Unit - 5
Estimation /Measurement for Various Items
Q1) Explain measurement for various items in detail.
A1) Estimation /Measurement for Various Items:
An estimate is defined as, "the process of calculating the probable quantities and costs of various item required in connection with work."
Estimate is prepared by calculating the quantities from the dimensions on the drawings for various items required to complete the project and multiplied by unit cost of item concerned.
Measurement:
The measurement of quantities of various items of building work forms and important stage in the planning.
Procedure followed for taking out quantities of various item of work differs from state to state and for different department in same state.
The tasks of bringing uniformity in measurement were entrusted to Indian Standard Institute (LSL) now renamed as Bureau of Indian Standard (B.L.S.) in year 1985.
The whole building is divided into different subheads to have control over the finance and material consumed.
1) Main head building works
2) Subheads
3) Earthwork
4) Brick work
5) Steel work
6) Concrete work
7) Stone work
8) Wood work
9) Roofing
10) Plastering and pointing
11) Finishing item such as white washing, colour washing
12) Painting
13) Miscellaneous items, etc.
Q2) Explain the process of estimation in detail.
A2) The accuracy of estimation improves if its miles achieved foundation WBS
Accuracy is likewise improved if estimation is achieved via way of means of the identical character that does the paintings
The historical facts offer essential insights into the method of estimation
Estimation might be more correct if there are minimum or no adjustments in agenda, fee and scope baselines
The venture manager must control the venture agenda with none deviations to the agenda baseline
The venture manager must control the venture finances with none deviations to the fee or cost baseline.
Integrated Change Control is used to approve or reject all extrude request
Any troubles associated to agenda, fee, scope, quality, or assets can result in extrude requests
A venture manager’s role is to research the venture requirements, create new estimates foundation inputs from group participants and his revel in with applicable projects, and solve any variations to provide sensible objectives
Periodic recalculation of Estimate to Complete (ETC) is needed to make certain ok time; funds, assets, and so forth are to be had for the venture
Project control plan must be revised as adjustments are authorized and the essential paintings is completed
A non-desirable venture control exercise is Padding
Any agreed-upon estimates ought to be met via way of means of the venture manager
Estimates ought to be reviewed periodically to peer if they're doable and to test for padding and dangers
Reduction or elimination of dangers can bring about reduced estimates
Providing correct and viable estimates is the duty of a venture manager
Q3) Explain use of relevant Indian standard specification.
A3) Use of Relevant Indian Standard Specification for the same:
Q4) Explain taking out quantities from the given requirement to the work.
A4) Taking out Quantities from the Given Requirement of the Work:
Different Methods of Taking out Quantities
The gadgets of labor like earth work in excavation in basis, basis concrete stone masonry or brick masonry in awesome shape may also through expected through both of the subsequent strategies.
The strategies of getting rid of portions are categorized as:
But P.W.D. technique is normally followed in our country.
Taking out portions includes following steps:
a) Taking out (dimensions from associated drawings)
b) Squaring the size
c) Abstracting
The time period getting rid of indicates measuring the size i.e., period, width and peak of diverse gadgets of production from drawings and those dimensions are recorded in dimension sheet shape.
That means of squaring the size shows the multiplication of dimensions period, width and intensity to locate amount of tem to be measured in cubic meter or multiplication of period and peak of object is measured in rectangular meters. And those are recorded dimension sheet shape
Typical dimension sheet shape-
Measurement sheet:
Item no. | Description Or particulars | No. | Dimensions | Quantity | Explanatory Notes | ||
length | breadth | height | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Measurement sheer is prepared.
Abstract sheet:
Items No | Description of an item | Quantity | Rate RS p. | Per
| Amount RS p. |
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
It is first and second columns are same in measurement and abstract sheet.
The rate of item of works are worked out or taken from DSR
Q5) Explain comparison of different alternative.
A5) Comparison of Different Alternatives:
In the actual world, the bulk of engineering economic evaluation troubles are opportunity comparisons. In those troubles, or more collectively exceptional investments compete for restricted funds. A sort of methods exists for choosing the advanced opportunity from a set of proposals. Each technique has its very own deserves and applications.
In maximum of the sensible choice environments, executives could be compelled to pick the satisfactory opportunity from a hard and fast of competing alternatives.
Let us anticipate that an organization has a big amount of cash for capacity investment and there are 3 distinctive tasks whose preliminary outlay and annual revenues at some points of their lives are known. The government has to pick the satisfactory opportunity amongst those 3 competing tasks.
There are several bases for evaluating the worthiness of the tasks. These bases are:
a) Present really well worth technique
b) Future really well worth technique
c) Annual equal technique
d) Rate of go back technique/ Rate of return
Q6) Explain what do you mean by bar bending schedule.
A6) Bar Bending Schedules
Bar Bending Schedule, generally cited as "BBS" is a complete listing that describes the location, mark, kind, size, length and wide variety, and bending information of every bar or cloth in a Reinforcement Drawing of a Structure. This procedure of listing the location, kind and size, wide variety of and all different information is known as "Scheduling In context of Reinforcement bars, its miles known as bar scheduling. In short, Be Bending Schedule is a manner of organizing re bars for every structural unit, giving specified reinforcement requirements.
Approximately the amount of steels for a RCC member can be calculated as below. When element drawing and designs and an available.
Quantity of metallic 0.7 to 1% of amount of concrete (m²) But metallic isn't always expressed on cubic meters so amount in quintal is calculated via way of means of thinking about the density of slight metallic.
As I cubic meters of metallic-78. fifty-nine quintals 7850 kg
1 - a thousand kg
2. For beams
Quantity of metallic-1 to 2%
3. For columns
Quantity of metallic 1 to five%
4. For basis and footing
Quantity of metallic 0. five to 0.8%
For R.C.C. works completing no greater price is made minimum cowl for metallic have to be furnished as below:
For slab Side cowl 4 cm to 5 cm; pinnacle and backside Lover L1-2 cm to 2
For beams 2-5 cm to 5cm
Measurement of duration of reinforcement:
Type of bar | Sketch of bar | Length of hoot | Total length of bar |
Straight bar |
| qd + ad = 18d | L + (8d) |
On side bent up |
| qd + ad = 18d | L + 18d + 0.24D |
Overlap:
qd + qd = 18d (40d or 50d+18d)
Bar bent-up both side:
qd+qd = 18d (L+18d+ 2x2.92Dx0.4)
Q7) Explain mass haul diagrams in detail.
A7) Mass Haul Diagrams:
This is a curve representing cumulative quantity of earthwork at any factor on curve, the way which earth to be removed. It is important to plot motion of excavated soil of labor web website online from cuts to fill in order that haul distance be minimal to lessen the fee or cost of earthwork.
This is a curve representing cumulative quantity of earthwork at any factor on curve, the way which earth to be removed.
It is important to plot motion of excavated soil of labor web website online from cuts to fill in order that haul distance be minimal to lessen the fee of earthwork.
The mass haul diagram enables to decide the economic system in higher way.
Construction of Mass Haul Diagram:
1) Workout amassed quantity as algebraic sum quantity of earth paintings at every station/change.
2) Draw a bottom line and mark the stations with appropriate scale
3) From each station draw vertical line and mark the appropriate scale for earth quantity.
4) On the ordinates of every station mark respective scaled cumulative heights. Thus, the peak of an ordinate at any factor on the bottom line represents algebraic sum of quantity of earthwork.
5) Join all of the factors via way of means of easy curve and this curve is known as Mass Haul Diagram.
6) From curve, exercising portions of earthwork which includes earth to be taken far from web website online or earth to be added at web website online.
Characteristics of mass haul diagram:
The Ordinate at any factor represents the cumulative fabric to that factor at the profile ii.
Within the limits of an unmarried reduce, the curve rises from left to proper; inside the limits of an unmarried fill, it falls from left to proper iii. Sections wherein the profile modifications from reduce to fill correspond to a most. Evidently the most and minimal factors at the mass diagram arise at or close to grade factors at the profile iv. Any horizontal line reducing a loop of a mass curve, intersects the curve at factors b/n which the reduce is same to the fill (adjusted for shrinkage); one of these lines is known as a BALANCE LINE v. The loop convex upward suggests that the haul from reduce to fill is to be in a single direction
Q8) Explain what is estimation of earthwork?
A8) Estimation of earthwork
For construction of roads, railways, canals etc., the amount of earthwork in reducing or in embankment required to be c dedication of the entire amount of earthwork is called earthwork computation. For this cause the
This and cross-segment for the precise duration of the avenue, canal or railway is essential. For revenue, dam, canal and railway embankment
Cross-segment of earthwork of an avenue or canal is commonly in the shape of trapezium, the portions of following methods:
Formula:
Cross sectional vicinity= vicinity of central + vicinity of each
square portion aspect of triangle portion
= Bd + 2 (1/2 Sd xd)
= Bd+ Sd^2
Diagram:
Depth of cutting = F.L.- R.L. of ground= top RL of road – RL of ground
Formation level= FL at previous chain age +or- 1/gradient X difference in chainage
At change from bunking chain age of GL is determined where depth of cutting or bunking is zero.
Diagram:
If side slope is given 1 in n, then S= n (Vin H)
If side is given 1:2 then S = ½ (H: V)
S = H/V side slope
Methods of calculating Earthwork:
Q9) Explain center line method of estimation and carryout the detailed estimation and obtained the quantity for following fig.
Door, D= 0.90x2.10
D1 = 0.75x2.10
D2 = 0.60x1.80
Window, W = 1.50x1.20
W1 = 1.20x0.90
W2 = 0.90x1.05
Ventilates, V = 0.45x0.60
Find earthwork excavation for foundation
A9)
Center line method:
Total center to center distance of wall =
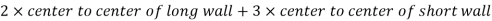
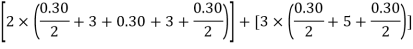
= 13.2 + 15.9 = 29.1 m
Total c/c distance of wall = 29.1 m
Total depth of foundation= 1.4
Detail measurement and calculation of substructure
Item no | Particular of item | No. | Length | Breath | Height | Quantity | Explanatory notes |
1 | Earth work excavation for foundation | 01 | 29.1 | 0.30 | 1.4 | 12.22cu.m | - |
Abstract estimation:
Item no | Description of item work | Quantity | Unit | Rate RS p. | Per | Cost Rs P. |
1 | Earth work in excavation in foundation | 12.22 | M3 | 465.00 | 10m3 | 5682.30 |
Q10) Preparation of an estimate of one room block as shown in fig. for the following item of work
1) Excavation for foundation
2) P.C.C (1:4:8) in foundation
3) U.C.R. masonry in foundation in C.M. (1:6)
4) O.R. masonry plinth in C.M. (1:6)
5) D.P.C. at plinth level
6) Brick work in super structure in C.M(1:6)
7) RCC slab 15 cm thick by
A10)
Item no | Description | No. | Dimension | Quantity | Explanatory notes | ||||||||||
Length | Breath | Height | |||||||||||||
1 | Excavation for foundation in earth soil of all types removal of the excavates material up to a distance of 50 m beyond the building area |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Long wall | 2 | 8.00 | 1 | 0.90 | 14.40 m3 |
| |||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 4.5 | 1 | 0.90 | 8.10 m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
| Total | 22.50 m3 |
| |||||||||
2 | Providing and laying in situ cement concrete (1:4:8) of trap metal for foundation and bedding including bailing out water, form work compacting and curing etc. complete |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Long wall | 2 | 8.00 | 1 | 0.20 | 3.2m3 |
| |||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 4.50 | 1 | 0.20 | 1.8m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
| Total | 5 m3 |
| |||||||||
3 | Providing un coursed rubble masonry of trap stone in cement mortar (1:6) |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Long wall | 2 | 7.80 | 0.80 | 0.60 | 7.48 m3 |
| |||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 4.70 | 0.80 | 0.60 | 4.52 m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
| Total | 12.00 m3 |
| |||||||||
4 | Providing coursed rubble masonry 11nd sort of trap stones in cement mortar (1:6) in external wall of plinth including bailing out water. |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
| Long wall | 2 | 7.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 3.75m3 |
| ||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 5.00 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 2.50 m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
| Total | 6.25 m3 |
| |||||||||
5 | Providing and lying damp proof course 5 cm thick in cement concrete (1:2:4) layer and bitumen using cement with water proofing compound |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
| Long wall | 2 | 7.50 | 0.50 | - | 7.5 m2 |
| ||||||||
| Short wall | 2 | 5.00 | 0.50 | - | 5.0 m2 |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
| Total | 12.5 m2 |
| ||||||||
6 | Providing second class burnt brick masonry with IS type brick or conventional type in cement mortar (1:6) |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Long wall | 2 | 7.30 | 0.30 | 2 | 8.76 m3 |
| |||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 5.20 | 0.30 | 2 | 6.24 m3 |
| |||||||||
Deduction for |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Door D | 1 | 1.20 | 0.30 | 2.00 | 0.72m3 |
| |||||||||
Window W1 | 2 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 1.50 | 0.90m3 |
| |||||||||
Window W2 | 1 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 0.30m3 |
| |||||||||
Lintel over door D | 1 | 1.50 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.68m3 |
| |||||||||
Lintel over W1 | 2 | 1.30 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.12m3 |
| |||||||||
Lintel over W2 | 1 | 1.30 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.06m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
| Total deduction | = | 2.17 m3 |
| |||||||||
| Net quantity of brick masonry (a-b) |
|
|
| = | 2.17 m3 | B | ||||||||
7 | Providing and casting in situ cement concrete M-15 (1:2:4) of trap [ metal for rcc slab 15 cm thick including centering formwork compacting and curing | 1 | 7.40 | 5.90 | 0.15 | 6.55 3 |
| ||||||||
Q11) Explain what is finishes, interiors and MPE work in detail.
A11) Finishes, Interiors, MPE work
1. Finishes:
Finishes are used within side the very last a part of the construction or manufacturing process, forming the very last floor of an element. From impact, water, frost, corrosion, abrasion, and so on, and/or they may be decorative.
Finishes usually relate to inner surfaces however they will additionally be carried out to external elements. They may be carried out moist or dry. Some elements are self-finished, this is the very last floor is a part of the material the element is fashioned from.
The utility of finishes may contain the buildup of greater than one layer, which, even as a number of the layers will form the very last uncovered floor, they may be although taken into consideration to be finishes. For example, an undercoat or primer is probably carried out to a wall before the very last paint.
NSB categories finish as:
Interior layout is the art and science of improving the indoors of a building to obtain a more fit and extra aesthetically alluring environment for the human beings the usage of the area. An indoors designer is a person who plans, researches, coordinates, and manages such enhancement projects. Interior layout is a multifaceted career that consists of conceptual development, area planning, web website online inspections, programming, research, speaking with the stakeholders of a project, production management, and execution of the layout.
2. MEP works:
MEP, or mechanical, electric and plumbing engineering, are the 3 technical disciplines that embody the systems that permit constructing interiors to be appropriate for human use and occupancy.
MEP layout is essential for planning, selection making, correct documentation, performance- and cost-estimation, construction, and operating/retaining the ensuing facilities. MEP specifically encompasses the in-intensity layout and choice of those systems, rather than a tradesperson surely putting in equipment.
Q12) Explain BIM and quality take off what is adding equipment cost and what is labour cost?
A12) BIM and Quality take off
BIM fashions can lessen this time because estimators are capable of extract measurements and material quantities straight from fashions.
The quantity of discount in time spent on may be as plenty as 80% at the same time as providing amount take-offs and estimates that are correct to inside 3%.
In correct amount takeoff interprets into particular scheduling and value estimation.
This makes it extraordinarily essential to behavior a complete amount takes off thru detailed evaluation of every detail of BIM geometry.
Estimating represents a crucial factor of the constructing technique which could advantage from computable constructing facts.
Quantity take-offs (QTO) are typically performed at one-of-a-kind degrees of the mission and with one-of-a-kind purposes (e.g., for value estimates and auditing). The traditional technique to carry out a QTO represents a time-eating and error-susceptible technique.
Relevant constructing facts needs to be extracted from drawings and un structured documents, which may be old or inconsistent.
Adding Equipment Costs
The original price of an asset takes into attention all the objects that may be attributed to its buy and to setting the asset to use. These costs include the buy price and such elements as commissions, transportation, appraisals, warranties and set up and testing.
Labour costs:
To calculate the labour price, it ought to be essential to know that the wide variety and wages of various classes of labours, professional and unskilled, specifically mason or carpenter, mazdoor etc. required for every unit of work.
Q13) What do you mean rate analysis?
A13) Rate Analysis:
In order to decide the price of a specific object, the elements affecting the price of that object are studied cautiously after which finally a price is determined for that object.
This method of figuring out the quotes of an object is termed as evaluation of quotes or price evaluation or rate analysis
The price of unique object of labor relies upon on the following
1) Specifications of works and fabric approximately their quality share and constructional Operation method.
2) Quantity of substances and their costs.
3) Cost of labours and their wages.
4) Location of site of labor and the distances from source and conveyance charges.
5) Overhead and established order charges.
6) Profit.
Purpose of Analysis of rate:
1) To exercise session the real price of according to unit of the objects.
2) To exercise session the not pricey use of substances and strategies in finishing the details object.
3) To exercise session the price of greater objects which aren't furnished within side the settlement bond, however are to be carried out as according to the instructions of the department
4) To revise the time table of quotes because of growth within side the price of fabric and labour or because of alternate in technique