Unit – 3
Modern Field Survey Systems
Q1) What do you mean by electronic distance measurement (EDM)?
A1) EDM is electronic distance measurement survey which is used to find the distance of two point or object. This techniques provide precise and more faster surveying than the old and conventional instruments that are used earlier. In old and conventional surveying, in linear measurement, chain and tape are used while in angular measurements compass are used, Dumpy level and a levelling staff are used in work of levelling. With this instrument, survey work become tedious
Q2) What are the types of EDM instrument used in survey?
A2) The following are the instrument which are used in EDM as carrier wave:
Microwave Instruments - other name is tellurometers, microwaves are used in this instrument.
Infrared Wave Instruments – it Uses prism reflectors that pick-up amplitude modulated infrared waves.
Visible Light Wave Instruments – it Uses modulated light waves to find out the specific range.
1. Microwave Instruments:
Microwaves are used in this instrument. In 1950 in South Africa by Dr. T.L. Wadley and named later as Tellurometers. The range of these instruments is up to 100 km. 12 to 24 V batteries are required in this instrument, That’s why light and portable. This instrument can be used in both day and night time.
It consists of two identical units.
pressing a button in instrument, master unit can be converted into a remote unit and vice versa. It requires two skilled persons to operate.
2. Infrared Wave Instruments:
These instruments are useful for the most of the civil works. In this instrument amplitude modulated infrared waves are used. The range of these instruments is up to 3 km. Prism reflectors is used at the end to find the line to be measured.
Accuracy up to ± 10 mm is achieved in this instrument. This instrument is economical and can be mounted on theodolite
DISTOMAT DI 1000 and DISTOMAT DI 55 are the name of instrument used as infrared wave instrument.
Distomat DI 1000:
Distomats are latest in the field of the EDM instruments. These instruments measure distances by using amplitude as it works on the same principle of infrared wave instrument The Distomat is a very small in size and very compact and mainly use in the construction and engineering works.
It measures distances up to and smaller than 500 meters by simply pointing the instrument to a reflector.
3. Visible Light Wave Instruments:
This was first developed in Sweden and was named as Geodimeter.
in day its range is up to 3 km and in night its range is up to 2.5 km. Accuracy of these varies from 0.5 mm to 5 mm/km distance in this instrument. These instruments use the propagation of modulated light waves. These instruments are also very useful and popular in civil works
Q3) What is total station?
A3) A total station is an electronic/optical instrument used in modern surveying and building construction that uses electronic transit theodolite in conjunction with electronic distance meter (EDM). It is also integrated with microprocessor, electronic data collector and storage system.
The instrument is used to measure sloping distance of object to the instrument, horizontal angles and vertical angles. This Microprocessor unit enables for computation of data collected to further calculate the horizontal distance, coordinates of a point and reduced level of point.
Data collected from total station can be downloaded into computer/laptops for further processing of information.
Total stations are mainly used by land surveyors and civil engineers, either to record features as in topographic surveying or to set out features (such as roads, houses or boundaries). They are also used by archaeologists to record excavations and by police, crime scene investigators, private accident Reconstructionist and insurance companies to take measurements of scenes.
Q4) Explain advantages and application of total station?
A4) Advantages of Using Total Stations:
Applications of Total Station:
The following application of total station are as given below:
Q5) What are error in total station survey?
A5) 1 CALIBRATION OF TOTAL STATIONS
Maintaining the high level of accuracy offered by modern total stations, there is much more emphasis on monitoring instrumental errors, and some construction sites require all instruments to be checked regularly using procedures outlined in the quality manuals.
Some instrumental errors can be eliminated by observing on two faces of the total station and averaging, but because one face measurements is the preferred method on site, it is important to determine the amount of instrumental errors and correct for them.
For total stations, instrumental errors are measured and corrected by electronic calibration procedures that are carried out at any time and are applied to the instrument on site.
Since calibration parameters can change due to mechanical shock, temperature changes and rough handling of high-precision instrument, an electronic calibration should be carried out on a total station as follows:
Before every calibration, it is essential to allow the total station enough to reach the ambient temperature.
2 HORIZONTAL COLLIMATION (OR LINE OF SIGHT ERROR)
This axial error happens when the line of sight is not perpendicular to the tilting axis. It affects all horizontal circle readings and increases parallel to steep sightings, but this is eliminated by observing on two faces. For single face measurements, an on-board calibration function is used to determine c, the deviation between the actual line of sight and a line perpendicular to the tilting axis. A correction will be applied automatically for this to all horizontal circle readings.
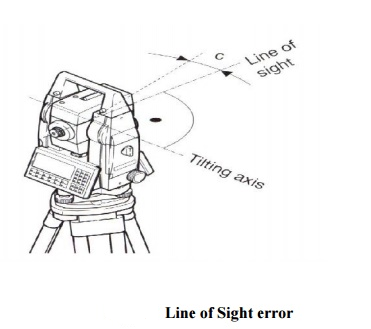
3 TILTING AXIS ERROR
Axial errors occur when the titling axis of the total station is not perpendicular to its vertical axis, this has no effect on sightings taken when the telescope is horizontal, but produces errors into horizontal circle readings when the telescope is tilted, especially for steep sightings.
But with horizontal collimation error, this error is erased by two face measurements, or the tilting axis error (a) is measured in a calibration procedure and a correction applied for this to all horizontal circle readings.
4 COMPENSATOR INDEX ERROR
Errors that were caused by not levelling a theodolite or total station carefully cannot be eliminated by taking face left and face right readings. If the total station is fitted with a compensator, it will measure residual tilts of the instrument and will apply corrections to the horizontal and vertical angles for these.
All compensators will have a longitudinal error l and traverse error t known as zero-point errors which are averaged using face left and face right readings but for single face readings must be determined by the calibration function of the total station.

A vertical collimation error exists on a total station if the 0o to 180o line in the vertical circle does not coincide with its vertical axis and this zero-point error is present in all vertical circle readings and like the horizontal collimation error, it is eliminated by taking FL and FR readings or by determining i
Any difference between the measured horizontal and vertical angles is then identified as an instrumental error and applied to all readings. The total station is thus calibrated and the procedure is the same for all of the error type.
Q6) What do you mean by GPS?
A6) GPS is a navigation system using satellites, a receiver and algorithms to synchronize location, velocity and time data for air, sea and land travel.
Q7) Explain surveying with GPS in modern system?
A7)
Q8) Explain GPS measurement?
A8)
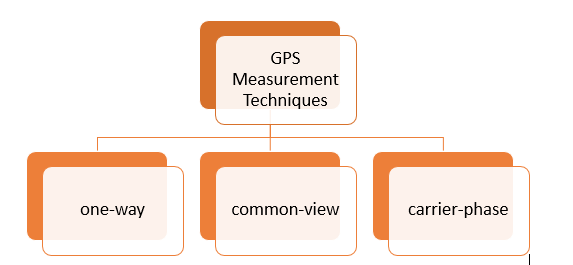
Common-view and carrier-phase measurements require more effort in processing of the measurement data. For this reason, they are usually used for small as possible.
1-Way GPS Measurements:
For frequency measurements, frequency output from GPSDO is used as input to a phase comparator, or used as the external time base for counting of freq
Q9) Write short note on distomat?
A9) Distomats are latest in the field of the EDM instruments. These instruments measure distances by using amplitude as it works on the same principle of infrared wave instrument The Distomat is a very small in size and very compact and mainly use in the construction and engineering works.
It measures distances up to and smaller than 500 meters by simply pointing the instrument to a reflector.
Q10) Explain the GPS segment or its part?
A10) GPS is made up of three different components, called as segments:
The three segments of GPS are:
Unit – 3
Modern Field Survey Systems
Q1) What do you mean by electronic distance measurement (EDM)?
A1) EDM is electronic distance measurement survey which is used to find the distance of two point or object. This techniques provide precise and more faster surveying than the old and conventional instruments that are used earlier. In old and conventional surveying, in linear measurement, chain and tape are used while in angular measurements compass are used, Dumpy level and a levelling staff are used in work of levelling. With this instrument, survey work become tedious
Q2) What are the types of EDM instrument used in survey?
A2) The following are the instrument which are used in EDM as carrier wave:
Microwave Instruments - other name is tellurometers, microwaves are used in this instrument.
Infrared Wave Instruments – it Uses prism reflectors that pick-up amplitude modulated infrared waves.
Visible Light Wave Instruments – it Uses modulated light waves to find out the specific range.
1. Microwave Instruments:
Microwaves are used in this instrument. In 1950 in South Africa by Dr. T.L. Wadley and named later as Tellurometers. The range of these instruments is up to 100 km. 12 to 24 V batteries are required in this instrument, That’s why light and portable. This instrument can be used in both day and night time.
It consists of two identical units.
pressing a button in instrument, master unit can be converted into a remote unit and vice versa. It requires two skilled persons to operate.
2. Infrared Wave Instruments:
These instruments are useful for the most of the civil works. In this instrument amplitude modulated infrared waves are used. The range of these instruments is up to 3 km. Prism reflectors is used at the end to find the line to be measured.
Accuracy up to ± 10 mm is achieved in this instrument. This instrument is economical and can be mounted on theodolite
DISTOMAT DI 1000 and DISTOMAT DI 55 are the name of instrument used as infrared wave instrument.
Distomat DI 1000:
Distomats are latest in the field of the EDM instruments. These instruments measure distances by using amplitude as it works on the same principle of infrared wave instrument The Distomat is a very small in size and very compact and mainly use in the construction and engineering works.
It measures distances up to and smaller than 500 meters by simply pointing the instrument to a reflector.
3. Visible Light Wave Instruments:
This was first developed in Sweden and was named as Geodimeter.
in day its range is up to 3 km and in night its range is up to 2.5 km. Accuracy of these varies from 0.5 mm to 5 mm/km distance in this instrument. These instruments use the propagation of modulated light waves. These instruments are also very useful and popular in civil works
Q3) What is total station?
A3) A total station is an electronic/optical instrument used in modern surveying and building construction that uses electronic transit theodolite in conjunction with electronic distance meter (EDM). It is also integrated with microprocessor, electronic data collector and storage system.
The instrument is used to measure sloping distance of object to the instrument, horizontal angles and vertical angles. This Microprocessor unit enables for computation of data collected to further calculate the horizontal distance, coordinates of a point and reduced level of point.
Data collected from total station can be downloaded into computer/laptops for further processing of information.
Total stations are mainly used by land surveyors and civil engineers, either to record features as in topographic surveying or to set out features (such as roads, houses or boundaries). They are also used by archaeologists to record excavations and by police, crime scene investigators, private accident Reconstructionist and insurance companies to take measurements of scenes.
Q4) Explain advantages and application of total station?
A4) Advantages of Using Total Stations:
Applications of Total Station:
The following application of total station are as given below:
Q5) What are error in total station survey?
A5) 1 CALIBRATION OF TOTAL STATIONS
Maintaining the high level of accuracy offered by modern total stations, there is much more emphasis on monitoring instrumental errors, and some construction sites require all instruments to be checked regularly using procedures outlined in the quality manuals.
Some instrumental errors can be eliminated by observing on two faces of the total station and averaging, but because one face measurements is the preferred method on site, it is important to determine the amount of instrumental errors and correct for them.
For total stations, instrumental errors are measured and corrected by electronic calibration procedures that are carried out at any time and are applied to the instrument on site.
Since calibration parameters can change due to mechanical shock, temperature changes and rough handling of high-precision instrument, an electronic calibration should be carried out on a total station as follows:
Before every calibration, it is essential to allow the total station enough to reach the ambient temperature.
2 HORIZONTAL COLLIMATION (OR LINE OF SIGHT ERROR)
This axial error happens when the line of sight is not perpendicular to the tilting axis. It affects all horizontal circle readings and increases parallel to steep sightings, but this is eliminated by observing on two faces. For single face measurements, an on-board calibration function is used to determine c, the deviation between the actual line of sight and a line perpendicular to the tilting axis. A correction will be applied automatically for this to all horizontal circle readings.

3 TILTING AXIS ERROR
Axial errors occur when the titling axis of the total station is not perpendicular to its vertical axis, this has no effect on sightings taken when the telescope is horizontal, but produces errors into horizontal circle readings when the telescope is tilted, especially for steep sightings.
But with horizontal collimation error, this error is erased by two face measurements, or the tilting axis error (a) is measured in a calibration procedure and a correction applied for this to all horizontal circle readings.
4 COMPENSATOR INDEX ERROR
Errors that were caused by not levelling a theodolite or total station carefully cannot be eliminated by taking face left and face right readings. If the total station is fitted with a compensator, it will measure residual tilts of the instrument and will apply corrections to the horizontal and vertical angles for these.
All compensators will have a longitudinal error l and traverse error t known as zero-point errors which are averaged using face left and face right readings but for single face readings must be determined by the calibration function of the total station.
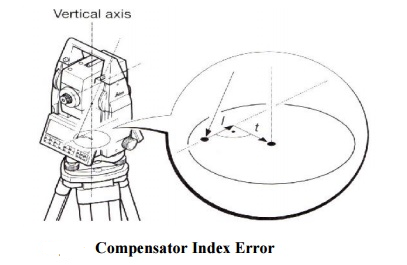
A vertical collimation error exists on a total station if the 0o to 180o line in the vertical circle does not coincide with its vertical axis and this zero-point error is present in all vertical circle readings and like the horizontal collimation error, it is eliminated by taking FL and FR readings or by determining i
Any difference between the measured horizontal and vertical angles is then identified as an instrumental error and applied to all readings. The total station is thus calibrated and the procedure is the same for all of the error type.
Q6) What do you mean by GPS?
A6) GPS is a navigation system using satellites, a receiver and algorithms to synchronize location, velocity and time data for air, sea and land travel.
Q7) Explain surveying with GPS in modern system?
A7)
Q8) Explain GPS measurement?
A8)

Common-view and carrier-phase measurements require more effort in processing of the measurement data. For this reason, they are usually used for small as possible.
1-Way GPS Measurements:
For frequency measurements, frequency output from GPSDO is used as input to a phase comparator, or used as the external time base for counting of freq
Q9) Write short note on distomat?
A9) Distomats are latest in the field of the EDM instruments. These instruments measure distances by using amplitude as it works on the same principle of infrared wave instrument The Distomat is a very small in size and very compact and mainly use in the construction and engineering works.
It measures distances up to and smaller than 500 meters by simply pointing the instrument to a reflector.
Q10) Explain the GPS segment or its part?
A10) GPS is made up of three different components, called as segments:
The three segments of GPS are:
Unit – 3
Modern Field Survey Systems
Q1) What do you mean by electronic distance measurement (EDM)?
A1) EDM is electronic distance measurement survey which is used to find the distance of two point or object. This techniques provide precise and more faster surveying than the old and conventional instruments that are used earlier. In old and conventional surveying, in linear measurement, chain and tape are used while in angular measurements compass are used, Dumpy level and a levelling staff are used in work of levelling. With this instrument, survey work become tedious
Q2) What are the types of EDM instrument used in survey?
A2) The following are the instrument which are used in EDM as carrier wave:
Microwave Instruments - other name is tellurometers, microwaves are used in this instrument.
Infrared Wave Instruments – it Uses prism reflectors that pick-up amplitude modulated infrared waves.
Visible Light Wave Instruments – it Uses modulated light waves to find out the specific range.
1. Microwave Instruments:
Microwaves are used in this instrument. In 1950 in South Africa by Dr. T.L. Wadley and named later as Tellurometers. The range of these instruments is up to 100 km. 12 to 24 V batteries are required in this instrument, That’s why light and portable. This instrument can be used in both day and night time.
It consists of two identical units.
pressing a button in instrument, master unit can be converted into a remote unit and vice versa. It requires two skilled persons to operate.
2. Infrared Wave Instruments:
These instruments are useful for the most of the civil works. In this instrument amplitude modulated infrared waves are used. The range of these instruments is up to 3 km. Prism reflectors is used at the end to find the line to be measured.
Accuracy up to ± 10 mm is achieved in this instrument. This instrument is economical and can be mounted on theodolite
DISTOMAT DI 1000 and DISTOMAT DI 55 are the name of instrument used as infrared wave instrument.
Distomat DI 1000:
Distomats are latest in the field of the EDM instruments. These instruments measure distances by using amplitude as it works on the same principle of infrared wave instrument The Distomat is a very small in size and very compact and mainly use in the construction and engineering works.
It measures distances up to and smaller than 500 meters by simply pointing the instrument to a reflector.
3. Visible Light Wave Instruments:
This was first developed in Sweden and was named as Geodimeter.
in day its range is up to 3 km and in night its range is up to 2.5 km. Accuracy of these varies from 0.5 mm to 5 mm/km distance in this instrument. These instruments use the propagation of modulated light waves. These instruments are also very useful and popular in civil works
Q3) What is total station?
A3) A total station is an electronic/optical instrument used in modern surveying and building construction that uses electronic transit theodolite in conjunction with electronic distance meter (EDM). It is also integrated with microprocessor, electronic data collector and storage system.
The instrument is used to measure sloping distance of object to the instrument, horizontal angles and vertical angles. This Microprocessor unit enables for computation of data collected to further calculate the horizontal distance, coordinates of a point and reduced level of point.
Data collected from total station can be downloaded into computer/laptops for further processing of information.
Total stations are mainly used by land surveyors and civil engineers, either to record features as in topographic surveying or to set out features (such as roads, houses or boundaries). They are also used by archaeologists to record excavations and by police, crime scene investigators, private accident Reconstructionist and insurance companies to take measurements of scenes.
Q4) Explain advantages and application of total station?
A4) Advantages of Using Total Stations:
Applications of Total Station:
The following application of total station are as given below:
Q5) What are error in total station survey?
A5) 1 CALIBRATION OF TOTAL STATIONS
Maintaining the high level of accuracy offered by modern total stations, there is much more emphasis on monitoring instrumental errors, and some construction sites require all instruments to be checked regularly using procedures outlined in the quality manuals.
Some instrumental errors can be eliminated by observing on two faces of the total station and averaging, but because one face measurements is the preferred method on site, it is important to determine the amount of instrumental errors and correct for them.
For total stations, instrumental errors are measured and corrected by electronic calibration procedures that are carried out at any time and are applied to the instrument on site.
Since calibration parameters can change due to mechanical shock, temperature changes and rough handling of high-precision instrument, an electronic calibration should be carried out on a total station as follows:
Before every calibration, it is essential to allow the total station enough to reach the ambient temperature.
2 HORIZONTAL COLLIMATION (OR LINE OF SIGHT ERROR)
This axial error happens when the line of sight is not perpendicular to the tilting axis. It affects all horizontal circle readings and increases parallel to steep sightings, but this is eliminated by observing on two faces. For single face measurements, an on-board calibration function is used to determine c, the deviation between the actual line of sight and a line perpendicular to the tilting axis. A correction will be applied automatically for this to all horizontal circle readings.
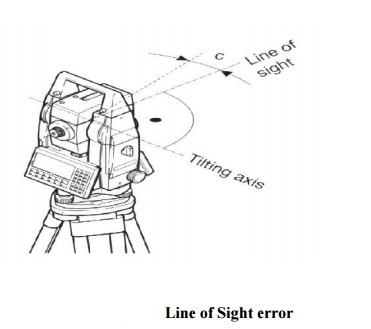
3 TILTING AXIS ERROR
Axial errors occur when the titling axis of the total station is not perpendicular to its vertical axis, this has no effect on sightings taken when the telescope is horizontal, but produces errors into horizontal circle readings when the telescope is tilted, especially for steep sightings.
But with horizontal collimation error, this error is erased by two face measurements, or the tilting axis error (a) is measured in a calibration procedure and a correction applied for this to all horizontal circle readings.
4 COMPENSATOR INDEX ERROR
Errors that were caused by not levelling a theodolite or total station carefully cannot be eliminated by taking face left and face right readings. If the total station is fitted with a compensator, it will measure residual tilts of the instrument and will apply corrections to the horizontal and vertical angles for these.
All compensators will have a longitudinal error l and traverse error t known as zero-point errors which are averaged using face left and face right readings but for single face readings must be determined by the calibration function of the total station.

A vertical collimation error exists on a total station if the 0o to 180o line in the vertical circle does not coincide with its vertical axis and this zero-point error is present in all vertical circle readings and like the horizontal collimation error, it is eliminated by taking FL and FR readings or by determining i
Any difference between the measured horizontal and vertical angles is then identified as an instrumental error and applied to all readings. The total station is thus calibrated and the procedure is the same for all of the error type.
Q6) What do you mean by GPS?
A6) GPS is a navigation system using satellites, a receiver and algorithms to synchronize location, velocity and time data for air, sea and land travel.
Q7) Explain surveying with GPS in modern system?
A7)
Q8) Explain GPS measurement?
A8)
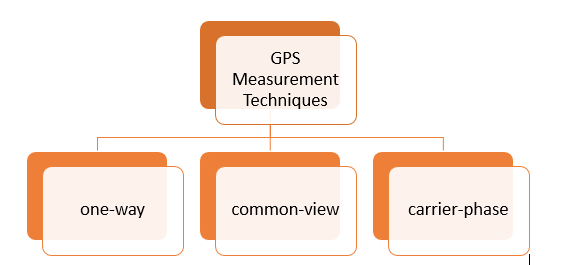
Common-view and carrier-phase measurements require more effort in processing of the measurement data. For this reason, they are usually used for small as possible.
1-Way GPS Measurements:
For frequency measurements, frequency output from GPSDO is used as input to a phase comparator, or used as the external time base for counting of freq
Q9) Write short note on distomat?
A9) Distomats are latest in the field of the EDM instruments. These instruments measure distances by using amplitude as it works on the same principle of infrared wave instrument The Distomat is a very small in size and very compact and mainly use in the construction and engineering works.
It measures distances up to and smaller than 500 meters by simply pointing the instrument to a reflector.
Q10) Explain the GPS segment or its part?
A10) GPS is made up of three different components, called as segments:
The three segments of GPS are: