Unit – 5
Design strength using shear-moment interaction
Q1) Write a short note on moment interaction.
A1) The moment interaction diagram is created for a specific axial force, and is used to show the interaction of the applied moments compared to the moment interaction failure envelope.
The resultant moment angle (both applied and resistance) and neutral axis angle are then measured anti-clockwise from this zero position.
Q2) What is Built up beams?
A2)
Q3) Give design procedure for built up beams.
A3) Here are the simple steps that are to be followed for the design of Built-up Beams.
Step one
Step two
Step three
Step four
Step five
Step six
I = Ibeam + 2(Ap)(h/2) (h/2)
Step seven
Step Eight
Step nine
Q4) What is meant by shear strength?
A4)
Q5) Write a short note on plate girders.
A5) A plate girder is a metal beam this is broadly utilized in bridge production. Depending at the layout necessities and as according to the character of the structure; steel thicknesses for internet, flanges, stiffness, and many others are decided.
The use of the right cloth (metal) having the desired electricity and doing the welding are the 2 major elements to be attended to while growing the plate girder.
Types of Plate Girders
There may be exclusive classifications relying at the requirements used or relying on the character of the manufacturing of the girders.
There varieties of plate girders.
1. Reverted Plate Girder
2. Welded Plate Girder
Q6) What Is Riveted type plate girder?
A6) It is an aggregate of flanges, internet, and different vital stiffness. There are related via way of means of a mechanical method, revert, and plates aren't welded collectively.
Q7) What is welded plate girder?
A7)
Q8) Enlist the parts of plate girder.
A8)
Q9) Write a short note on Web plate.
A9) The vertical plate of the girder is called the internet plate.
Its thickness is primarily based totally at the layout necessities and the peak can also be determined primarily based totally at the web page condition and as according to the hundreds carried out at the internet.
The internet typically includes the carried-out hundreds at the flange as shear forces. The impact of the internet isn't always usually taken into consideration while the layout for the bending.
Q10) Define stiffeners and their types.
A10) Stiffeners are furnished to enhance structural potential heading off the nearby buckling failures. In addition, they may be used to hold the hundreds carried out to the beam till it allotted into the beam.
The following varieties of stiffeners can be found in those varieties of metal elements.
Q11) What are the Applications of plate girder?
A11)
In addition, field girder bridges, beam bridges, navy girder composite bridges, and half – thru plate girder bridges are taken into consideration because it uses.
Q12) What are the advantage of plate girder?
A12)
Q13) What are the disadvantage of plate girder?
A13)
Q14) Design bearing stiffeners.
A14) Bearing stiffeners are provided where forces, applied through a flange by loads or reaction, are in excess of the local capacity of the web at its connection to the flange, F, calculated as follows:
Fw = 0.909 (b1 +n2) twfyw …………….7.15
where bw is the stiff bearing length, n2 is the length obtained by dispersion through the flange to the web junction at a slope of 1 :2.5 to the plane of the flange, tw is the thickness of the web, and fyw is the yield stress of the web.
Q15) Design load carrying stiffeners.
A15) Load carrying stiffeners are checked for their buckling and bearing resistances. For buckling check, Fx < Fxd ……………………………………. 7.16
where Fx is the external load or reaction and Fxd is the buckling resistance. In the event that the load carrying stiffeners also act as intermediate transverse web stiffeners, the bearing strength should be checked for the combined loads as given in Eqn (7.14). The bearing strength of the stiffener Fbsd is obtained as follows:
Fbsd = 1.136 Aqfyq ………………... 7.17
where A, is the area of the stiffener in contact with the flange in mm2
{the actual area A is generally less than the full cross-sectional area of the stiffener as the corners of the stiffener are often coped to clear the web-to flange fillet weld (see section 1-1 of Fig. 7.18)) and
Aq as the yield stress of the stiffener in N/mm2.
The bearing strength of the web stiffener Fbsd as calculated above should be greater than or equal to Fyq the load transferred.
Q16) What is longitudinal stiffeners?
A16)
Q17) Write note on lateral torsional buckling.
A17) The lateral torsional buckling is the deformation of the beam due to the applied loads away from its longitudinal axis. Further, it causes steel beams failures.
The deformation could occur as translational and rotational movement of the section, and these types of movements are identified as lateral torsional buckling. Figure 1 indicates the deformations that can be seen as a result of lateral torsional buckling.
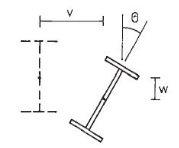
Figure: Lateral Torsional Buckling
Q18) What are the effect of restraints on beam?
A18)
Q19) Write a note on connections of load carrying stiffeners.
A19) Stiffeners which are subjected to load or reaction applied through a flange have to be connected to the web adequately. This connection is designed to transmit a force equal to the lesser of
(a) the tension capacity of the stiffener or
(b) the sum of the forces applied at the two ends of the stiffener when they act in the same direction or the larger of the forces when they act in different directions.
It should also be ensured that the shear stress in the web due to the design force transferred by the stiffener is less than the shear strength of the web. The stiffeners which resist tension should be connected to the flange with continuous welds or non-slip fasteners.
Q20) Give design procedure for torsional stiffeners.
A20) Torsional stiffeners provide torsional restraint at the supports and they should satisfy the following: (a) the local capacity of the web is exceeded as calculated in Eqn (7.15) (b) second moment of area of the stiffener section about the center line of the web Is should satisfy the following relation
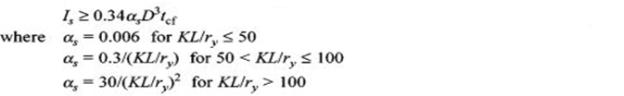
and D is the depth of the beam at support (in mm), tcf is the maximum thickness of the compression flange of the girder (in mm), KL is the effective length of the laterally unsupported compression flange of the girder (in mm), and ry is the radius of gyration about minor axis (in mm).
Q21) Write a short note on end connection.
A21)