UNIT-I
Financial System
Introduction
The country's economic development is reflected in the progress of various economic sectors, which are broadly divided into the corporate, public, and domestic sectors. Some places and people have more money, while others are shorter. The financial system or financial sector acts as a mediator, making it easier for funds to flow from residual to arrears. The financial system consists of various institutions, markets, regulations and laws, practices, financial managers, analysts, transactions, claims and liabilities.
The financial system consists of a set of sub-methods for financial institutions, financial markets, financial instruments and services that support capital formation. Provides how you save money that is converted into cash.
The term "system" in the term "financial system" means a set of complexes, closely related or related institutions, agents, mechanisms, markets, transactions, claims, and liabilities in the economy. The financial system prefers money, debt and finance. The three words are closely related, but slightly different from each other. The Indian financial system consists of financial markets, financial products and financial intermediaries.
Description of the Financial System
The financial system acts as a liaison between rescuers and investors. It facilitates the flow of funds from the residual area to the residual area. She is worried about money, debt and finances. These three parts are closely related and interdependent.
A financial plan can be defined as a set of institutions, methods, and markets to promote savings and efficiency. It has people (saver), mediators, markets, and savings users (investors).
In Van Horn's world, "the financial system is making good use of money in the economy for the end user, either through investment or the use of real assets."
According to Prasanna Chandra, "The financial system is made up of a variety of institutions, markets and related systems and provides key ways to turn savings into investment."
Therefore, a financial system is a complex and closely related set of financial institutions, financial markets, financial instruments, and services that facilitate money transfers. Financial institutions collect funds from providers and provide these funds to those who request them. Similarly, financial markets are required to transfer money from depositors to mediators and mediators to investors. In short, a financial system is a way of saving money and converting it into money.
Characteristics, importance, and function of the Indian financial system
- Issuing and collecting deposits.
- Loan supply from a pool of collected money.
- Implementation of financial transactions.
- Drive the growth of equity and other financial markets.
- Set up a legal commercial substructure.
- Providing financial and consulting services.
- Allows adaptation of portfolios of existing assets.
- Opportunity and risk allocation.
- It builds a connection between depositors and investors.
- By expanding its scope, we will expand the depth and breadth of our finances.
- It is responsible for the creation of capital.
- Add time value to assets and money.
- Set up the payment structure and the entire system.
- Allocate and dissipate economic resources.
- To maintain economic stability of the country and markets.
- Create a market where you can judge your investment performance.
- Components of Indian financial system
There are five main components:
1. Financial institution
- Their role is to act as an intermediary between lenders and borrowers.
- Lenders' savings are collected through various commercial markets.
- These can turn risky financing into a safe investment.
- Short-term debt can be turned into longer-term investments.
- These allow you to compare comparable large deposits and loans with small deposits and loans because of their uniform face value.
- These provide a balance between the recipient of the loan and the depositor of the amount.
There are two main types of financial institutions.
a. Banking or deposit handling institution
- Their role is to make money from the masses.
- Interest is paid on these deposits made by people.
- The loaned money is offered as a loan to those who need it.
- Interest will be charged on these loans given to those who need it.
- Examples are banks and other co-operatives.
b. Non-banking or non-depositing institution
- Their role is to sell commercial and financial goods and products to those who visit them.
- These are based on the provision of insurance, investment trusts, brokerage transactions and more.
- These examples primarily include businesses.
These have three additional categories:
- Regulation: Management and institutions that regulate and overlook commercial and financial markets. Example – RBI, IRDA, SEBI, etc.
- Intermediate: An institution that provides financial counselling and supports by providing loans and the like. Example – PNB, SBI, HDFC, BOB, Axis Bank.
- Non-Intermediate: These institutions support the finances of corporate visitors. Example – NABARD, SIDBI, etc.
2. Financial assets
These objectives are to provide convenient trading of securities in the commercial and financial markets, based on the requirements of credit seekers.
These are goods or products sold in the financial markets. Financial assets include:
- Call Money: Without guarantee, this is a one-day loan that will be repaid the next day.
- Notice: Without guarantee, this is the rent for a loan of 1 to 14 days.
- Term Money: When a certain amount of money deposited exceeds the maturity of 14 days.
- Treasury Short Term Securities: These belong to the government in the form of bonds or debt securities as they have a maturity of less than one year. These are purchased in the form of government T-Bills, which are received as government loans.
- Certificate of Deposit: This works in the form of electronic funds that remain in a particular bank for a period of time.
- Commercial Paper: A product used by a company that is unsecured despite short-term debt.
3. Financial services
- Their primary purpose is to provide counselling to visitors regarding the purchase or sale of real estate, transactions, transactions, loans, and investment permits.
- They also ensure the effectiveness of the investment and the placement of funding sources.
- These are usually picked up by asset and liability management companies.
Financial services are also included in them:
Banking Services: The functions that banks perform, such as providing loans, accepting debits, distributing credit or debit cards, opening accounts, and granting checks, are some of these services.
Insurance Services: These include services such as providing insurance, selling insurance, and brokerage transactions.
Investment Services: These services include oversight and management of investments, assets and deposits,
Forex Services: These include foreign currency exchange, foreign exchange, and foreign money transfers.
4. Financial market
These are the markets where bonds, stocks, money, investments and assets are traded and exchanged between buyers.
There are four main types of financial markets:
a. Capital market
- These deal with transactions and transactions that take place in the market.
- These are done for a year.
- These are the three main types:
- Corporate securities market
- Government securities market
- Long-term loan market
b. Financial market
- These are for short-term investments.
- They are built by governments, banks, and other institutions.
- This market is based on low-risk wholesale debt with transparent products and formats.
It has two main types:
a) organized money market
b) Unorganized money market
c. Forex market
- A highly developed market that handles several currencies.
- It is responsible for the foreign remittance of funds.
- This is based on the foreign currency rate.
d. Credit Market
- This includes both short-term and long-term loans.
- It is often given to both individuals and organizations.
- These are granted by some banks, financial institutions, non-banks and more.
5. Money
This is an important exchange that can be used to purchase goods and services. It also can act as a store useful. It is evenly accepted everywhere.
It facilitates trading, especially instant daily purchases. It serves as a verifiable record in the socio-economic context.
Conclusion
The above article on Indian financial system raises awareness about Indian financial system. It helps you prepare for a competitive exam.
It also encourages people to know more about their country's economic function and allows them to make useful decisions regarding various investments.
The role and importance of financial planning in economic development
- Connecting savers with investors. This helps to collect and allocate money efficiently and effectively. It plays an important role in economic development through the savings process. This process of saving money is called capital construction.
- It helps to monitor the performance of companies.
- Provides a way to manage uncertainty and risk control.
- Provides a way to transfer resources across local boundaries.
- Provides portfolio preparation skills (provided by financial markets and financial intermediaries).
- It helps to reduce transaction costs and increase profits. This will encourage people to save more.
- Guides the fundraising process.
- It helps to simplify the process of financial depth and expansion. Deepening funding means increasing the value of financial assets to GDP, and expanding finance means increasing the number and types of participants and methods.
- In order to achieve economic development, a financial system that encourages people to save by providing attractive interest rates is important. These funds are for the borrowing of various business concerns related to production and distribution.
- It helps to monitor business performance
- Connecting savers with investors. This process is known as capitalization
- It helps to reduce transaction costs, increase profits and encourage people to save more
- It helps government to make monetary policy decisions
In short, the financial system helps to accelerate economic development. We will contribute to growth through technological advancement.
The function of the financial system
The country's financial system serves certain key functions for the country's economic growth. The key functions of the financial system are outlined below.
1. Savings Work: An important function of a financial plan is to promote savings and invest in productive activities. With a financial plan, savings are converted into cash.
2. Liquidity Activity: The most important function of a financial system is to provide financial and financial resources in the production of goods and services. A financial asset is an asset that can be easily converted into cash or cash without losing its value. All financial system activities are related to cash payments, which can be the supply of goods or transactions.
3. Payment function: The financial system provides the most convenient payment method for goods and services. Checks and credit card schemes are the easiest ways to pay off in the economy. Transaction costs over time are greatly reduced.
4. Risk Work: Financial markets protect against life, health and income risks. These guarantees are available through the sale of life insurance, health insurance and property insurance.
5. Information Service: The financial system makes available price-related information available. This is an important resource for those who need to make financial and financial decisions. Financial markets disseminate information that enables participants to develop knowledgeable ideas about investing, withdrawing, renewing or retaining certain assets.
6. Transfer function: The financial system provides a means of transferring resources across local boundaries.
7. Transformation Work: A financial plan responsible for developing and delivering financial resources / equipment and reconstruction practices for existing assets, services, etc. To meet the new needs of lenders and investors. (Financial engineering and new engineering).
8. Other features: Helps you select funding projects and regularly evaluate the effectiveness of those projects. It also facilitates the fundraising process by combining savings and the need for investment.
Key takeaways:
- The financial system consists of people such as borrowers and lenders as well as institutions such as banks, stocks and insurance companies that are involved in the transfer of funds and assets.
- It empowers investors to grow their wealth and wealth, thereby contributing to economic development.
- It operates for a variety of economic purposes, including acting as a payment system, providing savings mechanisms, providing funding to financial markets, and protecting investors from unforeseen financial risks.
- A sustainable financial system operating at corporate, national and international levels requires a specific set of rules written under various government policies.
- A financial system is a set of international, regional, or company-specific institutions and practices used to facilitate currency exchange.
- Financial systems can be organized using market power, intermediate planning, or both your hybrid.
Financial Assets
Meaning of Financial Assets
A financial asset is a cash or cash equivalent used for production or consumption, or for the further creation of an asset. Cash, bank deposits, stocks, corporate bonds, gold, investments in land and buildings, and contractual rights to receive cash or other financial assets are called financial assets.
Classification of Financial Assets
Financial assets are categorized in two ways
1. Based on marketability
2. Based on nature
Classification of financial assets based on marketability
1. Marketability – Tradeable financial assets are called marketable financial assets. These include stocks, government securities, bonds, investment trusts, UTI units, and bearer bonds.
2. Non-marketable – Financial assets that cannot be bought or sold are called non-marketable financial assets. They include bank deposits, provided funds, LIC policies, corporate deposits and post office certificates.
Classification of financial assets based on nature
1. Money or cash assets – coins, banknotes, bank deposits
2. Debt assets – corporate bonds and bonds
3. Equity Assets – Equities and Preferred Stock
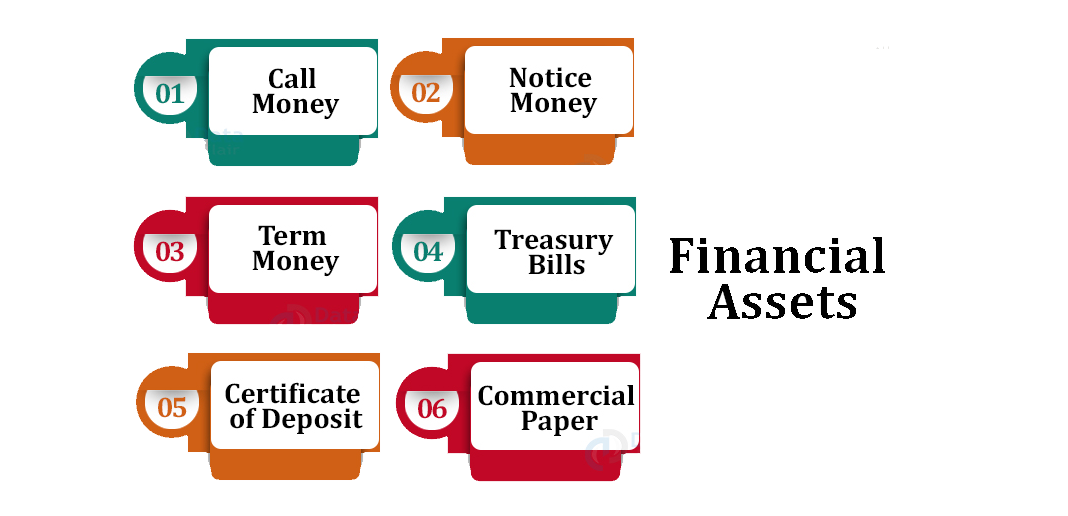
- Call Money: Without guarantee, this is a one-day loan that will be repaid the next day.
- Notice: Without guarantee, this is the rent for a loan of 1 day or more and less than 14 days.
- Term Money: When a certain amount of money deposited exceeds the maturity of 14 days.
- Treasury Short Term Securities: These belong to the government in the form of bonds or debt securities as they have a maturity of less than one year. These are purchased in the form of government T-Bills, which are received as loans from the government.
- Certificate of Deposit: This works in the form of electronic funds that remain in a particular bank for a period of time.
- Commercial Paper: A product used by a company that is unsecured despite short-term debt.
Financial Markets
What's a monetary market?
Financial markets, because the call implies, are a type of market that offers a way of purchasing and promoting property which includes bonds, shares, forex and derivatives. They are frequently cited by means of one-of-a-kind names, along with "wall street" and "capital markets," but they all have the same meaning. Without a doubt put, organizations and traders can every go to the monetary markets to elevate money, develop their business and make extra money.
To be greater explicit, imagine a financial institution where an character holds a financial savings account. Banks can use their cash and the money of different depositors to lend to different individuals and groups and claim interest.
Depositors themselves also earn via watching their money develop via the interest paid on it. Consequently, banks act as financial markets that advantage each depositor and borrowers.
Sorts of monetary markets
There are so many financial markets and that they vary in size. Has as a minimum one economic market. Some are small and others are across the world known, together with the new stock alternate, which trades trillions of greenbacks each day. There are several varieties of economic markets here.
1. Stock market
The stock market trades shares owned via public corporations. Every inventory has a charge, and investors make money with that stock once they perform nicely within the market. Buying stock is simple. The actual venture is selecting the proper shares to make money for buyers.
There are numerous indicators that investors can use to screen inventory marketplace tendencies, consisting of the Dow jones commercial average (djia) and the s & p 500. While a stock is sold at a decrease charge and sold at a higher charge, the investor gets from the sale.
2. Bond marketplace
The bond marketplace provides an opportunity for groups and governments to comfortable investment to fund tasks and investments. Inside the bond market, an investor buys a bond from an enterprise and the organisation returns the quantity of the bond plus interest in the agreed duration.
3. Commodity market
Commodity markets are wherein investors and investors purchase and sell natural assets and commodities including corn, oil, meat and gold. Unpredictable costs create a selected marketplace for such assets. There is a commodity futures market that has already identified the fees of commodities introduced at some future time and is sealed nowadays.
4. Derivatives marketplace
Such markets include valuable derivatives or contracts based totally available on the market value of the property traded. The above commodity marketplace futures are examples of derivatives.
Marketplace function
The role of economic markets in monetary achievement and electricity cannot be underestimated. Here are 4 crucial functions of economic markets
1. Leverage financial savings for extra efficient use
As cited in the instance above, a financial savings account that carries cash should no longer just maintain the money in a secure. Consequently, economic markets consisting of banks open it up to individuals and corporations that need a loan, student mortgage, or enterprise mortgage.
2. Determine the fee of the safety
Traders purpose to make a take advantage of their securities. However, not like items and services whose prices are determined through the legal guidelines of deliver and call for, securities costs are decided via monetary markets.
3. Liquidate financial property
Consumers and dealers can determine to alternate their securities at any time. They could use economic markets to promote securities and invest as needed.
4. Reduce transaction expenses
Inside the monetary markets, you may get loads of information about securities without spending.
The significance of financial markets
There are numerous matters the economic markets can do, including:
- Monetary markets provide an area for participants, which includes investors and borrowers, to receive honest and appropriate remedy, irrespective of size.
- They offer get admission to capital for people, corporations, and governmental corporations.
- Financial markets offer many employment possibilities that help lower the unemployment price.
Classification:
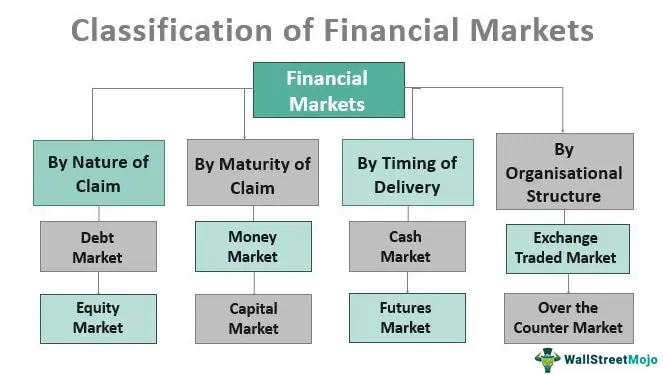
A financial market is a market in which financial assets such as stocks, bonds, corporate bonds, and commodities are created and traded, and is known as a financial market. Financial markets act as an intermediary between fund seekers (generally companies, governments, etc.) and fund providers (generally investors, households, etc.). It mobilizes funds among them and helps allocate the country's limited resources. Financial markets can be divided into four categories
- Depends on the nature of the claim
- By maturity of claims
- Depending on the timing of delivery
- By organizational structure
Let's elaborate on each –
# 1-Depends on the nature of the claim
Markets are categorized by the type of claim the investor has for the assets of the entity in which the investor has invested. There are two main types of claims: fixed claims and residual claims. There are two types of markets, based on the nature of the claim.
Bond market
The bond market is the market in which bonds such as corporate bonds and bonds are traded between investors. There is a fixed charge for such items. That is, those charges on a company's assets are limited to a certain amount. These goods generally carry a coupon rate commonly known as interest, which remains fixed for a period of time.
Stock Market
Equity products are traded in this market. Equity, as the name implies, refers to the owner's capital in the business, and therefore has a residual claim, which means that everything remaining in the business after repayment of fixed liabilities belongs to the shareholders. Regardless of the face value of the shares they hold.
# 2 – Depends on billing maturity
When making an investment, the amount of investment depends on the duration of the investment, so the duration plays an important role. Duration also affects the risk profile of your investment. Short-term investments are less risky than long-term investments.
There are two types of markets, based on the maturity of the claim.
Financial market
For short-term funds traded by investors who plan to invest within a year. This market deals with monetary assets such as government bonds, commercial paper and certificates of deposit. The maturity of all these products does not exceed one year.
Due to their short maturity, these products are generally in the form of interest, which is less risky for investors and provides a reasonable rate of return.
Capital Market
A market in which products with medium- to long-term maturities are traded. This is the largest exchange of funds market and helps companies access their funds through equity capital, preferred equity capital and more. It also provides access for investors to invest in and become a party to the company's equity capital. The profit that the company earned.
There are two industries in this market.
Primary Market
A market in which a company first lists securities, or a market in which an already listed company issues new securities. This market involves trading between companies and shareholders. The company receives the amount paid by the shareholders for the major issues. There are two main types of products for the primary market. Initial public offering (IPO) or further initial public offering (FPO).
Liquidity-When a company lists a security, it becomes available for trading on the exchange between investors. Markets that facilitate such transactions are known as secondary or stock markets.
In other words, it is an organized market where securities are traded among investors. Investors include individuals and merchant bunkers. Secondary market transactions do not affect a company's cash flow position, as receipts or payments on such exchanges are settled between investors without the involvement of the company.
# 3-Depending on the timing of delivery
In addition to the above factors such as duration and nature of billing, there is another factor that distinguishes the market into two parts: the timing of delivery of securities. This concept is generally prevalent in the secondary or stock markets. There are two types of markets based on the timing of delivery:
Cash Market
In this market, transactions are settled in real time and investors are required to pay the full amount of their investment through their own funds or borrowed capital commonly known as margin. This is allowed in the current holdings. Account.
Futures Market
In this market, settlement or delivery of securities or commodities will take place in the future. Transactions in these markets are usually settled in cash rather than delivered. Total amount of assets to trade in the futures market you don't have to pay. Rather, margins up to a certain percentage of the asset's value are sufficient for trading assets.
Key takeaways:
- A monetary asset is a liquid asset that represents and derives price from a organization's claim of ownership or contractual proper to future payments from the organization.
- The value of a economic asset can be based on the tangible or real belongings of the underlying asset, however market supply and demand additionally influences its fee.
- Equity, fixed earnings and coins financial markets widely talk to any market wherein securities are traded.
- There are different varieties of economic markets together with foreign exchange, money, stocks and bond markets.
- These markets might also include belongings or securities which are listed on regulated exchanges or traded over-the-counter (otc).
- Economic markets alternate all forms of securities and are critical to the smooth operation of a capitalist society.
- Failure of economic markets can cause economic turmoil which include recession and unemployment. CDs and financial institution deposits are examples of financial assets.
Preface
A financial instrument is defined as an individual / party contract that retains its monetary value. They can be created, traded, settled, or modified according to the requirements of the parties involved. Simply put, an asset that holds capital and can be traded on the market is called a financial instrument.
Examples of financial instruments include checks, stocks, stocks, bonds, futures and options contracts.
Understand Financial Products
Financial products can be divided into two main types: derivative products and cash products.
Derivative products can be defined as products whose characteristics and values can be derived, among other things, from underlying assets such as interest rates, indices and assets. The value of such equipment can be derived from the performance of the underlying components. You can also link to other securities such as bonds and stocks.
Cash products, on the other hand, are defined as products that are easily transferable and valuable in the market. Some of the most common examples of cash products are deposits and loans that lenders and borrowers need to agree on.
Other classifications
Financial instruments can also be categorized based on asset class, that is, equity-based and debt-based financial instruments.
- Equity-based financial instruments include securities such as equities / equities. Exchange-traded derivatives such as stock futures and stock options also fall into the same category.
- Debt-based financial products, on the other hand, consist of short-term securities with a maturity of one year or less, such as commercial paper (CP) and government bonds (T-bill).
- Cash products such as certificates of deposit (CD) also fall into this category. Similarly, exchange-traded derivatives such as short-term interest rate futures fall into this category.
- Securities such as fixed income fall into this category because long-term debt-based financial instruments have a maturity of more than one year. Listed derivatives include fixed income futures, and options are another example.
How to record Financial Products
On the accounting side, financial products can be a bit complicated. How they are recorded depends on whether the company buys or issues them, and of course it is related to the type of financial instrument as described above.
If a financial instrument involves an investment such as the sale of stocks, bonds, or credits (accounts receivable), these are considered financial assets. If an instrument has a balance of accounts payable or long-term loans, they are considered financial liabilities.
In accounting, bonds and receivables are considered assets, long-term loans and receivables are considered liabilities, and capital is considered capital. Derivatives are also financial products.
Issuance of Financial Products
When a company issues a financial instrument, this transaction is recorded as an asset in accounts receivable.
Purchase of Financial Products
If the business or party is on the purchaser side of a transaction involving financial instruments, this is recorded as a liability in accounts payable. Buyers and sellers are unknown to each other because transactions involving financial instruments can be done anonymously.
Weakness of Indian Financial System
After the introduction of the plan, rapid industrialization took place. It in turn led to the growth of the corporate and government sectors. Many innovative financial products have been introduced to meet the growing requirements of government and industry. What's more, there has been a rapid growth of financial intermediaries to meet the ever-growing financial requirements of different types of customers. Therefore, India's financial system is more developed and integrated today than it was 50 years ago. Still, there are some weaknesses, as listed below.
Lack of coordination between different financial institutions: There are numerous financial institutions. Most of the important financial institutions are owned by the government. At the same time, the government is also the governing authority for these institutions. In this situation, adjustment issues arise. Due to the large number of institutions in India's financial system, there is a lack of coordination in the operation of these institutions.
Exclusive Market Structure: In India, some financial institutions are so large that they have a monopoly market structure in their financial system. For example, most of the life insurance business is in the hands of LIC. UTI has more or less dominated the investment trust industry. The weakness of this major structure is that it can lead to inefficiencies or mismanagement of their work, or lack of effort to mobilize national savings. Ultimately, it will slow the development of the country's own financial system.
Development Bank Advantages in Industrial Finance: Development Banks form the backbone of India's financial system, which occupies an important position in the capital markets. India's industrial lending today is primarily through financial institutions established by the government at both the national and regional levels. These development banks only function as distributors, as they get most of their funding from their sponsors. Thus, they fail to mobilize national savings. This will be a serious bottleneck that impedes the growth of the country's efficient financial system. For foreign industries, institutional finance has been the result of institutionalization of personal savings through media such as banks, LIC, pension and fund funds, and unit trusts. But as far as industrial finance is concerned, they do not play a very important role in India's financial system. Recently, however, attempts have been made to raise funds from the general public through the issuance of bonds, units and corporate bonds. It is a great help in building a link between regular savings channels and distribution mechanisms.
Inactive and volatile capital markets: An important function of capital markets is to promote economic development through the mobilization of savings and the distribution to productive ventures. As far as India's industrial finance is concerned, corporate clients can raise funds through the Development Bank. Therefore, they do not have to go to the capital markets. Moreover, the capital markets are so volatile and inactive that we do not rely on them. Investors also prefer investing in physical assets to investing in financial assets. Weakness in capital markets is a serious problem for our financial system.
Careless Financial Practices: Development Bank's dominance has developed careless financial practices among corporate clients. Development banks provide most of their funding in the form of term loans. Therefore, the financial structure of a company is overwhelmingly debt-rich. This debt-capital advantage makes the capital structure of borrowing concerns uneven and biased. To make matters worse, when a company faces a financial crisis, these financial institutions allow the use of more debt than is guaranteed. This goes against the traditional notion of a sound capital structure.
But lately, every effort has been made to revitalize the capital markets. Integration is also taking place between different financial institutions. For example, UTI's unit-linked insurance scheme is generally available in collaboration with LIC. Similarly, the refinancing and redemption facilities offered by IUBI are for integration purposes. In this way, India's financial system has evolved.
The financial system is a system that facilitates the transfer of funds between people in the economy. This is just a way to exchange funds between investors, lenders and borrowers. The financial system is composed of various elements such as financial institutions, financial intermediaries, financial markets, and financial products, and enables smooth transfer of funds.
This system exists at the regional, national, and international levels. It is an efficient tool to support the country's economic development by linking savings and investment to the creation of wealth. The financial system makes money in the country by taking money from the people who let it play and distributing it to those who use it to earn income.
The financial system aims for efficient allocation of financial resources by channelizing funds between net savers and net spenders. The financial system plays an efficient role in minimizing risk by diversifying funds among a large number of people.
Benefits of the financial system
- Providing a payment system: The financial system provides a payment mechanism for the smooth flow of funds among people in the economy. Buyers and sellers of goods and services can trade with each other due to the existence of a financial system.
2. Link Savers and Investors: The financial system acts as a means of bridging the gap between savings and investment. It earns money from people it's lazy and transfers it to those who need it to invest in productive ventures.
3. Risk Minimization: The goal is to mitigate risk by distributing it across a large number of individuals. The financial system distributes funds to many people because many people share risks.
4. Supporting capital formation: The financial system plays an efficient role in national capital formation. This allows large corporations and industries to obtain the funds they need to carry out or expand their businesses, which leads to the formation of national capital.
5. Improving living standards: Improving people's living standards by promoting regional and rural development in the country. The financial system promotes the development of vulnerable parts of society through co-operatives and rural development banks.
6. Improving liquidity: Maintaining optimal liquidity in the economy is another important role of the financial system. It promotes the free transfer of funds from households (saver) to businesses (investors) and guarantees the full availability of funds in the economy.
7. Promoting Economic Development: The financial system influences economic growth or the pace of economic development. It aims to make the best use of all financial resources by investing all idle resources in useful means that lead to the creation of wealth.
Disadvantages of the financial system
- Under-coordination between financial institutions: The financial system faces under-coordination between various financial institutions. The presence of numerous financial institutions and the role of governments in controlling the authorities of these institutions leads to a lack of coordination.
2. Exclusive Market Structure: Many institutions in India's financial system occupy a monopoly position in the market. LIC and UTI are two institutions that have dominated the life insurance business and the investment trust industry. These large structures can lead to mismanagement and inefficiency of funds.
3. High interest rates: In Japan's financial system, multiple financial institutions may impose high interest rates. Due to the monopoly structure in the market, various institutions may charge high or unfair interest rates.
4. Inactive Capital Markets: Our financial system faces the problems of inactive capital markets. Most Indian companies can raise funds through development banks and do not have to go to the capital markets.
5. Careless financial practices: India's financial system has developed careless financial practices because of the superiority of development banks. Development banks fund companies in the form of term loans that make the capital structure of borrowing concerns uneven. These banks allow the use of unfair debt against a sound capital structure.
Key takeaways:
- An "economic gadget" is a machine that allows the alternate of funds among economic market individuals which includes lenders, investors and debtors.
- The monetary system operates at national and worldwide ranges.
- Economic institutions include complicated and carefully related services, markets and establishments that goal to provide green and normal links among buyers and depositors.
- In different phrases, the economic device of the economic medium (cash) while it is being reassigned to areas wherein price range are wanted (financial markets, corporations, banks) to take gain of the ideal money capacity.
- You may find out anywhere the trade exists after which use it to income. This complete mechanism is known as the economic system.
- Money, credit score, and finance are used as media for the exchange of monetary structures.
- They act as a medium of acknowledged value wherein goods and offerings can be exchanged instead of bartering.
- The present-day financial gadget may additionally encompass banks (public or private quarter), monetary markets, financial products, and financial services.
- The economic gadget allows finances to be allotted, invested, or transferred between financial sectors, permitting individuals and companies to share the dangers concerned.
- A measuring instrument is a tool for storing or transferring value or financial obligations.
- An economic device is a tradable or negotiable asset, safety, or agreement.
- Criminal files might also contain binding phrases, rights, and / or obligations.
References:
- Kohn, Meir: Financial Institutions and Markets, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Bhole L.M: Financial Institutions and Markets, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Desai, Vasantha: The Indian Financial System, Himalaya Publishing House.
- Machiraju.R.H: Indian Financial System, Vikas Publishing House.
- Varshney, P.N., & D K Mittal, D.K.: Indian Financial System, Sultan Chand & Sons
- Pathak, V. Bharati: Indian Financial System, Pearson Education.
- Gordon E. &Natarajan K.: Financial Markets & Services, Himalaya Publishing House.