MI
Unit 6 Digital Multimeter Q1) What is a digital multimeter?A1) A digital multimeter (DMM) is a testing tool that measures electrical values: current in amps, voltage in volts and resistance in ohms. Electricians use a digital multimeter as standard diagnostic tool. Q2) What are the components of digital multimeter?A2) The face of a digital multimeter usually has four components:Display Buttons Dial for selecting measurement values Input jacks Counts and digits are the terms that define a digital multimeter’s resolution. By knowing the proper resolution, a technician knows whether the multimeter can detect a certain signal. For example, if a multimeter offers 1mV on a 4V range, one can see a change of 1mV when reading 1V. Digital multimeters also offer additional testing capabilities like frequency, capacitance, and temperature. A multimeter has various purposes; for example, it can be used as a handheld device for field work or it can also be used to measure data in a controlled environment with high accuracy. Q3) What are true rms meters?A3) The True RMS measurement uses more complex mathematical formulas that allow getting a value closer to reality than the RMS. In addition to peak values, they take several samples of values along each cycle.
Q4) Why do we require clamp-on meters?A4) An electrical meter with an integrated AC current clamp is known as a clamp meter, a clamp-on ammeter, a tong tester or, colloquially, an amp clamp
Figure1. Clamp MeterIt measure any of these or we can say it is used to measure following parameters:-AC current, AC and DC voltage, Resistance, continuity, and, with some models, DC current, Capacitance Temperature Frequency and more Clamp meters are preferred because it measure of high- level currents.DMMs will not be able to measure 10 A of current for more than 30 seconds without risking meter damage.Q5) Why do we require megger?A5) The Megger is the instrument used for measuring the resistance of the insulation. It works on the principle of comparison, i.e., the resistance of the insulation compared with the known value of resistance. If the resistance of the insulation is high, the pointer of the moving coil deflects towards the infinity, and if it is low, then the pointer indicates zero resistance. The accuracy of the Megger is high as compared to other instruments.Q6) Explain the construction of megger?
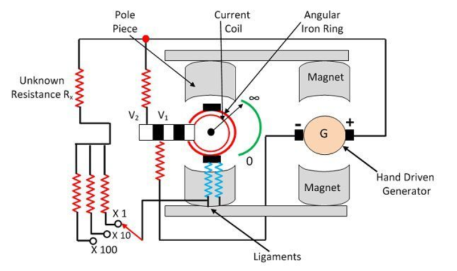
Figure 2 MeggerThe Megger has one current coil and the two voltage coils V1 and V2. The voltage coil V1 is passed over the magnet connected to the generator. When the pointer of the PMMC instrument deflects towards infinity, it means that the voltage coil remains in the weak magnetic field and thus experiences little torque.The torque experienced by the coil increases when it moves insides the strong magnetic field. The coil experience the maximum torque under the pole faces and the pointer set at the zero end of the resistance scale.For improving the torque, the voltage coil V2 is used. The coil V2 is so allocated that when the pointer deflects from infinity to zero coil moves into a stronger magnetic field.In Megger, the combined action of both the voltage coils V1 and V2 are considered. The coil comprises a spring of variable stiffness. It is stiff near the zero end of the coil and becomes very weak near the infinity end of the spring.Q7) Explain the working of megger?The Megger has three coils two pressure coils and one current coil. The pressure coil rotates the moving coil in the anticlockwise direction, whereas the current coil rotates it in the clockwise direction.When the unknown resistance is connected in the circuit, the pointer of the moving coil becomes stable. The pressure coil and the current coil balance the pointer and set it in the middle of the scale.The deflection of the pointer is directly proportional to the voltage applied to the external circuit. When the testing circuit is applied across the Megger, and if there is no shorting throughout the insulation then the pointer deflects towards the infinity. Which shows that the resistance has high insulation. For low resistance, the pointer moves towards zero.Q8) What are the advantages of megger?A8) Level of accuracy is very high.IR value is digital type, easy to read. One person can operate very easily. Works perfectly even at very congested space. Very handy and safe to use. Q9) What are the disadvantages of megger?A9) The external Power source is required to operateThe initial cost is high. Q10) Why the Instrument Initially shows infinity and Finally moves towards zero?A10) According to Ohm’s law
If we rotate the crank handle at a particular speed. This, in turn, leads to the production of voltage in this rotor, and the high value of current also flows in anti-clockwise, through the two coils A and B.Where this flow of current leads to the generation of deflecting torque like Td in the circuit. Hence the pointer varies the resistance ranges from infinity to zero.
V TRMS = √ V1 2 +V2 2+………Vn 2 / n |
|
|
R = V / I ; ——– (1) If the current is maximum in the instrument, resistance is zero, R α 1/I; ——– (2) If the current in minimum in the instrument, resistance is maximum. R α 1/ I↓ ——— (3) Which means, resistance and current are inversely proportional R α 1/I; ———-(4) |
0 matching results found