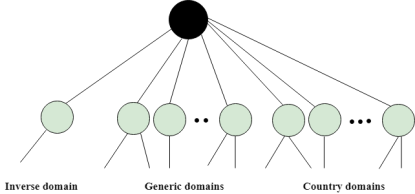
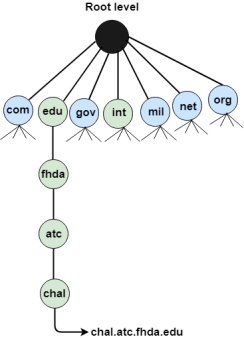
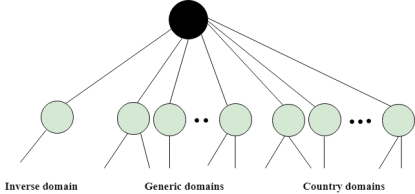
An application layer protocol defines how the application processes running on different systems; pass the messages to each other. DNS stands for Domain Name System. DNS is a directory service that provides a mapping between the name of a host on the network and its numerical address. DNS is required for the functioning of the internet. Each node in a tree has a domain name, and a full domain name is a sequence of symbols specified by dots. DNS is a service that translates the domain name into IP addresses. This allows the users of networks to utilize user-friendly names when looking for other hosts instead of remembering the IP addresses. For example, suppose the FTP site at EduSoft had an IP address of 132.147.165.50, most people would reach this site by specifying ftp.EduSoft.com. Therefore, the domain name is more reliable than IP address. DNS is a TCP/IP protocol used on different platforms. The domain name space is divided into three different sections: generic domains, country domains, and inverse domain.
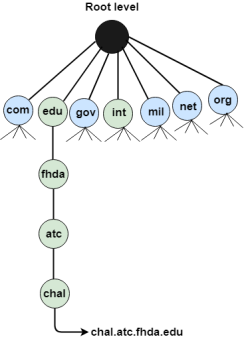
Generic Domains It defines the registered hosts according to their generic behavior. Each node in a tree defines the domain name, which is an index to the DNS database. It uses three-character labels, and these labels describe the organization type.
Country Domain The format of country domain is same as a generic domain, but it uses two-character country abbreviations (e.g., us for the United States) in place of three character organizational abbreviations. Inverse Domain The inverse domain is used for mapping an address to a name. When the server has received a request from the client, and the server contains the files of only authorized clients. To determine whether the client is on the authorized list or not, it sends a query to the DNS server and ask for mapping an address to the name. Working of DNS DNS is a client/server network communication protocol. DNS clients send requests to the. server while DNS servers send responses to the client. Client requests contain a name which is converted into an IP address known as a forward DNS lookups while requests containing an IP address which is converted into a name known as reverse DNS lookups. DNS implements a distributed database to store the name of all the hosts available on the internet. If a client like a web browser sends a request containing a hostname, then a piece of software such as DNS resolver sends a request to the DNS server to obtain the IP address of a hostname. If DNS server does not contain the IP address associated with a hostname, then it forwards the request to another DNS server. If IP address has arrived at the resolver, which in turn completes the request over the internet protocol. |
When DNS (Domain Name System) was designed, nobody expected that there would be so many address changes such as adding a new host, removing a host, or changing an IP address. When there is a change, the change must be made to the DNS master file which needs a lot of manual updating and it must be updated dynamically. Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) : It is a method of automatically updating a name server in the Domain Name Server (DNS), often in real-time, with the active DDNS configuration of its configured hostnames, addresses, or other information. In DDNS, when a binding between a name and an address is determined, the information is sent, usually by DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to a primary DNS server. The primary server updates the zone. The secondary servers are notified either actively or passively. Inactive notification, the primary server sends a message to secondary servers, whereas, in the passive notification, the secondary servers periodically check for any changes. In either case, after being notified about the change, the secondary requests information about the entire zone (zone transfer). DDNS can use an authentication mechanism to provide security and prevent unauthorized changes in DNS records. Advantages : It saves time required by static addresses updates manually when network configuration changes. It saves space as the number of addresses are used as required at one time rather than using one for all the possible users of the IP address. It is very comfortable for users point of view as any IP address changes will not affect any of their activities. It does not affect accessibility as changed IP addresses are configured automatically against URL’s. Disadvantages : It is less reliable due to lack of static IP addresses and domain name mappings. Dynamic DNS services alone can not make any guarantee about the device you are attempting to connect is actually your own. Uses : It is used for Internet access devices such as routers. It is used for for security appliance manufacturers and even required for IP-based security appliances like DVRs. |
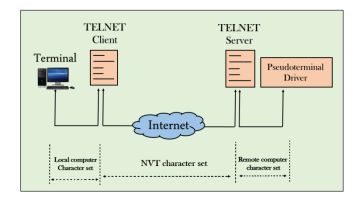
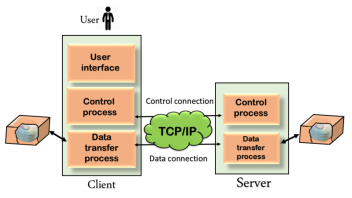
Telnet The main task of the internet is to provide services to users. For example, users want to run different application programs at the remote site and transfers a result to the local site. This requires a client-server program such as FTP, SMTP. But this would not allow us to create a specific program for each demand. The better solution is to provide a general client-server program that lets the user access any application program on a remote computer. Therefore, a program that allows a user to log on to a remote computer. A popular client-server program Telnet is used to meet such demands. Telnet is an abbreviation for Terminal Network. Telnet provides a connection to the remote computer in such a way that a local terminal appears to be at the remote side. There are two types of login: Local Login
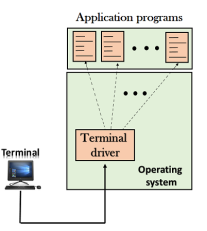
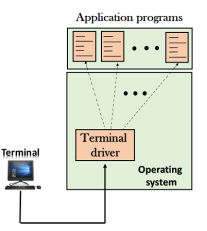
When a user logs into a local computer, then it is known as local login. When the workstation running terminal emulator, the keystrokes entered by the user are accepted by the terminal driver. The terminal driver then passes these characters to the operating system which in turn, invokes the desired application program. However, the operating system has special meaning to special characters. For example, in UNIX some combination of characters have special meanings such as control character with "z" means suspend. Such situations do not create any problem as the terminal driver knows the meaning of such characters. But, it can cause the problems in remote login. Remote login
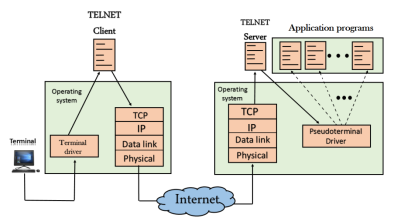
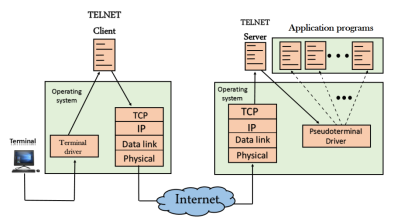
When the user wants to access an application program on a remote computer, then the user must perform remote login. How remote login occurs At the local site The user sends the keystrokes to the terminal driver, the characters are then sent to the TELNET client. The TELNET client which in turn, transforms the characters to a universal character set known as network virtual terminal characters and delivers them to the local TCP/IP stack At the remote site The commands in NVT forms are transmitted to the TCP/IP at the remote machine. Here, the characters are delivered to the operating system and then pass to the TELNET server. The TELNET server transforms the characters which can be understandable by a remote computer. However, the characters cannot be directly passed to the operating system as a remote operating system does not receive the characters from the TELNET server. Therefore it requires some piece of software that can accept the characters from the TELNET server. The operating system then passes these characters to the appropriate application program.
Network Virtual Terminal (NVT)
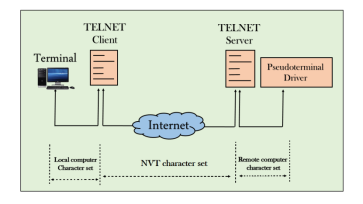
The network virtual terminal is an interface that defines how data and commands are sent across the network. In today's world, systems are heterogeneous. For example, the operating system accepts a special combination of characters such as end-of-file token running a DOS operating system ctrl+z while the token running a UNIX operating system is ctrl+d. TELNET solves this issue by defining a universal interface known as network virtual interface. The TELNET client translates the characters that come from the local terminal into NVT form and then delivers them to the network. The Telnet server then translates the data from NVT form into a form which can be understandable by a remote computer. |
|
|
|
|
An application layer protocol defines how the application processes running on different systems; pass the messages to each other. DNS stands for Domain Name System. DNS is a directory service that provides a mapping between the name of a host on the network and its numerical address. DNS is required for the functioning of the internet. Each node in a tree has a domain name, and a full domain name is a sequence of symbols specified by dots. DNS is a service that translates the domain name into IP addresses. This allows the users of networks to utilize user-friendly names when looking for other hosts instead of remembering the IP addresses. For example, suppose the FTP site at EduSoft had an IP address of 132.147.165.50, most people would reach this site by specifying ftp.EduSoft.com. Therefore, the domain name is more reliable than IP address. DNS is a TCP/IP protocol used on different platforms. The domain name space is divided into three different sections: generic domains, country domains, and inverse domain.
Generic Domains It defines the registered hosts according to their generic behavior. Each node in a tree defines the domain name, which is an index to the DNS database. It uses three-character labels, and these labels describe the organization type.
Country Domain The format of country domain is same as a generic domain, but it uses two-character country abbreviations (e.g., us for the United States) in place of three character organizational abbreviations. Inverse Domain The inverse domain is used for mapping an address to a name. When the server has received a request from the client, and the server contains the files of only authorized clients. To determine whether the client is on the authorized list or not, it sends a query to the DNS server and ask for mapping an address to the name. Working of DNS DNS is a client/server network communication protocol. DNS clients send requests to the. server while DNS servers send responses to the client. Client requests contain a name which is converted into an IP address known as a forward DNS lookups while requests containing an IP address which is converted into a name known as reverse DNS lookups. DNS implements a distributed database to store the name of all the hosts available on the internet. If a client like a web browser sends a request containing a hostname, then a piece of software such as DNS resolver sends a request to the DNS server to obtain the IP address of a hostname. If DNS server does not contain the IP address associated with a hostname, then it forwards the request to another DNS server. If IP address has arrived at the resolver, which in turn completes the request over the internet protocol. |
When DNS (Domain Name System) was designed, nobody expected that there would be so many address changes such as adding a new host, removing a host, or changing an IP address. When there is a change, the change must be made to the DNS master file which needs a lot of manual updating and it must be updated dynamically. Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) : It is a method of automatically updating a name server in the Domain Name Server (DNS), often in real-time, with the active DDNS configuration of its configured hostnames, addresses, or other information. In DDNS, when a binding between a name and an address is determined, the information is sent, usually by DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to a primary DNS server. The primary server updates the zone. The secondary servers are notified either actively or passively. Inactive notification, the primary server sends a message to secondary servers, whereas, in the passive notification, the secondary servers periodically check for any changes. In either case, after being notified about the change, the secondary requests information about the entire zone (zone transfer). DDNS can use an authentication mechanism to provide security and prevent unauthorized changes in DNS records. Advantages : It saves time required by static addresses updates manually when network configuration changes. It saves space as the number of addresses are used as required at one time rather than using one for all the possible users of the IP address. It is very comfortable for users point of view as any IP address changes will not affect any of their activities. It does not affect accessibility as changed IP addresses are configured automatically against URL’s. Disadvantages : It is less reliable due to lack of static IP addresses and domain name mappings. Dynamic DNS services alone can not make any guarantee about the device you are attempting to connect is actually your own. Uses : It is used for Internet access devices such as routers. It is used for for security appliance manufacturers and even required for IP-based security appliances like DVRs. |
Telnet The main task of the internet is to provide services to users. For example, users want to run different application programs at the remote site and transfers a result to the local site. This requires a client-server program such as FTP, SMTP. But this would not allow us to create a specific program for each demand. The better solution is to provide a general client-server program that lets the user access any application program on a remote computer. Therefore, a program that allows a user to log on to a remote computer. A popular client-server program Telnet is used to meet such demands. Telnet is an abbreviation for Terminal Network. Telnet provides a connection to the remote computer in such a way that a local terminal appears to be at the remote side. There are two types of login: Local Login
When a user logs into a local computer, then it is known as local login. When the workstation running terminal emulator, the keystrokes entered by the user are accepted by the terminal driver. The terminal driver then passes these characters to the operating system which in turn, invokes the desired application program. However, the operating system has special meaning to special characters. For example, in UNIX some combination of characters have special meanings such as control character with "z" means suspend. Such situations do not create any problem as the terminal driver knows the meaning of such characters. But, it can cause the problems in remote login. Remote login
When the user wants to access an application program on a remote computer, then the user must perform remote login. How remote login occurs At the local site The user sends the keystrokes to the terminal driver, the characters are then sent to the TELNET client. The TELNET client which in turn, transforms the characters to a universal character set known as network virtual terminal characters and delivers them to the local TCP/IP stack At the remote site The commands in NVT forms are transmitted to the TCP/IP at the remote machine. Here, the characters are delivered to the operating system and then pass to the TELNET server. The TELNET server transforms the characters which can be understandable by a remote computer. However, the characters cannot be directly passed to the operating system as a remote operating system does not receive the characters from the TELNET server. Therefore it requires some piece of software that can accept the characters from the TELNET server. The operating system then passes these characters to the appropriate application program.
Network Virtual Terminal (NVT)
The network virtual terminal is an interface that defines how data and commands are sent across the network. In today's world, systems are heterogeneous. For example, the operating system accepts a special combination of characters such as end-of-file token running a DOS operating system ctrl+z while the token running a UNIX operating system is ctrl+d. TELNET solves this issue by defining a universal interface known as network virtual interface. The TELNET client translates the characters that come from the local terminal into NVT form and then delivers them to the network. The Telnet server then translates the data from NVT form into a form which can be understandable by a remote computer. |
|
|
|
|