Unit 1
Introduction
Entrepreneurship refers to the process of creating a new enterprise with an innovative idea and bearing any of its risks, with the view of making the profit. It is an act of seeking investment and production opportunity, developing and managing a business venture, so as to undertake production function, arranging inputs like land, labour, material and capital, introducing new techniques and products, identifying new sources for the enterprise.
Entrepreneurship is a process of actions of an entrepreneur who is a person always in search of something new and exploits such ideas into gainful opportunities by accepting the risk and uncertainty with the enterprise. Entrepreneurship involves three aspects-
Some examples of entrepreneur are Bill Gates (Microsoft), Warren Buffet (Hathaway), Gordon Moore (Intel) Steve Jobs (Apple Computers), Jack Welch (GE) GD Birla, Jamshedji Tata (TATA), Dhirubhai Ambani (Reliance), Ritesh Agarwal (OYO) etc.
The figure 1 shows the concept of entrepreneurship-
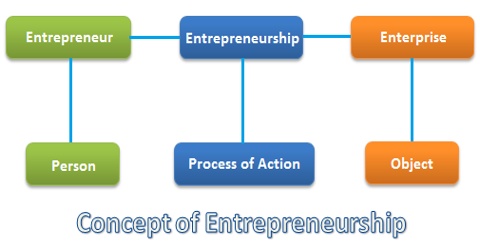


Figure 1: Concept of Entrepreneurship
Some of the essential characteristics of entrepreneurship are-
The steps involved in entrepreneurship are depicted in figure 2-
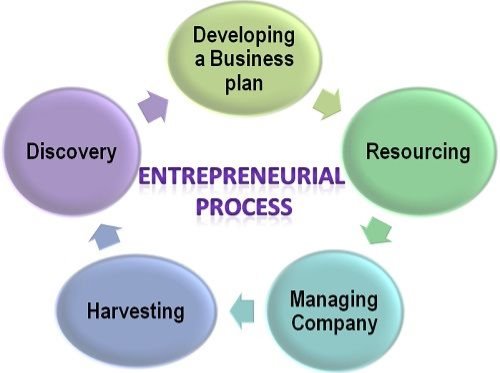
Figure 2: Entrepreneurship Process
Elements of entrepreneurship
The key elements of entrepreneurship are depicted in the figure 3,
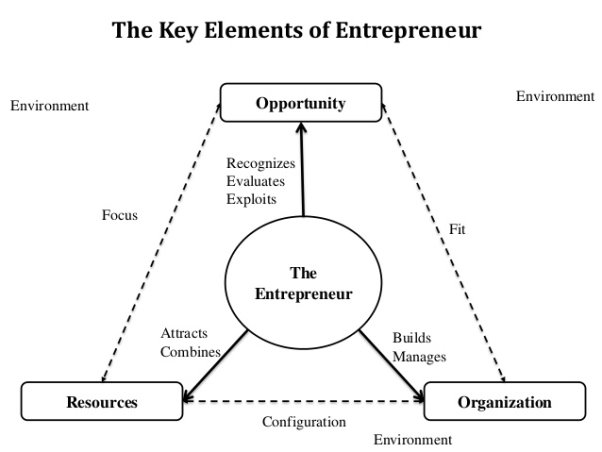
Figure 3: Key elements of entrepreneurship
The entrepreneur innovate ideas to exploit opportunities available in the market. The idea may be for new product, service, technology, production technique, marketing strategy, etc.
2. Resourcing:
In this step, the entrepreneur identifies the sources from fund, human resources and other material relevant resources.
3. Risk-Taking
Risk is inherent in entrepreneurship stagnate a business and excessive impulsive risk-taking can cause losses. But the willingness of an entrepreneur to take risks gives them a competitive edge in the economy.
4. Vision
Vision or foresight helps entrepreneurs to set out short term and long term goals for their business and also plan ways to achieve these objectives.
5. Organization
In entrepreneurship, an entrepreneur must be able to manage and organize his finances, his employees, his resources, etc. So his organizational abilities are one of the most important elements of entrepreneurship.
Determinants of entrepreneurship
The determinants of entrepreneurship are-
Central Govt. initiated different schemes like start up India, Made in India, Skill India, Mudra loan etc. for the promotion of entrepreneurship from time to time. Such schemes encourages youths for entrepreneurship by utilizing their skills and available natural resources.
2. The Rise of Technology:
The advancement of information technology provides facility for worldwide communication and easy accessibility of information. The potential entrepreneurs can collect information about potential market, competition, availability of raw materials etc. It promotes virtual businesses in the areas like e-commerce shopping sites, e-education, development of application software etc. For example, Byju, unacademy, facebook, flipkart etc.
3. Female Entrepreneurs:
The entrepreneurial wave is also being driven by women entrepreneurs who are carving a niche for themselves. Start-ups like Zivame, Kaaryah, Your Story and POPxo have become successful ventures.
4. Availability of resources:
Availability of resources in a locality also encourages local enthusiastic people to utilize the same for starting business venture. Different types of village and home based industries like handloom, handicraft, food processing industry etc. provides livelihood to a significant number of families in rural and semi urban areas of the country.
6. Attitude of self-independency:
Some people always interest to become self-independent rather than serving any private or public company or Government. Such people start their own business with innovative ideas and become boss of their own.
6. Education:
Educational institutions also play a significant role in promotion of entrepreneurship by making them aware and skilled to start a business venture. In educational institutions knowledge is provided about the entrepreneurship process, its pros and cons in different undergraduate and post graduate courses like B.com, M.com, BBA, MBA etc.
7. Availability of information:
The easy accessibility of information helps the entrepreneurs to get information about market accessibility, competition in the market, sources of funds, raw materials, cheap labour and other material information.
8. Accessibility to credit:
Accessibility to finance/credit is important to implement the plan into business venture. Banks and financial institutions extends credit under different schemes of Government like MUDRA loan, start-up India, Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme for Micro and Small Enterprises etc.
CHALLENGES FOR INDIAN ENTREPRENEURS
1. Raising Funds for the Business:
The challenge for any start-up lies in raising funds for the business. To do so, they need to have a dependable business plan and a strategy on how they want to enter the market. Start-ups get funds from venture capitalists once they have convinced them about the venture’s potential for success.
2. Knowledge on How to Run a Business:
Lack of skill and knowledge is a threat to entrepreneurship. Various business schools have started entrepreneurship courses to answer the requirements of interested students who seek to become an entrepreneur. These courses help the students get their expectations right and prepare themselves for a career in entrepreneurship.
3. Keeping Up with Technology:
This point is important for start-ups in the technology sector. It is important for them to keep track of the latest technology and stay ahead of the curve. These days, technological innovations are happening every day leading to technology getting obsolete quickly. They need to keep on improving their products and give new and innovative products to their customers. Innovations need to be useful for customers. They need to have good research backing their product launches. If the product does not answer any need gap in the market, then it will not be successful in the market even if there is cutting edge technology behind it.
4. Quality of Human Resources:
Any business’ success is dependent on the people who work for it. It is critical to have the right mix of people. These people should be trained for their job profiles. For example, a marketing manager should understand the industry and its customers and accordingly plan marketing campaigns. They should also have practical experience in performing their jobs properly. Additionally, they should have the right attitude and keen interest in doing their work to the best of their abilities.
5. Market competition:
The new entrepreneurs face competition in the market from existing service providers or producers. To compete and overcome with this competition the new business venture must provide quality service/product with reasonable price.
6. Market linkage:
At the initial stage the entrepreneurs face hurdles in getting market linkage for their products or service. Different fairs and exhibitions are organized by the government from time to time to provide market for the products of small scale industries.
Importance
Some of the significance of entrepreneurship is -
Creative response of entrepreneurship to the society’ problems and at work
1. Entrepreneurial thinking challenges tradition:
The most successful social entrepreneurs challenge themselves to be open-minded and approach problems with a filter that is void of established tendencies and stigmas. They are unconventional thinkers, not limited by the constraints of the systems in place, but instead challenge those systems with fresh ideas and techniques. Their ability to challenge commonly assumed principles or beliefs ushers in a completely new way of thinking. For example, Different e-learning education app like unacademy, Byju and other online communication platform like zoom, google meet etc. solves the problem of access to education to a great extent during the covid 19 pandemic period.
2. Entrepreneurial thinking combines creativity with market intelligence:
Entrepreneurial thinking naturally embodies creativity, a boundless imagination as to what is possible. But the most successful entrepreneurial endeavors balance creative solutions with comprehensive market intelligence. Knowledge of the problem and contributing factors empowers entrepreneurs to blend dissimilar concepts from different contexts and craft a new, differentiated or completely unique strategy.
3. Entrepreneurial thinking practices humility:
Humility is a core component of entrepreneurial thinking. It drives even the boldest leaders to challenge their own established tendencies and recognize their potential for continual improvement. Successful entrepreneurs strive for perfection, obsess over learning and iteration and recognize that they can always do better.
4. Entrepreneurial thinking embraces risk and failure:
The social sector has never taken failure lightly – funding protocols, public perception and the significance of the problems being addressed have contributed to a risk-adverse environment. But ideas that drive dramatic change are inherently risky propositions and they present the potential to fail. Entrepreneurial thinking acknowledges that uncertainty and accepts it as a necessary driver of progress.
5. Increased accountability and measurability:
Social entrepreneurs are accountable to their clients, employees, volunteers, investors and donors. Organizations measure social value using both quantitative metrics and qualitative data. Methods such as the social return on investment demonstrate the social value that is created for every dollar invested or donated to the organization. Thus, a back-to-work organization can measure money saved in welfare or Medicaid costs for each person who receives full-time employment, or a group that works with at-risk youth can measure the number of people who likely would have dropped out of high school but graduated because of the program, and the average difference in income made by high school graduates versus high school dropouts.
6. Sustainability:
Organizations often use a triple bottom line that measures the impact of the organization on people, the planet and profit. Even non-profit organizations benefit from financial sustainability, as they can fund new programs with profits from the venture and spend less time and resources on fundraising activities.
Key takeaways-
Dimensions of entrepreneurship
Intrapreneurship: The term intrapreneurship refers to a system that allows an employee to act like an entrepreneur within a company or other organization. Intrapreneurs are self-motivated, proactive, and action-oriented people who take the initiative to pursue an innovative product or service. An intrapreneurship creates an entrepreneurial environment by allowing employees to use their entrepreneurial skills for the benefit of both the company and the employee. For example, Ramzi Haidamus, the president of Nokia Technologies, is often considered an intrapreneur because of his initiatives with the company. It has the following characteristics-
a) Technopreneurship:
Technopreneurship allows the entrepreneurs to innovate and implement idea by using technology. The process of technopreneurship is a combination of technological advancements and entrepreneurial skills. A person who is engaged in technopreneurship creates a product or solution that uses technological solutions to change the way of doing something in an orthodox way. It improves how we have done something before and how it has to be done in the coming future. Some examples of successful technopreneurs are Bill Gates (Microsoft), Sergey Brin and Larry Page (Google), Jack Dorsey (Twitter), Steve Jobs (Apple), Kevin Systrom (Instagram), and so on.
b) Cultural entrepreneurship
Cultural entrepreneurship is an emerging discipline that examines how cultural products (such as art, theater, and literature) and cultural activities (like sports, music, food, and film events) have an impact on the growth of local, national, and global economies. Cultural Entrepreneurs are cultural change agents and resourceful visionaries who organize cultural, financial, social and human capital, to generate revenue from a cultural activity. Their innovative solutions result in economically sustainable cultural enterprises that enhance livelihoods and create cultural value and wealth for both creative producers and consumers of cultural services and products.”
c) International entrepreneurship
International entrepreneurship is the process of entrepreneurship that engaged in doing business with cross border countries like import-export, international service like banking, insurance, telecommunication etc.
d) Netpreneurship
It refers to the process of entrepreneurship that start business venture with new ideas by using internet. For example, youtuber, unacademy etc.
e) Ecopreneurship
Ecopreneurship is a term coined to represent the process of principles of entrepreneurship being applied to create businesses that solve environmental problems or operate sustainably. Such entrepreneurs generally started business venture to sustain ecology and environment. For example, establishment of resort, eco camp, eco part, local artisans producing furniture from bamboo, cane, decorative items from clay, stone etc.
f) Social entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurship uses business to offer new ideas for wide-scale social and environmental impact. Social entrepreneurship unites the passion of a social mission with an image of business-like discipline, innovation, and determination. Many social entrepreneurs launch whole new ventures applying innovative and often risk-taking approaches to create scalable solutions, which includes inventing new products and services. Others join existing social enterprises aligned with their interests and passions. For example, AMUL (Anand Milk Union Limited) Social Entrepreneur: Dr. Verghese Kurien Grameen Bank Social Entrepreneur: Muhammad Yunus.
Key takeaways-
References:
1.Enterpreneurial Development by S.S. Khanka
2.Entrepreneurship Development and Small Business Enterprises by M. Charantimath