UNIT II
Preparing Presentations
Every PowerPoint presentation is composed of a series of slides. To begin creating a slide show, you'll need to know the basics of working with slides. You'll need to feel comfortable with tasks such as inserting a new slide, changing the layout of a slide, arranging existing slides, changing the slide view, and adding notes to a slide.
Understanding slides and slide layoutsWhen you insert a new slide, it will usually have placeholders to show you where content will be placed. Slides have different layouts for placeholders, depending on the type of information you want to include. Whenever you create a new slide, you'll need to choose a slide layout that fits your content.
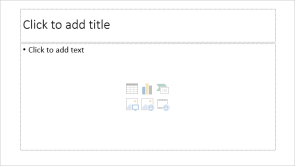
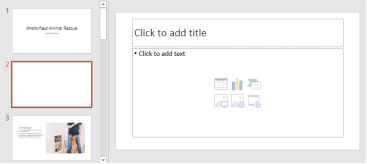
Placeholders can contain different types of content, including text, images, and videos. Many placeholders have thumbnail icons you can click to add specific types of content. In the example below, the slide has placeholders for the title and content.
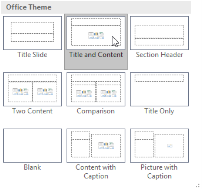
Whenever you start a new presentation, it will contain one slide with the Title Slide layout. You can insert as many slides as you need from a variety of layouts.
2. Choose the desired slide layout from the menu that appears.
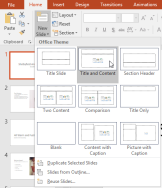
3. The new slide will appear. Click any placeholder and begin typing to add text. You can also click an icon to add other types of content, such as a picture or a chart.
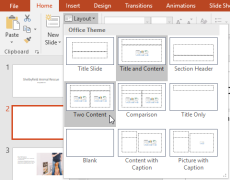
To change the layout of an existing slide, click the Layout command, then choose the desired layout.
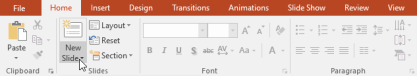
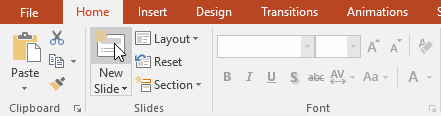
To quickly add a slide that uses the same layout as the selected slide, click the top half of the New Slide command.
Organizing slides
PowerPoint presentations can contain as many slides as you need. The Slide Navigation pane on the left side of the screen makes it easy to organize your slides. From there, you can duplicate, rearrange, and delete slides in your presentation.
2. Move slides: It's easy to change the order of your slides. Just click and drag the desired slide in the Slide Navigation pane to the desired position.

3. Delete slides: If you want to remove a slide from your presentation, you can delete it. Simply select the slide you want to delete, then press the Delete or Backspace key on your keyboard.
To copy and paste slides:If you want to create several slides with the same layout, you may find it easier to copy and paste a slide you've already created instead of starting with an empty slide.

2. In the Slide Navigation pane, click just below a slide (or between two slides) to choose a paste location. A horizontal insertion point will appear.

3. Click the Paste command on the Home tab. Alternatively, you can press Ctrl+V on your keyboard.
4. The slide will appear in the selected location.

Customizing slide layouts
Sometimes you may find that a slide layout doesn't exactly fit your needs. For example, a layout might have too many—or too few—placeholders. You might also want to change how the placeholders are arranged on the slide. Fortunately, PowerPoint makes it easy to adjust slide layouts as needed.
Adjusting placeholders
2. To move a placeholder: Select the placeholder, then click and drag it to the desired location.

3. To resize a placeholder: Select the placeholder you want to resize. Sizing handles will appear. Click and drag the sizing handles until the placeholder is the desired size. You can use the corner sizing handles to change the placeholder's height and width at the same time.
4. To delete a placeholder: Select the placeholder you want to delete, then press the Delete or Backspace key on your keyboard.
To add a text box:Text can be inserted into both placeholders and text boxes. Inserting text boxes allows you to add to the slide layout. Unlike placeholders, text boxes always stay in the same place, even if you change the theme.

2. Click and drag to draw the text box on the slide.

3. The text box will appear. To add text, simply click the text box and begin typing.
If you want even more control over your content, you may prefer to use a blank slide, which contains no placeholders. Blank slides can be customized by adding your own text boxes, pictures, charts, and more.
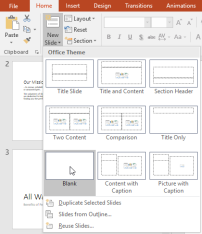
While blank slides offer more flexibility, keep in mind that you won't be able to take advantage of the predesigned layouts included in each theme.
To play the presentation:Once you've arranged your slides, you may want to play your presentation. This is how you will present your slide show to an audience.
2. The presentation will appear in full-screen mode.
3. You can advance to the next slide by clicking your mouse or pressing the spacebar on your keyboard. Alternatively, you can use the arrow keys on your keyboard to move forward or backward through the presentation.
4. Press the Esc key to exit presentation mode.
You can also press the F5 key at the top of your keyboard to start a presentation.
Customizing slides
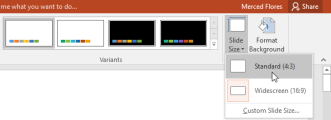
To change the slide size:By default, all slides in PowerPoint 2013 use a 16-by-9—or widescreen—aspect ratio. You might know that widescreen TVs also use the 16-by-9 aspect ratio. Widescreen slides will work best with widescreen monitors and projectors. However, if you need your presentation to fit a 4-by-3 screen, it's easy to change the slide size to fit.
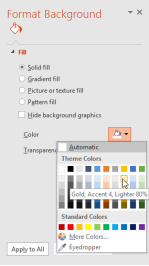
By default, all slides in your presentation use a white background. It's easy to change the background style for some or all of your slides. Backgrounds can have a solid, gradient, pattern, or picture fill.

2. The Format Background pane will appear on the right. Select the desired fill options. In our example, we'll use a Solid fill with a light gold color.
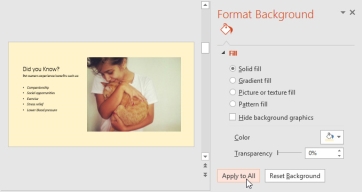
3. The background style of the selected slide will update.
4. If you want, you can click Apply to All to apply the same background style to all slides in your presentation.
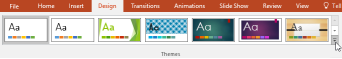
A theme is a predefined combination of colors, fonts, and effects that can quickly change the look and feel of your entire slide show. Different themes also use different slide layouts, which can change the arrangement of your existing placeholders. Select the Design tab on the Ribbon, then click the More drop-down arrow to see all of the available themes.
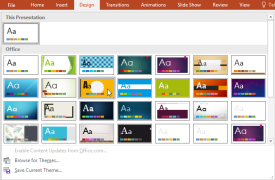
2. The theme will be applied to your entire presentation.

Try applying a few different themes to your presentation. Some themes will work better than others, depending on your content.
Create Presentation
PowerPoint offers a host of tools that will aid you in creating a presentation. These tools are organized logically into various ribbons in PowerPoint. The table below describes the various commands you can access from the different menus.
Menu Category | Ribbon Commands |
Home | Clipboard functions, manipulating slides, fonts, paragraph settings, drawing objects and editing functions. |
Insert | Insert tables, pictures, images, shapes, charts, special texts, multimedia and symbols. |
Design | Slide setup, slide orientation, presentation themes and background. |
Transitions | Commands related to slide transitions. |
Animations | Commands related to animation within the individual slides. |
Slide Show | Commands related to slideshow set up and previews. |
Review | Proofing content, language selection, comments and comparing presentations. |
View | Commands related to presentation views, Master slides, color settings and window arrangements. |
Besides these depending on the objects selected in the slide, there are other menu tabs that get enabled.
Add New Slides
Here are the steps that allow you to insert a new slide in the deck −
Step 1 −Right-click in the Navigation Pane under any existing slide and click on the New Slide option.
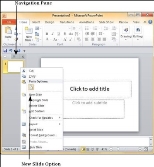
Step 2 − The new slide is inserted. You can now change the layout of this slide to suit your design requirements.
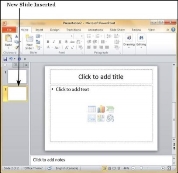
Step 3 − To change the slide layout, right-click on the newly inserted slide and go to the Layout option where you can choose from the existing layout styles available to you.
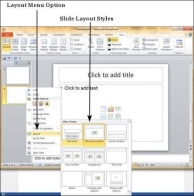
You can follow the same steps to insert a new slide in between existing slides or at the end on the slide list.
When we insert a new slide, it inherits the layout of its previous slide with one exception. If you are inserting a new slide after the first slide (Title slide), the subsequent slide will have the Title and Content layout.
You will also notice that if you right-click in the first step without selecting any slide the menu options you get are different, although you can insert a new slide from this menu too.
Adding Text in Boxes
PowerPoint allows users to add text to the slide in a well-defined manner to ensure the content is well distributed and easy to read. The procedure to add the text in a PowerPoint slide is always the same - just click in the text box and start typing. The text will follow the default formatting set for the text box, although this formatting can be changed later as required. What changes is the different kinds of content boxes that support text in a PowerPoint slide.
Given below are some of the most common content blocks you will see in PowerPoint.
Title Box
This is typically found on slides with the title layout and in all the slides that have a title box in them. This box is indicated by "Click to add title".
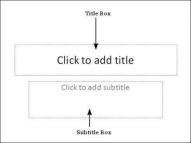
Subtitle Box
This is found only in slides with the Title layout. This is indicated by "Click to add subtitle"
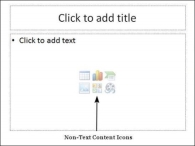
Content Box
This is found in most of the slides that have a placeholder for adding content. This is indicated by "Click to add text". As you can see, this box allows you to add text as well as non-text content. To add text to such a box, click anywhere on the box, except on one of the content icons in the center and start typing.
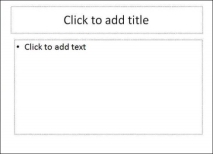
Text Only Box
This is not a default content box available in PowerPoint, but you can create it using Slide Master, if required. This is also indicated by "Click to add text". The only difference between the Text Only Box and the Content Box is that the former only supports text in the content area.
Adding New Text Boxes
Most of the standard layouts come with the text box option. As mentioned in the previous chapter, text boxes will have "Click to add text" as the default text. Here are the steps to add new text boxes in slide.
Step 1 − Click on the Text Box icon in the Home ribbon under the Drawing section.
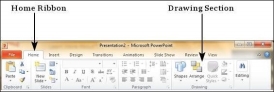
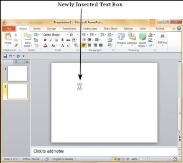
Step 2 − You will get the insert text box cursor that looks like an inverted cross.
Step 3 − Click to insert a text box. You can now start typing directly into the text box.
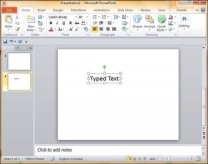
Step 4 − Alternately, you can click and drag the cursor without releasing the click to create a text box.
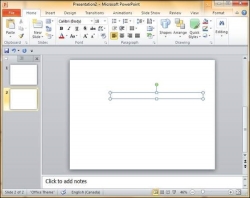
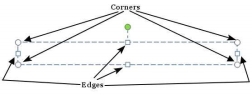
The size of the text box can be adjusted by selecting one of the edges marked by squares or corners marked by circles.
Deleting Existing Slide
There are times while building a slide deck, you may need to delete some slides. This can be done easily from PowerPoint. You can delete the slides from the Normal view as well as the Slide Sorter view. In each view, you can delete the slides in two ways.
Deleting from Normal View
Step 1 − Go to the Normal view.
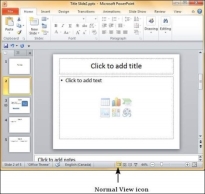
Step 2 −Right-click on the slide to be deleted and select the Delete Slide option.
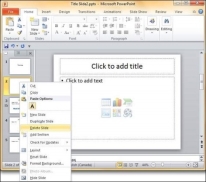
Alternately, you can select the slide and press the Delete button on your key board.
Deleting from Slide Sorter View
Let us now understand how to deleted slides from the Slide Sorter View.
Step 1 − Go to the Slide Sorter view.
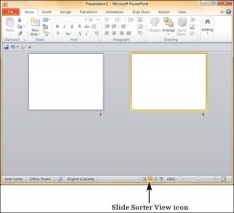
Step 2 −Right-click on the slide to be deleted and select the Delete Slide option.
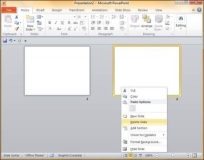
Alternately, you can select the slide and press the Delete button on your key board.
Rearranging Slides
Rearranging slides is important when it comes to organizing the overall presentation flow. While it is vital that you get the right content in every slide, it is equally important that you are able to present them in a format that makes it easier for the audience to understand the content too; most times this will require rearranging the slides.
You can rearrange slides from two views in PowerPoint - Normal View and Slide Sorter View. Given below are the steps to rearrange slides from different views.
Normal View
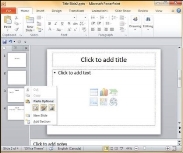
Step 1 − Select the slide to be moved.
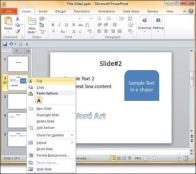
Step 2 − Left click on the slide and drag it to the position in the sequence where you want to place it. PowerPoint will indicate the insert position with a line in-between existing slides.
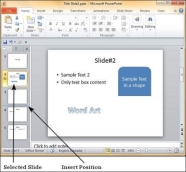
Step 3 − When you get to the right position release the left click button to insert the slide. Alternately you can also cut the selected slide and paste it back in the sequence as shown below.
Slide Sorter View
Let us now understand how the Slide Sorter View works.
Step 1 − Select the slide to be moved.
Step 2 − Left click on the slide and drag it to the position in the sequence where you want to place it. PowerPoint will indicate the insert position with a line in-between existing slides.
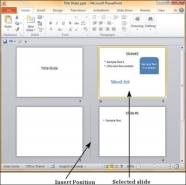
Step 3 − When you get to the right position release the left click button to insert the slide. Alternately you can also cut the selected slide and paste it back in the sequence as shown below.
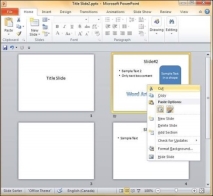
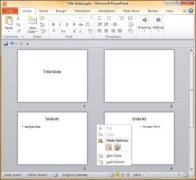
Adding Slide Notes
Slide notes can be very useful tools for presentation. These notes are not displayed on the screen in the Slideshow mode, but the presenter can see them so they can prepare well to present the slides. Depending on your Print settings, you can also print the slide notes along with the slides.
This chapter will show you how to add slide notes to an existing presentation.
Step 1 − To locate the slide notes, set the view in Normal mode.
Step 2 − The Slide Notes section is indicated by "Click to add notes".
Step 3 − You can click on the top border and drag the section to increase its size to make it easier to type.
Step 4 − Type your text in this section as slide notes.
You can only use bullets, numbering and alignment functions in the Slide Notes section. All other functions can be selected, but can be applied only to the selected slide, not the notes.
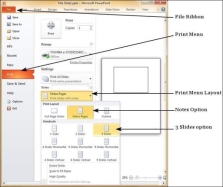
Slide notes can be printed from the print menu under the Backstage view. From the Print Layout option, select Notes Pages or 3 Slides. Notes Pages will print a single slide with the slide notes below it. The 3 Slides will print all three slides with notes on the right side.
Saving Presentation
One of the most basic tasks in PowerPoint is being able to save your work; this is probably the most important task as well. There are many users who have burnt their fingers for not saving their work in time and losing hours of hard work. The following are the basic steps to save a presentation.
Step 1 −Click on the File tab to launch the Backstage view and select Save.
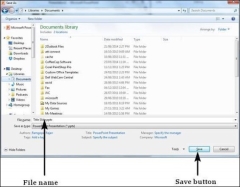
Step 2 −In the Save As dialog, type in the file name and click "Save".
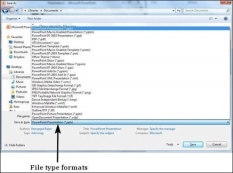
Step 3 − The default file format is .pptx. If you want to save the file with a different name, choose one of the file types from the "Save as type" dropdown list.
If you are working on an already saved file, the "Save" option in the Backstage view will directly save the file in the existing format with the existing name. If you want to change the format or filename of an existing file, use the Save As option instead.
Copy and Paste Content
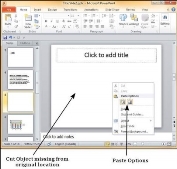
PowerPoint offers to the users a wide range of options when it comes to duplicating content. PowerPoint has the standard cut and copy functions but allows variations of paste options.
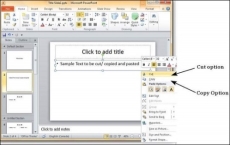
Cut Option
This option allows you to cut content from the slide - this means the original content is being moved to a different location hence the content will be deleted from its original location when you use this option. To cut a content, you need to select it and press "Ctrl + X" or right-click on the selected content and select Cut.
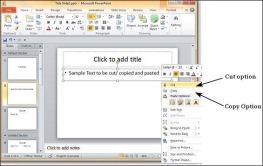
Copy Option
This option allows you to copy content from one location to another; hence the original content is retained it its place while the duplicate content can be pasted. To copy a portion of content, you need to select it and press "Ctrl + C" or right-click on the selected content and select Copy.
Paste Option
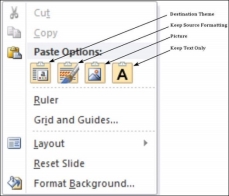
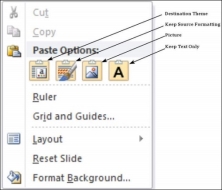
This option allows you to paste the cut or copied content at the desired location. There are multiple paste options for you to choose from. These options are indicated by different icons when you right-click at the desired location. Even if you do not remember the icons, you can hover your cursor on top of them for tooltip explanations. The table below describes the paste options in PowerPoint.
S.No | Paste Option & Description |
1 | Destination Theme Pasted content adopts the destination theme. |
2 | Keep Source Formatting Pasted content retains the source formatting - available for table or Excel content. |
3 | Picture Content is pasted as an image - once pasted as an image, the content cannot be modified. |
4 | Keep Text Only Pastes just the text - available for table or Excel content. |
You can also paste content using "Ctrl + V". In this case, you can make changes to the pasted object by pressing the Ctrl key to get access to the paste options. Note that these options are available only immediately after pasting. If you perform some other action, you will not be able to make changes based on the paste options.
Copy and Paste Content
PowerPoint offers to the users a wide range of options when it comes to duplicating content. PowerPoint has the standard cut and copy functions but allows variations of paste options.
Cut Option
This option allows you to cut content from the slide - this means the original content is being moved to a different location hence the content will be deleted from its original location when you use this option. To cut a content, you need to select it and press "Ctrl + X" or right-click on the selected content and select Cut.
Copy Option
This option allows you to copy content from one location to another; hence the original content is retained it its place while the duplicate content can be pasted. To copy a portion of content, you need to select it and press "Ctrl + C" or right-click on the selected content and select Copy.
Paste Option
This option allows you to paste the cut or copied content at the desired location. There are multiple paste options for you to choose from. These options are indicated by different icons when you right-click at the desired location. Even if you do not remember the icons, you can hover your cursor on top of them for tooltip explanations. The table below describes the paste options in PowerPoint.
S.No | Paste Option & Description |
1 | Destination Theme Pasted content adopts the destination theme. |
2 | Keep Source Formatting Pasted content retains the source formatting - available for table or Excel content. |
3 | Picture Content is pasted as an image - once pasted as an image, the content cannot be modified. |
4 | Keep Text Only Pastes just the text - available for table or Excel content. |
You can also paste content using "Ctrl + V". In this case, you can make changes to the pasted object by pressing the Ctrl key to get access to the paste options. Note that these options are available only immediately after pasting. If you perform some other action, you will not be able to make changes based on the paste options.
Find & Replace Content
PowerPoint offers its users the ability to search for specific text and if required replace it automatically. This is a very useful tool when you need to review a very large presentation or correct the same error in multiple places in the slide. Given below are the steps to find and replace text in PowerPoint. Although, you can only use this function for text, the text itself can be present in a text box, in another shape, as a WordArt, in SmartArt or tables.
Finding Content
The following steps will show you how to find content in PowerPoint.
Step 1 −In the Home tab, under the Editing section click on Find.
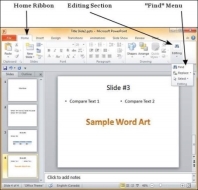
Step 2 − Type the text you want to search in the "Find what:" field.
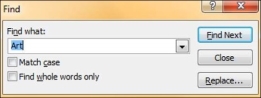
Step 3 − You can narrow your search by selecting "Match Case" - to find exact case match - and "Find whole words only" - to find whole words and not words where typed word is just a part of the word.
Step 4 − Press on "Find Next" to find the next occurrence of the search word.
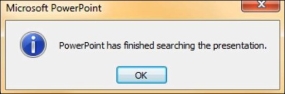
Step 5 − The Find dialog does not disappear after finding the first instance, so you can keep pressing "Find Next" multiple times till you reach the end of the search. At this point, you will receive a message from PowerPoint indicating the end of the search.
Replacing Content
Here are the steps to replace content in PowerPoint.
Step 1 −In the Home tab, under the Editing section click on the Replace button.
Step 2 − Type the text you want to replace in the "Find what:" field and the replaced text in "Replace with:" field
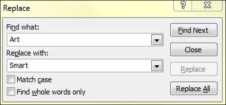
Step 3 − You can narrow your search by selecting "Match Case" - to find the exact case match - and "Find whole words only" - to find the whole words and not words where typed word is just a part of the word.
Step 4 − Press on "Find Next" to find the next occurrence of the search word. PowerPoint will show you the next occurrence and you can then click on "Replace" to replace the word. If you want to skip the occurrence, you can press "Find Next" again without pressing "Replace"
Step 5 − The Replace dialog does not disappear after finding the first instance, so you can keep pressing "Find Next" multiple times till you reach the end of the search. At this point, you will receive a message from PowerPoint indicating the end of the search.
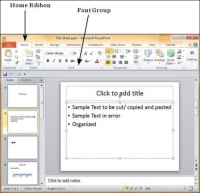
Font Management
One of the key elements of any good presentation is the text, hence managing the fonts in PowerPoint is vital to designing an impressive slideshow. PowerPoint offers extensive font management features to cover various aspects of fonts. The font management can be accessed from the Home ribbon in the Font group.
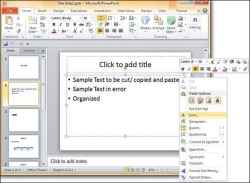
You can also access font management features by selecting a text box, right-clicking and selecting Font.
This opens up the Font dialog which contains all the font management features available under the font section in the Home ribbon.
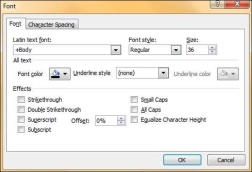
The table below describes various font management features available in PowerPoint.
S.No | Features & Description |
1 | Font Type Defines the font type like Arial, Verdana, etc. |
2 | Font Size Defines the font size. Besides, there are icons to increase and decrease the font size in steps in the Font group. |
3 | Font Style Defines font styles like Regular, Bold, Italics or Underlined. |
4 | Font Color Specifies the font color. |
5 | Font Effects Defines effects like shadow, strikethrough, subscript, superscript, etc. |
6 | Character Spacing Specifies character spacing like loose, tight, normal, etc. |
Setting Text Fonts
PowerPoint offers a wide range of pre-built fonts to choose from. Depending on the purpose of the presentation you may want to choose a more casual font or a formal one. This section will look at the steps to set the text fonts.
Step 1 − The default font in PowerPoint 2010 is Calibri.
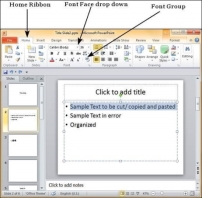
Step 2 − To change the text font, select that portion of text the font of which needs to be changed. If you select the entire text box or shape, the changes will apply to all the text in the selection. If you select specific text, the changes will apply to selection only.
Step 3 − In the Font group, under the Home ribbon, click on the font face dropdown.
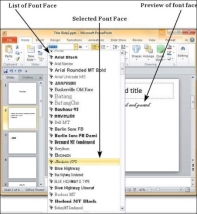
Step 4 − Scroll through the list of font faces to pick the one that suits your needs. As you move your cursor over the fonts, the selection will change accordingly to give you a preview.
Apply Formatting
One of the most powerful tools in Microsoft Office is the application of formatting feature. This feature basically lets you define the right format once and apply the same to a series of objects in the rest of the presentation or any other file. While working with large presentations or just working on slides for a long time, if you ever need to make a change in the style and want it applied across multiple content this is the tool to use.
The following are the steps to apply formatting to your presentation −
Step 1 − Select the content you want to copy the formatting from.
Step 2 − Go to the Clipboard group under the Home ribbon.
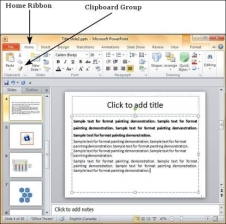
Step 3 − Click on the Format Painter icon.
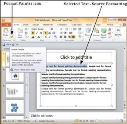
Step 4 − Select the content you want to format.
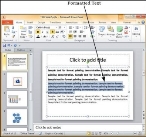
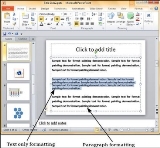
Here are some key aspects about the Format Painter −
Add & Format Tables
One of the most powerful data representation techniques is the use of tables. Table allows information to be segregated making it easy to read. PowerPoint has features that let you add tables in slides and also format them to enhance their visual effects. What's more, these tables are also compatible with Microsoft Excel, so you can basically take a spreadsheet or a section of a spreadsheet and paste it into a slide as a table.
The following steps will help you add a table in PowerPoint.
Step 1 − Go to the Tables group under the Insert ribbon.
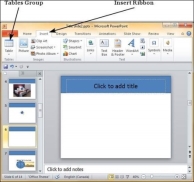
Step 2 − Click on the dropdown and select your table dimension from the matrix.
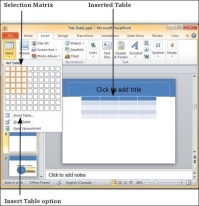
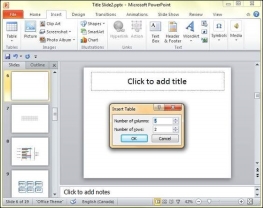
Step 3 − If you require more than 10 columns or 8 rows click on "Insert Table" to open the Insert Table dialog where you can specify the column and row count.
PowerPoint table is a simple table that does not support the mathematical features of an Excel spreadsheet. If you want to carry out some calculations, you can insert an Excel spreadsheet instead of a regular table.
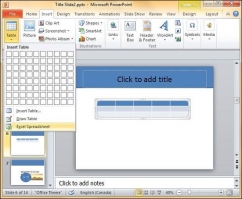
This will insert the spreadsheet in the slide and as long as the spreadsheet is selected, the ribbon at the top will be changed to an Excel ribbon instead of a PowerPoint one.
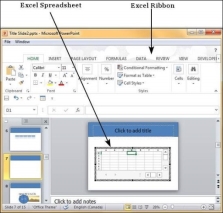
The PowerPoint table formatting features have been grouped under two ribbons: Design and Format. The sections below discuss the features under each ribbon. To access these ribbons, you must select the table first.
Table Design Features
We will now understand the table design features in PowerPoint.
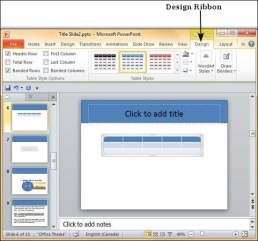
The following table shows the different table design features −
Feature | Sub Features | Description |
Table Style Options | Header Row | Adds a different shade to the first row to distinguish it. |
Total Row | Adds a different shade to the last row to distinguish it. | |
Banded Rows | Shades alternate rows in the table with the same color. | |
First Column | Adds a different shade to the first column to distinguish it. | |
Last Column | Adds a different shade to the last row to distinguish it. | |
Banded Columns | Shades alternate columns in the table with the same color. | |
Table Styles | Shading | Offers different shades to be added to selected table/ row/ column/ cell. You can pick from solid shade, texture, image or gradient shading. |
Border | Offers different border options for the table. You can edit the border color, thickness and style | |
Effects | Offers the ability to create table shadow or reflection. You can also create bevels for individual cells. | |
Word Art Styles | Text Fill | Allows you to change the color of the text within the table. |
Text Outline | Allows you to add an outline to the text within the table and change the outline color, weight and style. | |
Text Effects | Allows you to add special effects (like reflection, shadow etc.) to the text within the table. | |
Quick Styles | Contains a list of pre-defined Word Art styles that can be applied to the selected text within the table with a single click. | |
Draw Borders | Pen Style | Defines the style of the table border when you draw it. |
Pen Weight | Defines the thickness of the table border when you draw it. | |
Pen Color | Defines the color of the table border when you draw it. | |
Draw Table | Allows you to append new rows, columns, cells to existing table, split existing rows, columns or cells and draw brand new tables. | |
Eraser | Allows you to delete table borders and merge cells, rows or columns. |
Table Format Features
We will now understand the various table format features in PowerPoint.
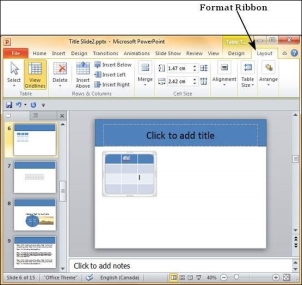
The following table shows the various table format features −
Feature | Sub Features | Description |
Table | Select | Allows you to select the entire table or the row(s) or column(s) depending on the position of your cursor. |
View Gridlines | Toggles the gridline display within the table. | |
Rows & Columns | Delete | Allows you to delete selected row(s) or column(s) or the entire table. |
Insert Above | Inserts a row above the row where the cursor is currently. If you haven't placed the cursor within the table, it adds a new row at the top of the table. | |
Insert Below | Inserts a row below the row where the cursor is currently. If you haven't placed the cursor within the table, it adds a new row at the bottom of the table. | |
Insert Left | Inserts a column to the left of the column where the cursor is currently. If you haven't placed the cursor within the table, it adds a new column to the left of the table. | |
Insert Right | Inserts a column to the right of the column where the cursor is currently. If you haven't placed the cursor within the table, it adds a new column to the right of the table. | |
Merge | Merge | Allows you to merge cells, rows or columns. This is enabled only if you have selected more than one cell, row or column. |
Split Cells | Allows you to specify the number of rows and columns into which the current section of cell(s) need to be split. | |
Cell Size | Height/ Width | Defines the height and width of the selected cell. Usually if you change these aspects for a single cell, the change affects the entire row or column too. |
Distribute Rows | Equalizes the height of all the rows to fit the current table height. | |
Distribute Columns | Equalizes the width of all the columns to fit the current table width. | |
Alignment | Horizontal Alignment | Allows you to align the selected text to the left, right or center of the cell. |
Vertical Alignment | Allows you to align the selected text to the top, bottom or middle of the cell. | |
Text Direction | Allows you to change the direction of the selected text within the cells. | |
Cell Margins | Allows you to define the margins within the cell. | |
Table Size | Height | Allows you to adjust the table height - it retains the relative heights of the individual rows while changing the overall table height. |
Width | Allows you to adjust the table width - it retains the relative widths of the individual columns while changing the overall table width. | |
Lock Aspect Ratio | Checking this box will ensure the ratio between the table height and width is maintained when one of these is changed. | |
Arrange | Bring Forward | Allows you to move the table up by one layer or right to the top. |
Send Backward | Allows you to move the table down by one layer or right to the bottom of the slide. | |
Selection Pane | Toggles the Selection and Visibility sidebar. | |
Align | Allows you to align the entire table with reference to the slide. |
Add & Format Charts
Charts are an effective way of representing data. Long list of confusing numbers can instantly become trends which can be spotted when they are captured as charts. PowerPoint supports the addition and formatting of charts.
Given below are the steps to add a chart to PowerPoint.
Step 1 − Go to the Illustrations group under the Insert ribbon.
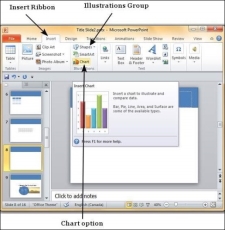
Step 2 − Click on the Chart option to open the Insert Chart dialog. You can choose the chart category and pick individual chart types from the list.
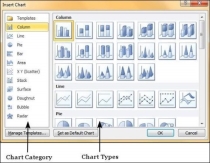
Step 3 − Select the chart type and click OK or double-click on the chart type to insert the chart in the slide.
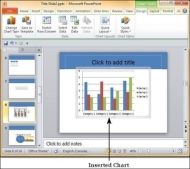
Step 4 − Along with the chart, an Excel spreadsheet is also launched. This spreadsheet is the source for your chart. You can change the category names, series names and individual values to suit your needs.
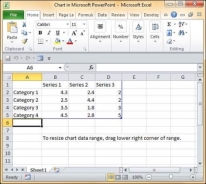
As you edit the values and the table in Excel the chart gets modified accordingly.
The PowerPoint chart formatting features have been grouped under three ribbons: Design, Layout and Format. The sections below discuss the features under each ribbon. To access these ribbons you must select the chart first.
Chart Design Features
We will now understand the various chart design features in PowerPoint.
The table given below describes the various chart design features −
Feature | Sub Features | Description |
Type | Change Chart Type | Changes the chart type retaining the same data. |
Save As Template | Saves current chart type as a template. | |
Data | Switch Row/Column | Transposes current excel data - this is enabled when you have the source data excel sheet open. |
Select Data | Changes the data range covered in the chart. | |
Edit Data | Changes the chart source data. | |
Refresh Data | Refreshes the chart to show the latest data. | |
Chart Layouts | Chart Layouts | Offers a list of predefined layouts which can be instantly applied to current chart with a single click. |
Chart Styles | Chart Styles | Offers a list of predefined styles which can be instantly applied to current chart with a single click. |
Chart Layout Features
We will now understand the various chart layout features in PowerPoint.
The following table describes the various chart layout features in PowerPoint.
Feature | Sub Features | Description |
Current Selection | Drop down | Shows the currently selected chart element. |
Format Selection | Shows the selection format dialog to update the selection. | |
Reset to Match Style | Discards all the chart customizations and matches the chart with the overall presentation theme. | |
Insert | Picture | Superimposes an image on top of the chart. |
Shape | Adds a shape to the slide. | |
Text Box | Adds a text box to the slide. | |
Labels | Chart Title | Defines the visibility, position and style of the chart title. |
Axis Titles | Defines the visibility, position and style of the axis titles. | |
Legend | Defines the visibility and position of the chart legend. | |
Data Labels | Defines the visibility and position of the data labels. | |
Data Table | Defines the visibility, position and format of the data table. | |
Axes | Axes | Defines the position and scale of axes. |
Gridlines | Defines the visibility and scale of axes. | |
Background | Plot Area | Toggles chart plot area - available only for 2D charts. |
Chart Wall | Toggles the chart wall - available only for 3D charts. | |
Chart Floor | Toggles the chart floor - available only for 3D charts. | |
3-D Rotation | Toggles the chart 3D rotation- available only for 3D charts. |
Chart Format Features
We will now understand the various chart format features in PowerPoint.
The following table describes the various chart format features in PowerPoint.
Feature | Sub Features | Description |
Current Selection | Drop down | Shows the currently selected chart element. |
Format Selection | Shows the selection format dialog to update the selection. | |
Reset to Match Style | Discards all the chart customizations and matches the chart with the overall presentation theme. | |
Shape Styles | Shape Fill | Offers different shades to be added to selected chart series item. You can pick from solid shade, texture, image or gradient shading. |
Border | Offers different border options for selected chart series item. You can edit the border color, thickness and style. | |
Effects | Offers the ability to add special effects to selected chart series item. | |
Word Art Styles | Text Fill | Allows you to change the color of the text within the chart. |
Text Outline | Allows you to add an outline to the text within the chart and change the outline color, weight and style. | |
Text Effects | Allows you to add special effects (like reflection, shadow etc.) to the text within the chart. | |
Quick Styles | Contains a list of pre-defined Word Art styles that can be applied to the selected text within the chart with a single click. | |
Arrange | Bring Forward | Allows you to move the chart up by one layer or right to the top. |
Send Backward | Allows you to move the chart down by one layer or right to the bottom of the slide. | |
Selection Pane | Toggles the Selection and Visibility sidebar. | |
Align | Allows you to align the entire chart with reference to the slide. | |
Group | Allows you to group multiple charts as one group object, or split a group object into individual charts. | |
Size | Height | Allows you to adjust the chart height. |
Width | Allows you to adjust the chart width. |
HYPERLINK
In Microsoft PowerPoint, there are times when users need to insert a link to a web page or a file in a network folder. Links can be useful for directing others who view the slides to a specific site, file, or linking to an external bibliography for a school assignment. Adding this type of link, called a hyperlink, can be done by following the steps below.
Inserting a hyperlink
How to highlight or select text.
4. In the menu bar or Ribbon at the top of the PowerPoint program window, click the Insert tab.
5. On the Insert tab, in the Links section, click the Link option.
6. In the Insert Hyperlink window, type in the web page address you want to link to in the Address text field. If you're not sure what the address is, go to the website in a web browser and copy the URL from your browser's address bar.
7. Once, you're done, click OK.
Tip
You can also press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+K to create a hyperlink out of any highlighted text.
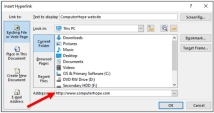
As you can see in the image below, the highlighted text is now a hyperlink, set to the Computer Hope website.
Tip
To set a link to a location in the same slide deck, click the Place in This Document option on the left side. Then, you can choose the location you'd like to link your highlighted text.
Printing Presentation
It is sometimes necessary that you share your slides with your audience in printed format before you begin presenting them so they can take notes. There are other times when you want to give your audience handouts with additional notes.
To print slides, you must go to the Backstage view under the File tab and click on the Print menu.
The following table describes the various printing options available in PowerPoint.
Main Settings | Options | Description |
Printing Slides | Print All Slides | Prints all the slides in the presentation. |
Print Selection | Prints just the selected objects. | |
Print Current Slide | Prints just the selected slide. | |
Custom Range | Defines the slides you want printed. | |
Slides | This is same as the Custom Range. | |
Print Layout | Full Page Slides | One slide per page. |
Notes Page | Slide and notes for every slide printed one below another - one slide per page. | |
Outline | Print Slide outline. | |
Handouts | Prints 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 6 or 9 slides per page - aligned vertically or horizontally. When you print handouts with 3 slides, you get the slide and the notes printed next to each other. | |
Collation | Collating Options | Prints slides in sequence or prints multiple copies of each slide one after another. |
Printing Color | Color | Selects color, greyscale or black & white printing options. Although you can select any color settings, the output will depend on the kind of printer you use. A non-color printer cannot print color slides. |
Saving Presentation
One of the most basic tasks in PowerPoint is being able to save your work; this is probably the most important task as well. There are many users who have burnt their fingers for not saving their work in time and losing hours of hard work. The following are the basic steps to save a presentation.
Step 1 − Click on the File tab to launch the Backstage view and select Save.
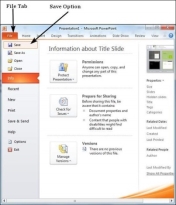
Step 2 − In the Save As dialog, type in the file name and click "Save".
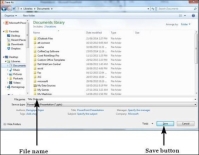
Step 3 − The default file format is .pptx. If you want to save the file with a different name, choose one of the file types from the "Save as type" dropdown list.
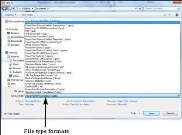
If you are working on an already saved file, the "Save" option in the Backstage view will directly save the file in the existing format with the existing name. If you want to change the format or filename of an existing file, use the Save As option instead.
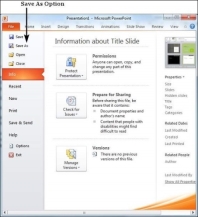
The commands for saving, opening, and closing presentations are on the File menu.
To save a new presentation:
3. Type a descriptive name in the File Name text box.
4. If necessary, choose a different disk or folder by navigating the dialog box as you would any standard Windows file dialog.
5. Click Save.
TIP
You can do this entire operation from the keyboard, if you prefer (it's often faster). Press Ctrl+S to invoke the Save As dialog box; if necessary, type the path into the File Name box (like c:\my documents\pres), press Enter, type the filename, and then press Enter.
To open an existing presentation:
The Open dialog box appears.
2. If necessary, choose a different disk or folder by navigating the dialog box as you would any standard Windows file dialog.
3. Click the name in the list and click Open.
To close the current presentation:
TIP
The names of recently opened presentations appear at the bottom of the File menu. To open one of these files, just click the name.
When saving presentations, don't use names like "My Presentation." Instead, name your files so you will remember what they contain. Presentation filenames can be many characters long and contain several words.
Key takeaways:
References-