Unit 5
Financial Services
Financial services refers to the monetary benefit or satisfaction derived from the services provided by financial service providers like Banks, Non- banking companies financial intermediaries, stock brokers, financial agents etc. Depending on the nature, financial services are categorized under two heads, namely;
a) Fund based financial services;
b) Fee based financial Services;
Characteristics of financial services
The features of financial services are highlighted below-
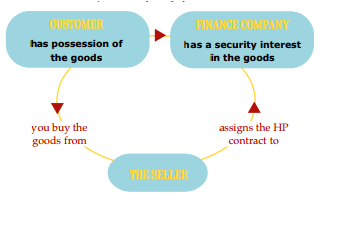
Figure: Features of financial services
8. Financial services are perishable in nature. The users of financial service must receive the service at the spot of financial service providers.
Functions of financial services
The functions of financial services are highlighted below-
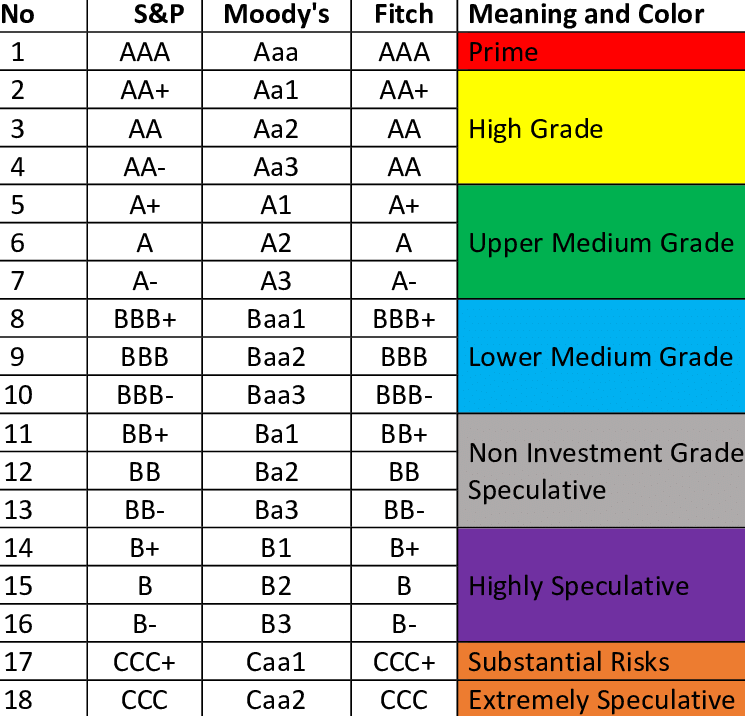
Figure: Functions of financial services
Merchant banking services facilitates the companies for proper utilisation of fund by providing them services like issue management, financial management etc.
2. Maintains liquidity:
It helps to maintain liquidity in the economy by connecting the potential investors and borrowers.
3. Better relation with customers:
Financial service providers always maintain better relation with customers by satisfying their priorities and protecting consumer interest.
4. Increases standard of living:
Hire purchase and consumer credit allows the people to purchase durable and luxuries goods on instalment basis. It facilitates increase in standard of living of people in the economy.
5. Promotes economic development:
It promotes economic development of a country by facilitating trade and industry, promoting savings and investment etc.
Types of financial services
The financial services are broadly divided into two parts and further sub-classified as follows-
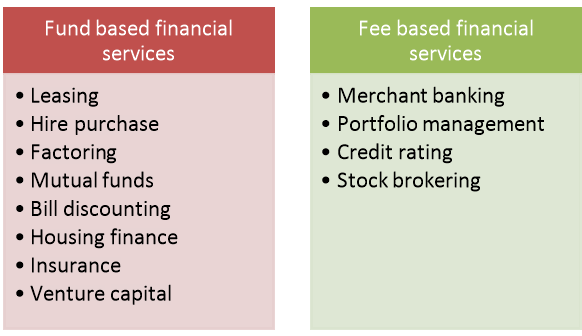
c) Fund based financial services;
Lease/leasing/lease financing is a contract between lessee and lessor for hire of an asset on payment rent for a specific period generally for long duration. The assets covered under lease agreements are land, real estate, mines, quarries, plant and equipment, aircraft etc. the owner of the leased property is known as lessor and user of the property is known as lessee. Some examples of lease financing company in India are Mahindra finance, Bajaj finance, Shriram trans etc.
Hire purchase is an agreement between hire purchaser (hirer) and hire seller (hiree) where the later transfers the possession of property to former party, payment is made on instalment basis and on payment of last instalment the hirer get the right of ownership over the property. Hire purchase agreement is governed under the Hire Purchase Agreement Act, 1972.
Factoring refers to selling of trade receivables (bills of exchange and promissory note) by the owner of business firm (client) to a factor (financial intermediary) to get immediate cash to manage short term finance for his business. Under this method of financing the trade receivables are sold at a discount to the factor.
Mutual fund is a non-banking financial company that collects and pool small savings from investors and invest in selected securities of securities market to get maximum return with minimum risk. The profits yielded from mutual fund investment are shared among the investors according to the share of investment. The mutual fund investment is managed by the portfolio manager by carefully selecting the combination of different types of efficient securities.
Bill discounting is a method of extending short term credit by commercial banks to the traders against the bills of exchange. The commercial banks charges commission from the borrowers for the bill discounting process.
Housing finance refers to extension of loan to consumers for construction of residential house, purchase of house, purchase of flat, repayment of housing loan etc. National Housing Bank is the apex institution in housing finance sector.
Insurance is a contract between insurer and insured where the former assured the later to cover the loss arising from the third party on payment of periodical premium. Insurer is the insurance company and insured is the person or institution that purchases the policy.
Venture capital is a type financing where the financing company provides equity capital to the highly risky projects related to involvement of sophisticated technology. The Venture Capital Company makes equity participation with the project and provides all technical and financial guidance for the growth of the project. Once the project started earning profit it makes disinvestment from the project. Some examples of venture capital company are-Blume Ventures, IDG Ventures, Accel Partners etc.
d) Fee based financial Services;
Merchant bankers are non-banking financial companies engaged in providing wide range of financial services like issue management, corporate counselling, portfolio management, mergers and acquisitions etc. to corporate houses.
Portfolio management refers to management of collection of fund for investment to maximise return with minimum risk. The services provided by the portfolio manager who has expertise in field of economy, financial market, financial management, industry, accountancy etc. The portfolio management concept is related to mutual fund.
Credit rating simply means rating of the credit worthiness of a company and assessment of the capacity of an issuer for repayment of principal and interest on debt by an independent agency. According to CRISIL, “Credit rating is an unbiased and independent opinion as to issuer’s capacity to meet its financial obligations. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy/ sell or hold a particular security”. Different credit rating agencies like CRISIL, CARE etc. provide ratings for financial institutions, banks, financial products and instruments, financial services etc. depending on which the investors make investment decision.
Stock Broker is member of a stock exchange registered with SEBI to perform the brokering business. Some examples of stock broker are Sharekhan, IHDFC securities, Motilal Oswal etc.
It is the presence of financial services that enables a country to improve its economic condition whereby there is more production in all the sectors leading to economic growth.
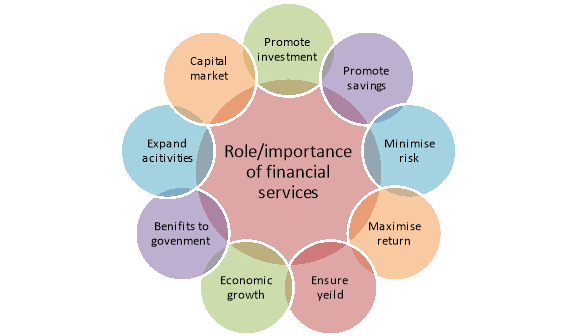
Figure: Role/importance of financial services
1. Promoting investment
The presence of financial services creates more demand for products and the producer, in order to meet the demand from the consumer goes for more investment. At this stage, the financial services come to the rescue of the investor such as merchant banker through the new issue market, enabling the producer to raise capital. The stock market helps in mobilizing more funds by the investor. Investment from abroad is attracted. Factoring and leasing companies, both domestic and foreign enable the producer not only to sell the products but also to acquire modern machinery/technology for further production.
2. Promoting savings
Financial services such as mutual funds provide ample opportunity for different types of saving. In fact, different types of investment options are made available for the convenience of pensioners as well as aged people so that they can be assured of a reasonable return on investment without much risks. For people interested in the growth of their savings, various reinvestment opportunities are provided. The laws enacted by the government regulate the working of various financial services in such a way that the interests of the public who save through these financial institutions are highly protected.
3. Minimizing the risks
The risks of both financial services as well as producers are minimized by the presence of insurance companies. Various types of risks are covered which not only offer protection from the fluctuating business conditions but also from risks caused by natural calamities. Insurance is not only a source of finance but also a source of savings, besides minimizing the risks. Taking this aspect into account, the government has not only privatized the life insurance but also set up a regulatory authority for the insurance companies known as IRDA, 1999 (Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority) .
4. Maximizing the Returns
The presence of financial services enables businessmen to maximize their returns. This is possible due to the availability of credit at a reasonable rate. Producers can avail various types of credit facilities for acquiring assets. In certain cases, they can even go for leasing of certain assets of very high value. Factoring companies enable the seller as well as producer to increase their turnover which also increases the profit. Even under stiff competition, the producers will be in a position to sell their products at a low margin. With a higher turnover of stocks, they are able to maximize their return.
5. Ensures greater Yield
As seen already, there is a subtle difference between return and yield. It is the yield which attracts more producers to enter the market and increase their production to meet the demands of the consumer. The financial services enable the producer to not only earn more profits but also maximize their wealth. Financial services enhance their goodwill and induce them to go in for diversification. The stock market and the different types of derivative market provide ample opportunities to get a higher yield for the investor.
6. Economic growth
The development of all the sectors is essential for the development of the economy. The financial services ensure equal distribution of funds to all the three sectors namely, primary, secondary and tertiary so that activities are spread over in a balanced manner in all the three sectors. This brings in a balanced growth of the economy as a result of which employment opportunities are improved. The tertiary or service sector not only grows and this growth is an important sign of development of any economy. In a well developed country, service sector plays a major role and it contributes more to the economy than the other two sectors.
7. Economic development
Financial services enable the consumers to obtain different types of products and services by which they can improve their standard of living. Purchase of car, house and other essential as well as luxurious items is made possible through hire purchase, leasing and housing finance companies. Thus, the consumer is compelled to save while he enjoys the benefits of the assets which he has acquired with the help of financial services.
8. Benefit to Government
The presence of financial services enables the government to raise both short-term and long-term funds to meet both revenue and capital expenditure. Through the money market, government raises short term funds by the issue of Treasury Bills. These are purchased by commercial banks from out of their depositors’ money. In addition to this, the government is able to raise long-term funds by the sale of government securities in the securities market which forms apart of financial market. Even foreign exchange requirements of the government can be met in the foreign exchange market.
9. Expands activities of Financial Institutions
The presence of financial services enables financial institutions to not only raise finance but also get an opportunity to disburse their funds in the most profitable manner. Mutual funds, factoring, credit cards, hire purchase finance are some of the services which get financed by financial institutions. The financial institutions are in a position to expand their activities and thus diversify the use of their funds for various activities. This ensures economic dynamism.
10. Capital Market
One of the barometers of any economy is the presence of a vibrant capital market. If there is hectic activity in the capital market, then it is an indication of the presence of a positive economic condition. The financial services ensure that all the companies are able to acquire adequate funds to boost production and to reap more profits eventually.
Lease/leasing/lease financing is a contract between lessee and lessor for hire of an asset on payment rent for a specific period generally for long duration. The assets covered under lease agreements are land, real estate, mines, quarries, plant and equipment, aircraft etc. the owner of the leased property is known as lessor and user of the property is known as lessee. Some examples of lease financing company in India are Mahindra finance, Bajaj finance, Shriram trans etc.
The essential characteristics of lease are-
The lease contract is classified under the following heads depending on nature of the contract-
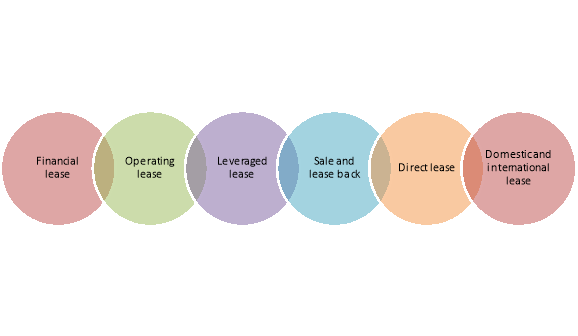
Figure: Types of lease
Evolution of Indian Leasing Industry
The leasing business in India is originated in the recent past. The first leasing business in India was started in India by ‘Leasing Company of India’ in 1973. From 1986 to 1996 there was significant boom in the industry. As per RBI’s record there were 339 leasing company in India by 31st March, 1886. Dahotre Committee provide recommendations for and accordingly RBI formed guidelines for commercial banks to enter into the lease financing. Later on commercial banks and other sector financial institutions like IDBI, IFCI, ICICI, SFC etc. has started providing leasing financing. The factors that contributed to growth of leasing in India are-
Some of the lease finance companies operating in India are-
Legal Aspects of Leasing: present Legislative Framework
There is no specific act relating to leasing. The Indian Contract Act, 1872, provides guidelines relating to bailment which also governs the lease agreement. Since same provision governs the bailment and lease agreement, it is assumed that the rights and obligation of lessee and lessor are similar to bailor and bailee. The obligations are-
Hire purchase is an agreement between hire purchaser (hirer) and hire seller (hiree) where the later transfers the possession of property to former party, payment is made on instalment basis and on payment of last instalment the hirer get the right of ownership over the property. Hire purchase agreement is governed under the Hire Purchase Agreement Act, 1972.
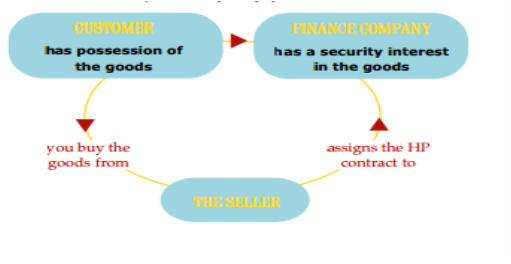
Figure: Concept of hire purchase
Characteristics of hire purchase
The essential characteristics of Hire purchase are-
Basis of difference | Hire purchase | Leasing |
| Hire purchase is an agreement between hire purchaser (hirer) and hire seller (hiree) where the later transfers the possession of property to former party, payment is made on instalment basis and on payment of last instalment the hirer get the right of ownership over the property | Lease financing is a contract between lessee and lessor for hire of an asset on payment rent for a specific period generally for long duration. |
2. Parties | Two parties- hirer and hiree. | Two parties- lessee and lessor. |
3. Consideration | Consideration is hire charge i.e instalment. | Consideration is rent. |
4. Transfer of ownership | Ownership is transferred from hiree to hirer on payment of last instalment. | Ownership cannot be transferred from lessor to lessee. |
5. Duration. | It is taken place for short and medium term. | It is taken place for long term. |
6. Risk of obsolescence | Risk of obsolescence is on the hirer. | Risk of obsolescence is on the lessor. |
7. Right to sell | The hirer has the right to sell the asset. | The lessee has no right to sell the asset. |
8. Governance | It is governed under the Hire Purchase Act, 1972. | It is governed under the companies act. |
5.7 SEBI guidelines: Credit rating
Credit rating simply means rating of the credit worthiness of a company and assessment of the capacity of an issuer for repayment of principal and interest on debt by an independent agency. According to CRISIL, “Credit rating is an unbiased and independent opinion as to issuer’s capacity to meet its financial obligations. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy/ sell or hold a particular security”. Different credit rating agencies like CRISIL, CARE etc. provide ratings for financial institutions, banks, financial products and instruments, financial services etc. depending on which the investors make investment decision.
Features of credit rating
Some of the essential features of credit rating are mentioned below-
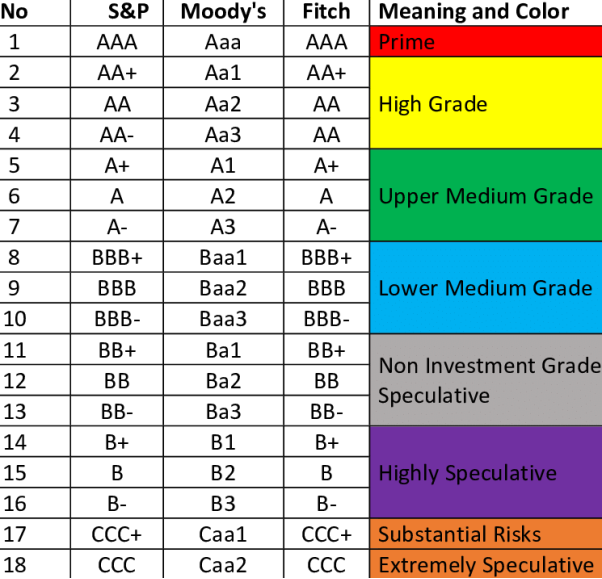
Figure: rating symbols of different credit rating agencies
Credit rating agencies in India
The credit rating agencies operating in India are discussed below-
CRISIL is the first credit rating agency in India. It is a public limited company established in 1987 in the private sector. It is promoted jointly by ICICI and UTI. It started its operations on 1st January 1988. Its objectives is to accord credit rating to public limited companies which desire to float share capital, debentures, public deposits or commercial paper to raise finance from the public.
Objectives of CRISIL-
1. To assist the investors in making investment decisions in fixed interest securities.
2. To guide the investors in understanding the risk associated with a particular debt instrument.
3. To help the companies raise large funds at a lower cost.
4. To create awareness of the concept of credit rating amongst corporations, merchant bankers, brokers, regulatory bodies.
5. To provide regulators with a market driven system in order to ensure discipline and a healthy growth of capital markets.
The services rendered by CRISIL may be summarised as below:
b. Information services: CRISIL offers information services also. Its main product ‘CRISIL CARD’ provides corporate and balance sheet data for the sake of analysis. It assesses the outlook and solvency of the concerned companies on the basis of published data. CRISIL 500 Equity Index is an index newly launched on the basis of 500 companies representing 74% of market capitalization of the Mumbai Stock Exchange.
c. Advisory services: It also offers services to the Governments, banks, financial institutions etc. It provides advisory services in the areas of energy, transport, urban infrastructure, tourism, economy, corporate, capital markets, and financial services. It also undertakes credit and counter party ratings for corporates.
2. Investment Information of Credit Rating Agency of India Ltd. (ICRA)
It is promoted by IFCI Ltd. It started operations in 1991. It offers credit rating services for rating debentures or bonds, preference shares, medium term debts, including certificates of deposits as well as short term instruments including commercial paper. It has entered into an area called Earning Prospects and Risk Analysis. ICRA also provides credit assessment and general assessment. The primary objective of ICRA is to provide information and guidance to investors/creditors for determining the credit risk associated with a debt instrument/credit obligation. ICRA Limited is a Public Limited Company, with its shares listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange and the national Stock Exchange. Today, ICRA and its subsidiaries together form the ICRA Group of Companies (Group ICRA).
Objectives of ICRA are-
1. To provide information and guidance to investors and creditors.
2. To enhance the ability of the borrower/issuer to enter into financial markets for raising resources from a wide range of investing public.
3. To help the regulators in promoting the transparency in the financial markets.
4. To enable the banks, investment bankers and brokers in placing debt with investors by providing them with a marketing tool.
Services/Functions of ICRA are discussed below-
1. Rating Services
ICRA rates rupee-denominated debt instruments, such as bonds and debentures (long-term), fixed deposit programmes (medium term), commercial paper and certificates of deposit (short-term), and structured obligations and sector-specific debt obligations (issued by Power, Telecom, and Infrastructure companies).
2. Grading Services
ICRA has developed highly specialised evaluation methodologies for grading of construction entities; real estate developers and projects; healthcare entities; maritime training institutes; and initial public offers (IPOs). These grading methodologies have been developed in association with reputable and specialised bodies, associated with the domain.
3. Advisory Services:
ICRA offers a wide range of management advisory services. These include: (a) strategic counselling, (b) risk management, (c) restructuring solutions, (d) inputs for policy formulation, (e) client specific need based studies in the banking and financial services, manufacturing and services sector etc.
4. Outsourcing:
ICRA Online Ltd, a subsidiary of ICRA, provides technology solution, targeted at distributors of third party financial products, insurance brokers, and stock broking houses. The BPO Division of ICRA Online serves financial service companies, financial institutions, investment banks, private equity and venture capital funds, market researchers and the like. The focus is on high and knowledge processing like financial modelling, data analysis valuation etc.
5. Software development:
ICRA Techno Analysis Ltd., a subsidiary of ICRA offers complete portfolio information technology solutions to meet the dynamic needs of present day businesses. The services range from the traditional development of client server, web centric and mobile applications to the generation of cutting edge business analysis.
3. Credit Analysis and Research Ltd. (CARE)
It is promoted by the IDBI. It began its operations from October 1993. It offers a wide range of services. Credit rating is conducted for debentures, fixed deposits, commercial papers etc. CARE ratings are recognised by the Government of India and regulatory agencies in India. It is registered with the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). The ratings are also recognised by RBI, NABARD, NHB and NSIC. The three largest shareholders of CARE are IDBI Bank, Canara Bank and State Bank of India. CARE is a full service rating company offering a wide range of rating and grading services. These includes rating debt instruments/enterprise ratings of corporates, banks, Financial Institutions (FIs), Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), state government bodies, municipal corporations, NBFCs, SMEs, microfinance institutions, Structured finance and Securitisation transactions.
Services or Functioning of CARE are-
a) Credit rating: It undertakes the credit rating of all types of debt instruments. The rating provides a relative ranking of the credit quality of debt instruments. It also rates quasi-debt obligations such as the ability of insurance companies to meet policy holders’ obligations.
b) Information services: It makes available information on any company, industry, or sector required by a business enterprise. This information will enable the users to make informed decisions regarding investments.
c) Advisory services: It conducts sector studies and provides advisory services in the areas of financial restructuring, valuation and credit appraisal systems.
d) Equity research: It conducts the detailed study of the shares listed in the major stock exchanges. On the basis of this study, it can identify the potential winners and losers on the basis of the fundamentals affecting the industry, economy, market share, management capabilities and other relevant factors.
e) Other services: It undertakes performance rating of parallel marketers of LPG and Superior Kerosene Oil (SKO) as notified by Central Government. It also provides a valuable input in assisting decision making process in banks and Development Financial Institutions. It has a strong structured finance team and has been instrumental in developing rating methodologies for innovative asset backed securities in the Indian capital market.
Credit rating symbols
AAA: highest safety
AA: high safety
A: adequate safety
BBB: inadequate safety
B: high risk
C: substantial risk
D: default.
Regulatory framework
SEBI Regulations, 2003 require every credit rating agency to follow the code of conduct as given below:
1. A credit rating agency shall make all efforts to protect the interests of investors.
2. A credit rating agency, in the conduct of its business, shall observe high standards of integrity, dignity and fairness in the conduct of its business.
3. A credit rating agency shall fulfil its obligations in a prompt, ethical andprofessional manner.
4. A credit rating agency shall at all times exercise due diligence, ensure proper care and exercise independent professional judgement in order to achieve and maintain objectivity and independence in the rating process.
5. A credit rating agency shall have a reasonable and adequate basis for performing rating evaluations, with the support of appropriate and in depth rating researches. It shall also maintain records to support its decisions.
6. A credit rating agency shall have in place a rating process that reflects consistent and international rating standards.
7. A credit rating agency shall not indulge in any unfair competition nor shall it wean away the clients of any other rating agency on assurance of higher rating.
8. A credit rating agency shall keep track of all important changes relating to the client companies and shall develop efficient and responsive systems to yield timely and accurate ratings. Further a credit rating agency shall also monitor closely all relevant factors that might affect the creditworthiness of the issuers.
9. A credit rating agency shall disclose its rating methodology to clients, users and the public.
10. A credit rating agency shall not make any exaggerated statement, whether oral or written to the client either about its qualification or its capability to render certain services or its achievements with regard to the services rendered to other clients.
11. A credit rating agency shall not make any untrue statements, suppress any material fact or make any misrepresentation in any documents, reports, papers or information furnished to the Board, stock exchange or public at large.
12. A credit rating agency shall maintain an appropriate level of knowledge and competence and abide by the provisions of the Act, regulations and circulars, which may be applicable and relevant to the activities carried on by the credit rating agency. The credit rating agency shall also comply with award of the Ombudsman passed under Securities and Exchange Board of India (Ombudsman) Regulations, 2003.
13. A credit rating agency shall ensure that there is no misuse of any privileged information including prior knowledge of rating decisions or changes.
14. A credit rating agency or any of his employees shall not render, directly or indirectly any investment advice about any security in the publicity accessible media.
15. A credit rating agency shall maintain an arm’s length relationship between its credit rating activity and any other activity.
References-