UNIT 1
Introduction of service marketing
Marketing is defined on the basis of products and services. Service marketing means services are provided to those who are in need of services. Services are intangible and more perishable component of any business offering.
Service is the process of delivering value to customers in connection with the sale of goods in a way that benefit the organization and stakeholders. Services is not physical output or construction, it is generally the added value to the products such as amusement, comfort, convenience, etc
Few examples of service marketing are as follows education, transportation, hospitality, finance, real estates, accounting, banking, insurance, taxation, consultancy, health care etc.
Goods and services are produced in every economy. Goods can be taken after purchase as it is tangible. While service can be taken as it is intangible but still can be consumed. For examples, a person uses the service of a dentist and in return gets the relief. Thus there are no physical commodities but still the service is consumed.
Goods provider also provides service as a part of their business. For example, repair services are provided by the automobile manufacturer. Thus business integrates tangible goods with intangible services.
The main purpose of service marketing is to deliver consumable and perishable benefits to customers to ensure customer satisfaction.
Definition
The American Marketing Association defines services as “activities, benefits or satisfactions, which affect sale or are provided in connection with the sale of goods.”
According to William Stanton, “Services are those separately identifiable, essential intangible activities which provide want satisfaction and are not necessarily tied to the sale of a product or another service.”
In the words of Philip Kotler, “A service is any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything.”
Characteristic of service marketing
The characteristics of the services differentiate the services from the physical goods. The following are the characteristics of business
- Intangible – a service are intangible which cannot be seen, touched, smelt or taster like physical product before they are purchased. It can only be experienced. Selling physical goods is much easier as it can be touched, seen, tasted before making the purchase. While service is intangible in nature, so to sell services we need to focus on the benefits and satisfaction that the buyer can get after he purchase the service. Intangibility of services includes other important implication such as
- Services has no inventories
- It is not possible to provide precise standardization of services
- Services can never be owned can only be used.
For example, surgery, airlines, banking etc
2. Perishability – perishability means a service cannot be stored for future use like tangible goods. It has to be consumed simultaneously with its production. This is a very significant characteristic of service marketing as it impact on financial results. A service not used in time is lost forever. It can’t be preserved or stored for future. For example an empty seat of a plane after departure cannot be used or charged. The revenue from those seats is lost forever. Unutilized services are economic waste such as vacant bed in hotels, hospital, credit card unutilized, etc
3. Inseparability - inseparability means services are produced and consumed simultaneously or at the same time. In case of physical goods, commodities are produced can be preserved and used in the later time. But this is not the case in service marketing, here the services are sold first, and then produced and consumed at the same time. Donald Cowell says, “Goods are produced, sold and then consumed whereas the services are sold and then produced and consumed.” The producer of the service and consumer of the service should be present at the same time.
For example – without the presence of the individual, haircut is not possible.
4. Heterogeneity – heterogeneity means a service cannot be standardized. Every service is unique. The qualities of services are not uniform. The prices charged can be too high or too low. The consumer cannot get same type of service even if they pay same price. For example, a doctor treats many patients on the same say, but the level of satisfaction will never be same to all the patients after treatment. A doctor cane charge high price to rich people and low price to poor people. Incase of tangible goods standardization can be maintained but not possible in case of service sector. Services vary with each other.
5. Ownership – in case of tangible goods, the products can be owned and stored. But this is not in the case of service; services are created with no ownership. A consumer can consume the service but cannot own it. For example, a consume use hotel room, but the ownership is with the provider. An expert opines, “A service is any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that it is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything.”
6. Simultaneity – services are produced and consumed at the same time. As soon as the consumer request for the service, the producer generate the service from the scratch without any delay and then the consumer use the service to satisfy his wants. Therefore, production and consumption is always done simultaneously. Also the services cannot be delivered to the consumer like physical goods. For example, hotel rooms or aero plane are not brought to the customers.
7. Nature of demand – the demand of services has high degree of fluctuations. The demand of services in peak season has high demand, normal demand and low demand on off period. For example, during festive season, the mobility of passenger increases. In winters, the cricket stadium is used and golf course remains unused.
Service marketing triangle
In service sector, relationship is very important. The service triangle outlines the relationship between various service providers and the customers who utilize the services. The key players of the service marketing triangle are company, customers, and employees. It not only shows the relationship between the company, the employees and the customers but also underlines how the system of service industry helps in achieving customer satisfaction.
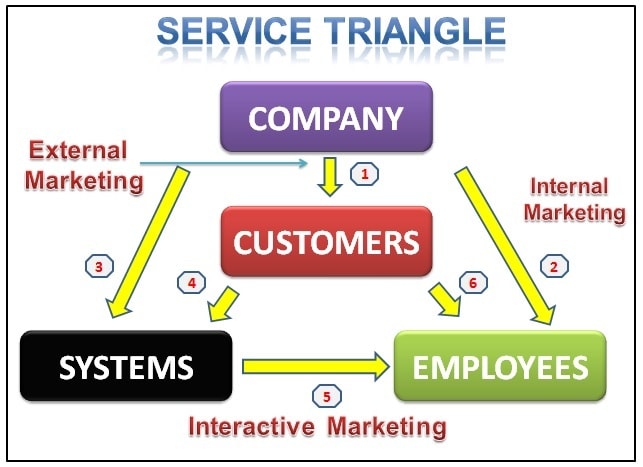
The following are the 6 relationship in service marketing triangle.
- Company to customers – the most critical thing is to communicate the service to the customers. Communication between the company and the customers helps in building trust of customers. This results in converting the customers to be loyal to the company.
2. Company to employees – relationship between company and employees are very important. In case the employees are frustrated with the company then the customers will get the poorest service. Thus, the company should focus on building value and trust, training and empowering employees which will make them motivated and land up with good service.
3. Company to system –efficient and productive systems need to be developed to keep the customers happy. Earlier all the banking transaction was taken place through lot of paper work which was a tedious process. Hence, due to advanced systems, nowadays banking transaction are done sitting at home. In service marketing triangle system plays an important role.
4. Customers to system - the system should be build in a way that it is useful to the customers. A system is service industry promises various service advantages, and when the system fails to provide those services then the customer are dissatisfied. For ex, a banking system, when we go to the bank, we find long queue which leads to dissatisfaction. Thus the company should build the system which give excellence experience to customers.
5. Employees to systems – not only system get customer dissatisfied, it also makes the employee frustrated. For example, in McDonalds, order are taken in the front desk but it is not reaching to employees in kitchen due to bad system. Thus customer gets dissatisfied and get angry on employees. Due to system issue delay in work put pressure on employees. Thus excellent system results in good work flow.
6. Employee to customer- this is a very important relationship. The employee to customer interaction is also known as the “moment of truth” or “critical incidents”. Employee treatment towards the customers leads to satisfied or dissatisfied customers. Well trained employees and employees should be given power to take decision result in providing high satisfaction to the customers.
Points of triangle
At the top of the triangle business organization sits. Customers and employees are at each corners of the triangle bottom.
- Internal marketing – internal marketing is that side of the triangle between organization and employees who provide service to the customers. Organization should provide adequate training on the services to be delivered, customer satisfaction techniques, performance rewards system for employees which will result in high level of customer satisfaction.
2. External marketing – external marketing is the side of triangle between the business and the customers. Organization interacts with the end user to meet their needs. External marketing includes advertising, promotional strategies, social media efforts to fill the business pipeline with future business.
3. Interactive marketing - The side of the triangle between your employees and customers is called interactive marketing. This involves how employees deliver service to the customers. The purpose of interactive marketing is to highly satisfied customers who become long-term, repeat customers.
Purchase Process for Services
When a customer decides to purchase services to meet its requirement, they go through the purchase process. The process is divided into three stages - the pre purchase stage, the service encounter stage, and the post purchase stage.
Pre purchase stage
Pre purchase stage involves the decision to buy and use the services. In this stage customers look for different alternative which will fulfill their needs and expectations. After identifying alternatives, then weight the benefits and risk of each option to make a final decision. If it is a routine purchase relatively low risk then the customers quickly select a specific service provider and use them. If more is at stake or using a service for the first time, then the customers does intensive information search. Then identifies the potential service provider, weight the benefits and risk related to all the alternative before making a final decision.
In case the customers feel more risk, then at pre purchase stage they use variety of method to reduce them. The following are the risk reduction strategy before deciding to purchase a strategy.
- Seeking information from family, friends, peers
- Relying on a firm with a good reputation
- Looking for guarantees and warranties
- Visiting service facilities or trying aspects of the service before purchasing
- Asking knowledgeable employees about competing services
- Examining tangible cues or other physical evidence
- Using the Web to compare service offerings One strategy to help reduce the risk perceived by customers is to educate them about the features of the service, describe the types of users who can most benefit from it, and offer advice on how to obtain the best results
Service counter stage
Under this stage, customers experience a variety of element which provides a clue of service quality.
Service environments – customers are exposed to all the tangible characteristics of service provider. The appearance of buildings, nature of furnishing and equipment, behavior with other customers can make expectations and perceptions of service quality.
Service personnel – this includes direct and face to face interactions with the customers. This is most important in high contact service. Employees should have right personalities and learned skills to satisfy the customers with their service.
Support services – under this employee gets materials and equipment plus all of the backstage processes to do their work properly. This is a critical step, as many employs cant perform well without any proper support result in dissatisfied customers.
Other customers – in these other customers also influence the purchase decisions. For example, waiting room in hospitals, trains, bus, etc any customer behave badly thus detracting from the service experience. Providers should have plan for how to deal with the different types of problems that might occur.
Post purchase stage
In this stage, the customers evaluate the service quality and how much they are satisfied or dissatisfied with the service experiences. The result of this process will affect their future intension, whether they will use the service again and become loyal customers, whether they a spread a good word of mouth to friends, family and relatives. Customers evaluate the service quality by comparing from expected to actually received services. If it exceeds the expected service, then it is high quality service and customers are highly satisfied. This will result in repeat purchase and a loyal customer.
Incase the experience is below customer expectation, then customer are highly dissatisfied and switch to other service providers.
Marketing challenges in service business
In service business, the following are the marketing challenges.
- Intangibility – like physical goods, customers cannot see and touch the products. In physical goods, customer exactly knows what they are buying when they are spending the money. But this is not the case in services. Sometimes to get the result of service, customers have to wait for months. Like physical products, services lack emotional impulse which compels the customers to buy. The customers sometimes feel difficulty in understanding he details involved in what is done for them by a service business due to its intangible nature.
2. Lack of ownership – physical goods are brought and taken at home. This is not the case in service sector. The service is used for a specific period of time and then its over – unless it is paid again. The lack of physical ownership makes it harder to sell services. The delivery of service all depends on the interactions between the service provider’s employees and customers. Thus the marketers cant control as done in physical goods.
3. Perishability – services cannot be stored like physical goods. For example an unsold seat in airlines is waste once the plane is departed. Thus it’s a challenge to sell the service which are usually performed at specific times and on stated dates. If not sold in specific time, then it cannot be sold in future result in financial loss.
4. Heterogeneity – services are heterogeneous. The service delivery process involves a lot of human interaction. Human behavior is unpredictable. Thus it’s a challenge to provide same service to all the customers.
5. Interactivity – the service delivery depends on interaction between customer and service provider. All activities of service provider is to satisfy the customers. The employees should be given proper training and improved their skill for interacting with the customers. The cost involved in training the employees is high.
Role of Services in Modern Economy
Service sector plays an important role in developed and developing economies. In developed economies, service sector account for more than half of the gross domestic products. In developing economies, it is one of the single largest sectors. The economy is divided into primary, secondary and tertiary sector. Primary sector includes agriculture, forestry, animal and husbandry and fisheries etc., the secondary sector activities incorporate mining, manufacturing, electricity, gas, water supply, construction etc., the tertiary sector includes service sector of the economy is expanding at a faster rate.
The service sector activities include trade, commerce, transport, communications, hotel and restaurant, banking and finance, health and education, tourism, share market, film industry, insurance, astrology industry, advertisement industry, sports, legal service, publishing industry, mass media etc.,
The successful growth of primary and secondary sector is largely depends on territory sector (service offered by banking, insurance, trade, commerce, entertainment, maintenance of machinery and equipment and numerous other services)
Service sector can be classified into public and private services. Private services include hotel, restaurant, transport, commerce, sports, health, education, etc. Public sector includes government establishment including legislature, executive, and judiciary.
Role of service sector in economic development
The country economic development depends on the growth of the three sector of the economy. Recently in developing economy, service sector is growing at a faster rate and is contributing in output, income and employment. When compared to agriculture and industrial sectors, productivity per worker is becoming higher in service sector. New services are emerging in service sector and making the economy grow. Hence service sector plays an important role in economic development of the country.
Finance as service sector plays an important role in development of economy. Finance refers to money required by individual, business houses and the government. People use funds to meet their day to day expenses. Business requires fund to pay wages, buy new machinery, raw materials, etc. government uses fund t o provide various services. Thus in this process the service sector activities provides income and employment to the people of a country.
Service sector distributes output of the primary and secondary sectors to the final consumer for consumption. Trade, transport and storage activities ensure distribution of goods and services to the final consumer where and when needed.
In India service sector accounts more than 50 percent of India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Both in terms of employment potential and national income, service sector contributes larger part of the Indian economy. In 1950-51 the teritary sector was contributing about 29.9 percent to the Indian GDP. During 1990-91 the share of service sector in India GDP was 42.8 percent. During 2008-09 the share of service sector increased to 56.4 percent. Over a period of time, share of tertiary sector is raising constantly.
Service marketing environment
Growth of service sector is affected by different environmental factors. There are two types of environment in which a service firm works:
- The external or macro-environment.
- The internal or micro-environment.
The external or macro-environment – macro environment are those factors which are external of the firm. These factors are not in control of the service firm. The marketers should understand the changes and developments in the environmental factors and adopt them in framing the strategy.
The external factors are as follows
- Socio cultural factors – this external factor is the combination of social and cultural factors which affect the service firm. The factors include life style, social values, beliefs that affect the marketing of services. Cultural aspects include education, language, law, religion, values and attitude. Presently, service like insurance legal, medical, security is increasing tremendously. Cultural factors affect the service more than goods. Language is a major cultural influence. Marketers selling services should subject to local norms and local system
2. Legal factors – legal factors are external factors which refer to how law affects the service firm and customers behavior. Service firm are closely regulated than any other firms. Over the year’s insurance, banking and accountancy are gown in complexity. Service providers must understand the impact of regulation on their strategies. For example, bank have to follow strict guidelines. Banks compulsorily put more than 50% CRR and SLR. They are fined if they do not follow the law.
3. Economic factors – economic factors includes inflation, interest rates, income of consumers and so on. These factors have tremendous impact on the service firms. Economic factors influence the service firm strategies and consumers buying behavior.
4. Technological factors – technological factors influence the lifestyle and consumption patterns. Now a day’s consumer evaluates the alternatives with respect to technological capabilities. Service providers should technology as an important tool to improve the function and increase customer satisfaction. Some technological developments that affect the service firms are ATM, Internet, data mining, etc.
5. Political factors –political factors are influenced by government – central, state and local bodies. Service firms greatly affected by the government decisions. The growth of service firm is largely affected by the government plans and policies.
The internal or micro environment – micro environment or task environmental factors are internal to the organization and affect the service firm directly. Internal factors can be controlled for decisive competitive advantages.
- Internal customers – internal customers consist of employees, sales agent, channel partner, etc. they directly affect the service firm and are controllable. The service firm accomplishes the objectives and goals through the action of their employees. This factor can be strength and weakness to firm. If the employees are not skilled and demotivated with the system, then customers will not be satisfied with the employee service. While a skilled and motivated employees deliver value to customers and make the customers highly satisfied.
2. Suppliers – they are external to the service firm and can be threat and opportunity to the firm. The service provider should choose supplierwho offer best quality, reliability, credit, at low cost. The development in the suppliers environment affect the function of service firm. For ex, banks buy ATM machine from the suppliers.
3. Competitors – to gain competitive advantages the firm should provide equal service and deliver value more efficiently than its rivals at lower cost. Also operate in unique way, and create a greater product vale and sell at premium price.
Goods vs Services Marketing
Product marketing – product marketing refers to marketing of tangible goods which can be seen, felt, touch. Products are easier for the audience to understand in tersm of value. The aim of marketers is to find the right market for the product and promoting it to the target audience in brst possible manner.
Service marketing – service marketing refers to marketing intangible goods which cannot be seen, touched and felt. The aim of service marketers is to build trustworthy relationship with the target audience. Here you sell yourself.
Difference between products and service marketing
- Meaning – goods are physical objects which can be touched, felt, seen by the customers before making any final decision. The product marketing identifies appropriate market for the products and promote the product in best possible manner to the target audience. Where as services is an activity performed for others. The marketers create good relationship with the customer as it is intangible in nature.
2. Objective – the objective of product is to fulfill the requirements of the consumer and satisfy their unfulfilled needs. Whereas service provider creates good relationship with the customers and gains their trust. They offer solution or counseling to the customers experiencing difficulties.
3. Marketing mix – product marketing involved 4P’s of marketing mix which are product, pricing, place and promotion. While service marketing consist of 7Ps of marketing mix, out of which 4Ps are same as product marketing and other 3 is solely for service marketing which are process, people and physical evidence
4. What is being marketed – product marketing involves tangible goods which can be seen, touched and felt. Whereas service marketing sell services which are intangible in nature, which cannot be seen, touched, felt. Here only the final results are observed.
5. Ownership – in case of tangible goods, the products can be owned and stored. But this is not in the case of service; services are created with no ownership. A consumer can consume the service but cannot own it.
6. Storage – the products can be stored for future. While service cannot be stored. It has to be consumed simultaneously with its production. A service not used in time is lost forever. It can’t be preserved or stored for future.
7. Separable – goods can be separated from the seller. While service cannot be separated from the service provider as service provider sell themselves.
8. Production and Consumption - There is a time lag between production and consumption of goods. While production and Consumption of services occurs simultaneously.
Tabular form
Basis for comparison | Goods | Services |
Meaning | Goods are the material items that can be seen, touched or felt and are ready for sale to the customers. | A service is any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything |
Nature | Tangible in nature | Intangible in nature |
Ownership | The products can be owned | The service cannot be owned |
Marketing mix | 4ps | 7ps |
Seperable | Goods can be separated from the seller | Services cannot be separated from the seller |
Storage | Goods can be stored | Services cannot be stored |
Return | Goods can be returned | Services cannot be returned |
Production and consumption | There is a time lag between production and consumption of goods. | Production and Consumption of services occurs simultaneously. |
Goods Services Continuum
Goods service continuum are those products which have elements of both goods and services in varying composition. Pure goods are those which do not have any services. At the pure services end are services which are not associated with physical products. Product which involves combination of both goods and services fall in the center.
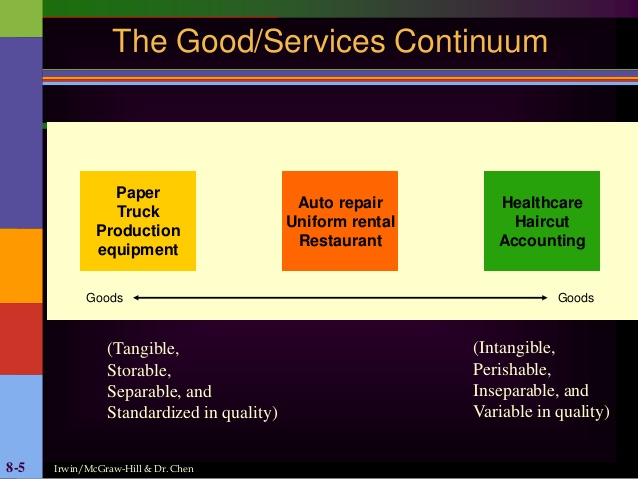
Product service continuums are classified in three ways from highly tangible to highly intangible.
- Highly tangible services – here service are rendered over certain goods ex, car rentals. The service is based entirely on the cars. The place where there is no car, this service does not exist. Here the marketer can easily persuade the offer to customers as he just have to discuss car in his communication and the service are easily sold to the customers. During the rental service , the car breaks down then the customer have poor impression on the car rental services. The customer will blame the car rental company and will not consider that the car broke down.
2. Service liked to tangible goods – here the service linked to the goods either independently or as a part of the offer. For ex, home appliances includes repair as a part of its marketing mix. Even if the service not includes, home appliance repair is a service that is linked forever to the goods.
3. Highly intangible services – under this classification of continuum model, services is highly intangible. These services cannot be seen, touched or felt. For ex, counseling, consultancy, lecture, etc.
Consumer behavior
When it comes to the purchase of physical products, there are several information about consumer buying behavior. While service product have unique characteristics so the marketers requires different marketing strategy.
The unique characteristics of service marketing are its intangibility. The physical products are tangible and can be promoted by giving sample. This option is not available in service product.
In case of service product, the client should be shown picture to make the service look tangible. For example, when trying a new hair cut, customer should be shown pictures of different styles of haircut.
Word of mouth plays an important role in making decision for service. Marketers should make sure that they create awareness about the service and their providers. The marketers should provide all types of information such as features, advantages, benefits to the consumer before making the final decision.
The firm perceived professionalism and competencies is important in deciding which service to use, as sometimes customer find difficultly in choosing service product from others
Thus good service reputation is an important factor that makes customer prefers the service from others.
Due to intangibility and subjectivity involved in service, customers perceive high risk in buying a service than purchasing physical goods. The risk is also greater because there is no standardization and the outcome of service is different is different whenever used. Also if the customers are not happy with the service then the service cannot be returned as physical goods.
Thus price is an important factor that service marketer can apply to customer in the buying process. The price should be maintained keeping in mind customer’s expectation. Sometimes many customers is ready to pay high price for a service as they think higher the price, higher will be the quality.
It has been observed, service provider should provide information related to price, benefits, features, service guarantee. This will reduce the perceived risk in buying the product.
Positioning a service in the marketplace
After determining the company strategy, a company must focus on positioning its service product effectively. The concept of positioning involves creating a distinctive image in the mind of the customers.
The following four principles are involved in positioning
- A company must establish a position in the mind of its target customer
- The position should be made with one single and consistent message
- The positioning should set apart from its competitors
- The company must focus its efforts
Positioning statement
Positioning statement focus on primary benefit of the services to the target market. Positioning statement is as follows
- The statement begins with describing target market and what is their need. This helps the business to understand their market and customer properly
- Define how the service meets the need of the customers.
- What differentiates the services from the competitors and how the differentiator resolves the customer problems
- Explain the customers with evidence to believe your brand claims in your positioning
Determine a positioning strategy
A successful positioning relies on deep understanding of market place where you want to compete in. It helps in making the company different from its competitors. Clear positioning strategy helps the customer in understanding Whether the brand is competing on price or quality.
There are five main strategies upon which businesses can base their positioning.
- Positioning based on service characteristics- the positioning is done based on service characteristics or benefits which is beneficial to the customers. Positioning strategy associates the brand with certain characteristics that differentiate from the competitors. Brands communicate the characteristics to the customers.
2. Positioning based on price - positioning your services based on price, associate the brand with competitive pricing. The brand aims to be cheapest in the market. Price sensitive buyer often purchase cheapest option. Companies find gap in the market at a certain price point, position their brand based on price.
3. Positioning based on quality - customers have a perception that higher the price, higher will be the quality. Positioning the product based on quality is different from positioning the product based on price. The brand which communicate the service based on quality , create a desire to purchase the service irrespective to the price.
4. Positioning based on application - positioning the brand based on its use is another way of positioning strategy. For ex insurance companies, different plan is designed for different customer range. Customer purchase policy based on its usage.
5. Positioning based on Competition- positioning the services based on competition as a reference point for differentiation. Services offered in the market should have unique benefits than other options in the market. Service firms can follow the similar strategy of their competitors. If a particular brand has a large market share, their positioning strategy must be attractive to a large group of customers, so you try and convert some of their customers by offering a similar product with similar benefits at the same price point.
Variation in customer involvement
Depending on the consumer knowledge and experience, some consumer take quick decision whereas some customers require more information and be more involved in decision making before making a purchase decision.
The level of involvement outlines how much the customer is interested in consuming the service and how much information required making a decision. The level of involvement ranges from decision that are routine (customer are not involved much) to high level of involvement.
Low involvement – this type of decision are considered routine response or habitual decision. Here the consumers do not do any research as the products or service are brought on regular basis. For example, household items are purchased all the time, the consumer know what they want to buy. These buying decisions are called impulse buying.
High involvement – this type of decision takes time and requires research. This is a complex purchasing, the consumer pay more to such services such as insurance policy. It involves high risk if the buyer fails. These services are not purchased often but are important and relevant to the buyer. In this situation consumer is not sure about their purchase or find difficulty in deciding between two alternatives. Here the service provider provide lot of information which helps in making decision
Limited problem solving – this falls between low involvement and high involvement. In limited problem solving, customers have some information about a goods or service and continue to search little more information and come to decision relatively quickly.
Impact of Service Recovery Efforts on Consumer Loyalty
Recently, service recovery has drawn attention in both business practices and marketing study. The cause of service failure is the nature of service product themselves, which increases the possibilities of service failure and hence the need of recovery arises. The possibility of service failure is due to the perspective of the customers and marketers finds difficulty to understand and meet the expectation of customers.
The benefits of service recovery are better customer’s loyalty, customer retention, positive word of mouth in a competitive market place.
Definition of service recovery
Service recovery refers to the ‘actions taken by an organization in response to a service failure’……………….according to Zethamal and Bitner
Service recovery refers to the actions a supplier takes in order to seek out dissatisfaction and as a response to poor service quality. …………….according to Andreassen and Johnston.
Service recovery refers to the actions a taken by the service firms in response of service failure. The main objective is to maintain a good relationship between the customers and the business. Effective service recovery leads to customer loyalty, repeat sales, and positive word of mouth. It also create favorable image in terms of quality and value.
Service recovery plays an important role in customer satisfaction and retention. In every organization its happens that things go wrong and it have negative impact on the relationship with its customers. The true test of the firm how they respond if something go wrong to maintain customer loyalty. The procedure of resolving the problem and handling unhappy customer is the main aim of effective service recovery,
Justice recovery
In service recovery evaluation, justice recovery is an important factor.just recovery consists of three dimensions: distributive, procedural, interactional.
Distributive justice recovery focuses on allocating cost and benefits on service provided to the customers. The customer should receive benefits in terms of the cost associated with that service. When the customer do not receive the expected quality, then they are dissatisfied. Thus service recovery comes into picture.
Procedural justice focuses on evaluation of system and procedures used to determine outcomes. The customers are not only involved in outcomes. They are also involved in service production and consumption. The firm should fix the problem occurred in the process.
Interactional justice – interpersonal treatment is very important to main the customer satisfied. Employees should act quickly if the customer is having negative experience. The employee should show concern and welcome the customers and remain pleasant, helpful appearance.
Service recovery paradox –
The recovery paradox theory shows the customers satisfaction may exceed pre failure levels, if the service firms provide an excellent recovery in response of service failure.
Research suggest that “ a good recovery can turn angry, frustrated customers into loyal ones”
Stages of service recovery maturity
- Moribund – in this stage, complaints are not taken care. Angry customers are ignored. Even the CEO and VPs do not answer the complaints.
2. Reactive – in this stage, the customer complaints are heard and answered. But this is a haphazard process with no definite goals and no one responsible for this response
3. Active listening - in this stage, specific people are responsible to respond the complaints. However, it is still reactive.
4. Solicitous – at this stage proactively the customers complaint are taken care. They encourage the customers to voice their complains.
Impact of service recovery
The impact of service recovery is based on the assumption it decreases customer dissatisfaction and increases customer loyalty and satisfaction. Adissatisfied customers will result in negative word of mouth, which affects existing and potential customers. This will result in loss of potential future revenues.
To meet the objectives the firm should follow estimating the recovery
- Improvement in customer satisfaction as a result of customer and employee recovery
- Decrease service failure through process and employee recovery and its impact on customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Good attitude of staff , help in retention of customer and also increases customer base
- Service recovery helps in positive word of mouth and customer satisfaction and loyalty
Services are classified according to the level of contact with the customers.
- High contact – in high contact services includes greater level of contact exist between the service providers and customers. In this contact, high level of customization of service delivered to the customers which limit the amount of activities the service provider can perform. This includes most people-processing services. Customer remains throughout the service delivery after visiting the service facility.
Ex – hotels, health centers, schools, transportation
2. Low contact services – low contact services includes low level of contact exist between the service provider and customers. In this situation, reduction in contact allows the service provider to perform other task. Here, work is more standardized with less customization of service to individuals. Here introduction of new technology such as web help reduce customer levels.
Ex – repairs. Real estate firms
Design for high level and low level contact
Design decision | High level contact | Low level contact |
Facility location | Convenient to customers | Near labor or transportation |
Facility layout | Must look presentable and accommodate customers need | Designed for efficiency |
Quality control | Since customer involved in this process, it is more variable. Customer expectation and perception of quality may differ. | Measured against established standards, testing and rework possible to correct defects |
Capacity | Excess capacity required to handle peaks in demand | Planned for average demand |
Worker skills | Must interact well with the customers in decision making | Technical skills |
Scheduling | Must accommodate customer schedule | Customer concerned only with completion date |
Service process | Mostly front room activities, service changes in response to customers | Mostly back room activities; planned and executed with minimal interference of customers |
Service package | Varies with customer and are expensive | Fixed and less expensive |
One of the most important task is to facilitate changes smoothly. People basic nature is to keep the methods and customs constant. Successful organization strive to adapt to changes.
Innovation creates change in consumer routine or day to day activities.
Customers face several barriers to adopt innovation and these barriers include functional and physiological barriers. The functional barrier includes service usage patterns, service value and risk associated with service usage. The psychological barrier arises due to tradition and norms of the customers. These barriers are created by the customers’ prior beliefs.
Functional barriers
- Usage barriers - under this barrier, customer resistance to innovation as it is not compatible with the existing work flow or habits. Changes in the customer day to day activities require a long development process before gaining customers acceptance.
2. Value barrier – the second functional barrier is based on the value of innovation. Changes must offer strong performance to price value compared to alternatives.
3. Risk barrier – to some extent, all innovation represents uncertainty that cannot be anticipated. If the customers are aware of the risk associated in adopting the innovation they try to postpone adopting change until they learn more about it. Risk can be economic risk, functional risk, social risk
- Economic risk- the higher the cost of change, the higher will be the perceived economic cost. For ex, service such as insurance, mutual fund, financial institution, etc customers try to postpone their purchase waiting for new plan at low price
- Functional risk – the risk arises due to performance uncertainty. The customer worries that changes may not function reliably.
- Social risk – customer may resist change because they feel when they adopt changes they have to face social ostracism or peer ridicule
Psychological barriers
- Traditional barrier – the first psychological barriers is the cultural change created due to innovation for the customers. Innovation deviates the customers from established traditions, so it is resisted by the customers. The greater change in tradition, greater will be the resistance.
2. Image barrier – image barrier is a perceptual barrier arises due to stereotyped thinking. Innovation has a certain identity against the country where they are manufactured. The customer creates an unfavorable image and there is a barrier to adoption.
Overcoming resistance
Changes will always face resistance, the firm firstly helps their employees adjust to changes and facilitate new variations in functioning. The manager should convince the employees that the change are necessary and how will the change benefit the firm and the employees.
Secondly the management should implement changes smoothly. The following consideration should be kept in mind
- Changes should happen in stages and not in one go.
- Changes should never cause security problems for the employees
- Opinions of all the employees should be considered while making changes
- Prior training should be given to accept the changes with confidence.