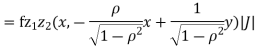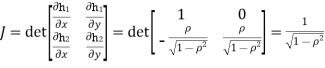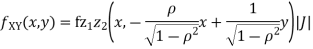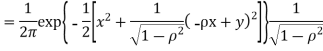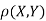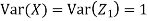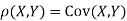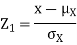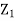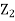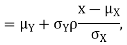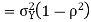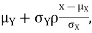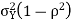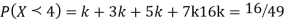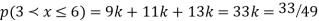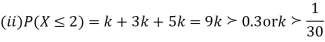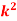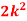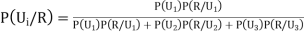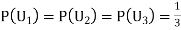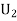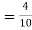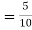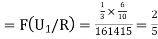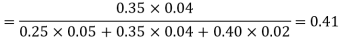M3
Unit-3Bivariate Distributions Q1) Let  be two independent N (0, 1) random variables. Define
be two independent N (0, 1) random variables. Define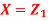
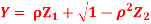 Where
Where  is a real number in (-1, 1).
is a real number in (-1, 1).Show that X and Y are bivariate normal. Find the joint PDF of X and Y. Find  (X,Y)
(X,Y) S1)First note that since 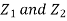 are normal and independent they are jointly normal with the joint PDF
are normal and independent they are jointly normal with the joint PDF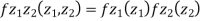
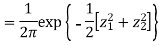
We need to show aX + bY is normal for all. We have 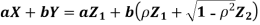
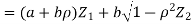 Which is the linear combination of
Which is the linear combination of 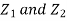 and thus it is normal.b. We can use the method of transformations (theorem 5.1) to find the joint PDF of X and Y. The inverse transformation is given by
and thus it is normal.b. We can use the method of transformations (theorem 5.1) to find the joint PDF of X and Y. The inverse transformation is given by
Q2) Let X and Y be jointly normal random variables with parameters  Find the conditional distribution of Y given X =x.S2) One way to solve this problem is by using the joint PDF formula since X
Find the conditional distribution of Y given X =x.S2) One way to solve this problem is by using the joint PDF formula since X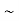 N
N 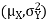 we can use
we can use
Q3) A die is tossed thrice. A success is getting 1 or 6 on a toss. Find the mean and variance of the number of successes.S3)Probability of success 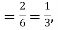 probability of failures
probability of failures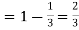 Probability of no success= probability of all three failures
Probability of no success= probability of all three failures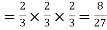 Probability of one successes and two failures
Probability of one successes and two failures 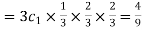 Probability of Two successes and one failure
Probability of Two successes and one failure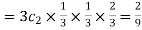 Probability of three successes
Probability of three successes 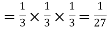
Mean 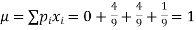
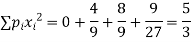 Variance,
Variance,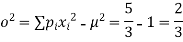 Q4) The probability density function of a variate X is
Q4) The probability density function of a variate X is
S4) (I) If X is random variable then
Q5) Random variable X has the following probability function
(i) Find the value of the k(ii) Evaluate P (X < 6), P (X≥6)(iii) 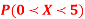 S5) (i) if X is a random variable then
S5) (i) if X is a random variable then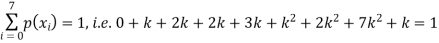
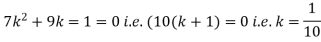 (ii)P (X < 6) =P( X=0) +P(X=1)+P(X=2)+ P(X=3) +P(X=4) + P (X=5)
(ii)P (X < 6) =P( X=0) +P(X=1)+P(X=2)+ P(X=3) +P(X=4) + P (X=5)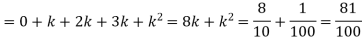
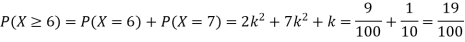 (iv)
(iv) 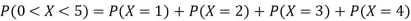
 Q6) A bag contains 12 pens of which 4 are defective. Three pens are picked at random from the bag one after the other.Then find the probability that all three are non-defective.S6) here the probability of the first which will be non-defective = 8/12By the multiplication theorem of probability,If we draw pens one after the other then the required probability will be-
Q6) A bag contains 12 pens of which 4 are defective. Three pens are picked at random from the bag one after the other.Then find the probability that all three are non-defective.S6) here the probability of the first which will be non-defective = 8/12By the multiplication theorem of probability,If we draw pens one after the other then the required probability will be-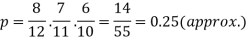 Q7) An urn
Q7) An urn 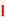 contains 3 white and 4 red balls and an urn lI contains 5 white and 6 red balls. One ball is drawn at random from one ofthe urns and isfound to be white. Find the probability that it was drawn from urn 1.S7) Let
contains 3 white and 4 red balls and an urn lI contains 5 white and 6 red balls. One ball is drawn at random from one ofthe urns and isfound to be white. Find the probability that it was drawn from urn 1.S7) Let 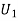 : the ball is drawn from urn I
: the ball is drawn from urn I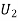 : the ball is drawn from urn II
: the ball is drawn from urn II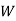 : the ball is white.We have to find
: the ball is white.We have to find 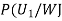 By Bayes Theorem
By Bayes Theorem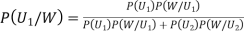 ... (1) Since two urns are equally likely to be selected,
... (1) Since two urns are equally likely to be selected,  (a white ball is drawn from urn
(a white ball is drawn from urn  )
) 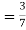
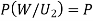 (a white ball is drawn from urn II)
(a white ball is drawn from urn II) 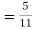 From(1),
From(1), 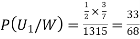 Q8) Three urns contains 6 red, 4 black, 4 red, 6 black; 5 red, 5 black balls respectively. One of the urns is selected at random and a ball is drawn from it. lf the ball drawn is red find the probability that it is drawn from the first turn.S8)Let
Q8) Three urns contains 6 red, 4 black, 4 red, 6 black; 5 red, 5 black balls respectively. One of the urns is selected at random and a ball is drawn from it. lf the ball drawn is red find the probability that it is drawn from the first turn.S8)Let 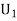 : the ball is drawn from urn 1.
: the ball is drawn from urn 1.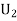 : the ball is drawn from urn lI.
: the ball is drawn from urn lI.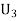 : the ball is drawn from urn 111.
: the ball is drawn from urn 111.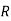 : the ball is red.We have to find
: the ball is red.We have to find 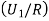 .
.
Q9) ln a bolt factory machines  and
and  manufacturerespectively 25%, 35% and 40% of the total. lf their output 5, 4 and 2 per cent are defective bolts. A bolt is drawn at random from the product and is found to be defective. What is the probability that it was manufactured by machine B.
manufacturerespectively 25%, 35% and 40% of the total. lf their output 5, 4 and 2 per cent are defective bolts. A bolt is drawn at random from the product and is found to be defective. What is the probability that it was manufactured by machine B. ?S9) bolt is manufactured by machine
?S9) bolt is manufactured by machine 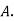
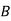 : bolt is manufactured by machine
: bolt is manufactured by machine 
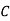 : bolt is manufactured by machine
: bolt is manufactured by machine 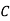
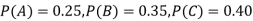 The probability of drawing a defective bolt manufactured by machine
The probability of drawing a defective bolt manufactured by machine 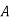 is
is 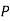 (D/A)
(D/A) 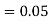 Similarly,
Similarly, 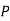 (D/B)
(D/B) 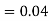 and
and 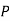 (D/C)
(D/C) 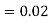 By Bayes’ theorem
By Bayes’ theorem
 be two independent N (0, 1) random variables. Define
be two independent N (0, 1) random variables. Define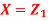
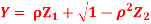 Where
Where  is a real number in (-1, 1).
is a real number in (-1, 1). (X,Y)
(X,Y)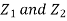 are normal and independent they are jointly normal with the joint PDF
are normal and independent they are jointly normal with the joint PDF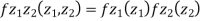
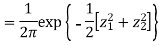
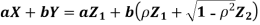
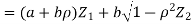 Which is the linear combination of
Which is the linear combination of 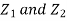 and thus it is normal.b. We can use the method of transformations (theorem 5.1) to find the joint PDF of X and Y. The inverse transformation is given by
and thus it is normal.b. We can use the method of transformations (theorem 5.1) to find the joint PDF of X and Y. The inverse transformation is given by
We have
Where, Thus we conclude that
Therefore,
|
 Find the conditional distribution of Y given X =x.S2) One way to solve this problem is by using the joint PDF formula since X
Find the conditional distribution of Y given X =x.S2) One way to solve this problem is by using the joint PDF formula since X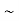 N
N 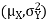 we can use
we can use
Thus given X=x, we have
And,
Since
We conclude that given X=x,Y is normally distributed with mean
|
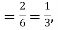 probability of failures
probability of failures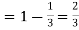 Probability of no success= probability of all three failures
Probability of no success= probability of all three failures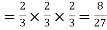 Probability of one successes and two failures
Probability of one successes and two failures 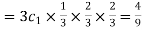 Probability of Two successes and one failure
Probability of Two successes and one failure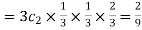 Probability of three successes
Probability of three successes 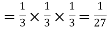
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 4/9 | 2/9 | 1/27 |
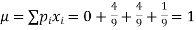
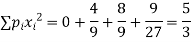 Variance,
Variance,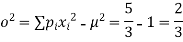 Q4) The probability density function of a variate X is
Q4) The probability density function of a variate X is X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
P (X) | k | 3k | 5k | 7k | 9k | 11k | 13k |
|
x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
P (x) | 0 | k | 2k | 2k | 3k |
|
|
|
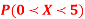 S5) (i) if X is a random variable then
S5) (i) if X is a random variable then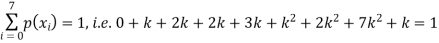
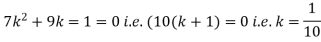 (ii)P (X < 6) =P( X=0) +P(X=1)+P(X=2)+ P(X=3) +P(X=4) + P (X=5)
(ii)P (X < 6) =P( X=0) +P(X=1)+P(X=2)+ P(X=3) +P(X=4) + P (X=5)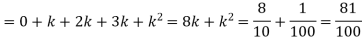
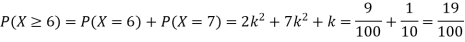 (iv)
(iv) 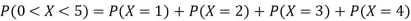
 Q6) A bag contains 12 pens of which 4 are defective. Three pens are picked at random from the bag one after the other.Then find the probability that all three are non-defective.S6) here the probability of the first which will be non-defective = 8/12By the multiplication theorem of probability,If we draw pens one after the other then the required probability will be-
Q6) A bag contains 12 pens of which 4 are defective. Three pens are picked at random from the bag one after the other.Then find the probability that all three are non-defective.S6) here the probability of the first which will be non-defective = 8/12By the multiplication theorem of probability,If we draw pens one after the other then the required probability will be-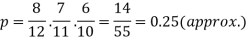 Q7) An urn
Q7) An urn  contains 3 white and 4 red balls and an urn lI contains 5 white and 6 red balls. One ball is drawn at random from one ofthe urns and isfound to be white. Find the probability that it was drawn from urn 1.S7) Let
contains 3 white and 4 red balls and an urn lI contains 5 white and 6 red balls. One ball is drawn at random from one ofthe urns and isfound to be white. Find the probability that it was drawn from urn 1.S7) Let  : the ball is drawn from urn I
: the ball is drawn from urn I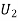 : the ball is drawn from urn II
: the ball is drawn from urn II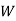 : the ball is white.We have to find
: the ball is white.We have to find 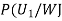 By Bayes Theorem
By Bayes Theorem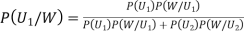 ... (1) Since two urns are equally likely to be selected,
... (1) Since two urns are equally likely to be selected,  (a white ball is drawn from urn
(a white ball is drawn from urn 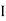 )
) 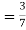
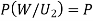 (a white ball is drawn from urn II)
(a white ball is drawn from urn II) 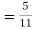 From(1),
From(1), 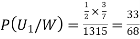 Q8) Three urns contains 6 red, 4 black, 4 red, 6 black; 5 red, 5 black balls respectively. One of the urns is selected at random and a ball is drawn from it. lf the ball drawn is red find the probability that it is drawn from the first turn.S8)Let
Q8) Three urns contains 6 red, 4 black, 4 red, 6 black; 5 red, 5 black balls respectively. One of the urns is selected at random and a ball is drawn from it. lf the ball drawn is red find the probability that it is drawn from the first turn.S8)Let 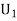 : the ball is drawn from urn 1.
: the ball is drawn from urn 1.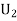 : the ball is drawn from urn lI.
: the ball is drawn from urn lI.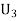 : the ball is drawn from urn 111.
: the ball is drawn from urn 111.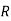 : the ball is red.We have to find
: the ball is red.We have to find 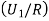 .
.By Baye’s Theorem,
Since the three urns are equally likely to be selected Also
From (1), we have
|
 and
and  manufacturerespectively 25%, 35% and 40% of the total. lf their output 5, 4 and 2 per cent are defective bolts. A bolt is drawn at random from the product and is found to be defective. What is the probability that it was manufactured by machine B.
manufacturerespectively 25%, 35% and 40% of the total. lf their output 5, 4 and 2 per cent are defective bolts. A bolt is drawn at random from the product and is found to be defective. What is the probability that it was manufactured by machine B. ?S9) bolt is manufactured by machine
?S9) bolt is manufactured by machine 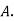
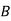 : bolt is manufactured by machine
: bolt is manufactured by machine 
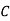 : bolt is manufactured by machine
: bolt is manufactured by machine 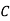
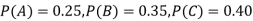 The probability of drawing a defective bolt manufactured by machine
The probability of drawing a defective bolt manufactured by machine 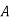 is
is 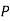 (D/A)
(D/A) 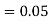 Similarly,
Similarly, 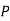 (D/B)
(D/B) 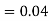 and
and 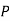 (D/C)
(D/C) 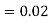 By Bayes’ theorem
By Bayes’ theorem
|
0 matching results found