UNIT 4
Structures
- Explain structure in detail
A structure can be considered as a template used for defining a collection of variables under a single name. Structures help programmers to group elements of different data types into a single logical unit (Unlike arrays which permit a programmer to group only elements of same data type).
- Why Use Structures
• Ordinary variables can hold one piece of information
• arrays can hold a number of pieces of information of the same data type.
For example, suppose you want to store data about a book. You might want to store its name (a string), its price (a float) and number of pages in it (an int).
If data about say 3 such books is to be stored, then we can follow two approaches:
Construct individual arrays, one for storing names, another for storing prices and still another for storing number of pages.
Use a structure variable.
Suppose we want to create a employee database. Then, we can define a structure
Called employee with three elements id, name and salary. The syntax of this structure is as
Follows:
Struct employee
{ int id;
Char name[50];
Float salary;
};
Note:
Struct keyword is used to declare structure.
Members of structure are enclosed within opening and closing braces.
Usually structure type declaration appears at the top of the source code file, before any variables or functions are defined or maintained in separate header file.
Declaration of Structure reserves no space.
It is nothing but the “ Template / Map / Shape ” of the structure .
Memory is created , very first time when the variable is created / Instance is created.
- Structure variable declaration:
We can declare the variable of structure in two ways
- Declare the structure inside main function
- Declare the structure outside the main function.
1. Declare the structure inside main function
Following example show you, how structure variable is declared inside main function
Struct employee
{
Int id;
Char name[50];
Float salary;
};
Int main()
{
Struct employee e1, e2;
Return 0;
}
In this example the variable of structure employee is created inside main function that e1 ,e2.
2. Declare the structure outside main function
Following example show you, how structure variable is declared outside the main function
Struct employee
{
Int id;
Char name[50];
Float salary;
}e1,e2;
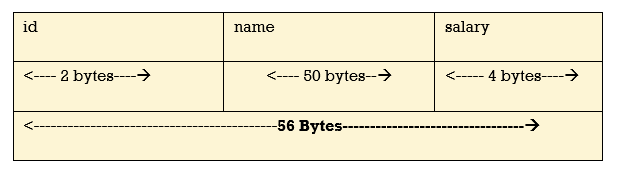
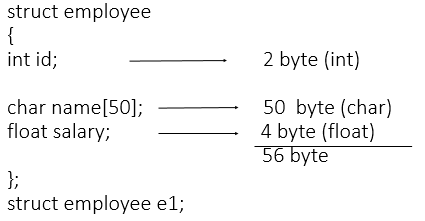
2. Explain Memory allocation for structure
Memory is allocated to the structure only when we create the variable of structure.
Consider following example
3. Explain Structure Initialization in different ways
1. When we declare a structure, memory is not allocated for un-initialized variable.
2. Let us discuss very familiar example of structure student , we can initialize structure variable
In different ways –
Way 1 : Declare and Initialize
Struct student
{
Char name[20];
Int roll;
Float marks;
}std1 = { "Poonam",89,78.3 };
In the above code snippet, we have seen that structure is declared and as soon as after declaration we
Have initialized the structure variable.
Std1 = { "Poonam",89,78.3 }
This is the code for initializing structure variable in C programming
Way 2 : Declaring and Initializing Multiple Variables
Struct student
{
Char name[20];
Int roll;
Float marks;
}
Std1 = {"Poonam" ,67, 78.3};
Std2 = {"Vishal",62, 71.3};
In this example, we have declared two structure variables in above code. After declaration of variable we have initialized two variable.
Std1 = {"Poonam" ,67, 78.3};
Std2 = {"Vishal",62, 71.3};
Way 3 : Initializing Single member
Struct student
{
Int mark1;
Int mark2;
Int mark3;
} sub1={67};
Though there are three members of structure,only one is initialized , Then remaining two members
Are initialized with Zero. If there are variables of other data type then their initial values will be –
4. Explain Data Type Default value if not initialized in different ways
Integer 0
Float 0.00
Char NULL
Way 4 : Initializing inside main
Struct student
{
Int mark1;
Int mark2;
Int mark3;
};
Void main()
{
Struct student s1 = {89,54,65};
- - - - --
- - - - --
- - - - --
};
When we declare a structure then memory won’t be allocated for the structure. i.e only writing below
Declaration statement will never allocate memory
Struct student
{
Int mark1;
Int mark2;
Int mark3;
};
We need to initialize structure variable to allocate some memory to the structure.
Struct student s1 = {89,54,65};
5. Give syntax for declaring structure array give example
Structure is collection of different data type. An object of structure represents a singlerecord in memory, if we want more than one record of structure type, we have tocreate an array of structure or object. As we know, an array is a collection of similartype, therefore an array can be of structure type.
Syntax for declaring structure array
Struct struct-name
{
Datatype var1;
Datatype var2;
- - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - -
Datatype varN;
};
Struct struct-name obj [ size ];
Example for declaring structure array
#include<stdio.h>
Struct Employee
{
Int Id;
Char Name[25];
Int Age;
Long Salary;
};
Void main()
{
Int i;
Struct Employee Emp[ 3 ]; //Statement 1
For(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
Printf("\nEnter details of %d Employee",i+1);
Printf("\n\tEnter Employee Id : ");
Scanf("%d",&Emp[i].Id);
Printf("\n\tEnter Employee Name : ");
Scanf("%s",&Emp[i].Name);
Printf("\n\tEnter Employee Age : ");
Scanf("%d",&Emp[i].Age);
Printf("\n\tEnter Employee Salary : ");
Scanf("%ld",&Emp[i].Salary);
}
Printf("\nDetails of Employees");
For(i=0;i<3;i++)
Printf("\n%d\t%s\t%d\t%ld",Emp[i].Id,Emp[i].Name,Emp[i].Age,Emp[i].Salary);
}
Output :
Enter details of 1 Employee
Enter Employee Id : 101
Enter Employee Name : Suresh
Enter Employee Age : 29
Enter Employee Salary : 45000
Enter details of 2 Employee
Enter Employee Id : 102
Enter Employee Name : Mukesh
Enter Employee Age : 31
Enter Employee Salary : 51000
Enter details of 3 Employee
Enter Employee Id : 103
Enter Employee Name : Ramesh
Enter Employee Age : 28
Enter Employee Salary : 47000
Details of Employees
101 Suresh 29 45000
102 Mukesh 31 51000
103 Ramesh 28 47000
In the above example, we are getting and displaying the data of 3 employee using
Array of object. Statement 1 is creating an array of Employee Emp to store the records
Of 3 employees.
6. Explain Array within Structure with example
As we know, structure is collection of different data type. Like normal data type, It can
Also store an array as well.
Syntax for array within structure
Struct struct-name
{
Datatype var1; // normal variable
Datatype array [size]; // array variable
- - - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - -
Datatype varN;
};
Struct struct-name obj;
Example for array within structure
Struct Student
{
Int Roll;
Char Name[25];
Int Marks[3]; //Statement 1 : array of marks
Int Total;
Float Avg;
};
Void main()
{
Int i;
Struct Student S;
Printf("\n\nEnter Student Roll : ");
Scanf("%d",&S.Roll);
Printf("\n\nEnter Student Name : ");
Scanf("%s",&S.Name);
S.Total = 0;
For(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
Printf("\n\nEnter Marks %d : ",i+1);
Scanf("%d",&S.Marks[i]);
S.Total = S.Total + S.Marks[i];
}
S.Avg = S.Total / 3;
Printf("\nRoll : %d",S.Roll);
Printf("\nName : %s",S.Name);
Printf("\nTotal : %d",S.Total);
Printf("\nAverage : %f",S.Avg);
}
Output :
Enter Student Roll : 10
Enter Student Name : Kumar
Enter Marks 1 : 78
Enter Marks 2 : 89
Enter Marks 3 : 56
Roll : 10
Name : Kumar
Total : 223
Average : 74.00000
In the above example, we have created an array Marks[ ] inside structure representing
3 marks of a single student. Marks[ ] is now a member of structure student and to
Access Marks[ ] we have used dot operator(.) along with object S.
7. What is C File management?
A File can be used to store a large volume of persistent data. Like many other languages 'C' provides following file management functions,
- Creation of a file
- Opening a file
- Reading a file
- Writing to a file
- Closing a file
Following are the most important file management functions available in 'C,'
Function | Purpose |
Fopen () | Creating a file or opening an existing file |
Fclose () | Closing a file |
Fprintf () | Writing a block of data to a file |
Fscanf () | Reading a block data from a file |
Getc () | Reads a single character from a file |
Putc () | Writes a single character to a file |
Getw () | Reads an integer from a file |
Putw () | Writing an integer to a file |
Fseek () | Sets the position of a file pointer to a specified location |
Ftell () | Returns the current position of a file pointer |
Rewind () | Sets the file pointer at the beginning of a file |
8. Write a C File Example: Storing employee information
Let's see a file handling example to store employee information as entered by user from console. We are going to store id, name and salary of the employee.
- #include <stdio.h>
- Void main()
- {
- FILE *fptr;
- Int id;
- Char name[30];
- Float salary;
- Fptr = fopen("emp.txt", "w+");/* open for writing */
- If (fptr == NULL)
- {
- Printf("File does not exists \n");
- Return;
- }
- Printf("Enter the id\n");
- Scanf("%d", &id);
- Fprintf(fptr, "Id= %d\n", id);
- Printf("Enter the name \n");
- Scanf("%s", name);
- Fprintf(fptr, "Name= %s\n", name);
- Printf("Enter the salary\n");
- Scanf("%f", &salary);
- Fprintf(fptr, "Salary= %.2f\n", salary);
- Fclose(fptr);
- }
Output:
Enter the id
1
Enter the name
Sonoo
Enter the salary
120000
Now open file from current directory. For windows operating system, go to TC\bin directory, you will see emp.txt file. It will have following information.
Emp.txt
Id= 1
Name= sonoo
Salary= 120000
9. Write into a file in file handling with examples
Se the code to get the idea how we write into a file
Example Code
#include <stdio.h>
Int main() {
FILE *fp;
Char *filename = "sample.txt";
Char *content = "Hey there! You've successfully created a file with content in c programming language.";
/* open for writing */
Fp = fopen(filename, "w");
If( fp == NULL ) {
Printf("%s: failed to open. \n", filename);
Return -1;
} else {
Printf("%s: opened in write mode.\n", filename);
}
/* Write content to file */
Fprintf(fp, "%s\n", content);
If( !fclose(fp) )
Printf("%s: closed successfully.\n", filename);
Return 0;
}
Output
Sample.txt: opened in write mode.
Sample.txt: closed successfully.
10. Explain Appending into a file in file handling.
Se the code to get the idea how we can append lines into a file.
Make a file (file_append.txt)
This text was already there in the file.
Example Code
#include <stdio.h>
Int main() {
FILE *fp;
Char ch;
Char *filename = "file_append.txt";
Char *content = "This text is appeneded later to the file, using C programming.";
/* open for writing */
Fp = fopen(filename, "r");
Printf("\nContents of %s -\n\n", filename);
While ((ch = fgetc(fp) )!= EOF) {
Printf ("%c", ch);
}
Fclose(fp);
Fp = fopen(filename, "a");
/* Write content to file */
Fprintf(fp, "%s\n", content);
Fclose(fp);
Fp = fopen(filename, "r");
Printf("\nContents of %s -\n", filename);
While ((ch = fgetc(fp) )!= EOF) {
Printf ("%c", ch);
}
Fclose(fp);
Return 0;
}
Output
Contents of file_append.txt -
This text was already there in the file.
Appending content to file_append.txt...
Content of file_append.txt after 'append' operation is -
This text was already there in the file.
This text is appeneded later to the file, using C programming.