Unit I
Introduction
Electronic commerce or e-commerce refers to buying and selling of products and services over the internet or electronic platform. It facilitates the buyers and sellers from different geographical locations to connect with each other for purchase and sale of goods and services without physical interactions. For example purchase of products from online shopping site, purchase of railway tickets etc.
Scope of ecommerce
Ecommerce has great potential in developed and developing markets globally. With the advancement of information technology, busy schedule of households, innovations in financial sector and service sector the demand for ecommerce has increased tremendously. Ecommerce has great scope in the sectors like-

Figure: Scope of ecommerce
- Banking: Internet banking, mobile banking, SMS banking etc. services are provided by banks to the consumers through online.
- Financial service: Financial services like insurance, stock trading, depositories, mutual fund services are provided through their websites.
- Telecommunication: Different telecom companies widely use the ecommerce services for delivering their services to the consumers.
- Transportation: Transport companies like railway, buses, airlines companies etc. provides e-ticket, travel information in mail, phone etc. for the convenient of customers.
- Communication: Ecommerce facilitates quick communication through G-mail, Fax, Wats up, Skype, Google meet, Zoom platform etc.
- OTT: Ecommerce facilitates different OTT flatforms like Netflix, Amazon pime, Disney hot star, Zee premium, sony liv etc. provide entertainment services to the customers.
- Online shopping: Ecommerce facilitates online shopping websites like Amazon, Flipkart, Myntra, Ajio, Snapdeal etc. to sells variety of products and services to the target group.
- Tourism: Ecommerce also extends to tourism sector. Travel tickets booking, hotel booking, travel insurance etc. services are provided online by different ecommerce sites like Trivago, Make my trip, Red bus, Oyo, Goibibo etc. provide tourism services to the customers.
- Real estate: Real estate sector also use the services of ecommerce to sell and purchase flats, apartments, houses, property, rented house etc.
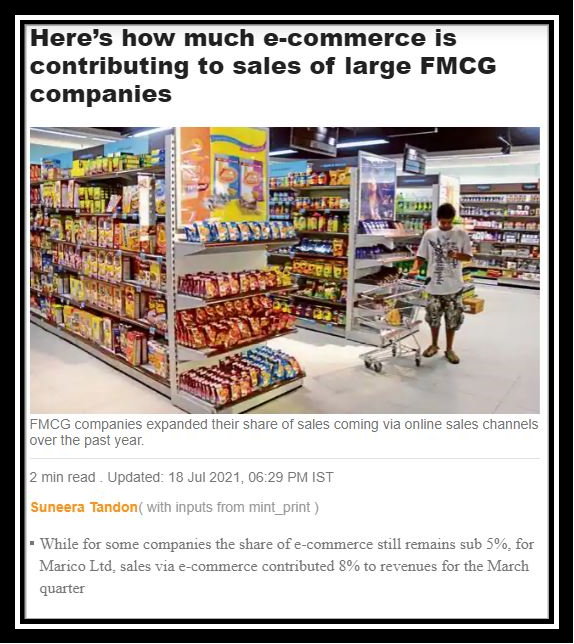
Functions of ecommerce
The major functions of ecommerce are-
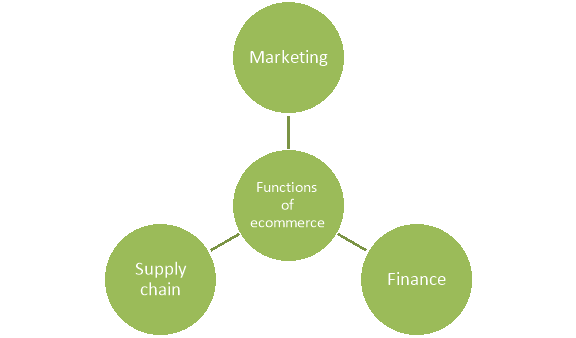
Figure: Functions of ecommerce
- The marketing of ecommerce:
Different marketing activities of ecommerce are mentioned below-
- Conduct market research that helps to identify and validate the opportunity as part of the e-Commerce planning process.
- Creation of brand by managing the marketing mix i.e. product, price, place, promotion, process and physical evidence of goods/services.
- Formulate communication and digital marketing plans to create a network with the potential target customer group.
2. The finances of e-commerce:
In e-commerce exchange of money is taken place through online mode. Hence, the business organisations must manage their finances effectively by considering the following elements-
- Establish a payment gateway to guide the order to delivery process.
- Charge system is designed to protect shoppers and businesses. Payment gateway handle the transfer of money back from your bank account to the buyer’s card when there needs to be a refund. These refund transfers are called chargebacks.
- Tracking of financial performance by considering profit and loss on sales, delivery charge, profit and loss on cost, transaction cost, delivery cost etc.
3. The Supply chain of e-commerce:
It is the system that stores and delivers products from producers to the end buyer. Decisions are taken regarding where to store, how to store and who will store the e-commerce products. The business also estimates the cost associated with storage and delivery of e-commerce products.
It also provides services to customers for the scenarios like-
- If products never arrives with the customer.
- If the product arrives damaged.
- If wrong product or quantity is delivered.
- If the product is stolen.
The significant objectives of e-commerce are highlighted under the following points-
a) To reduce management cost:
It reduces cost of management on marketing and communication because ecommerce uses digital marketing tools and social media platforms for communication.
b) To develop business relations:
The e-commerce able to develop better relation between customer and business because of direct communication between them. All issues can be solved within a short period to provide them better satisfaction.
c) To increase customer base:
Digital marketing and communication helps to reach greater customer. Better customer service also helps to retain the customer.
d) To provide variety in choice:
E-commerce able to provide wide choices on product and service because the customers able to access different sellers from wide geographical locations.
e) To increase sales:
The aggressive marketing plans, variety of products, differentiation in products of e-commerce helps to attract more customers and increase its sales accordingly.
f) To boost efficiency in services:
It demands innovations and efficiency in services like delivery process, payment gateway, after sale service etc. It ultimately boosts the efficiency in services and customer satisfaction.
g) To improve brand image:
It improves brand image of the business by planning the marketing mix like product, price, place, promotion, process and physical evidence of e-commerce products and services.
h) To provide customer services:
It is one of the important objectives of ecommerce to provide innovative and better customer service to satisfy their needs.
i) To conduct market research:
It conducts market research to identify the customer needs and preferences, market competition, market opportunity for development of plans for start-up or expansion and diversification business
Key takeaways
- Electronic commerce or e-commerce refers to buying and selling of products and services over the internet or electronic platform. For example purchase of products from online shopping site, purchase of railway tickets etc.
The key features/nature of ecommerce is discussed below-
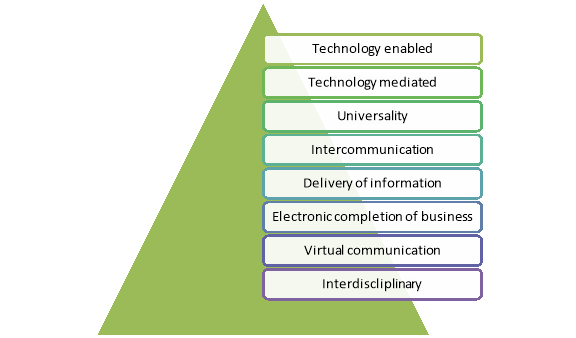
Figure: Nature of ecommerce
1. E-Commerce is Technology-Enabled:
Traditional commerce is taking place since times immemorial but E-commerce is result of integration of digital technology with business processes and commercial transactions. The technological foundations of E-commerce are internet, WWW and various protocols.
2. Technology Mediated:
In E-commerce buyers and sellers meet in cyber space rather than physical place. Hence E-commerce does not involve face to face contact.
3. Universality:
Buying and selling take place through websites in E-Commerce. The websites can be accessed from anywhere around the globe at any time therefore it possess the feature of universality.
4. Intercommunication:
E-commerce technology ensures two way communications between buyer and seller. On one hand by using E- commerce firms can communicate with customers through E-commerce enabled websites. On the other end, customers can also fill order forms, feedback forms and can communicate with business operating firms.
5. Delivery of Information:
E-commerce serves as the best channel of communication. E-commerce technologies ensure speedy delivery of information at very low cost and considerably increase information density as well.
6. Electronic Completion of Business Processes:
By using E- commerce we can perform business transactions like accounting and inventory through computers at global level.
7. Virtual Communities:
Virtual Communities are online communities created by means such as chat rooms and specifically designed sites like, where people can interact with each other having common interest using the internet.
8. Inter-Disciplinary in Nature:
Implementation of E-Commerce needs a lot of knowledge of managerial, technological, social and legal issues. Besides this, understanding of consumer behaviour, marketing tools and financial aspects is as crucial as designing interactive E- Commerce websites.
Key takeaways
- E-commerce is result of integration of digital technology with business processes and commercial transactions.
The concepts of ecommerce that facilitate to execute the transactions smoothly are discussed below-
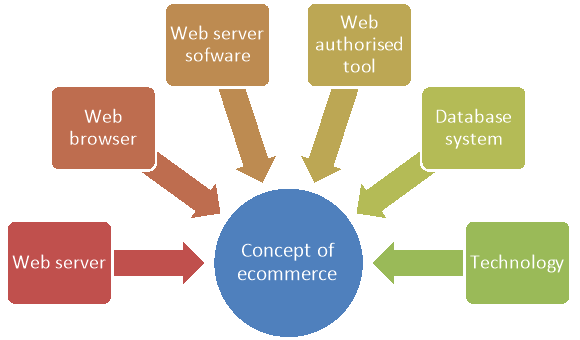
Figure: Concept of ecommerce
1. Web server: It is used to host an ecommerce website.
2. Web browser: It is a software application that facilitates the customers to access the internet.
3. Web server software: It manages access attempts to a website.
4. Web authorised tools: it is used to create HTML & CSS files that connect to integrated database.
5. Database system: It is used to store information about the ecommerce products and services.
6. Technologies: it is used to communicate between the website and database management system.
The popularity of ecommerce is increasing day by day because it is beneficial for customers, business and society as a whole. Some of the benefits of ecommerce are-
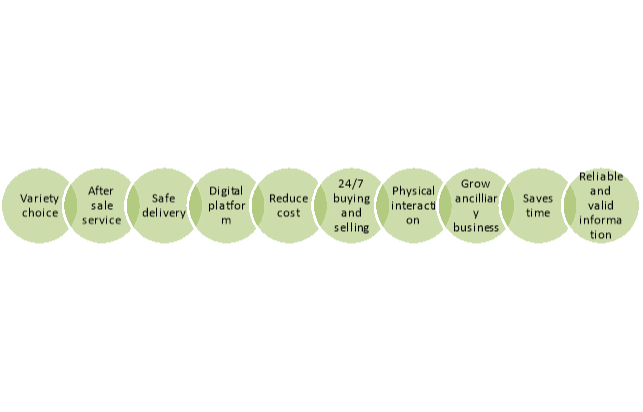
Figure: Advantages of ecommerce
- It provides variety in choices to the customers for products and services.
- It provides better after sale services to customers increase their brand loyalty.
- It provides quick and safe delivery of products and services at the provided address.
- It uses digital platform for marketing and communication which helps to access the target customer group in a convenient way.
- It reduces the cost of storage, production, business operation, raw material cost etc.
- It provides 24/7 buying & selling of products and services unlike traditional one.
- There is no need for physical interaction between buyers and sellers. Thus buyers and sellers from far-away places can buy and sell products and services over internet.
- It helps to establish and grow ancillary businesses like logistic, marketing firms, packaging material suppliers, internet service provider etc.
- It saves time of customers by delivering the products at their provided address and convenient time.
- It provides reliable and valid information to potential consumers to attract towards their products and services.

Ecommerce also suffers from some disadvantages. Some of them are-
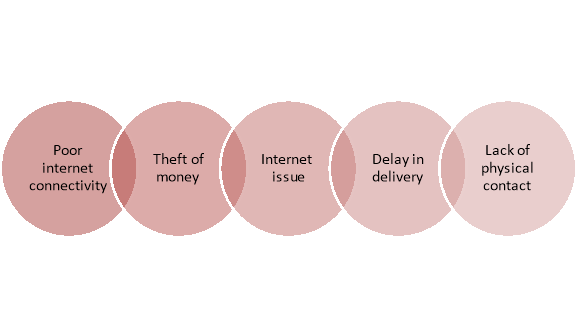
Figure: Disadvantages of ecommerce
- Sometimes issues related to financial transaction arises due to poor internet connectivity or poor payment gateway.
- Customers may suffer from theft of money if the payment gateway is not highly secured.
- Access to ecommerce website is not possible if there is no internet connectivity.
- Delay in deliver issues arises if the logistic and supply system is not efficient.
- Due to lack of physical contact sometimes the customers choose wrong products or services.
Key takeaways
- The popularity of ecommerce is increasing day by day because it is beneficial for customers, business and society as a whole.
Online transactions are growing popularity day by day among the people especially among working group and young population. Moreover, Digital India scheme also give push for online transaction. The reasons for the growth of online transaction are discussed below-

Figure: Reasons for online business
1) Eliminate geographical boundaries.
When a person travels to a different country or continent, they have to adapt what’s in their wallet. This may include exchanging currency, and even using a different credit card than they would typically use. Online payments eliminate the obstacles to participating in a global marketplace. Many payment processors equip businesses to accept a range of different currencies, automatically calculate the proper exchange rate based on the type of currency — and even adapt the language and information prompted in checkout forms to accommodate the different languages buyers might speak, based on the currency used.
2) Convenient
Payment technology has evolved to the point that consumers can complete an online payment even if they don’t have a card or physical wallet on hand. Mobile wallets, like BHIM, google pay, airtel money, paytm etc. provide a convenient platform to transfer and pay money from one end to another end instantly without consuming time.
3) Time value
Online payments aren’t just convenient in the sense of transaction speed — they eliminate the need for consumers to travel to a store, invest their time, and wait in line to pay.
4) Purchase protection.
Buying from a small business, whether in person or online, requires that customers establish some degree of trust with a merchant with whom they may have no previous experience. Regardless of how clearly a business communicates its return, exchange, and customer satisfaction policies, there may be a sense of hesitancy for consumers. Online payments can overcome this obstacle. When online payments are made using a credit card that guarantees the lowest price for a stated number of days, extends manufacturer warranties, and offers a cardholder the right to dispute a purchase, for example, the customer has peace of mind that they will be protected, regardless of the merchant’s policy.
5) Provide cost-free benefits
In addition to all of the benefits customers can gain from online payments, they cost consumers nothing in return. In a world where so few things are free, online payments offer consumers a value-added convenience, with no additional investment required. Though businesses may incur a small fee for accepting credit cards, the fact that consumers are given the option to pay in the means they prefer will likely negate the nominal fee that’s involved in the transaction.
6. Eliminates currency issues
A client traveling to a different country have to exchange currency at his local bank before he leaves or upon arrival at his destination so he can settle the fees at the company’s office or shop. Many people prefer the online payment method for travel-related services because it usually accepts major credit cards which automatically calculate the current exchange rate on the day of the transaction.
7. Rewards and bonuses
Customers may also prefer online credit card transactions because many companies reward frequent cardholders users with points that they can exchange with exciting gifts, miles, or rebates to cover for other expenses.
8. Bridges gaps:
E-commerce bridges the gap between local sellers and global audiences, thereby helping them in widening their reach across the global market segment without making further investments.

Key takeaways
- Online transactions are growing popularity day by day among the people especially among working group and young population. Moreover, Digital India scheme also give push for online transaction.
Ecommerce provides platform to customers, retailers, wholesalers, producers, service providers etc. to sell or purchase the desirable products. The different categories of ecommerce are discussed below-
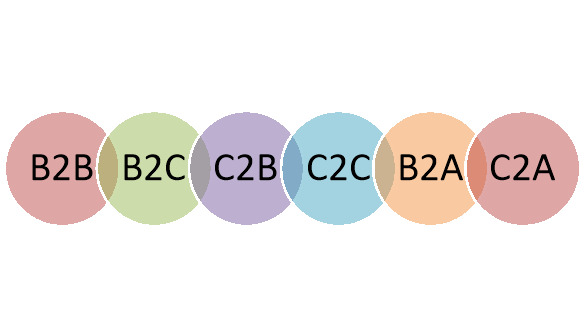
Figure: Categories of ecommerce
- Business to business (B2B):
It refers to buying and selling of goods or services electronically between the companies. Such transactions are bulk in nature. The channels of such trade generally include conventional wholesalers and producers who are dealing with retailers. For example, Alibaba.
2. Business to consumer (B2C):
It refers to buying and selling of goods and services electronically between businesses and final consumers. It is also termed as retail section of e-commerce. This mode of purchase has proved to be beneficial to the consumers when compared to the traditional method, as they are endowed with access to helpful contents which may guide their purchases appropriately. For example, Netflix, Amazon etc.
3. Consumer to consumer (C2C):
It refers to buying and selling of goods and services electronically between consumers. Generally, these transactions are conducted through a third party. For example, eBay and Craigslist are online marketplaces where individuals buy and sell products to each other.
4. Consumer to business (C2B):
In this type of e-commerce model, individuals make their services or products available for purchase for companies. Here, paintings, images, photos etc. are purchased and sold. For example, Freelancer connects workers and companies.
5. Business-to-Administration (B2A)
This model enables online dealings between companies and public administration, i.e. the Government by enabling the exchange of information through central websites. It provides businesses with a platform to bid on government opportunities such as auctions, tenders, application submission, etc. The scope of this model is now enhanced, thanks to the investments made towards e-government. An example of a B2A model, is that of Accela.com, a software company that provides round the clock public access to government services for asset management, emergency response, permitting, planning, licensing, public health, and public works.
6.Consumer-to-Administration (C2A)
The C2A platform is meant for consumers, who may use it for requesting information or posting feedbacks concerning public sectors directly to the government authorities/administration. Its areas of applicability include:
- The dissemination of information.
- Distance learning.
- Remittance of statutory payments.
- Filing of tax returns.
- Seeking appointments, information about illnesses, payment of health services, etc.
Examples of applications include:
- Education – disseminating information, distance learning, etc.
- Social Security – through the distribution of information, making payments, etc.
- Taxes – filing tax returns, payments, etc.
- Health – appointments, information about illnesses, payment of health services, etc.

Key takeaways
- Ecommerce provides platform to customers, retailers, wholesalers, producers, and service providers etc. to sell or purchase the desirable products.
Supply chain management means the management of flow of goods and services and it includes the process of transforming of raw material to final goods and then sale it to the final consumers. It helps the producers to reduce cost by managing production, logistic, marketing and sales. The fig below shows the supply chain management flow-
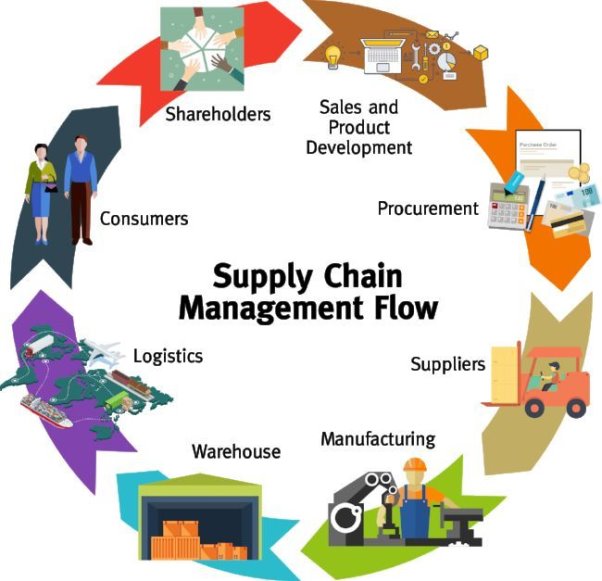
Fig 1: Supply chain management flow
Source: jyler.com
The supply chain management consist of the elements like-
- Purchasing: The producer purchases raw materials from different sources at competitive prices at right time.
- Production: The produces manufactures final goods form the raw materials which is offered to the public for sale.
- Market and sales: Before sale the produces must promote the product in the market with the help of different marketing tools and techniques to attract consumers towards the products.
- Logistics: It is one of the crucial elements of supply chain management that facilitates transfer of products from the place of producers to consumers. Logistic services are provided by currier service companies, airlines, railways, roadway transport companies etc.
- Finance: There is huge requirement of funds to manage the supply chain of a company. Such finances are managed from shareholders, banks and other investors.
- Research and development: The research and development is necessary to identify the need for supply chain managements, improvements and developments for the same.

Key takeaways
- Supply chain management means the management of flow of goods and services and it includes the process of transforming of raw material to final goods and then sale it to the final consumers. It helps the producers to reduce cost by managing production, logistic, marketing and sales.
Customer relationship management (CRM) refers to the principles, practices, and guidelines that an organization follows when interacting with its customers. From the organization's point of view, this entire relationship encompasses direct interactions with customers, such as sales and service-related processes, forecasting, and the analysis of customer trends and behaviours. Ultimately, CRM serves to enhance the customer's overall experience.

Features of CRM
The benefits of CRM are discussed below-
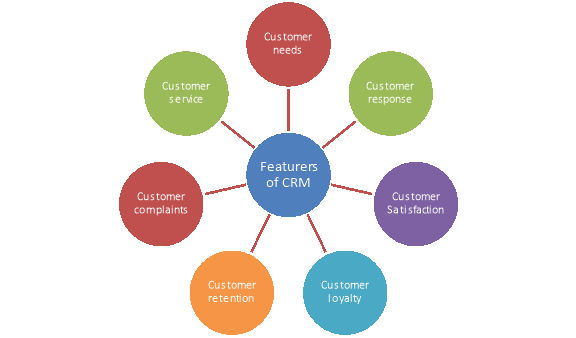
Figure: Features of CRM
- Customer Needs-
An organization can never assume what actually a customer needs. Hence it is extremely important to interview a customer about all the likes and dislikes so that the actual needs can be ascertained and prioritized. Without modulating the actual needs it is arduous to serve the customer effectively and maintain a long-term deal.
2. Customers Response-
Customer response is the reaction by the organization to the queries and activities of the customer. Dealing with these queries intelligently is very important as small misunderstandings could convey unalike perceptions. Success totally depends on the understanding and interpreting these queries and then working out to provide the best solution. During this situation if the supplier wins to satisfy the customer by properly answering to his queries, he succeeds in explicating a professional and emotional relationship with him.
3. Customer Satisfaction-
Customer satisfaction is the measure of how the needs and responses are collaborated and delivered to excel customer expectation. In today’s competitive business marketplace, customer satisfaction is an important performance exponent and basic differentiator of business strategies. Hence, the more is customer satisfaction; more is the business and the bonding with customer.
4. Customer Loyalty-
Customer loyalty is the tendency of the customer to remain in business with a particular supplier and buy the products regularly. This is usually seen when a customer is very much satisfied by the supplier and re-visits the organization for business deals, or when he is tended towards re-buying a particular product or brand over times by that supplier. To continue the customer loyalty the most important aspect an organization should focus on is customer satisfaction. Hence, customer loyalty is an influencing aspect of CRM and is always crucial for business success.
5. Customer Retention-
Customer retention is a strategic process to keep or retain the existing customers and not letting them to diverge or defect to other suppliers or organization for business. Usually a loyal customer is tended towards sticking to a particular brand or product as far as his basic needs continue to be properly fulfilled. He does not opt for taking a risk in going for a new product. More is the possibility to retain customers the more is the probability of net growth of business.
6. Customer Complaints-
Always there exists a challenge for suppliers to deal with complaints raised by customers. Normally raising a complaint indicates the act of dissatisfaction of the customer. There can be several reasons for a customer to launch a complaint. A genuine reason can also exist due to which the customer is dissatisfied but sometimes complaints are launched due to some sort of misunderstanding in analyzing and interpreting the conditions of the deal provided by the supplier regarding any product or service. Handling these complaints to ultimate satisfaction of the customer is substantial for any organization and hence it is essential for them to have predefined set of process in CRM to deal with these complaints and efficiently resolve it in no time.
7. Customer Service-
In an organization Customer Service is the process of delivering information and services regarding all the products and brands. Customer satisfaction depends on quality of service provided to him by the supplier. The organization has not only to elaborate and clarify the details of the services to be provided to the customer but also to abide with the conditions as well. If the quality and trend of service go beyond customer’s expectation, the organization is supposed to have a good business with customers.
Benefits of customer relations management
The benefits of CRM are discussed below-
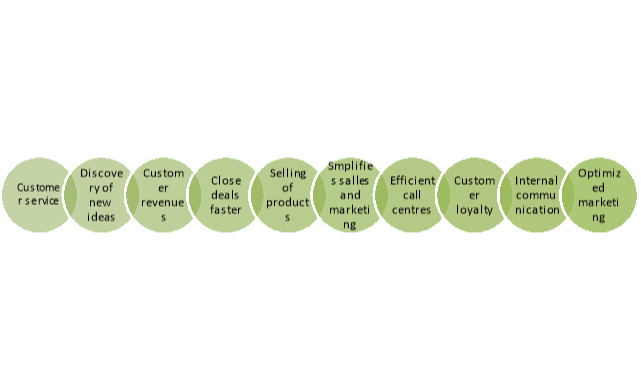
Figure: Benefits of CRM
- Enhances Better Customer Service
CRM systems provide businesses with numerous strategic advantages. One of such is the capability to add a personal touch to existing relationships between the business and the customers. It is possible to treat each client individually rather than as a group, by maintaining a repository on each customer’s profiles. This system allows each employee to understand the specific needs of their customers as well as their transaction file. The organization can occasionally adjust the level of service offered to reflect the importance or status of the customer. Improved responsiveness and understanding among the business employees results in better customer service. This decreases customer agitation and builds on their loyalty to the business. Moreover, the company would benefit more by getting feedback over their products from esteemed customers. The level of customer service offered is the key difference between businesses that lead the charts and those that are surprised with their faulty steps.
2. Facilitates discovery of new customers
CRM systems are useful in identifying potential customers. They keep track of the profiles of the existing clientele and can use them to determine the people to target for maximum clientage returns. New customers are an indication of future growth. However, a growing business utilizing CRM software should encounter a higher number of existing customers versus new prospects each week. Growth is only essential if the existing customers are maintained appropriately even with recruitment of new prospects.
3. Increases customer revenues
CRM data ensures effective co-ordination of marketing campaigns. It is possible to filter the data and ensure the promotions do not target those who have already purchased particular products. Businesses can also use the data to introduce loyalty programs that facilitate a higher customer retention ratio. No business enjoys selling a similar product to a customer who has just bought it recently. A CRM system coordinates customer data and ensures such conflicts do not arise.
4. Helps the sales team in closing deals faster
A CRM system helps in closing faster deals by facilitating quicker and more efficient responses to customer leads and information. Customers get more convinced to turn their inquiries into purchases once they are responded to promptly. Organizations that have successfully implemented a CRM system have observed a drastic decrease in turnaround time.
5. Enhances effective cross and up selling of products
Cross – selling involves offering complimentary products to customers based on their previous purchases. On the other hand, up – selling involves offering premium products to customers in the same category. With a CRM system, both cross and up – selling can be made possible within a few minutes of cross – checking available data. Apart from facilitating quicker offers to customers, the two forms of selling helps staff in gaining a better understanding of their customer’s needs. With time, they can always anticipate related purchases from their customer.
6. Simplifies the sales and marketing processes
A CRM system facilitates development of better and effective communication channels. Technological integrations like websites and interactive voice response systems can make work easier for the sales representatives as well as the organization. Consequently, businesses with a CRM have a chance to provide their customers with various ways of communication. Such strategies ensure appropriate delivery of communication and quick response to inquiries and feedback from customers.
7. Makes call centers more efficient
Targeting clients with CRM software is much easier since employees have access to order histories and customer details. The software helps the organization’s workforce to know how to deal with each customer depending upon their recorded archives. Information from the software can be instantly accessed from any point within the organization. CRM also increases the time the sales personnel spend with their existing customers each day. This benefit can be measured by determining the number of service calls made each day by the sales personnel. Alternatively, it could also be measured through the face – to – face contact made by the sales personnel with their existing customers.
8. Enhances customer loyalty
CRM software is useful in measuring customer loyalty in a less costly manner. In most cases, loyal customers become professional recommendations of the business and the services offered. Consequently, the business can promote their services to new prospects based on testimonials from loyal customers. Testimonials are often convincing more than presenting theoretical frameworks to your future prospects. With CRM, it could be difficult pulling out your loyal customers and making them feel appreciated for their esteemed support.
9. Builds up on effective internal communication
A CRM strategy is effective in building up effective communication within the company. Different departments can share customer data remotely, hence enhancing team work. Such a strategy is better than working individually with no links between the different business departments. It increases the business’s profitability since staff no longer have to move physically move while in search of critical customer data from other departments.
10. Facilitates optimized marketing
CRM enables a business understand the needs and behavior of their customers. This allows them to identify the correct time to market their products to customers. The software gives ideas about the most lucrative customer groups to sales representatives. Such information is useful in targeting certain prospects that are likely to profit the business. Optimized marketing utilizes the business resources meaningfully. CRM software will remain relevant for quiet long as long as businesses desire a quick balance between product provision and customer acquisition. Inarguably, the advantages of customer relationship management will remain relevant as long as businesses desire to build a competitive advantage over their competitors.
Key takeaways
- Customer relationship management (CRM) refers to the principles, practices, and guidelines that an organization follows when interacting with its customers. From the organization's point of view, this entire relationship encompasses direct interactions with customers, such as sales and service-related processes, forecasting, and the analysis of customer trends and behaviours.
References-
- Pandey U.S – E.Commerce& Mobile Commerce Technology – S. Chand
- Amor, Daniel - Pearson Edude. E Business R (Evolution).
- 2.Greenslein & Feinman. Electronic Commerce. TMH.
- 3.David Whiteley. E-Commerce: Strategy, Technologies and Applications. TMH.
- Kotlar, P. (2019). Marketing management (4th edition.). New Delhi, Pearson Education India.
- Retailnext.net
- Www.bigcommerce.com