Unit – 1
Introduction
Q1) Define steel structures and their types.
A1) Steel shape is a steel shape that is made of structural metal* additives join with every different to hold hundreds and offer complete rigidity. Because of the high electricity grade of metal, this shape is dependable and calls for much less raw substances than different styles of shape like concrete shape and timber shape.
Main structural types
Q2) What are the properties of the material required in steel industry?
A2) The houses that want to be taken into consideration with the aid of using designers when specifying metal creation merchandise are:
For design, the mechanical houses are derived from minimal values special withinside the relevant product standard.
Q3) Write a short note on Toughness.
A3)
A handy degree of longevity is the Chirpy V-notch effect take a look at - see photograph at the right. This takes a look at measures the effect strength required to interrupt a small notched specimen, at a special temperature, with the aid of using an unmarried effect blow from a pendulum.
The various product standards specify minimal values of effect strength for distinctive sub-grades of every electricity grade.
Q4) What are the requirements for good weldability of material?
A4)
The following are the essentials of the weldability:
Q5) What are design methods of steel design, enlist them.
A5)
1. Working Stress Method (WSM)
2. Ultimate Load Method (ULM)
3. Limit State Method (LSM).
Q6) Write a short note on LSM.
A6)
Q7) What are the Restriction in limit state method?
A7) There are 2 sorts of restrict states
It makes use of more than one protection elements for the desired protection and serviceability on the closing load and running load respectively through thinking about all restrict states. These are called “partial protection elements”.
Q8) What are the methods of steel design?
A8)
1. Simple Design of Steel Structure
2. Continuous Design of Steel Structure
3. Semi-Continuous Design of Steel Structure
Q9) What are the limitations of LSM?
A9)
Q10) Write short notes on wind velocity.
A10)
(Vz): Design wind velocity is given with the aid of using the equation
Vz= Vb K1 K2 K3
wherein Vz =Design wind speed (m/sec)
Vb= Basic wind velocity in m/sec (Based on Appendix -A of diverse towns in IS 875 –Part three)
Basic wind velocity Vb, relies upon at the place of the building.
Basic wind velocity is primarily based totally on gust speed averaged over a quick time c programming language of three seconds at 10m peak from imply floor degree in an open terrain and for fifty years return period. Vb has 6 values 33, 39,44,47,50 & fifty-five m/sec.
Q11) Elaborate concept of wind load analysis.
A11) Buildings are difficulty to horizontal hundreds because of wind strain appearing at the buildings. Wind load is calculated as in step with IS 875(Part III)-1987.
Q12) What are codes used in analysis of loads?
A12) IS: 800: 2007 - Code of Practice for trendy production in Steel
IS: 802 Part 2: 1978 - Code of Practice to be used of Structural Steel in Overhead Transmission Towers-Fabrication, Galvanizing, Inspection and Packing
IS: 806: 1968 - Code of Practice for USE OF Steel Tubes in General Building Construction
IS: 808: 1989 - Dimensions for Hot Rolled Steel Beam, Column, Channel and Angle Sections
IS:814: 2004 - Covered Electrodes for Manual Metal Arc Welding of Carbon and Carbon Manganese Steel Specification
IS:816: 1969 - Code of Practice to be used of Metal Arc Welding for General Construction in Mild Steel.
IS:1161: 1998 - Specification for Steel Tubes for Structural Purposes.
Q13) What are the types of section used in steel structures?
A13) Plastic
Compact
Semi – compact
Slender
Q14) Write note on plastic section.
A14) Cross-sections which could broaden plastic hinges and feature the rotation potential required for failure of the shape with the aid of using formation of plastic mechanism fall beneath Neath this class. The width to thickness ratio of plate factors will be much less than that particular beneath Neath Class 1 (Plastic), in Table 2 of IS 800:2007.
Q15) Give load combination for limit state of collapse as per IS code.
A15)
Load Combination | DL | LL | WL/EL |
DL+LL | 1.5 | 1.5 | - |
DL+WL/EL | 0.9/1.5 | - | 1.5 |
DL+LL+WL/EL | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
Q16) Write short note on Semi Compact section.
A16)
Load Combination | DL | LL | WL/EL |
DL+LL | 1.5 | 1.5 | - |
DL+WL/EL | 0.9/1.5 | - | 1.5 |
DL+LL+WL/EL | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
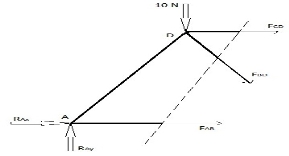
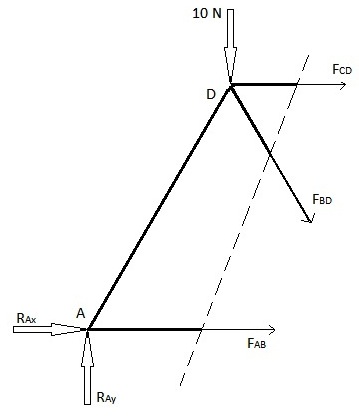
Q17) Explain Method of section.
A17) This method can be used when the truss element forces of only a few members are to be found. This method is used by introducing a single straight line cutting through the member whose force wants to be calculated. However, this method has a limit in that the cutting line can pass through a maximum of only 3 members of the truss structure. This restriction is because this method uses the force balances in the x and y direction and the moment balance, which gives us a maximum of 3 equations to find a maximum of 3 unknown truss element forces through which this cut is made. Let us try to find the forces FAB, FBD and FCD in the above example
Q18) Give explanation on semi continuous design of steel structure.
A18)
Q19) What are the simplified approaches in designs?
A19)
Q20) What is partial safety factors? And what is safety factor?
A20) Partial safety Factor
These are the factors which can applied to the individual input variables. In a design equation to give target reliability without having to carry out the probabilistic calculations.
Safety Factor:
The factor by which the yield stress of a material of a member is divided to arrive at the permissible stress in the material.