Unit 4
Functionaries on Stock Exchanges
Stock Broker is member of a stock exchange registered with SEBI to perform the brokering business. Some examples of stock broker are Sharekhan, IHDFC securities, Motilal Oswal etc.
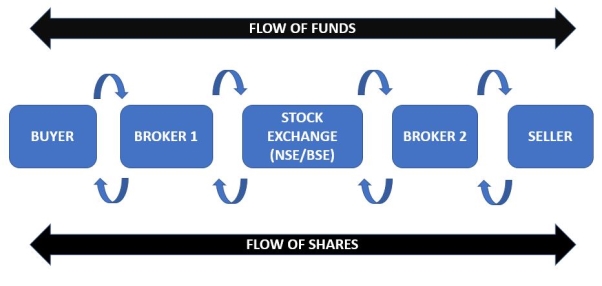
The registration procedure of stock brokers are-
On fulfilment of following conditions, the registrar will provide registration certificate to the stock brokers—
(a) the stock broker holds the membership of any stock exchange;
(b) he shall abide by the rules, regulations and bye-laws of the stock exchange which are applicable to him;
(c) where the stock broker proposes to change his status or constitution, he shall obtain prior approval of the Board for continuing to act as such after the change;
(d) he shall pay fees charged by the Board in the manner provided in these regulations; and
(e) he shall take adequate steps to redress of grievances, of the investors within one month of the date of receipt of the complaint and keep the Board informed about the number, nature and other particulars of the complaints received from such investors.
A stock broker perform the following activities-
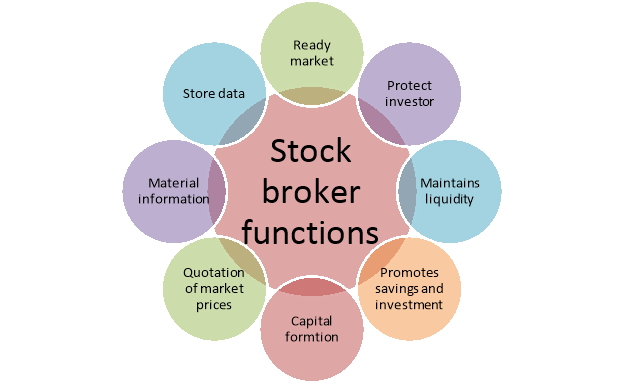
Figure: Functions of stock broker
1) Stock broker provides a ready market to the investors for continuous buying and selling of securities.
2) Stock brokers safeguard the activities for investors by complying with the rules and regulations provided by the SEBI.
3) Stock broker maintains liquidity in the financial market by continuously buying and selling of securities.
4) Stock broker promotes the habit of saving and investment among the general masses by facilitating them investment avenues.
5) Stock broker promotes capital formation in the economy by mobilising resources from deficit sector to surplus sector.
6) Stock broker provide different quotation of market prices for various securities to the potential investors to make their investment decision.
7) Stock brokers persuade material information to the potential investors that help them to make correct investment decision.
8) Stock broker keep storage and protection of customer data.
Key takeaways-
Sub-broker in a stock exchange is a person appointed by the broker to act as an agent for him. In others words, sub-brokers are agent of brokers to deal with investors on behalf the brokers but they are not the members in stock exchange. Section 2 (gc), “sub-broker means any person not being a member of stock exchange who acts on behalf of a stock broker as an agent or otherwise for assisting the investors in buying, selling or dealing in securities through such stock brokers”. The sub- brokers should apply in “Form B” for registration with SEBI. The registration procedure of sub-brokers are-
1) The application form shall be accompanied by a recommendation from stock broker in “Form C”.
2) The application should be submitted to the same stock exchange where the stock broker is the member.
3) On receipt of application the stock exchange will verify the eligibility of applicant as sub-broker.
4) After satisfactory verification the stock exchange will forward the application to the board within 30 days from the receipt of application.
5) The Board on being satisfied that the sub-broker is eligible, shall grant a certificate in ‘Form E’ to the sub-broker and send the intimation to that effect to the stock exchange or stock exchanges.
Benefits of sub-broker
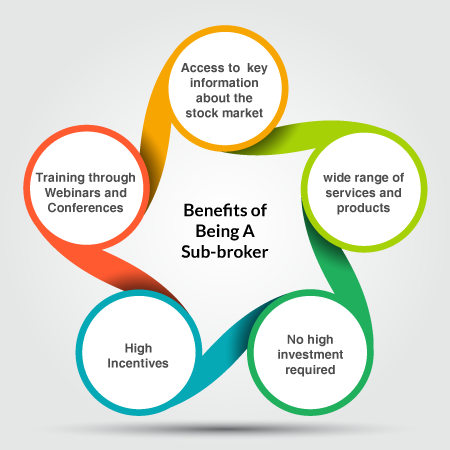
Working under a broker provides sub brokers with key information about the stock market that they can use to further their market knowledge and personal trades. While they cannot function as brokers, they can still trade privately with any broker with their own funds. This self-sufficient cycle not only enables sub brokers to cater to their clients better, but also lets them fuel their investments as well.
2. High investment:
Another benefit of being a sub broker is that the brokerage firm you work with might also enable you to provide customers with services beyond just investment tips and strategy. For example, some brokers allow their sub broker franchisees to offer clients mutual fund distribution and loan options as well.
3. No high investment:
A third benefit is that as a sub broker, you do not require a high investment amount, as your franchiser takes care of a majority of the expenses. Sub brokers only require a small investment amount, say 10,000 rupees or above in order to begin their quest as a sub broker.
4. Wide range of services and products:
Without becoming a member of stock exchange, the sub-broker able to provide services and products to the clients. It provides all services and provides that broker able to provide.
5. Training:
Sub-brokers are trained through seminars, webinars and conferences from time to time to impart technical knowledge and skills and also upgrade their knowledge.
Key takeaways-
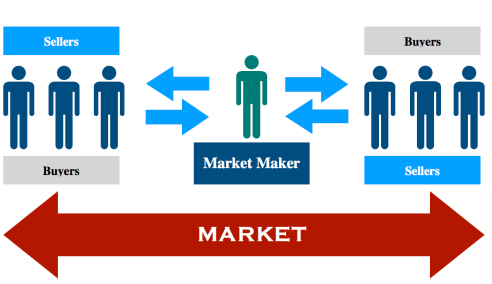
Market maker is an individual who operates under stock exchange to buy and sell securities through its own account. They are members of stock exchange operate with the primary goal of profiting on the bid-ask spread, which is the amount by which the ask price exceeds the bid price a market asset. Market makers are compensated for the risk of holding assets because they may see a decline in the value of a security after it has been purchased from a seller and before it's sold to a buyer.
Some of the examples of market maker of national Stock exchange are
1 AIRAN FINSTOCKS PRIVATE LIMITED
2 AJCON GLOBAL SERVICES LIMITED
3 AJMERA ASSOCIATES LIMITED
4 ALACRITY SECURITIES LTD.
5 ALMONDZ GLOBAL SECURITIES LIMITED
6 ANS PVT. LTD.
7 ARCADIA SHARE & STOCK BROKERS PRIVATE LIMITED
8 ARHAM WEALTH MANAGEMENT PRIVATE LIMITED
9 ARIHANT CAPITAL MARKETS LIMITED
10 ARYAMAN CAPITAL MARKETS LIMITED
Some of the significant roles of market makers are discussed below-
Figure: Benefits/importance of market maker
It is due to the presence of market makers that the volumes in a stock are created. Without the market makers, the stock will be highly illiquid and traders will not be too keen on trading it. Effectively, these market makers make the market a lot safer and secure. Since they provide two way quotes, they reduce the basis risk and the trading risk for the market players. In the process, the market makers take the risk of market volatility and provide liquidity in the market.
2. Conduct smooth functioning:
The purpose of market makers in a financial market is to keep up the functionality of the market by infusing liquidity. They do so by ensuring that the volume of trades is large enough such that trades can be executed in a seamless fashion.
3. Marketing of securities:
In the absence of market makers, an investor who wants to sell their securities will not be able to unwind their positions. It is because the market doesn’t always have readily available buyers.
4. Wholesalers of financial markets:
If a bondholder wants to sell the security, the market maker will purchase it from them. Similarly, if an investor wants to purchase a given stock, market makers will ensure that shares of that company are available for sale. Thus, they act as wholesalers in financial markets.
5. Influence demand and supply:
The prices set by market makers are a reflection of demand and supply. Stockbrokers can also perform the function of market makers at times. It, however, represents a conflict of interest because brokers may be incentivized to recommend securities that make the market to their clients.
Key takeaways-
Jobbers are market makers operate under the stock exchanges engage in buying and selling of securities. They earn profit by speculating security prices. A jobber is a slang term for a market maker on the London Stock Exchange prior to October 1986. The term jobber was used prior to October 1986, but little is known of their actual activities as they kept few records. Depending on the nature of activities performed by jobbers, the following classifications are made-
Bulls the price will rise and sell them at gain. When a market is dominated by bulls (buyers predominate sellers), it is said to be bullish. The share prices are generally rising. Therefore, the market is characterized by an upward trend in security prices. It signifies investors’ confidence/optimism in the future of economy.

2. Bears:
It is speculator/jobber who sells security on expectation of decline in prices in future. The intention is to buy same securities at lower prices in future thereby making a gain. When market is dominated by bears (sellers predominate buyers) it is said to be bearish. It is characterized by general downward trend in share prices. It signifies investors’ pessimism about the future prospects of the economy.

3. Stage:
This is a jobber found in primary markets He buys new securities offered to the public and believes that they are undervalued. He believes the price will rise and sell them at a gain to the ultimate investors. Stags are vital because they ensure full subscription of the share issue.
Key takeaways-
For an NRI to invest and trade in the stock market in India on a repatriation basis, it needs PIS permission letter from RBI. The PIS letter enables NRIs to buy and sell shares on the stock exchange in India. All these transactions are routed through the NRE bank account. Also, the bank in which you hold the NRI account helps you get this permission. On the other hand, if a person plan to invest on a non-repatriation basis, his account linked to a demat and trading account.
References:
1. Jones, C.P. Investments Analysis and Management, Wiley, 8th ed.
2. Chandra, Prasanna. Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management. McGraw Hill Education.
3. Rustogi, R.P. Fundamentals of Investment. Sultan Chand & Sons, New Delhi.
4. Vohra N.D. & Bagri B.R., Futures and Options, McGraw Hill Education.