Unit – 3
Series solution of differential equation
Working Rule
Step 1 Let 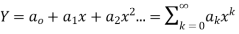 be the solution of the given differential equation.
be the solution of the given differential equation.
Step 2: Find 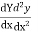 etc.
etc.
Step 3: Substitute the expression of 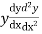 in the given differential equation.
in the given differential equation.
Step 4: Calculate 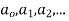 coefficient of various powers of x by equating coefficients to zero.
coefficient of various powers of x by equating coefficients to zero.
Step 5: Substitute the values of 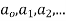 in the differential equation to get the required series solution.
in the differential equation to get the required series solution.
Example. Solve in series the equation
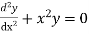
Ans. 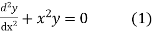
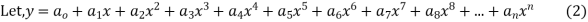
Since x=0 is the ordinary point of the equation (1)
Then 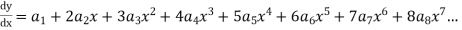
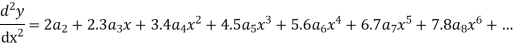
Substituting in (1) we get
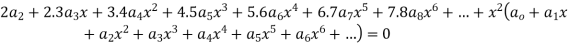
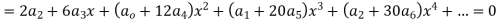
Equating to zero the coefficient of the various powers of x we obtain
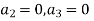
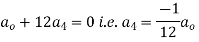
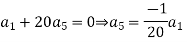
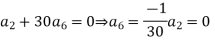
Substituting these values in (2) we get
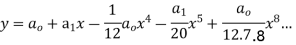
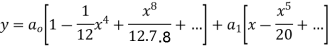
Solve. 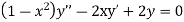
Ans. Let, 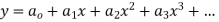
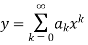
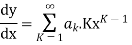
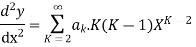
Substituting the value of 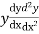 in the given equation we get
in the given equation we get
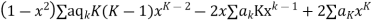
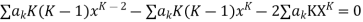
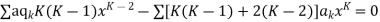
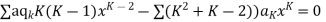
Where the first summation extends over all values of K from 2 to 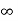
And the second from K =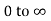
Now equating the coefficient of 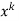 equal to zero we have
equal to zero we have
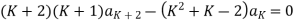
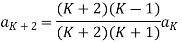
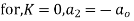
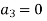
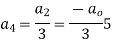
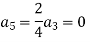
For K =4
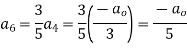
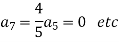
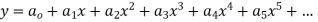
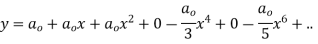
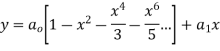
Solve. 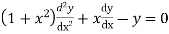
Ans. Let 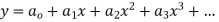
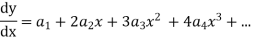
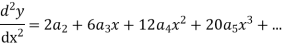
Substituting for 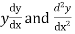 in the given differential equation
in the given differential equation
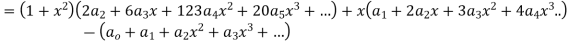
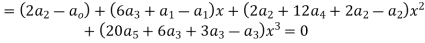
Equating the coefficients of various powers of x to zero we get
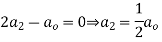
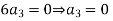
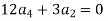
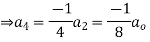
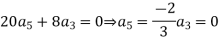
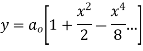
Legendre’s equation is 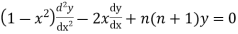
And 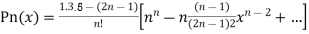
Prove that 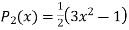
Ans. We know that 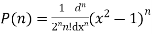
Put n=2
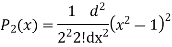
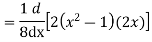
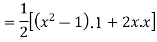
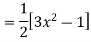
Prove that  .
.
Ans. We know
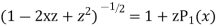 +
+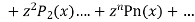
Put x = 1 both sides we get
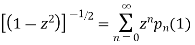
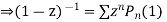
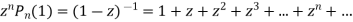
Equating the coefficient of 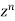 on both sides we get
on both sides we get
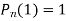
Prove that 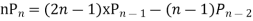
Ans. We know 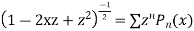
Differentiating with respect to z we get
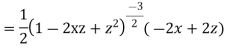
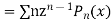
Multiplying both sides by 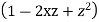 we get
we get
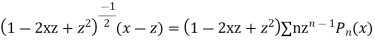
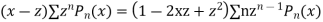
Equating the coefficient of 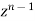 from both sides we get
from both sides we get
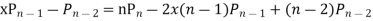
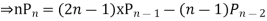
Solve. Statement 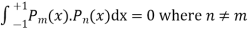
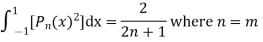
Proof. Let 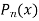 is a solution of
is a solution of
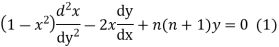
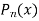 is the solution of
is the solution of
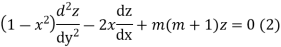
Multiplying (1) by z and (2) by y and subtracting we get
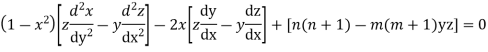
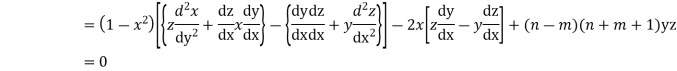
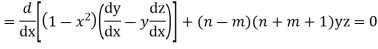
Now integrative -1 to 1 we get
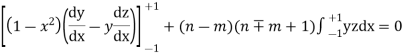
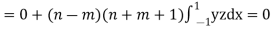
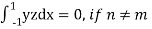

Now we have to prove that
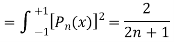
We know that,
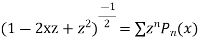
Squaring both sides we get
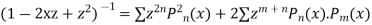
Integrating both sides between -1 to +1 we get
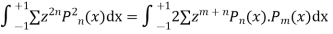
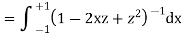
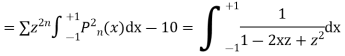
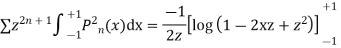
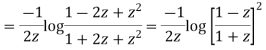
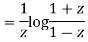
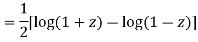
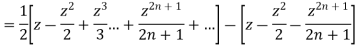
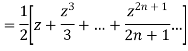
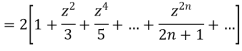
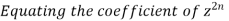 on both sides we get
on both sides we get
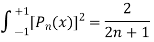

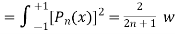 here n = m
here n = m
Prove that 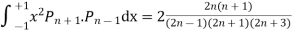
Ans. The Recurrence formula is
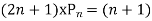 Pn+1+nPn-1
Pn+1+nPn-1
Replacing n by (n+1) and (n-1) we have
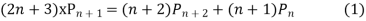
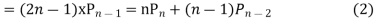
Multiplying (1) and (2) and integrating in the limits -1 to 1 we get
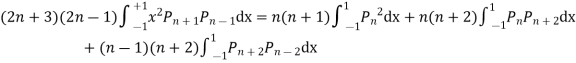
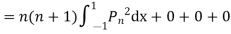 (By orthogonality property)
(By orthogonality property)
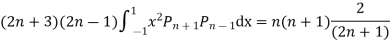
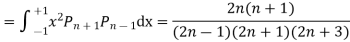
Rodrigues' Formula: The Legendre Polynomials 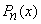 can be expressed by Rodrigues' formula
can be expressed by Rodrigues' formula
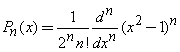 where
where 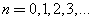
Generating Function: The generating function of a Legendre Polynomial is
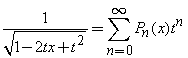
Orthogonality: Legendre Polynomials 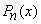 ,
, 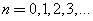 , form a complete orthogonal set on the interval
, form a complete orthogonal set on the interval 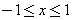 . It can be shown that
. It can be shown that
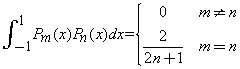
By using this orthogonality, a piecewise continuous function 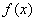 in
in 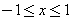 can be expressed in terms of Legendre Polynomials:
can be expressed in terms of Legendre Polynomials:
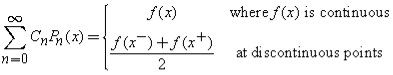
Where:
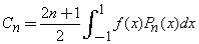
This orthogonal series expansion is also known as a Fourier-Legendre Series expansion or a Generalized Fourier Series expansion.
Even/Odd Functions: Whether a Legendre Polynomial is an even or odd function depends on its degree 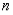 .
.
Based on 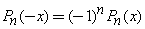 ,
,
• 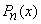 is an even function when
is an even function when 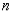 is even.
is even.
• 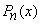 is an odd function when
is an odd function when 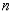 is odd.
is odd.
In addition, from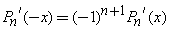 ,
,
• 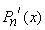 is an even function when
is an even function when 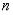 is odd.
is odd.
• 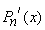 is an odd function when
is an odd function when 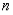 is even.
is even.
Recurrence Relation: A Legendre Polynomial at one point can be expressed by neighboring Legendre Polynomials at the same point.
• 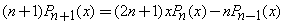
• 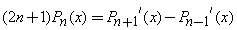
• 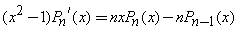
• 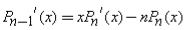
• 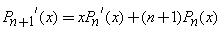
The Bessel equation is
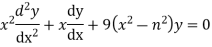
The Bessel equation is
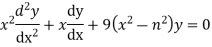
Bessel function of first kind
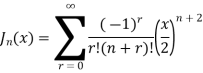
Bessel function of second kind
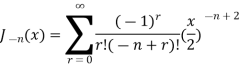
Recurrence Formula
1) xJn'=nJn-xJn+1
2) 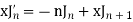
3) 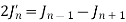
4) 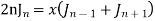
5) 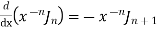
6) 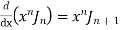
Prove that (1) 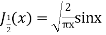
Ans. We know
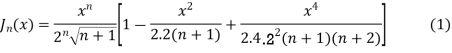
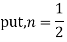
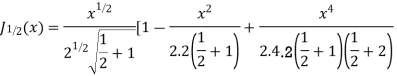
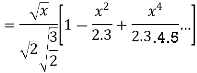
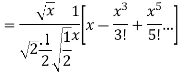
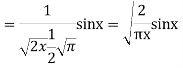
(b) Prove that 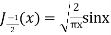
Ans. We know that
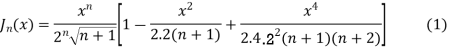
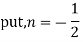
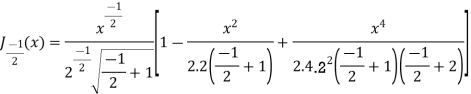
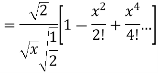
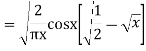
(3) Prove that 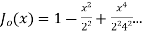
Ans. We know that
Jn(x)=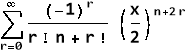
If n = 0
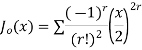
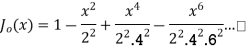
If n = 1
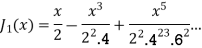
Note General solution of Bessel Equation
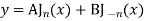
Text Book:
1) Calculus: Gorakh Prasad
2) Advance Engineering Mathematics – E. Kreyszig, John Wiley & Sons Inc.