MI
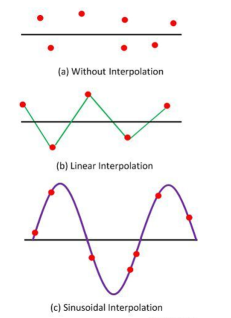
Unit 7Digital Storage OscilloscopeQ1) Why digital storage oscilloscope are required?A1) The digital oscilloscope digitises and stores the input signal which can be done by the use of CRT and digital memory. The digitisation can be done by taking the sample input signals at periodic waveforms.Q2) What are the factors in which the frequency of digital oscilloscope is measured?A2) These factors are theSampling rate Nature of converter. Sampling Rate – For safe analysis of input signal the sampling theory is used. The sampling theory states that the sampling rate of the signal must be twice as fast as the highest frequency of the input signal. The sampling rate means analogue to digital converter has a high fast conversion rate.Converter – The converter uses the expensive flash whose resolution decreases with the increases of a sampling rate. Because of the sampling rate, the bandwidth and resolution of the oscilloscope are limited.The need of analogue to digital signal converters can also be overcome by using the shift register. The input signal is sampled and stored in the shift register. From the shift register, the signal is slowly read out and stored in the digital form. This method reduces the cost of the converter and operates up to 100 mega sample per second.The only disadvantage of the digital oscilloscope is that it does not accept the data during digitisation, so it had a blind spot at that time.Q3) Explain the waveform reconstruction?A3) For visualising the final wave, the oscilloscopes use the technique of inter-polarization. The inter-polarization is the process of creating the new data points with the help of known variable data points. Linear interpolation and sinusoidal interpolation are the two processes of connecting the points together.
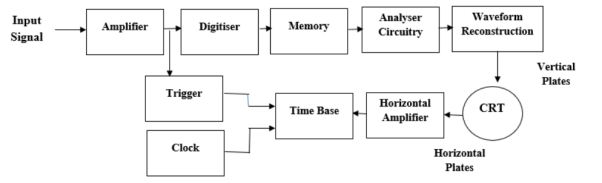
Figure 1 Waveform ReconstructionIn interpolation, the lines are used for connecting the dot together. Linear interpolation is also used for creating the pulsed or square waveform. For sine waveform, the sinusoidal interpolation is utilised in the oscilloscope.Q4) With a neat block diagram explain the working of digital oscilloscope?A4)
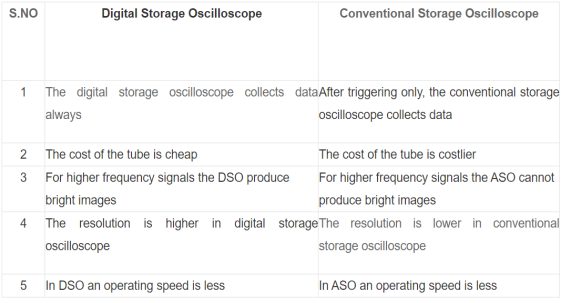
Figure 2 Digital OscilloscopeAs seen in the above figure, at first digital storage oscilloscope digitizes the analog input signal, then the analog input signal is amplified by amplifier if it has any weak signal. After amplification, the signal is digitized by the digitizer and that digitized signal stores in memory. The analyser circuit process the digital signal after that the waveform is reconstructed (again the digital signal is converted into an analog form) and then that signal is applied to vertical plates of the cathode ray tube (CRT).The cathode ray tube has two inputs they are vertical input and horizontal input. The vertical input signal is the ‘Y’ axis and the horizontal input signal is the ‘X’ axis. The time base circuit is triggered by the trigger and clock input signal, so it is going to generate the time base signal which is a ramp signal. Then the ramp signal is amplified by the horizontal amplifier, and this horizontal amplifier will provide input to the horizontal plate. On the CRT screen, we will get the waveform of the input signal versus time.The digitizing occurs by taking a sample of the input waveform at periodic intervals. At the periodic time interval means, when half of the time cycle is completed then we are taking the samples of the signal. The process of digitizing or sampling should follow the sampling theorem.When the analog signal is properly converted into digital then the resolution of the A/D converter will be decreased. When the input signals stored in analog store registers can be read out at a much slower rate by the A/D converter, then the digital output of the A/D converter stored in the digital store, and it allows operation up to 100 mega samples per second. Q5) Explain the modes of operation of digital oscilloscope?A5) The digital storage oscilloscope works in three modes of operations they are roll mode, store mode, and hold or save mode.Roll Mode: In roll mode, very fast varying signals are displayed on the display screen.Store Mode: In the store mode the signals stores in memory.Hold or Save Mode: In hold or save mode, some part of the signal will hold for some time and then they will be stored in memory.Q6) Explain the difference between digital and conventional oscilloscope?
Q7) What are the applications of digital oscilloscope?A7)It checks faulty components in circuits Used in the medical field Used to measure capacitor, inductance, time interval between signals, frequency and time period Used to observe transistors and diodes V-I characteristics Used to analyse TV waveforms Used in video and audio recording equipment’s Used in designing Used in the research field For comparison purpose, it displays 3D figure or multiple waveforms Q8) What are the advantages?A8) The advantages of the DSO arePortable Have the highest bandwidth The user interface is simple Speed is high Q9) What are the disadvantages?A9) The disadvantages of the DSO areComplex High cost Q10) What is the difference between digital and analog oscilloscope?A10) The waveforms in an analog device are shown in original form whereas in digital oscilloscope the original waveforms are converted into digital numbers by sampling.
|
|
|
0 matching results found