most benefits in the marketplace. For instance: as maximum American eat fast food, McDonald’s stands to realize the most. The reason behind this is often, McDonald’s has a large market share than its nearest competitors Subway & Burger King. As a market leader, MacDonald’s attempt to convince its consumer that fast food is that the best eating –out choice, if possible then it ‘ll benefit over its competitors
Selecting a new market segment the market leader can be developing new users, new uses & more usage of its product they will develop them in many places.
Protect market share
At the time of expanding the market growth, the leader firm must attempt to protect its current business position against competitor’s attacks. for instance, Wal-Mart always to protect their current business against Target & Costco. McDonald’s protect against Wendy’s & Burger King.
What can the market leader do to protect its position?
They want to prevent the weak point as possible; so that the competitors cannot get any advantages. It tries to keep the value proposition that they promise to deliver. they need to figure hard to keep strong relationships with valued consumers. they must set their pricing at the moderate level that can be purchased & the price should be according to the brand value. The leader should develop “Plug holes” so the competitors don't jump in.
But the most effective revenge is to continuous innovation. Market leader continuously develops new products, customer’s services, distribution, promotion & cutting cost. The market leaders enjoy competitive advantages than others & deliver value to consumers. Sometimes, a leader may attack by the challengers, and then the leader reacts decisively.
Expand market share
Growing market share is one among the ways of keeping the first position in the market. Market share eventually increases as sales are increased. For example: within the shampoo market 1% increase in share is worth $14 million in annual sales. The carbonated soft drink is worth $757million.
On one study shows that probability rises because the increasing of market share. based on the probability, companies improved their strategies. For example: if a company wants to be number one or two in the market position, it must develop a unique business plan.
Market challenger strategies
The market challenges are always a second, third or lower position within the industry. like PepsiCo, Ford, Hertz, Lowe’s. These firms adopt one or two marketing strategies. They challenge the market leader & other competitors aggressively. They decide which competitors to challenge & what their strategic objective. High risks bring high gain strategy. The challenger wants to dominate the market leader or wants more market share. However, the challenger takes the second mover advantage. Besides, the challenger follows what makes the leader lead the market.
Market follower strategies
Sometimes not all the runner-up companies want to challenge the market leader. They only follow the leader on the market. If the challenger reduces its prices, improved their services, add a further feature in their product then the market leader attempt to match these changes to attack.
Probably, the leader has some power to encourage customers. For example, Kmart introduced a blue light special product that's containing low price. due to the low price, Kmart competes with Walmart’s everyday low prices. They started a price competition but Kmart loses the market. So, there are some companies who don’t want to compete; they only follow the market leader.
A follower may have some advantages. The market leader always must expenses huge money for developing a new product, distribution & promotion. In contrast, challenger & the follower can learn from the leader’s experience. The follower can copy or improve the leader’s product.
Usually, they need less investment. a follower may know how to carry the present market share & its customer. Follower gives some distinct advantages to the customers like location, services, financing. The main goals of a follower are to attack the market challenger. They always attempt to reduce their manufacturing cost & charge low prices. They keep their product quality & services high. However, they need to enter the new markets as they open up.
Market Nicher strategies
Almost every company features a special segment in which they can serve well. This company chooses only sub-segments. They’re called the market nicher. They have smaller firms with limited resources. Through smart niching, the firms are often highly profitable & successful with low shares. The reason behind this is often that the market nicher knows all target customers so well & know to meet their needs. The niche always tries to find out one or two segments to enter that are safe & profitable.
The niche market is always in specialization in nature. A market nicher is specialized in a particular sector that it can serve best like product features, quality, services or marketing mix. One nicher selects to serve a small group of individuals who are neglected by the majors.
Some may choose one or a few specific customers. Wal-Mart is selling only in a certain location, region or area within the world. HP specializes in pricing & quality.
The market nicher has some major risks. The chosen segment may dry up, and then what’ll nicher do those situations. That’s why many companies practice multi-niche. Through this manner, nicher can serve the entire market.
Key Take Away TECHNOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENT Technological environment refers to the state of science and technology within the country and related aspects like rate of technological progress, institutional arrangements for development and application of latest technology, etc. IMPACT OF TECHNOLOGY ON BUSINESS
Technology and society
Technology and economy
Technology and plant level changes
COMPETITIVE ENVIRONMENT
A competitive environment is the dynamic external system in which a business competes and functions. The more sellers of a similar product or service, the more competitive the environment in which you compete. Look at nutriment restaurants - there are numerous to choose from; the competition is high. However, if you look at airlines servicing Hawaii, very few actually fly to the islands.
5 forces model of Michael Porter
The Generic strategies by Michael Porter mean that you can select from four strategies as a corporation. As a corporation, consistent with Michael Porter, you have to make sure that you concentrate on one of these strategies and that you do not get stuck within the middle of anything. The four Generic strategies of Michael Porter are:
Cost Leadership Strategy Cost leadership strategy is difficult to implement for small scale businesses because it involves making long term commitment for offering products and services at lower prices within the market. For this purpose, firms got to produce products at low cost otherwise it'll not make profit.
Differentiation Leadership Strategy Identifying attribute of a product which are unique from competitors in the industry is that the driving factor in the differentiation leadership strategy. When a product is able to differentiate itself from other similar products or services within the market through superior brand quality and value added features it'll be able to charge premium prices to cover the high cost.
Differentiation Focus Strategy Similar to the cost focus strategy, differentiation focus strategy targets a specific segment within the market; however, rather than offering lower prices to consumer; firms differentiate itself from its competitors. Differentiation strategy offers unique features and attributes to appeal its target segment.
Market Leader Strategies Almost every company follow a market leader who has the biggest market share. Usually, the leader leads the opposite firms in new product developments, price changes. Distribution systems & promotion event However, the leader might not be respected by others. But others may concede its dominance
Cost Focus Strategy This strategy is sort of a resemblance to the cost leadership strategy; however, a major difference is that the value focus strategy businesses target a particular segment within the market which segment is offered the lowest price of the product or service. this sort of strategy is extremely useful to satisfy your consumer and increase brand awareness
|
References
- Business Environment by Veena Keshav Pailwar
- Business Environment by Dr. V.C. Sinha
- Business Analytics by S.Christian Albright