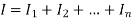Unit – 6
Electrical Installations
Q1) Why do we require Fuse?
A1) These are used to prevent the home appliances from the high current or overload damage. If we use a fuse in the homes, the electrical faults cannot happen in the wiring and it doesn't damage the appliances from the fire of wire burning. When the fuse gets break or damage, then an abrupt sparkle happens which made direct to damage your home appliances. That is the reason we required different types of fuses to guard our home appliances against damage.
Q2) Explain the working principle of Fuse.
A2)
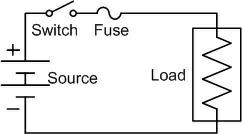
The working principle of the fuse is “ heating consequence of the current”. It is fabricated with a lean strip for thread of metallic wire. The connection of the fuse in an electrical circuit is always in series. When the too much current is produced due to the heavy flow of current in the electrical circuit the fuse get soft and it opens the circuit. The extreme flow of current main direct to the collapse of the wires and prevents the supply. Diffuse can be changed by the new fuse with an appropriate rating. It can be designed with elements like copper, zinc, aluminium and silver. They also perform like a circuit breaker for breaking the circuit while the abrupt fault happens in the circuit. This works like a safety measure for protector for humans from risk. Like this, the fuse works
Fuse rating = 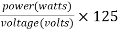
The selection of a fuse can be done by calculating the fuse rating by using the above formula
Q3) What is MCB? Draw and explain the construction of MCB.
A3) Miniature Circuit breakers (MCB) are electromechanical devices which are used to protect electrical equipment from an over current. MCB is a a mechanical switching device which is capable of making, caring and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions and also making, caring for a specified time and automatically breaking currents under specified abnormal circuit conditions such as those of short circuit. In short MCB is a device for over load and short circuit protection.
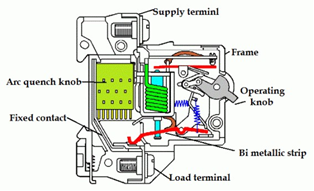
A) Construction :- The construction of miniature circuit breakers is very simple, robust and maintenance free. MCB is replaced by a new one when it is failing because MCB is not repaired or maintained. There are three types of miniature circuit breakers in construction,
1) Frame:- Frame is a rigid, strong, insulated housing in which the other components are mounted. It is a molded case.
2) Trip unit : For the proper working of the miniature circuit breaker trip unit is responsible. Two main types of trip mechanism are provided in Miniature circuit breaker (MCB). a bimetallic strip provides protection against overload current and an electromagnet provides protection against short circuit current. Trip unit is the main part of the MCB.
3) Operating Mechanism :- The operating mechanism of MCB provides with the manual operation for closing and opening operation of the miniature circuit breaker. It has three positions “ON”, “OFF”, “TRIPPED”. By observing the position of the switching latch one can determine the condition of MCB whether it is closed, tripped or manually switched off. If the MCB is tripped due to overcurrent or overheating.The external switching latch in the “TRIPPED” position. When manually switch off the miniature circuit breaker, the switching latch will be in “OFF” position. The switch is positioned at “ON”, in a closed condition of the miniature circuit breaker.
Q4) Explain various types of MCB.
A4) There are three standard characteristics are available for domestic as well as commercial MCB are given by B,C and D. Each type has its own function
Type B

MCB are mainly used where switching surges are small or non exist and are generally suitable for domestic applications and light commercial applications. There are no devices with long high starting current in domestic applications and has the best suited MCB is type B. these are designed to trip at fault currents in the range of 3 to 5 times the rated current. Suppose if the rated current is 10 ampere then the MCB trips at 30-50 A.
Type C

MCB are designed for high inductive circuits where surge currents are expected. These are generally used for commercial and industrial applications where a number of fluorescent lamps been turned ON or starting of small motors may give high search currents.
These are more sensitive than type B MCB and causes reduced nuisance trips. Type C MCB are designed to operate for trip at the fault currents of 5 to 10 times that of rated current. For 10 A type C MCB, the operating current range is 50 – 100 A.
Type D

MCBs are designed for heavy industrial applications where normal surge currents are very high. These are ideal for electrical welders and site Transformers where frequent high surge currents are expected.
The most common applications of type D MCBs include motors, UPS systems comma x-ray machines, Transformers and battery charging systems. These are designed to trip at 10 – 20 times The rated current. For 10 A type D MCBs, the operating current range is 100 – 200 A.
The setting or characteristics of an MCP are fixed in the factory itself by the manufacturer and they are not adjustable at the user end or at the site. Tripping currents for operation at 0.1 second or less different MCBs are given below.
Type B | 3-5 times rated current |
Type C | 5-10 times rated current |
Type D | 10-20 times rated current |
Q5) What is ELCB? Write the types of ELCB.
A5) An ECLB is one kind of safety device used for installing an electric device with high Earth impedance to avoid shock. These device is identify small stray voltages of the the electrical device on the metal enclosures and intrude the circuit if a dangerous voltage is identified. The main purpose of Earth leakage circuit breaker is to stop damage to humans and animals due to electric shock. Earth leakage circuit breaker is a device used to directly detect currents leakage to earth from an installation and cut the power and mainly used in TT earthing systems.
There are two types of ELCBs :
1) Voltage Earth leakage Circuit Breaker (voltage ELCB)
2) Current Earth Leakage Circuit System (Current ELCB)
Q6) Explain Working Principle of Voltage ELCB:
A6)
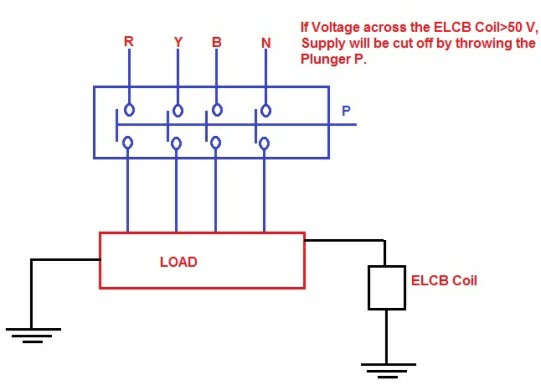
ELCB is a voltage operated device. It has a coil and if the voltage across the coil exceeds as a predetermined value such as 50 V, the current through the coil will be sufficient enough to trip the circuit. Voltage ELCB is connected in between the metallic part of equipment and the Earth. If we take an example of insulation failure then the voltage across the coil of voltage ELCB will drive enough Karan to cut the power supply till the manually reset. The way to identify an ELCB is by looking for green or green and yellow Earth wire entering the device. They relay on voltage returning to the trip via the earth wire during a fault and effort only limited protection to the installation and no personal protection at all. You should use plugin 30 mA RCD's for any appliances and extension leads that may be used outside as a minimum.
Q7) Explain Working Principle of Current (ELCB).
A7)
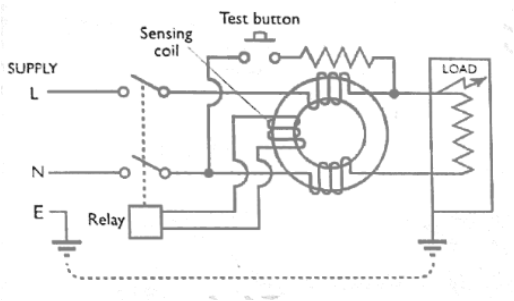
The working of current ELCB is quite interesting but easy. Current operated ELCB is also known as Residual Current devices (RCD). Residual current device (RCD) has a toroidal iron core over which phase and neutral windings are wound. A search coil is also mood on the same iron core which in turn is connected to the trip coil. Figure below shows the constructional detail of RCD or current ELCB.
Under normal operating condition, the current through the phase building and neutral building are same but both the windings are wound in such a manner to oppose the mmfs of each other, therefore net mmf in the toroidal iron corewill be zero. Let us consider a condition where Earth leakage current exists in the lord side. In this case the current through the phase and neutral will no longer be equal rather phase current will be more than the neutral current. Does MMF produced by face building will be more than the MMF produced by neutral building because of which a net MMF will exist in the toroidal iron core.
Net MMF in core = MMF by phase winding - MMF by neutral winding
This net MMF in the core will link with the search coil and aa MMF is changing in nature (current is AC),an EMF will be induced across the terminals of search coil. This will intern drive a current through the trip coil which will pull (because of current flow through the trip coil ok, it will behave as an electromagnet and hence will pull the lever to open contact) the supply contacts to isolate the power supply. Notice that current ELCB works on residual current that is the reason it is also called residual current device. A RCD/ Current ELCB is also provided with test button to check the healthiness of the safety device. If you carefully observe the figure, you will notice that, when we press the test button, load and face building are bypassed due to which only MMF because of neutral winding will exist in the core (as there is no opposing MMF as was the case with both the windings in service) which will cause RCD to trip to isolate supply.
Q8) Compare Types of MCCB.
A8)
Types of MCCB | Operating current | Operating time | Application |
Type B | Trips between 3 and 5 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 13 seconds | Domestic applications (lighting and resistive elements) |
Type C | Trips between 5 and 10 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 5 seconds | Commercial or industrial applications |
Type D | Trips between 10 to 20 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 3 seconds | Commercial or industrial applications |
Type K | Trips between 8 to 12 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 5 seconds | Industrial applications |
Type Z | Trips between 2 to 3 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 5 seconds | Highly sensitive to short circuit and are used for protection of highly sensitive devices such as semiconductor or devices |
Q9) Explain series and parallel grouping of batteries.
A9) Series grouping
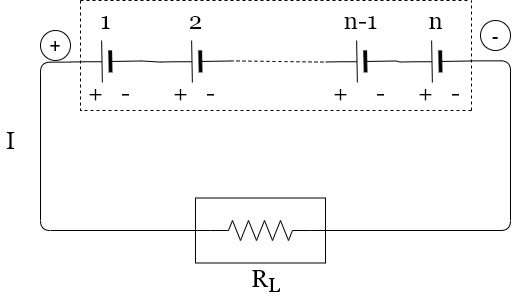

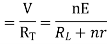
E= EMF of each batteries
r= Internal resistance of each battery
V=Total voltage =n×E volts
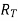 =Total resistance
=Total resistance
= Total batteries
= 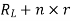
In series circuit current remain same so in this method does not improve current capacity. The current capacity is same as that of each battery connected in series. But voltage can be increased by increasing number of batteries n.
Parallel grouping
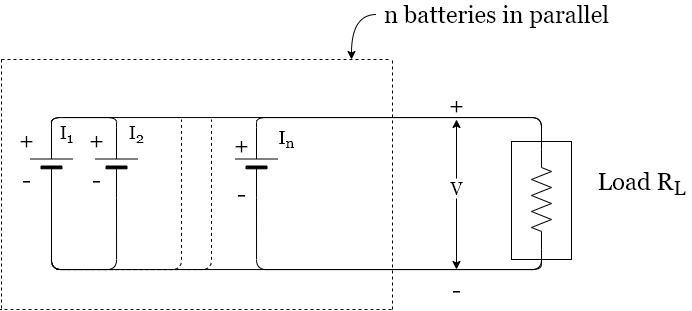
V=battery voltage=E=EMF
r=internal resistance of each battery
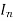 =Current through nth branch.
=Current through nth branch.
I=Total current