UNIT 3
Managing quality aspects of service marketing
Improving service quality and productivity are discussed below
Service quality emphasizes on availability of quality services to the ultimate users. Service quality is the comparison of expected service with the actual service. Service quality is linked to customers’ satisfaction which means high service quality leads to satisfied customers.
For example, customers leaving a restaurant are asked to give feedbacks for the service they received. In case, they give negative feedback means the customers are not satisfied with the service.
Different perspective of service quality
- Transcendent – quality = excellence. Recognized only through experience. This means quality is understood in mind but difficult to communicate such as beauty or love
- Manufacturing based - Quality is in conformance to the firm’s developed specifications.
- User based - Quality lies in the eyes of the beholder
- Value based – quality is the tradeoff between price and value.
GAP model
GAP model is also known as customer service gap model or the 5 gap model. It is a framework which helps to understand customer satisfaction. The model was first proposed by A. Parasuraman, Valarie Zeithaml, and Leonard L. Berry in 1985. In gap model, customer satisfaction is the function of perception. If the customers perceive that the service meets and exceeds the expectation then the customer is satisfied. If they perceive the service do not meet the expectation then they are dissatisfied. The dissatisfaction is because of one of the gap shown below.
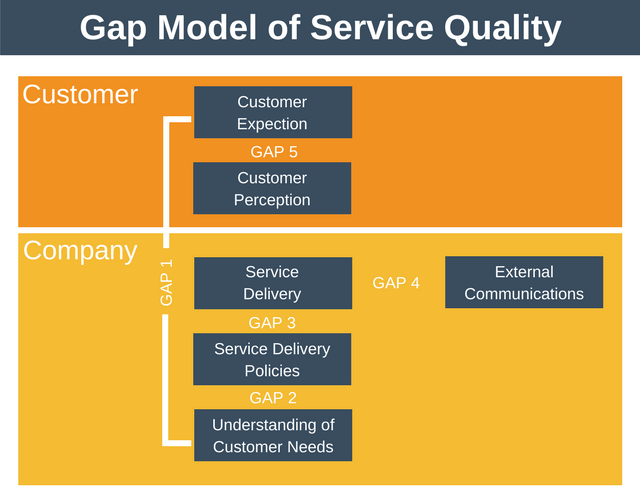
GAP 1 – Knowledge gap
- This is commonly known as management perception gap
- It refers to the difference between customer expectation of the service and what management perceives these expectation to be
- This gap arises when the management does not know what the customers expect. There are number of reasons including
- Lack of interaction between management and customers
- Insufficient market research
- Lack of communication between employees and management
- Insufficient focus towards relationship
- Failure to listen customer complaints
- For ex, management of a company perceives that customer expects low price on its service. But in fact customer expects value for money service
GAP 2 – The policy gap
- Commonly known as quality specification gap
- It refers to the difference between management understanding of customers needs and translating that understanding into service delivery policies and standards.
- There are number of reasons for the gap to occur
- Lack of customer service standards
- Service level standards are not updated regularly
- Service levels are defined poorly
- For ex, most hotels do not do housekeeping on the day when customer checks out. But the management has not realized that when the customer is doing late checkout wants a clean room
GAP 3 –The delivery gap –
- Commonly known as service delivery gap
- It refers to the difference between service delivery policies and standards and the actual delivery of the service.
- There are number of reasons for the gap to occur
- Human resource policies are not defined properly
- Mismatch in supply and demand
- Employee have lack of knowledge of the product
- Lack of team work to deliver the service
- For ex, all restaurant needs to attend the customer request and orders. But very often the customers do not receive the order or waiter get confused with other customer order.
GAP 4 – The communication gap
- The gap refers to difference between the delivery of customer experience and what is promised to the customer through advertisement.
- Discrepancy between actual service and promised one
- Communication gap leads to customer dissatisfaction
- There are number of reasons for the gap to occur
- Overpromising
- Internal communication is different to external communication
- Insufficient communication between the operation and advertising team
For ex, company advertises slimming products will lose 5Kg weight in one week. But in actual it does not happen
GAP 5 – the customer gap
- The customer gap is the difference between customer expectations and customer perceptions.
- Gap 5 is the combination of gap1 to 4
- The quality of service perceived by the customers incorrectly
- Gap 5 may result in lost customers, bad reputation, negative corporate image.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking is the process of measuring the performance of company’s services , products, process against the best business (leader) in the industry. Benchmarking is the process to create top class service which will satisfy the customers expectation and surpass the service of competitors.
Benchmarking has been classified into two distinct categories: technical and competitive.
Technical benchmarking – technical benchmarking is performed by the design staff to examine the capabilities of product or services in comparison to the leading competitors’ products and services
Competitive benchmarking – with respect to attributes, functions, or values associated with the organization’s products or services, it compares the how well the organization is doing with respect to the leading competition.
Step-by-Step Benchmarking
- Choose services to benchmark
- Determine the best in class companies which will be used to compare
- Internal performance or metrics information need to be gathered
- Compare the data from both the organization and identify your company’s performance gap
- Adopt policy and process of best in class performers
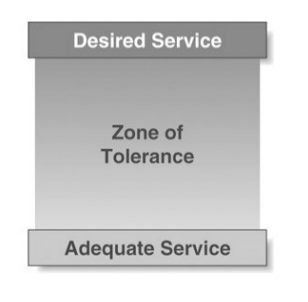
Measuring Service Quality -Zone of Tolerance and Improving Service Quality
The zone of tolerance (ZOT) is defined as “the difference between desired service and the level of service considered adequate”. The larger that gap, the more likely the customer will be dissatisfied.
Zone of tolerance is the zone in which customer do not notice any gaps in the service performance
Zone of tolerance is the extent to which customers recognize and willing to accept variations in service. It is the range where customer does not particularly notice service performance of a service provider. Service provider firms must try to perform better than the best during this time period. It generates customer loyalty, footfall, brand image and profit maximization.
The service provider must consider following point for the better facilitation of services.
- Make realistic accurate promises that reflect the service actually delivered rather than idealized version of service
- Feedback are asked by the people on the accuracy of promise made in advertising and selling
- Use market research to determine sources of derived customer expectation and their requirement
- Educate customers to understand their role and perform better.
- Identify influencers and opinion leaders for the service and concentrate marketing efforts on them.
Measuring and improving service quality
- SERVQUAL - To measure the service quality, author created a scale which is popularly known as SERVQUAL. SERVQUAL rate the service quality on 5 dimension known as Tangibles, Reliability, Responsiveness, assurance and Empathy. Service quality is defined as closing the gap between expectation and perception if service
2. Mystery shopping – this is popularly used in hotel and restaurant but also works in any other service as well. If involves hiring of undercover customers to test the service quality. The undercover assess the services based on number of criteria. This offers more insights than simply observing the employees.
3. Post service rating – it involves asking the customer to rate the services after it is delivered. Different scales can be used for the post service rating. Thus after getting the feedback necessary steps can be taken to improve the quality of service
4. Follow up survey - In this method you ask your customers to rate your service quality through an email survey – for example via Google Forms . It has a couple advantages over the post-service rating. The customers are sent SERVQUAL type of survey with multiple questions instead of one. The follow up survey measures the customers overall opinion for your service.
5. In app survey - With an in-app survey, the questions are asked while the visitor is on the website or in the app, instead of after the service or via email. The main advantages of in app survey is Convenience and relevance.
6. Social media monitoring -This method has been gaining momentum with the rise of social media. Social media is a place where people frustrations are heard. Facebook and Twitter are customer choices, but also review platforms like TripAdvisor or Yelp can be very relevant which provide unfiltered opinion of the customers.
7. Documentation analysis – the recorded service records are read or listened. You can go through documentation of low-rated service deliveries and the documentation of service agents that always rank high. We can analyze what they are doing better than the rest. Its easy to document live chats and email support. But for phone support it requires an annoying voice at the start of the call: “This call could be recorded for quality measurement.”
8. Objective service metrics – the objective service metrics plays an crutial role in showing the areas you should improve in.
- Volume per channel. This tracks the amount of inquiries per channel. It allows which channel to promote or cut down
- First response time - This metric tracks how quickly a customer receives a response on her inquiry.
- Response time. This is the total average of time between responses.
- Replies per ticket. This shows how many replies your service team needs on average to close a ticket. It’s a measure of efficiency and customer effort.
- Customer success ratio – this shoes whether the customers have right ideas about the offering
- Things Gone Wrong. The number of complaints or failures per customer inquiry. It helps you identify departments or service agents that need some "fixing."
- Problem Resolution Time. The average time before an issue is resolved.
- Average Queueing Waiting Time. The average time that queued customer has to wait to be served.
9. Employee surveys and panels – this determines the perception of the quality of service delivered to the customers on specific dimensions. It analyse the barriers for better service. Employee provide suggestions for improvements.
SERVQUAL model is also known as RATER model. It was developed in mid 1980’s by Zeithaml, Parasuraman and Berry who are well-known academic researchers in the field of services marketing. The SERVQUAL model is based on expectation – perception gap model.
The service quality originally had 10 dimensions which were reliability, responsiveness, competence, access, courtesy, communication, credibility, security, understanding/knowing the customer, tangibles. Later in 1988, the element reduced to five factor which are namely: reliability, assurance, tangibles, empathy and responsiveness.
Service quality is linked to the concept of expectations and perception. Customer compares the service quality from what they expect and how a service provider actually performs. Thus service quality is equal to the difference between customer expectation and perception of actual service performance. Delivering quality service means reaching a customer expectation on a consistent basis.
If expectation exceeds the performance of the service, then service is considered excellent and vice versa. To measure the service quality, author created a scale which is popularly known as SERVQUAL. SERVQUAL rate the service quality on 5 dimension known as Tangibles, Reliability, Responsiveness, assurance and Empathy. Service quality is defined as closing the gap between expectation and perception if service.
SERVQUAL is designed to compare the customers expectation and perception along the five dimension of service quality. The questionnaire consist of matched pair of items which includes 22 expectation items and 22 perceptions items.
Dimension | No. Of items in questionnaire |
Reliability | 5 |
Assurance | 4 |
Tangibility | 4 |
Empathy | 5 |
Responsiveness | 4 |
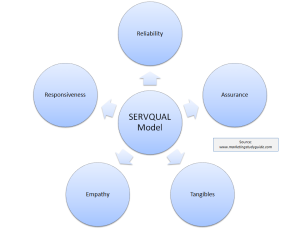
- Reliability – reliability has been classified as the first dimension of the SERVQUAL service quality model which refers to the ability to provide services to customers accurately, on time and credibly. The organization ensures that they fulfill the promise and pay attention to the results.
2. Responsiveness - responsiveness measures the ability of employees to solve the customer problems fast and willing to help customers to meet their requirements. It involves telling the customer when things will be done, promoting services, giving undivided attention. Thus responsiveness is the firms willingness to help customer with prompt services.
3. Tangibles – tangibles refers to the physical facilities and tools used in order to provide the services. Physical facilities include equipments, communication materials, manuals, information, and machines. The atmosphere is also called as servicescapes which influence both customers and employees.
4. Assurance – assurance refers to creating trust and credibility for customers through excellent technical knowledge, good communication skills, attitude courtesy and professional services.
5. Empathy – customer needs to feel that they are the priority for the service organization. Sympathy means caring, paying attention when providing the services to the customer. The main purpose is te make the customer feel unique and special.
SERVQUAL gap model
The model of service quality identifies five gaps that may cause customers to experience poor service quality. In this model, gap 1 is the only gap that can be measure through SERVQUAL. Gap 2 to 5 cannot be measured.
Gap 1 - The Knowledge Gap - Difference between the target market's expected service and management's perceptions of the target market's expected service
Gap 2 – The standards gap - Difference between management's perceptions of customer expectations and the translation into service procedures and specifications
Gap 3 – The delivery gap - Difference between service quality specifications and the service actually delivered
Gap 4 – The communication gap - Difference between service delivery intentions and what is communicated to the customer
Advantages
- SERVQUAL can be used frequently to tract the customers perception and the data can be analyzed visually presented to identify the opportunity and weekness.
- The organization can examine the quality service on the basis of each dimension separately as well as the entire dimension.
- Based on SERVQUAL rating, It allow the firm to classify its customers into different sections
- It can be used in various service sector, countries, on different context and backgrounds to check their capabilities
- SERVQUAL can be used for benchmarking purpose.
- SERVQUAL helps in comparison
- To regulate how service improvements have affected customers' perceptions and objectives of the service over time
Disadvantages
- Face validity – many researchers argued that it considers only customer satisfaction rather than service quality. A number of researchers have questioned the validity of SERVQUAL as a gap.
2. Construct validity - SERVQUAL scale has been tested and retested for reliability and viability. Any attempt to modify the scale has implications for the validity of the dimensions of reliability, assurance, tangibles, empathy and responsiveness.
3. Ambiguity of expectants construct – SERVQUAL is created to administer the respondents after experiencing the service. They are asked to recall the expectation which is not always accurate. Also studies showed that expectation changes over time. Thus a concern raised that expectation may change after experiencing the service.
4. Questionnaire length – the questionnaire includes total of 22 expectation items plus 22 perception items which is equal to 44 total items. If the researcher adds demographic and other behavioural items such as age, gender, etc the questionnaire will be around 60 items. It takes more than an hour in face to face interview and the respondent get fatigue which may affect the data reliability. Lengthy questionnaire is time consuming and expensive.
5. Dimensional inability – studies shown that the five dimensions of service quality is unstable when the research is replicated in different countries, different industries, in different market segments or even at different time periods.
Productivity is defined as ratio between the output volume and the volume of inputs. Production measures how efficiently production input such as land, labour is used to produce a given level of output. Production is utilize the resources and creating value to the customers. Production requires both efficiency and effectiveness. Effectiveness means doing the right things and efficiency means doing things right.
Efficiency is utilizing the resources in the best way to run the desired operation in a given system. It influences the input of the productivity ratio
Effectiveness is the creation of value to the customers and influence the output of the productivity ratio.
Combination of effectiveness and efficiency in the transformation process leads to higher productivity values.
Definition
The term of productivity economically is defined as the ratio between output and input (Mohanty, 1998).
Productivity = output / input
Ways to improve productivity
- Improving staff – in service industry importance of people cannot be undermined. Based on the interaction with employees, customer to large extent form his perception. Productivity can be improved by improving the skills, knowledge, attributes, behavior of existing and new staff who are involved in service delivery. Staffs are the main input of service productivity they should be trained in handling complaints and queries, in product knowledge, operations of internal system. Training should be considered as investment and not cost.
2. Introducing system and technology – service industry productivity is heavily dependent on fast growing technology and system. For ex, customers not only interact with person but also transact using ATM, Website.
The system approach of services are applied in three ways
- Hard technology means substituting tools and machinery for people. For ex, automatic car wash, automatic car parking, computers,etc
- Soft technology means substituting pre planned system for individual service operations. For ex, prepackaged tour, fast food outlets
- Hybrid technology is the combination of equipment with planned systems to give greater order, speed and efficiency to the service process
3. Reducing service level - productivity can be increased by allotting less time to a service offering. For ex, doctor gives less time to each patient so that he can see more patients in a given day. But in this case quality should not be suffered as it will lead to dissatisfied customers.
4. Substituting products for services – productivity can be improved by providing product substitute for the service. For ex, telegram service has been removed by new data transfer technology.
5. Introducing new services – this is another way of increasing productivity. Introducing more effective service will increase more productivity and satisfy maximum customers. For ex, hotels can add event planner on their list of service offerings.
6. Recruitment planning – human resource is an important factor in service industry. Productivity largely depends on human resource. Thus each department as per the job should find the best suited employees. Better suited employees’ leads to increased productivity.
7. Reduce the mismatch between demand and supply – the objective in marketing services is to get control mismatch over supply and demand and to obtain a better balance between the two. For example, seta should be made available if more people wants to use airplane, unsold seats in cinema means revenue lost for ever.
Since services are perishable in nature and cannot be stored as an inventory for future use, hence the demand becomes critical. Once the demand is not catered its lost forever. The marketers should understand the demand patterns and develop strategies for matching supply and demand.
Demand capacity variations
At any given moment, a fixed capacity service may face one of the four conditions-
- Excess demand – the level of demand exceeds the maximum available capacity, which results in denying the customer for service and the business is lost
- Demand exceeds optimum capacity – all the customers are welcomed and no one actually turned away. This result the condition are crowded and all customers perceive a decline in service quality
- Demand and supply are well balanced at the level of optimum capacity – here the staff and facilities are available to all the customers. The customer receives good service without any delay
- Excess capacity – here the demand is below optimum capacity. The productivity resources are underutilized, resulting in low productivity.
Demand patterns
Marketers need to understand the demand patterns with respect to time, place and person. Then the relevant strategies can be developed.
- Sketching demand patterns – companies need to keep the demand recorded on daily, weekly, monthly, seasonal and yearly basis and are represented through graphical chart, sketch which determine the demand pattern accurately.
- Predictable cycle- on the basis of predictable or foreseeable cycle the services can be planned.
- Random demand variation – some demands are not predictable and can randomly occur. For ex, flood, earthquake
- Demand patterns by market segment – a data base is created keeping the different demand patterns of customer of different segments.
Capacity constraints
Capacity of company is defined as the ability to meet the demand and the extent to which it can do it. For service it is difficult as four critical factors are involved.
- Time – time is limited and mostly specialized professional have this constraints. They extend hours when demand is more and vice versa. For example doctors have more consulting hours when demand is more. Service providers like legal, consulting, accounting, etc must be willingly to accept the change in situation.
2. Labour – labour is another area of constraints. Labour is a key element in all high contact and low contact services. Professional services require highly skilled staff to create high value added and information-based output. Staff should be given training to develop their skill to interact with customers and make them satisfied.
3. Equipment – when demand is more, equipment like machinery, transport, etc are needed. For limited period company cant buy extra machinery or equipment. Absence of equipment for a given level of demand can bring down the service.
4. Facility – these are mostly the infrastructure like building, hotel rooms, restaurant, hospital rooms, etc which cant be increased quickly when there is a increase in demand.
Strategies to match demand and capacity
- Shifting demand and capacity – by shifting the demand and capacity the organization seeks to shift customers away from periods in which demand exceeds capacity. The service provider tries to convince the customer to use the service when the demand is low. The prices are more during the peak period and less in low demand period. There are some other methods to shift the demand and capacity as follows
- Vary the service offering - the nature of the service offering depends on the season of the year, day of the week, or time of day. The change in the nature of offering is one of the approach. During low demand period bigger service provider offers smaller services. Such as marriage caterers offer small parties of birthdays, business gatherings, etc.
b. Communication with the customers- communicating with the customers is another approach for shifting demand and capacity. Effective communication with the customers helps then to know the time of peak demand , so that they can shift their requirement timing to avoid crowding or delays. Such as customer knows the busiest hours in banks and post office. To avoid delay the customer can shift their demand to another time
c. Modify timing and location of service delivery – some firms adjust the time of service as per the customer demands. Earlier banks working hour was 10am to 2 pm. Now the public banks timings are 10 am to 3pm. Private banks have 9:30 am to 4:30 pm. This leads to better customer demand patterns.
d. Differentiate on price – during low demand the service price are discounted. This concept works on the basis of supply and demand economics. Price differentiation depends on customer price sensitivity and demand curves.if price is low hotels, airlines, restaurants could be filled with customers. The industry profits are suffered to attract customers through price discounting. The organization ensures highest level of capacity utilization without sacrificing profits.
2. Align capacity with demand fluctuations – this is also known as chase demand. By adjusting the service resources creatively, the organization can match the capacity with customers demand patterns. Specific actions might include the following:
- Use part time employees – most of the organization hire extra workers during the busiest period. Here the labour resources are aligned with the demand. For ex, during peak season tourist resorts bring in extra workers. During tax season, tax accountant engage in temporary help.
Outsourcing – organization having peak demand in services that they cannot perform themselves, the company outsource the entire service as a temporary solution.
b. Rent or share facilities or equipment – during peak demand periods, organization rent additional equipment and facilities. Firms with complementary demand pattern can share the facilities. For ex, church share its facilities with Montes son preschool during week days. As the church needs the facilities evenings and on the weekend.
c. Schedule downtime during periods of low time – to ensure 100 percent of capacity (equipment and facility) is available during the peak period then repair, renovation; maintenance should be conducted when the demand is low. This ensures when the resources are most needed they are in top condition.
d. Cross train employees – the employees are cross trained so that they can shift among task when they are most needed. For ex, many airlines cross train their employees to move from ticketing to assist in baggage when needed.
e. Modify or move facilities and equipment – sometimes it is possible to adjust, move or creatively modify the existing capacity to meet the demand fluctuation. Such as when demand occurs the total conference hall is partitioned into two to three halls.