Unit - 3
Elements of Business/ Managerial Economic and Forms of Organization
Q1) Explain cost and cost control technique in detail.
A1) Cost and Cost Control Technique:
Cost: When we speak approximately the "price" of something, what we're regarding is the quantity of cash that we've spent or will need to spend to make that unique product. For example, whilst businessmen speak approximately the price of a car, they're regarding the quantity they have got spent production it.
Cost is regularly cut up into elements:
Cost control technique:
1) Cost manipulates with the aid of using control way a look for higher and extra low in cost methods of completing every operation.
2) Cost manipulate is actually the prevention of waste inside the current surroundings.
3) These surroundings are made of agreed working strategies for which requirements were developed.
4) These requirements can be expressed in a whole lot of methods, from huge price range stages to distinctive general expenses.
5) Cost manipulate is the process wherein real consequences are in comparison towards the usual in order that waste may be measured and suitable movement taken to accurate the activity.
6) Cost manipulate is described because the law with the aid of using govt. movement of the expenses of working an undertaking.
7) Cost manipulates pursuits at reaching the goal of income.
8) Cost manipulate includes placing requirements.
9) The company is anticipated to fix to the requirements.
Advantages:
1) It enables the company to enhance its profitability and competitiveness.
2) In the absence of value manipulate, income can be extensively decreased regardless of a huge and growing income volume.
3) It is imperative for reaching extra productivity.
Q2) Explain various types of cost in detail.
A2) Types of costs:
1. Fixed Costs (FC):
Fixed expenses or cost are expenses that don't range with the extent of output within side the brief term.
2. Variable Costs (VC):
Costs which depend upon the output produced. A variable cost varies in direct percentage with the extent of output.
3. Semi-Variable Cost:
Labor is probably a semi-variable cost. If you produce extra cars, you want to employ extra people that are a variable cost. However, even in case you did not produce any cars, you could nonetheless want a few people to appearance after an empty factory.
4. Total cost:
The total cost is addition of fixed cost and variable cost.
Total Cost (TC) = Fixed cost + Variable Cost.
Q3) Explain lifecycle of cost.
A3) Lifecycle of cost:
The lifestyles-cycle cost of a plant is one of the maximum essential elements whilst planning and specifying equipment.
Over the 20–25 12 months lifestyles of a big SWRO facility, the running fee will have a tendency to outweigh the preliminary capital investment.
Life cycle cost (LCC) is a technique that assesses the total fee of an asset over its lifestyles cycle consisting of preliminary capital costs, maintenance costs, running costs and the assets residual cost on the quit of its lifestyles.
Life-cycle cost analysis (LCCA) is a device to decide the maximum cost-effective choice amongst unique competing options to purchase, own, operate, keep and, finally, cast off an item or process, whilst every is similarly suitable to be carried out on technical grounds.
Lifecycle of cost calculated:
LCC = C+PV Recurring – PV Residual Value
a) LCC is the lifestyles cycle fee or cost.
b) C is the 0-12 month’s construction fee or cost.
c) PV habitual is the gift cost of all habitual costs.
d) PV residual cost is the existing cost of residual cost on the quit of the project.
Q4) What do you mean by budgets? Explain application of break-even analysis.
A4) Budgets:
Budget is annual monetary declaration displaying the predicted receipts and expenditure in recognize of monetary yr, earlier than graduation of that yr.
To enable authorities to decide the relative urgency of the needs and made towards the quantities probable to be to be had for expenditure on one of a kind works head of account at some point of resulting yr, statements of normal estimates referred to as price range estimates for subsequent yr are put together and submitted to ministry involved.
The estimates of expenditure are required to be voted through the legislature.
Late receipts of estimate retard the price range programmer and motive considerable inconveniences.
So, every endeavor has to be made to make sure their well-timed submission.
Originally estimates are organized from the one-of-a-kind department after which submitted to the superintending engineers.
The chief engineer proposes the once-a-year price range estimates after receiving the estimates from superintending engineers below his control.
The price range declaration thus, is dispatched to the secretary of the branch who after scrutiny submits to the minister involved and to the monetary branch.
Applications of Break Even Analysis
Break even evaluation lets in an enterprise company
a) To Measure earnings and losses at diverse degrees of manufacturing
b) To Measure earnings and losses at diverse degrees of income.
c) To are expecting and calculate the impact of adjustments in rate of income.
d) To observe the connection among constant fee and variable fee.
e) To forecast the impact on profitability whilst fee and performance adjustments.
Q5) What do you mean by breakeven point?
A5) Break even analysis:
Break even evaluation is the analytical method used to observe the impact on earnings with adjustments in fee of manufacturing, quantity of manufacturing and charges of very last products.
This analytical method is referred to as CVP evaluation. The spoil even evaluation is maximum typically recognized shape of CVP evaluation. Break even evaluation establishes a courting among fee and sales with recognize to quantity.
Break even evaluation is undertaken to pick out the Break Even Point (BEP) manufacturing BEP fees and revere are identical That is there aren’t any earnings and no loss. It is an equilibrium factor at which the organization does now no longer make any income nor incuse any loses
This manner that if the amount bought is under the BEP the organization will incur a louse and if manages to sell above the BEP it's going to make income. However, if the organization fails to boom the amount that its income it is able to as an alternative make income through reshaping the constant prices.
Reduction of fixed cost
Reduction of variable cost
Increasing the promoting rate in their products
The organization may want to undertake one or all the above alternatives to enhance its backside line. However, through doing so it might be decreasing the breakeven factor The organization might now have a brand-new breakeven factor which might be decrease than the only before thereby permitting the organization to make income.
Q6) Explain BEP calculation and assumption of break-even analysis.
A6) BEP Calculations:
In the linear CVP (Cost Volume Profit) evaluation model, the spoil-even factor may be measured in phrases of Total Revenue (TR) and Total Costs (TC)
BEP is in which the full sales are precisely identical to total cost
That is total revenue is equal to total costs
TR= TC
Total sales are the quantity of sales generated through the organization and is identical to amount (Q) improved through promoting rate (P)
Total cost is the sum of constant (P) and variable (V)
TR-TC = profit
P x Q – (F+V x Q) = 0
Q= F x (P-V)
BEP = FC/ (P-VC)
Assumptions of Break Even Analysis:
Break even evaluation is primarily based totally on the subsequent assumptions
Q7) Explain capital budgeting and methods of capital budgeting and application of linear programming.
A7) Capital budgeting:
Capital budgeting is the manner that an enterprise makes use of to decide which proposed constant asset purchases it need to accept, and which need to be declined.
This manner is used to create a quantitative view of each proposed constant asset funding, thereby giving a rational foundation for creating a judgment.
The sum of money concerned in a set asset funding can be so big that it ought to result in the bankruptcy of a company if the funding fails.
Consequently, capital budgeting is an obligatory interest for large constant asset proposals.
This is much less of a problem for smaller investments; in those latter cases, it's miles higher to streamline the capital budgeting manner substantially, in order that the focal point is greater on getting the investments made as expeditiously as possible; via way of means of doing so, the operations of earnings centers aren't hindered via way of means of the evaluation in their constant asset proposals.
1) NPV
2) Payback period
1) Selecting worthwhile initiatives: An organization comes throughout diverse worthwhile initiatives frequently. But due to capital restrictions, an organization desires to choose the proper blend of worthwhile initiatives with a view to boom its shareholders’ wealth.
2) Capital expenditure control: Selecting the maximum worthwhile funding is the primary goal of capital budgeting. However, controlling capital fees is likewise a vital goal. Forecasting capital expenditure necessities and budgeting for it and making sure no funding possibilities are misplaced is the crux of budgeting.
3) Finding the proper re assets for budget: Determining the quantum of budget and the re assets for buying them is some other vital goal of capital budgeting. Finding the stability among the value of borrowing and returns on funding is a vital intention of capital budgeting.
Application of linear programming
Linear programming is used to obtain ideal answers for operations research.
Using linear programming allows researchers to locate the best, maximum within your means strategy to a trouble inside all of its limitations, or constraints.
Many fields use linear programming strategies to make their tactics extra efficient.
These encompass meals and agriculture, engineering, transportation, production and energy.
Q8) Explain in detail net present value.
A8) NPV (Net Present Value)
The Net Present Value (NPV) Method and the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) Method are sorts of discounted coins go with the drift strategies that are followed to adopt the monetary appraisal of tasks.
In the Discounted Cash go with the drift strategies all of the projected coins inflows and outflows for a capital budgeting venture are discounted to their present price the usage of an approximate hobby charge.
Three discounted coins go with the drift strategies are usually used in capital budgeting
a) Net Present Value (NPV)
b) Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
c) Profitability or Desirability Index
All discounted coins go with the drift strategies are primarily based totally at the time price of cash this means that a sum of money acquired nowadays is really well worth extra than an identical sum of money acquired in future.
To simplify the method of comparing proposals the usage of discounted coins flows, the idea is made that money go with the drift from a venture arise on the give up of accounting period.
Under the NPV approach, all coins inflows and outflow are discounted at a minimal suited charge of go back. N normally the companies’ value of capital.
If the existing price of the coins inflows is extra than the gift price of the coins outflows, the venture is appropriate Le NPV>0, take delivery of and NPV <0> must be extra than the NPV of expenses of that venture. The distinction among the 2 NPVs must be positive. In different words, a positive NPV approach the venture ears a charge of go back better than the companies’ value of capital.
The Net Present Value is predicated at the time price of cash and the timings of coins flows in comparing tasks. All coin’s flows are discounted on the value of capital and NPV assumes that every one-coin inflows from tasks are re-invested on the value of capital.
As a choice criterion, this approach may be used to make a desire among jointly exceptional tasks. The venture with the very best NPV could be assigned the primary rank, observed with the aid of using others within side the descending order.
Q9) Explain merits and demerits of net present value.
A9) Merits:
1) NPV recognizes the time price of cash thereby making the approach extra credible.
2) The complete movement of coins flows at some stage in the venture existence is considered.
3) A converting cut price charge may be constructed into the NPV calculations with the aid of using changing the denominator.
4) This approach is beneficial for choice of jointly exceptional tasks.
Limitations:
1) It is hard to calculate in addition to apprehend and use in contrast with the payback approach.
2) The calculation of cut-price charge that's important to the approach gives extreme problems. In fact, there may be distinction of opinion even concerning the precise approach of calculating it.
3) This approach might not provide best outcomes in case of tasks having distinct powerful lives.
Q10) Excel Constructions wants to buy a mixer with a cost of Rs. 35,000 and annual cash savings of Rs. 11,000 for each of 5 years. The cost of capital is 12%.
A10) With uniform cash flows, the present value (PV) is computed using the present value of and annuity of 5 payments of Rs. 11,000 each at 12 percent; the NPV is calculated as follows:
PV of Cash inflows = 11,000 (PV 1-5 years @ 12%)
= Rs. 39,634
Present Value of Cash outflows 35, 0000 Net sent value of the project 4634
S NPV is positive the project is acceptable since the net - ve of earnings exceed by Rs. 4634 the amount paid for of the funds to finance the investment.
Q11) Explain return on investment in detail and IRR calculation.
A11) ROI: (Return on investment)
ROI is calculated via way of means of subtracting the preliminary price of the funding from the very last price of the funding (which equals the internet return), then dividing this new number (the internet return) via way of means of the value of the funding, and, finally, multiplying it via way of means of 100.
Return on funding (ROI) is an overall performance degree used to assess the performance or profitability of a funding or examine the performance of some of exceptional investments. ROI attempts to immediately degree the quantity of return on a selected funding or investment, relative to the investment cost.
Return on Investment (ROI) is a famous profitability metric used to assess how nicely a funding has performed.
ROI is expressed as a percent and is calculated with the aid of using dividing an investments internet profit (or loss) with the aid of using its preliminary price or outlay.
ROI may be used to make apples-to-apples comparisons and rank investments in exceptional tasks or assets.
ROI does now no longer keep in mind the maintaining length or passage of time, and so it is able to pass over possibility prices of making an investment elsewhere.
The calculation of IRR is a chunk complicated than different capital budgeting techniques. We understand that at IRR, Net Present Value (NPV) is 0, thus
NPV = 0; or PV of destiny coins flows-Initial Investment = 0; or
NPV= 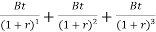
Q12) Explain internal rate of return and advantages and limitation respectively.
A12) IRR: Internal Rate of Return:
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is the hobby fee that reductions an investments destiny coins flows to the prevailing.
The hobby fee equates the prevailing cost of coins inflows with the prevailing cost of the coin’s outflows. This in flip way that at this hobby fee the NPV is zero
While placing the bargain fee in NPV the price of capital is taken into consideration in dedication of the internet gift cost at the same time as in inner fee of return, the internet gift cost is ready to 0 and the bargain fee which satisfies this situation is determined.
The cut price fee at which the NPV is 0 is known as Internal Rate of Return.
The method for calculating IRR relies upon on whether or not the coins flows are annuity (identical 12 months wise) or non uniform.
Steps in figuring out IRR for an annuity
Determine the payback length of the proposed investment.
From the desk of Present cost of Annuity search for 12 months this is identical to or near the lifestyles of the venture.
From the 12 months column, locate cut price elements closest to payback length, one large and different smaller than it.
From the hobby column locate the 2 hobby charges similar to those cut-price elements.
Determine IRR through interpolation.
However, while coins flows aren't uniform, trial and blunders techniques or a laptop need to be used to locate the IRR.
If the IRR is computed manually, step one is to select an interest rate that appears affordable after which compute the internet rate cost of the man or woman coins flows the use of that cost positive, then the interest rate used is low, i.e., IRR is better than the hobby fee If the decided on
A better hobby fee needs to then be decided on and the gift cost of the coin’s flows be computed again. If the brand-new hobby charges outcomes in poor internet gift cost, then the hobby fee decided on is high and a decrease hobby fee is to be decided on
The method is to be repeated till the prevailing cost of coins influx is identical to the prevailing cost of the coins cut flows.
Above trial and blunders technique of calculating the hobby fee is tedious consequently computer systems are utilized in calculating IRR
1) Like NPV, IRR too considers the time cost of money
2) IRR is simpler to recognize and relate to, consequently is conveniently followed through businesses.
3) It is constant with the general goal of selecting the venture with the most yields because the popularity of a venture is based on evaluation of the IRR with the specified fee of return.
1) It includes tedious calculations because it produces multiple charges which might be confusing.
2) In comparing collectively unique proposals, the venture with the very best IRR could be decided on. However, that is no assure that it is the maximum worthwhile and constant with the goals of the firm.
Q13) Explain payback period. Merits and limitations of same.
A13) Payback Period
The payback length is the conventional approach of assessing venture investments and makes use of the non discounting technique.
This approach is a computationally easy venture evaluation method that has been used for lots years. The technique is to decide how lengthy it takes a venture to go back the price of the unique investment.
1) This approach is pretty easy and clean to understand, and is primarily based totally on the idea that there may be no earnings of any venture until the payback is over. When budget is constrained its miles constantly higher to choose tasks having shorter payback periods. This approach is appropriate to industries wherein the risks of obsolescence are very high.
2) The payback length may be in comparison to a break-even factor, the factor at which charges are absolutely recovered however earnings are but to commence.
3) The chance related to a venture arises due to uncertainty related to the coin’s inflows. A shorter payback length method much less uncertainty closer to chance.
1) The approach does now no longer deliver any issues to time fee of money. Cash flows taking place in any respect factors of time are without a doubt added.
2) This approach will become a totally insufficient degree of comparing tasks wherein coins inflows are uneven.
3) It stresses capital healing as an alternative than profitability. It does now no longer do not forget the returns from a venture after its payback length. Therefore, this approach might not be an amazing degree to compare wherein the assessment is among tasks one concerning a protracted gestation length and different yielding short outcomes handiest for a brief length.
Q14) Explain depreciation in detail.
A14) Depreciation:
It is the loss in the value of property due to its use, life, wear, tear, decay and obsolescence.
This is an assessment of physical wear and tear of building or property and is naturally dependent on its original condition, quality of maintenance and mode of use.
There are different methods for calculation of depreciation.
Straight line method in this method is assumed to lease value by constant amount every year and thus fixed amount of original cost is written off every year, so that at the end of the term when the asset is worn out, only scrap value remains.
Annual depreciation = (Original cost - Scrap value) / Life in years
D = (C- Sc) / n
Quantity surveying method in the property studied in detail and extent of physical deterioration worked out in the endeavor to calculate depreciation.
Constant percentage method is also called a declined balanced method.
In this method the property is assumed to lose value annually at constant percentage of the value.
P = 1- (Sc/C) ^ (1/n)
Where,
P- Percentage rate of annual depreciation.
C- Original cost
Sc- Scrap value
N- life of property in a year.
Sinking fund method in depreciation assumed to be an annual sinking fund till that end.
An amount of Re 1/- per annum in ‘n’ year
= (1+ i) ^n - 1 / i = (y)
Thus, value of building or property decreases gradually up to the utility period due to depreciation.
Q15) What is time value of money?
A15) Time value of money (present and future worth of cash flow):
Have an impact on over selections made through organizations and through us in non-public lives.
Corporations pay lakhs of Rupees in hobby every yr for the usage of cash they have got borrowed. We earn cash on sums we've got invested in financial savings accounts, certificates of deposit, and cash marketplace funds. We additionally pay for the usage of cash which we've got borrowed for college loans, mortgages. or credit score card purchases. We will first look at the character of hobby and its computation.
Then we can speak numerous funding answers and computations associated with every.
Time Value of Money (TVM) is an essential idea in economic management. It may be used to examine funding options and to resolve troubles regarding loans, mortgages, leases, financial savings, and annuities.
TVM is primarily based totally at the idea that a rupee which you have nowadays is really well worth extra than the promise or expectation that you may acquire a rupee in the destiny.
Money which you keep nowadays is really well worth extra due to the fact you can make investments it and earn hobby. After all, you should acquire a few repayments for foregoing spending. For instance, you may make investments your rupee for three hundred and sixty-five days at a 6% annual hobby fee and collect 1.06 on the give up of the yr. You can say that the destiny fee of the rupee is 1.06 given a 6% hobby fee and a one-yr period. It follows that the prevailing fee of the 1.06 you anticipate to acquire in three hundred and sixty-five days is best 1.
A key idea of TVM is that an unmarried amount of money or a collection of equal, evenly-spaced bills or receipts promised within side the destiny can be transformed to an equal fee nowadays.
Conversely, you may decide the fee to which an unmarried sum or a chain of destiny bills will develop to at a few destiny date.
Q16) Explain cash flow and financial statement in detail.
A16) Statement- Cash Flow
A coin’s glide assertion is one of the maximum essential financial statements for a mission or commercial enterprise. A coin’s glide assertion is a list of the flows of coins into and out of the commercial enterprise or mission. Think of it as your bank account on the bank. Deposits are the coins influx and withdrawals (checks) are the coins outflows. The stability to your bank account is your internet coins glide at a particular factor in time.
A coin’s glide assertion is a list of coins flows that took place at some stage in the beyond accounting period. A projection of destiny flows of coins is referred to as a coin’s glide budget.
A coin’s glide assertion isn't always best involved with the amount of the coins flows however additionally the timing of the flows. Many coins flows are built with more than one time periods. For example, it is able to listing month-to-month coins inflows and outflows over a year’s time. It now no longer bests tasks the coins stability closing on the cease of the 12 months however additionally the coins stability for every month.
Statement- Financial
Financial statements are written information that delivers the enterprise sports and the economic overall performance of an enterprise. Financial statements are regularly audited through government agencies, accountants, firms, etc. to make sure accuracy and for tax, financing, or making an investment purpose.
Financial statements include:
a) Balance sheet
b) Income assertion
c) Cash go with the drift assertion.
d) Economic statements are written information that delivers the enterprise sports and the economic overall performance of an enterprise.
e) The stability sheet offers an assessment of assets, liabilities, and stockholders fairness as a photo in time.
f) The profits assertion primarily specializes in an enterprise’s sales and charges for the duration of a selected period. Once charges are subtracted from sales, the assertion produces companies’ earnings determine referred to as internet profits.
g) The coins go with the drift assertion (CFS) measures how properly an enterprise generates coins to pay its debt obligations, fund its running charges, and fund investments.
Q17) Explain steps or procedure involved in methods study.
A17) Steps or Procedure Involved in Methods Study:
The simple technique to approach has a look at includes the subsequent 8 steps.