Unit 2
Capital Market
Security market also known as known as stock exchange is an organised and well regulated platform for buying and selling of securities. According to section 2(j) of the Securities Contract Regulation Act 1956 “stock exchange” means— for the purpose of assisting, regulating or controlling the business of buying, selling or dealing in securities-
(a) anybody of individuals, whether incorporated or not, constituted before corporatisation and demutualisation under sections 4A and 4B, or
(b) a body corporate incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 (1 of 1956), whether under a scheme of corporatisation and demutualisation or otherwise.
Some of the examples of stock exchange are Bombay Stock Exchange, National Stock Exchange, Regional Stock Exchange etc.
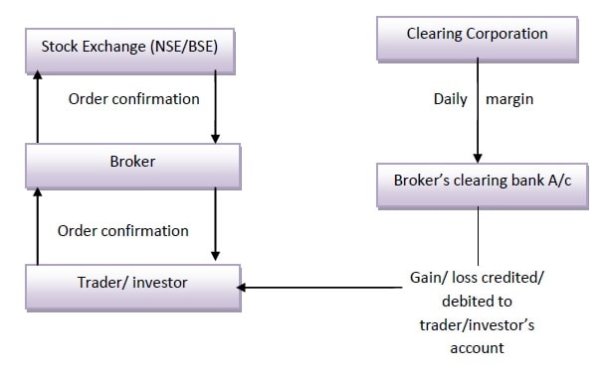
Figure: Working under stock exchanges
Features of security market
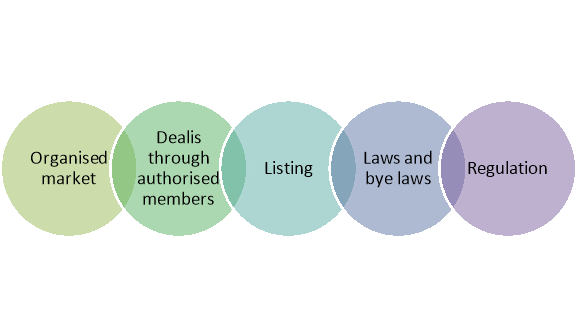
Figure: Features of securities market
Stock exchange is an organised market. Every stock exchange has a management committee, which has all the rights related to management and control of exchange. All the transactions taking place in the stock exchange are done as per the prescribed procedure under the guidance of the management committee.
2. Deals through Authorised Members:
Investors can sell and purchase securities in stock exchange only through the authorised members. Stock exchange is a specified market place where only the authorised members can go. Investor has to take their help to sell and purchase.
3. Listing of securities:
Only those securities are traded in the stock exchange which is listed there. After fulfilling certain terms and conditions, security gets listed on the stock exchange.
4. Necessary to Obey the Rules and Bye-laws:
While transacting in Stock Exchange, it is necessary to obey the rules and bye-laws determined by the Stock Exchange.
5. Regulation:
It is regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). SEBI provides provisions for stakeholders of securities market for dealings in the security trading with objective to protect the interest of investors. All brokers and sub-brokers, market makers, mutual fund companies, custodians must get register with the SEBI to operate under the stock market.
Key takeaways-
1) Security market also known as known as stock exchange is an organised and well regulated platform for buying and selling of securities.
The stock exchange performs variety of functions to conduct buying and selling of securities. Such functions are discussed below-
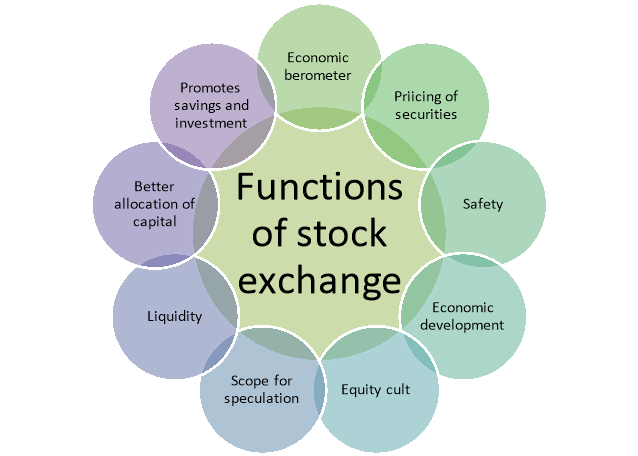
Figure: Functions of stock exchange
1. Economic Barometer:
A stock exchange is a reliable barometer to measure the economic condition of a country. Every major change in country and economy is reflected in the prices of shares. The rise or fall in the share prices indicates the boom or recession cycle of the economy. Stock exchange is also known as a pulse of economy or economic mirror which reflects the economic conditions of a country.
2. Pricing of Securities:
The stock market helps to value the securities on the basis of demand and supply factors. The securities of profitable and growth oriented companies are valued higher as there is more demand for such securities. The valuation of securities is useful for investors, government and creditors. The investors can know the value of their investment, the creditors can value the creditworthiness and government can impose taxes on value of securities.
3. Safety of Transactions:
In stock market only the listed securities are traded and stock exchange authorities include the companies names in the trade list only after verifying the soundness of company. The companies which are listed they also have to operate within the strict rules and regulations. This ensures safety of dealing through stock exchange.
4. Contributes to Economic Growth:
In stock exchange securities of various companies are bought and sold. This process of disinvestment and reinvestment helps to invest in most productive investment proposal and this leads to capital formation and economic growth.
5. Spreading of Equity Cult:
Stock exchange encourages people to invest in ownership securities by regulating new issues, better trading practices and by educating public about investment.
6. Providing Scope for Speculation:
To ensure liquidity and demand of supply of securities the stock exchange permits healthy speculation of securities.
7. Liquidity:
The main function of stock market is to provide ready market for sale and purchase of securities. The presence of stock exchange market gives assurance to investors that their investment can be converted into cash whenever they want. The investors can invest in long term investment projects without any hesitation, as because of stock exchange they can convert long term investment into short term and medium term.
8. Better Allocation of Capital:
The shares of profit making companies are quoted at higher prices and are actively traded so such companies can easily raise fresh capital from stock market. The general public hesitates to invest in securities of loss making companies. So stock exchange facilitates allocation of investor’s fund to profitable channels.
9. Promotes the Habits of Savings and Investment:
The stock market offers attractive opportunities of investment in various securities. These attractive opportunities encourage people to save more and invest in securities of corporate sector rather than investing in unproductive assets such as gold, silver, etc.
Key takeaways-
1) The stock exchange performs variety of functions to conduct buying and selling of securities like economic barometer, promotes savings and investment, economic growth, maintains liquidity etc.
A company, desirous of listing its securities on the Exchange, shall be required to file an application, in the prescribed form, with the Exchange before issue of Prospectus by the company, where the securities are issued by way of a prospectus or before issue of 'Offer for Sale', where the securities are issued by way of an offer for sale. The company shall be responsible to follow all the requirements specified in the Companies Act, the listing norms issued by SEBI from time to time and such other conditions, requirements and norms that may be in force from time to time and included hereafter in these Bye-laws and Regulations to make the security eligible to be listed and for continuous listing on the Exchange. The procedures are discussed below-
Except when otherwise allowed by the Governing Board or Managing Director or Relevant Authority in any particular case and subject to compliance with such conditions as it or he may impose, tenders or applications for subscription or purchase or book-building in respect of any new issue or offer for sale of any security shall not be submitted unless the issuer or offerer offers to all a fair and equal opportunity for subscription or purchase and on the same terms as to brokerage to all the trading members and unless it is provided that all tenders and applications for subscription or purchase or book-building shall rank alike for allotment or sale. The issuer or the offerer, prior to issuing further securities or offering securities for sale, shall obtain an in principle approval from the Exchange for listing these securities on the Exchange.
2. Application for Admission to Dealings:
The issuer shall submit an application for admission of its securities to dealings on the Exchange in such form, as may be prescribed by the Exchange from time. to time, after ensuring compliance with the applicable provisions in the SCRA, SCRR, Companies Act and the Rules, Regulations and norms as may be issued by SEBI / Exchange in this regard from time to time.
3. Units and Exchange Traded Funds:
Units of Mutual Funds may be admitted to dealings on the Exchange subject to such conditions and requirements, as may be prescribed by the Governing Board or Relevant Authority from time to time.
4. Options or Futures in Securities:
Options and futures in securities and in securities index or indices shall be admitted to dealings on the Exchange by the Governing Board or Relevant Authority in accordance with the provisions of SCRA and norms issued by SEBI from time to time and as may be specified in the relevant Bye-laws and Regulations framed in this regard.
5. Notice of Application for Admission to Dealings:
Notice of any application for admission to dealings on the Exchange shall be posted on the notice board or displayed on the ATS or Website of the Exchange for the information of trading members and others, atleast one week prior to its consideration by the Exchange.
6. Underwriting, Placing and Preliminary Arrangements:
Except when otherwise allowed by the Relevant Authority in any particular case and subject to compliance with such conditions as it may impose, a trading member shall not enter into an underwriting contract nor shall he contract either as a principal or agent to subscribe or purchase or to procure, whether through the market or otherwise, nor shall he act or agree to act as broker or underwriter in connection with any floatation or issue of any security, unless the trading member fulfills the capital adequacy requirements, as may be specified by SEBI or the Exchange from time to time, and the issuer conforms or agrees to conform to the listing requirements prescribed in these Bye-laws and Regulations and/or as provided under the SCRA and SCRR and undertakes to apply for admission of such security to dealings on the Exchange.
7. Listing Conditions and Requirements
a) The Governing Board or Managing Director or Relevant Authority may not grant admission to dealings on the Exchange to a security of an issuer unless the issuer complies with the listing conditions, requirements and norms, under the SCRA, SCRR, the Companies Act, the Rules, Bye-laws and Regulations of the Exchange and the norms, as may be prescribed by the Exchange and/or SEBI from time to time.
b) The Governing Board or Managing Director or Relevant Authority shall ensure that no listing or trading permission is granted unless the issuer complies with all the conditions, requirements or norms, as may be provided in the relevant Regulations from time to time, including despatch of physical share certificates to, and/or credit of demat shares to the accounts of all the security-holders, maintained with the depositories.
c) Where the Exchange is the stock exchange with whose consultation the basis of allotment is decided, the Governing Board or Managing Director or Relevant Authority of the said stock exchange shall intimate the depositories about approval granted for admission to dealings on the Exchange for any security.
d) The company shall execute a Listing Agreement, in the prescribed form with the Exchange, prior to approval of the listing application of the company. Any addition or amendment to the provisions of the Listing Agreement, as may be prescribed by SEBI and/or the Exchange shall become applicable to the company as if such addition or amendment was part of the Listing Agreement.
e) In the case of a new issue or further issue by any issuer the Governing Board or Managing Director or Relevant Authority may grant permission for trading in any security at the Exchange on the same day as on all other stock exchanges where such security admitted to dealings is granted permission for trading.
8. Applicability of Listing Conditions and Requirements:
In the case of a body corporate, fund or other entity registered or formed outside India, the Governing Board or Managing Director or Relevant Authority may, for reasons to be recorded in writing, waive or dispense with the strict enforcement of any or all of the listing conditions and requirements prescribed in these Byelaws and Regulations, except those prescribed in Bye Law 4.9 provided that the securities of such body corporate, fund or other entity are admitted to dealings on any stock exchange outside India and the Governing Board or Managing Director or Relevant Authority is satisfied that it is in the interest of trade or in the public interest, so to do.
9. Grant or Refusal of Admission to Dealings:
The Governing Board or Managing Director or Relevant Authority may, in its/his discretion, approve subject to such terms as it/he deems proper or defer or reject any application for admission of a security of an issuer to the dealings on the Exchange, without assigning any reason whatsoever, within the time provided under the SCRA, the Companies Act and the Rules, Regulations and norms as may be issued by SEBI / Exchange, that may be in force from time to time.
10. Listing Approval:
The Exchange may grant approval to the issuer for any security sought to be listed on the Exchange on completion of the listing conditions, requirements and norms by the issuer, as may be specified by the Exchange from time to time. Such security shall be called listed security.
11. Admission to Dealings:
Admission to dealings shall mean permission granted by the Exchange to a security for commencement of trading on the ATS of the Exchange as provided in these Bye-laws and the relevant Regulations.
12. Trading in Securities Admitted to Dealings on Other Stock Exchanges:
The Governing Board or Relevant Authority may, in its discretion and subject to such conditions as it may deem proper, allow trading in any security or securities, admitted to dealings on any other stock exchange. Such security shall be called permitted security.
13. Listing Fees:
The Board or the Relevant Authority of the Exchange shall fix the listing fees at such rates and in such manner as may be deemed fit from time to time.
Key takeaways-
1) A company, desirous of listing its securities on the Exchange, shall be required to file an application, in the prescribed form, with the Exchange before issue of Prospectus by the company, where the securities are issued by way of a prospectus or before issue of 'Offer for Sale', where the securities are issued by way of an offer for sale.
Public issue is a method of issuing securities under the securities market. The public issue consist of the methods like initial public offer (IPO), further public offer and offer for sale.
This method is used by an unlisted company is a public company that is neither listed on a stock exchange nor its shares are traded in any recognized stock exchange.
When a listed company makes an offer for sale or comes out with a new issue of shares to the public to increase capital, it is known as Further Public Offer.
The shareholders can offer a portion of their shareholding to the public in consultation with the BOD (Board of Directors). The prospectus of a company is considered as its LOI (Letter of Offer). Also, the shareholders of the Company reimburse any expenses regarding the offer. Hence, any dividend paid or declared on these shares is paid to the transferee.
Pricing of public issue
The SEBI provided that the companies eligible to make public issue can freely price their equity shares or any security convertible at later date into equity shares in the following cases:
A listed company whose equity shares are listed on a stock exchange, may freely price its equity shares and any security convertible into equity at a later date, offered through a public or rights issue.
2. Public Issue by Unlisted Companies
An unlisted company eligible to make a public issue and desirous of getting its securities listed on a recognised stock exchange pursuant to a public issue, may freely price its equity shares or any securities convertible at a later date into equity shares.
3. Infrastructure company
An eligible infrastructure company shall be free to price its equity shares subject to the compliance with the disclosure norms as specified by SEBI from time to time.
4. Initial public Issue by Banks
The banks (whether public sector or private sector) may freely price their issue of equity shares or any securities convertible at a later date into equity share subject to approval by the Reserve Bank of India.
5. Differential Pricing
Any unlisted company or a listed company making a public issue of equity shares or securities convertible at a later date into equity shares, may issue such securities to applicants in the firm allotment category at a price different from the price at which the net offer to the public is made provided that the price at which the security is being offered to the applicants in firm allotment category is higher than the price at which securities are offered to public.
6. Price Band
Marketing of public issue
In the case of a public issue the company is required to take certain steps by which the potential investing community is apprised of the features of the forthcoming issue. The need for marketing the public issue arises because of the highly competitive nature of the capital market. Following are the steps involved in the marketing of the issue of securities to be undertaken by the lead manager:
The first step towards the successful marketing of securities is the identification of a target market segment where the securities can be offered for sale. This ensures smooth marketing of the issue. Further it is possible to identify whether the market comprises of retail investor or institutional investors.
2. Target concentration:
After chosen the target market for selling the securities steps are to be taken to assess the maximum number of subscriptions that can be expected from the market would work to the advantage of the company if it concentrates on the regions where it is popular among prospective investors.
3. Pricing:
After assessing market expectations, the kind and level of price to be charged for the security must be decided. Pricing the issue also influences the design of capital structure. The offer has to be made more attractive by including some unique features such as safety net, multiple options for conversion, attaching warrants etc.
4. Mobilizing intermediaries:
For successful marketing of public issues, it is important that efforts are made to enter into contracts with financial intermediaries such as an underwriter, broker/sub-broker fund arranger etc.
5. Information contents:
Every effort should be made to ensure that the offer document of the issue is educative and contains maximum relevant information. Institutional investors and high net worth investors should also be provided with detailed research on the project, specifying its uniqueness and its advantage over other exiting or upcoming projects in a similar field.
6. Launching advertisements campaign:
In order to push the public issue, the lead manager should undertake a high voltage advertisement campaign. The advertising agency must be carefully selected for this purpose. The task of advertising to issue shall be entrusted to those agencies that specialize in launching capital offerings. The theme of the advertisement should be finalized keeping in view SEBI guidelines. An ideal mix of different advertisement vehicles such as the press, the radio and the television, the hoarding etc. should be used. Press meets, brokers and investors conference etc. shall be arranged by the lead managers at targeted regions. It would be appropriate to make use of the services of Market Research organizations that specialize in carrying out opinion polls. These services would be useful in collecting data on investors’ opinion and reactions relating to the public issue of the company. Such a task would be to develop an appropriate marketing strategy. This is because there are vast numbers of potential investors in semi-urban and rural areas. This calls for sustained efforts on the part of the company to educate them about the various avenues available for investment.
7. Brokers’ and investors’ conference:
As of the part issue campaign the lead manager should arrange for brokers’ and investors’ conferences in the metropolitan cities and other important centres which have sufficient investor population. In order to make such endeavours more successful advance planning is required, It is important that conference materials such banners, brochures, application forms, posters etc reach the conference venue in time. In additions, invitation to all the important people, underwriters, bankers at the respective places, investors’ association should also be sent.
8. Timing of the Issue:
A critical factor that could make or break the proposed public issue is its timing .the market conditions should be favourable. Otherwise, even issue from a company with a recent track record, and whose shares are highly priced might flop. Similarly the number and frequency of issues should also be kept to a minimum to ensure success of the public issue.
Key takeaways-
1) Public issue is a method of issuing securities under the securities market. The public issue consist of the methods like initial public offer (IPO), further public offer and offer for sale.
National stock Exchange
The National Stock Exchange of India Limited is the country’s leading financial exchange, with headquarters in Mumbai. It was incorporated in 1992 and, since then, has evolved into an advanced, automated, electronic system offering trading facilities to investor across the country. In 2015, this exchange system ranked in the fourth place in the world according to the metric of its trading volume. This stock exchange began its operations in 1994 at the behest of the Indian government to bring a level of transparency to the country’s capital market. Set up by an assembly of leading financial institutions and at the recommendations formulated by Pherwani Committee, this stock exchange comprised of diverse shareholding assets from both global and domestic investors. It was also the first stock exchange in the country to introduce electronic trading facilities, thus facilitating the integration of investors throughout the country into a single base. As of 2018, NSE had a total market capitalisation exceeding the US $2.25 Trillion, putting it in 11th place in the list of the largest stock exchanges in the world. However, unlike the USA, where trading from corporate sector accounts for about 70% of the country’s GDP, this sector in India accounts for only 12-14% of its total GDP. Out of this entire corporate sector, around 7800 companies are listed with about 4000 among those trading at Indian stock exchanges.

Purpose of NSE
To improve the financial well-being of people.
Vision of NSE
To continue to be a leader, establish global presence, facilitate the financial well-being of people.
Benefits of Listing with National Stock Exchange of India –
NSE offers several benefits of listing with it. Some of them are as follows –
This trading system is efficient in providing various trade and post-trade information. Investors can easily look up the top buy and sell orders on the trading system, along with the total number of securities available for a transaction. It helps investors to gauge the market’s depth easily.
2. Makes for a premier marketplace
The volume of trading activity in this stock exchange helps to lower the impact cost on it, which decreases the expenses of trading for investors. Additionally, the exchange’s automated trading system helps to maintain transparency and consistency with an investor.
3. Biggest exchange in the country
In terms of trading volume, the National Stock Exchange is the country’s largest exchange with its market capitalisation exceeding $2.25 Trillion.
4. Fast transactions
The pace at which orders are processed in this Exchange helps investors to avail the best prices. For instance, on May 19th 2009, the stock exchange recorded 11,260,392 trades, which was its highest number in a day.
5. Trade statistics
Listed companies can avail the provision of receiving trade statistics each month, to help track the performance of companies listed on the exchange.
Products of NSE
The Equities section provides you with an insight into the equities segment of NSE with Current Market Reports, Historical Data and Product Information. It includes equity market, exchange traded funds, indices, mutual funds, security lending & borrowing scheme, sovereign gold bond, initial public offering (IPO), institutional placement program (IPP), offer for sale.
2. Derivatives:
The Derivatives section provides you with an insight into the derivatives segment of NSE with Current Market Reports, Historical Data and Product Information. It includes equity derivatives, commodity derivatives, currency derivatives, interest rate derivatives.
3. Fixed Income & Debt:
The Debt section provides you with an insight into the debt segment of NSE with Current Market Reports, Historical Data and Product Information. It includes corporate bonds, Electronic Debt Bidding platform (EBP), Negotiated trade reporting platform, Non Competitive Bidding in Government Securities, Tri-party Repo.
Major Indices in this Exchange System –
A stock market’s index is created by choosing a collection of stocks that represent the whole market, or a specific segment of it. Following are some of the most important broad market indices, consisting of the liquid stocks that are listed on this stock exchange –
Some of the listed companies of NSE are- Reliance, TCS, HDFC, Infosys, Kotak Mahindra, ICICI bank, Bajaj Finance, SBI etc.
Over the Counter Exchange of India (OTCEI)
OTCEI was incorporated in 1990 as a Section 25 company under the Companies Act 1956 and is recognized as a stock exchange under Section 4 of the Securities Contracts Regulation Act, 1956. The Exchange was set up to aid enterprising promoters in raising finance for new projects in a cost effective manner and to provide investors with a transparent & efficient mode of trading. Modelled along the lines of the NASDAQ market of USA, OTCEI introduced many novel concepts to the Indian capital markets such as screen-based nationwide trading, sponsorship of companies, market making and scripless trading. As a measure of success of these efforts, the Exchange today has 115 listings and has assisted in providing capital for enterprises that have gone on to build successful brands for themselves like VIP Advanta, Sonora Tiles & Brilliant mineral water, etc. OTC Exchange of India has been co-promoted by the leading financial institutions of the country:
Features of the Over-The-Counter Exchange of India (OTCEI)
The OTCEI has some special features that make it a unique exchange in India as well as a growth catalyst for small- to medium-sized companies. The following are some of its unique features:
Key takeaways-
1) The National Stock Exchange of India Limited is the country’s leading financial exchange, with headquarters in Mumbai. It was incorporated in 1992 and, since then, has evolved into an advanced, automated, electronic system offering trading facilities to investor across the country.
2) OTCEI was incorporated in 1990 as a Section 25 company under the Companies Act 1956 and is recognized as a stock exchange under Section 4 of the Securities Contracts Regulation Act, 1956.
References
1. Jones, C.P. Investments Analysis and Management, Wiley, 8th ed.
2. Chandra, Prasanna. Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management. McGraw Hill Education.
3. Rustogi, R.P. Fundamentals of Investment. Sultan Chand & Sons, New Delhi.
4. Vohra N.D. & Bagri B.R., Futures and Options, McGraw Hill Education