Unit 05
Question Bank
Q-1What are Portland cement?
Portland cement used as the basic ingredient of the concrete worldwide. It is the most common type of cement in general use. It is the mixture of calcium silicates and calcium aluminates with small amount of gypsum in it. On mixing the powder of Portland cement with water it gives the hard, stone like mass which resembles like Portland rock this is the reason why it is named as the Portland cement.
Q-2Enlist the compositions of Portland cement.
Hydraulic cement produced by pulverizing clinkers that consists of calcium silicate, usually containing one or more of the forms of calcium sulfate as a inter ground station. A good sample of Portland cement consists of:
(i) Silica(SiO2): - 20-24%
(ii) Calcium Oxide: -60-70%
(iii) Alumina (Al2O3): -5-7%
(iv) Magnesia(MgO): -2-3%
(v) Ferric Oxide (Fe2O3): -1-2.5%
(vi) Sulphur trioxide (SO3): -1-1.5%
(vii) Sulphur Oxide: -1%
(viii) Potassium Oxide (K2O): -1%
Q-3Explain wet process manufacturing.
On using the calcareous as a raw material then chalk must be crushed into minute particles and hence dispersed it in water in a wash mill. Wash mill used to break the solid materials into lumps/slurry. In similar wash mill clay is also broken up and mixed with water. Then this slurry is stored in the silo called as slurry silo where it is consistently stirred. The composition of raw material is checked again and if required corrected by adding clay or chalk materials as per requirement.
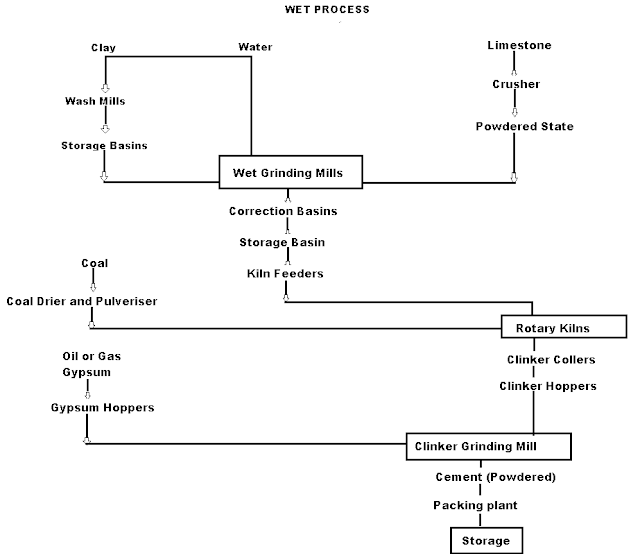
Q-4Explain dry process manufacturing.
This type of process for manufacturing the cement is available in the places where hard crystalline limestone and shales are available. The advantage of using this type of process is that fuel consumption is low.
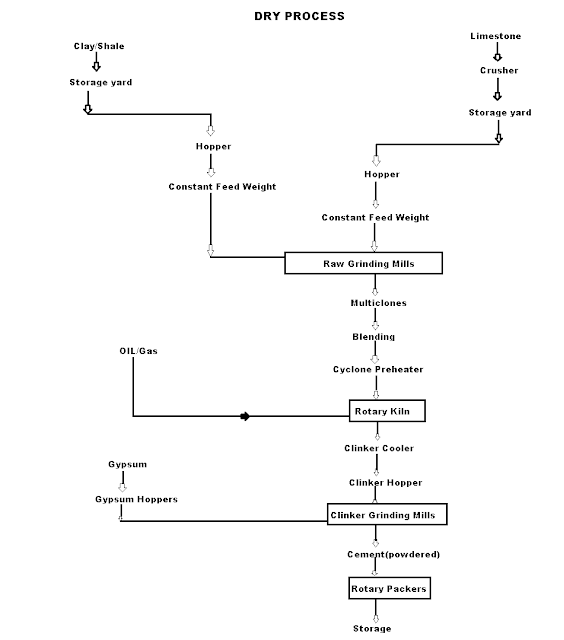
Q-5Explain the hardening of cement.
The hardening starts after setting as because of gradual progress of crystallization in the interior mass of cement. The strength developed by cement paste at any time depends upon the amount of gel formed and the extent of crystallization. The setting and hardening of cement is due to the formation of inter locking crystals reinforced by rigid gels formed by the hydration and hydrolysis of the constitutional compounds.
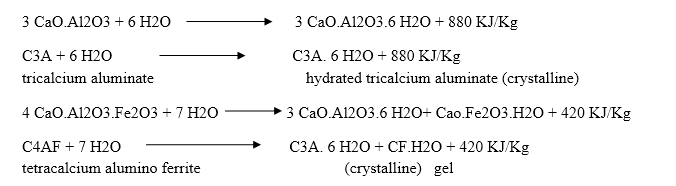
Dicalcium silicate also hydrolyses to tobermonite gel which contributes to initial setting.

Final setting and hardening of cement paste is due to the formation of tobermonite gel and crystallization of calcium hydroxide and hydrated tricalcium aluminate.
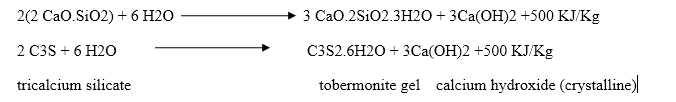
During setting and hardening of cement, some amount of heat is liberated due to hydration and hydrolysis reactions. The quantity of heat evolved during hydration of cement is 500 KJ/Kg.
Q-6What are gypsum?
Tri calcium aluminate combines with water very rapidly.

After the initial setting, the paste becomes soft and the added gypsum retards the dissolution of tri calcium aluminate by forming insoluble calcium sulpho aluminate.
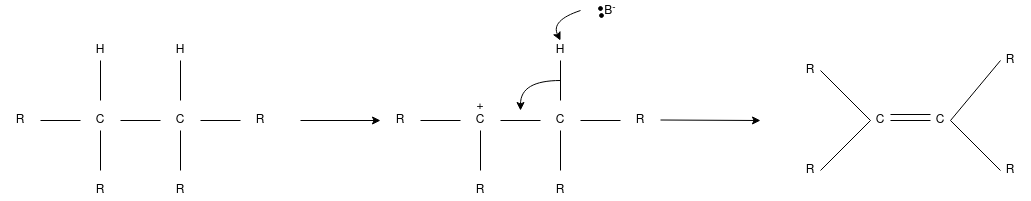
Q-7Explain E1 Reaction.
- This is also called as unimolecular elimination reaction, there are usually two steps involved – ionization and deprotonation.
- During ionization, there is a formation of carbocation as an intermediate. In deprotonation, a proton is lost by the carbocation.
- This happens in the presence of a base which further leads to the formation of a pi-bond in the molecule.
- In E1, the reaction rate is also proportional to the concentration of the substance to be transformed.
- It exhibits first-order kinetics.
Q-8Explain the synthesis of Aspirin.
The chemical name for the Aspirin is Acetylsalicyclic acid. It is used as pain killer and fever reducer. Salicyclic acid derive from the willow family of plants which were widely used for treating headache. For the preparation of aspirin the salicyclic acid is reacted with the excess acetic anhydride. Phospohoric acid is used for boosting the procedure of reaction. The excess acetic acid will be quenched with the addition of water. The aspirin product is not very soluble in water so the aspirin product will precipitate when water is added. The synthesis reaction of aspirin is shown below:
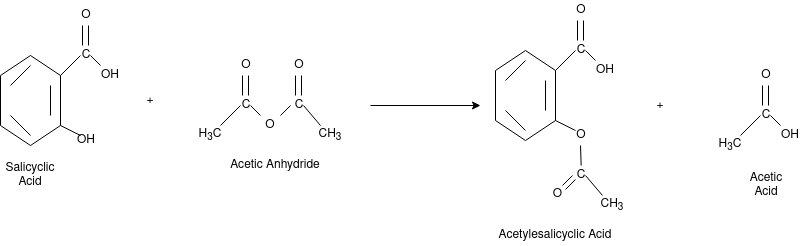
Since acetic acid is very soluble in water, it is easily separated from the aspirin product. The aspirin isolated in this step is the “crude product”. A “purified product” can be obtained through re-crystallization of the crude product in hot ethanol. In this experiment, the crude product will be the desired product. The percent yield of the crude product will be determined for this reaction. The purity of the product will also be analyzed. The product will be analyzed by three different methods: melting point, titration, and spectroscopic assay. C and the melting point range of the salicylic acid. The melting point range of pure aspirin is 138-140 C. If impurities are present in your crude sample, the melting point rangestarting material is 158-161 for your product will be lower than the range of pure aspirin. Also, your melting point range may be greater than 2 degrees.
Q-9Explain the synthesis of paracetamol from phenol.
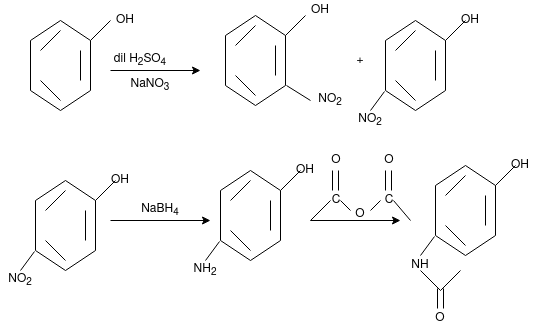
Q-10Synthesis of paracetamol from para nitro phenol.
