Unit 4
Disaster Risk Reduction
Q1. What do you mean by disaster risk reduction? Explain disaster management cycle.
A1. Disaster Risk Reduction:
Disaster risk reduction is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing and reducing the risk of disaster. It aims to reduce socio-economic vulnerabilities to disaster s well as dealing with the environmental and other hazards that trigger them.
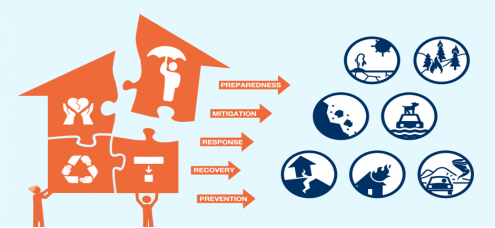
Disaster Risk Reduction
Disaster management cycle:
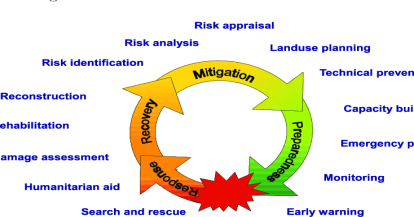
Disaster management cycle
Q2. Explain sustainable development, reduction, readiness and also explain role and responsibilities of government in case of disaster.
A2. Sustainable development:
Reduction:
Readiness:
Roles and Responsibilities of Government:
Teams are in the area of disaster management
Local governments appoint local disaster management teams.
Their role is to:
Q3. What do you mean by men’s action, prevention of hazard and also explain building and non building properties, community.
A3. Man's Action:
Prevention:
Building and non-building properties:
Non-structural measures are measures that do not involve bodybuilding using information, making or agreeing to reduce risks and impacts, especially on policies and laws, public awareness, training and education.
Explanation:
Community:
Q4. Explain structural and non-structural measures, risk analysis and steps involves in risk assessment.
A4. Structural and non-structural measures:
Risk analysis:
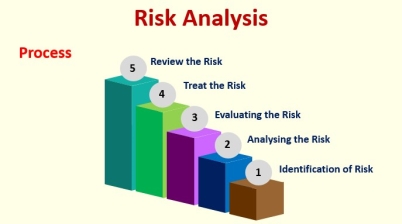
Risk analysis
Risk Assessment Steps:
Hazard Assessment:
Q5. Explain Vulnerability assessment, capacity assessment, risk and energy testing, local institutions involved in disaster.
A5.
2. Capacity Assessment:
People's View of the Risk:
Risk and energy testing:
Local Institutions:
Q6. Explain various objectives of VCA, explain NGOs and other stakeholders involved in disaster.
A6. The objectives of the VCA are to:
"We used to work for people, but now we work with them."
VCA Objectives:
NGOs and other stakeholders:
Vulnerable communities need to be aware of the potential dangers and impacts of exposure and be able to take certain steps to reduce the risk of loss or damage.
The most important determinant of disaster risk selection to focus on is the geographical location of those communities.
For example, while coastal communities need to be educated and prepared for the possibility of a tsunami, the Himalayan community can be taught to respond to the first earthquake and earthquake warning program.
Local governments
World governments
Q7. Explain Early warning system
A7. Early warning system:
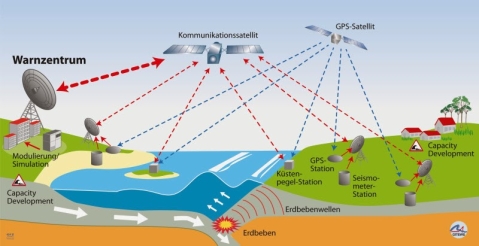
Early warning system
Monitoring system
Satellite data transfer
Control centers
Q8. Explain post disaster environmental response
A8. Post Disaster Environmental Response:
Water:
Q9. Explain sanitation, food safety, waste management in disaster.
A9. Sanitation:
Food Safety:
Waste management:
Q10. Explain disease control, security and communication in disaster.
A10. Disease Control:
Security:
Communication: