Unit – 3
Semiconductor Lasers
Question and Answer
1) Define Laser dynamics with the help of equation?
Answer:
Definition: The dynamic performance of a laser is determined by the interaction of the intracavity light field with the gain medium.
With certain estimates, including a not too high laser gain, the dynamics of the intracavity power p and the gain coefficient g in a continuous-wave laser can be described with the following joined differential equations:
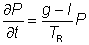
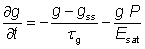
Where,
TR is the cavity round-trip time,
l the cavity loss,
gss the small-signal gain (for a given pump intensity),
τg the gain relaxation time ,
Esat the saturation energy of the gain medium.
2) What is Input-Output Characteristics?
Answer:

The above figure shows a laser diode’s output optical power versus injected electrical current – P/I Curve.
Slope Efficiency
The P/I curve slope above threshold current is called a LD’s slope competence and is defined as dP/dI.
Here,dP is the change in the light power output,
DI is the change in the forward current through the diode.
Slope efficiency has a unit of mW/mA.
The increase in the number of electrons injected per unit time into the laser is dI/e,
Where, e is the electronic charge.
The additional number of photons exiting the laser is dP/hv,
Where, v is the frequency of the radiation
h is the Planck constant
Differential external quantum efficiency of the laser ηD is defined as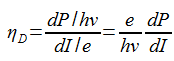
ηD has a value between 0.25 and 0.6 for continuous wave lasers.
3) What is Semiconductor Laser: Structure, Materials, Device Characteristics, And Figures Of Merit?
Answer:
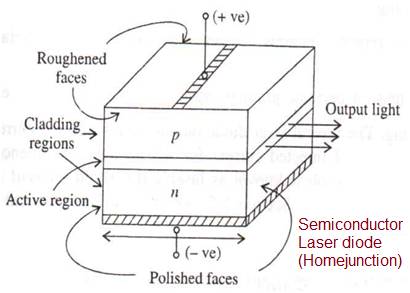
Lasers are devices which produce intense beams of light which are monochromatic, coherent and highly collimated.
We are aware that LASER is acronym for "Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation".
Semiconductor lasers are compact in size as they are made using semiconductor materials on nanometre scale accuracy.
It is similar to transistor and has operation like LED, but the output beam has characteristics of laser light.
The material most often used in semiconductor laser is GaAs (Gallium Arsenide).
Henceforth it is known as gallium arsenide laser.
It is also named as injection laser.
The character depicts simple semiconductor p-n junction structure known as homojunction laser diode.
In semiconductor laser diode, optical gain is shaped in semiconductor material.
The recombination of injected holes and electrons (and consequent emission of photons) in a forward biased semiconductor p-n junction signifies direct conversion of electricity to light.
The multiple reflections of emitted radiation within the optical cavity region helps to build up photons for maintainable stimulated emission from the junction laser diode.
If rate of stimulated emission is made meaningfully higher compare to loss rate, then the device turns to the lasing state.
This situation is known as gain state of the system.
Based on their creation and materials used, Semiconductor laser types include simple homojunction laser diode, DH (Double Heterojunction) laser, QW (Quantum Well) laser, DFB ( Distributed Feedback ) laser, Tunable laser, Surface emitting laser etc.
Based on types of laser, it is used in various applications such as storing information in(Compact disk) CDs and DVDs, high speed show of information over fiber optic cable, welding, surgery, military, holography etc.
Hence, it is used as natural transmitter of digital data.
Next are the profits or benefits of Semiconductor Laser:
It occupations passive cooling technique in its design.
It consumes fewer power.
It suggestions excellent competence with very high process duration.
Semiconductor lasers are inexpensive and cheap to afford.
It proposals long life, highly monochromatic, tuneable and nonstop beam.
It is modest in design/construction and compact in size.
4) What do you mean byDfb, Dbr, And Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers (Vecsel), Tunable Semiconductor Laser?
Answer:
A Distrubuted Bragg Reflector laser (DBR) is a kind of single frequency laser diode. Additional practical types of single frequency laser diodes include DFB lasers and external cavity diode lasers.
DBR lasers are frequently similar with DFB lasers.
Both exhibit thin linewidth and stable single frequency process.
However, the location of the feedback element (the grating) causes the DBR and the DFB to have separate operational features.
Since, the grating is distributed all along the gain area in the DFB, the grating and gain area involvement like conditions as the device is tuned by current and temperature.
The DFB can exhibit a nonstop tuning range of 2 nm or more.
Conversely, over a sufficiently long current or temperature range, the emitted wavelength() will abruptly jump to a longer wavelength (red shift), exit a gap in the tuning range.
The vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is a type of semiconductor laser diode with laser beam emission perpendicular from the top surface, dissimilar to conventional edge-emitting semiconductor lasers which emit from surfaces shaped by cutting the individual chip out of a wafer.
VCSELs are used in various laser products, including computer mice ,fiber optic communication , laser printer, Face ID, and smart glasses.

Definition : A tuneable laser is a laser whose wavelength of process can be different in a controlled manner. While all laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength(), only a few types of lasers allow nonstop tuning over a important wavelength range.
Types of tenability
Single line tuning
Since, no real laser is truly monochromatic, all lasers can emit light ended approximately range of frequencies, known as the linewidth of the laser switch
Multi-line tuning
Most laser gain media have a number of transition wavelengths on which laser process can be attained
Narrowband tuning
Distributed feedback (DFB) semiconductor lasers and vertical cavity surface emitting lasers (VCSELs) usage periodic distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) structures to form the mirrors of the optical cavity.
Widely tenable lasers
Outside cavity lasers using multiple-prism grating arrangements for wide-range tenability
5) Define vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL)?
Answer:
The vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is a kind of semiconductor laser diode with laser beam emission perpendicular from the top surface, dissimilar to conventional edge-emitting semiconductor lasers which emit from surfaces shaped by cutting the individual chip out of a wafer.
VCSELs are used in various laser products, including computer mice ,fiber optic communication , laser printer, Face ID, and smart glasses.

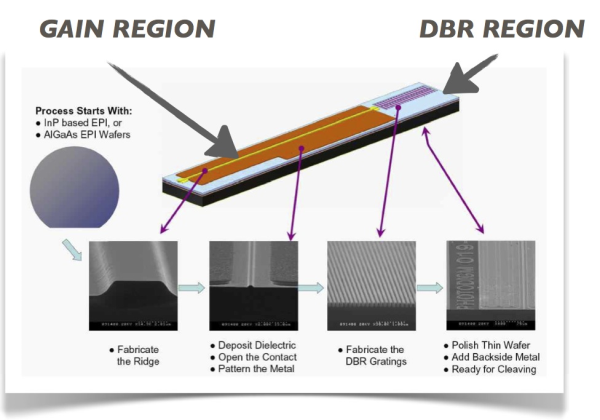
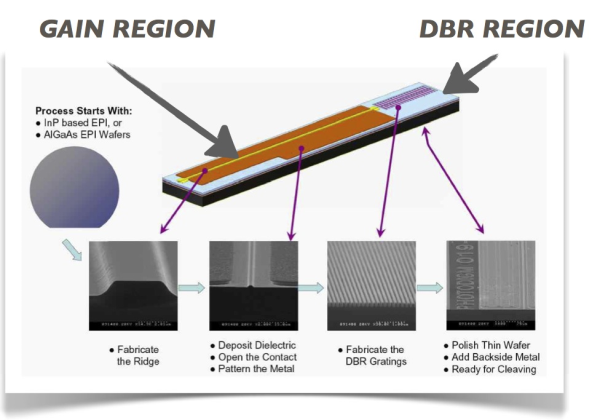
6) Draw the diagram of Gain and DBR Region?
Answer:
A Distributed Bragg Reflector laser (DBR) is a kind of single frequency laser diode. Additional practical types of single frequency laser diodes include DFB lasers and outside cavity diode lasers.
DBR lasers are frequently similar with DFB lasers.
Both exhibit narrow line width and stable single frequency process.
Though, the location of the feedback element (the grating) reasons the DBR and the DFB to have separate operational features.
Meanwhile, the grating is dispersed all along the gain region in the DFB, the grating and gain region information similar conditions as the device is tuned with current and temperature.
The DFB can exhibit a continuous tuning range of 2 nm or more.
Though, over a sufficiently long current or temperature range, the emitted wavelength() will suddenly jump to a longer wavelength (red shift), leaving a gap in the tuning range.
7) Give the equation of Differential external quantum efficiency?
Answer:
Differential external quantum efficiency of the laser ηD is defined as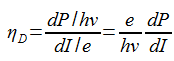
ηD has a value between 0.25 and 0.6 for constant wave lasers.
Here,dP is the change in the light power yield,
DI is the change in the forward current concluded the diode.
Slope efficiency has a unit of mW/mA.
The rise in the number of electrons inserted per unit time into the laser is dI/e,
Where, e is the electronic charge.
The extra number of photons exiting the laser is dP/hv,
Where, v is the frequency of the radiation
h is the Planck constant