|
|
Comparison | DNA | RNA |
Full Name | Deoxyribonucleic Acid | Ribonucleic Acid |
Function | DNA replicates and stores genetic information. The special feature is it is the blueprint for all genetic information contained within an organism | RNA converts the genetic information contained within DNA to a format used to build proteins, and then moves it to ribosomal protein factories. |
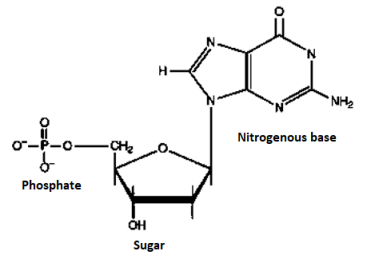
Structure | DNA consists is double stranded, arranged in a double helix. These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, a nitrogenous base and a 5-carbon sugar molecule. | RNA only is single stranded, but like DNA, strand is made up of nucleotides. RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands. RNA sometimes forms a secondary double helix structure, but only occasionally. |
Length | DNA is a much longer polymer than RNA. A chromosome, for example, is a single, long DNA molecule, when opened would be several centimetres in length. | RNA molecules vary in length, but are found to be much shorter than long DNA polymers. A large RNA molecule may be a thousand base pairs in length. |
Sugar | The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, which contains one less hydroxyl group than RNA’s ribose. | RNA contains ribose sugar molecules, without the hydroxyl modifications of deoxyribose. |
Bases | The bases in DNA are Adenine (‘A’), Thymine (‘T’), Guanine (‘G’) and Cytosine (‘C’). | RNA shares Adenine (‘A’), Guanine (‘G’) and Cytosine (‘C’) with DNA, but contains Uracil (‘U’) rather than Thymine. |
Base Pairs | Adenine and Thymine pair (A-T) Cytosine and Guanine pair (C-G) | Adenine and Uracil pair (A-U) Cytosine and Guanine pair (C-G) |
Location | DNA is found in the nucleus, with a small amount of DNA also present in mitochondria. | RNA forms in the nucleolus, and then moves to specialised regions of the cytoplasm depending on the type of RNA formed. |
Reactivity | Due to its deoxyribose sugar, which contains one less oxygen-containing hydroxyl group, DNA is a more stable molecule than RNA, which is useful for a molecule which has the task of keeping genetic information safe. | RNA, containing a ribose sugar, is more reactive than DNA and performs enormous tasks but is not stable in alkaline conditions. RNA’s larger helical grooves mean it is more easily affected by the attack of enzymes. |
Ultraviolet (UV) Sensitivity | DNA is vulnerable to damage by ultraviolet light. | RNA is more resistant to damage from UV light than DNA. |
|
|
Q8. Write a short note on Cellulose?A8. Cellulose a complex carbohydrate, or polysaccharide, consisting of 3,000 or more glucose units. They form the basic structural component of plant cell walls; cellulose comprises about 33 percent of all vegetable matter and is the most abundant naturally occurring organic compounds. Cellulose cannot be digested by man, cellulose is a source of food for herbivorous animals (e.g., cows, horses) because they retain it long enough for digestion by microorganisms present in the alimentary tract; protozoans in the gut of insects such as termites also digest cellulose. It has great economic importance, cellulose is processed to produce papers and fibres and is chemically modified to yield substances used in the manufacture of such items as plastics, photographic films, and rayon. Other cellulose derivatives are used as thickening agents for foods adhesives, explosives, and in moisture-proof coatings.Q9. Define Denaturation?A9. A protein’s shape is critical to its function, and, many different types of chemical bonds may be important in maintaining this shape. Changes in temperature and pH, as well as the presence of certain chemicals, may disrupt a protein’s shape and cause it to lose functionality, a process known as denaturation.Denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose the quaternary structure, tertiary structure, and secondary structure which is present in their native state, by application of some external stress or compound such as a strong acid or base, a concentrated inorganic salt, an organic solvent (e.g., alcohol or chloroform), radiation or heat. Since denaturation reactions are not strong enough to break the peptide bonds, the primary structure (sequence of amino acids) remains the same after a denaturation process. Denaturation disrupts the normal alpha-helix and beta sheets in a protein and uncoils it into a random shape Q10.Short notes on starch?A10. Starch, is a granular, white, organic chemical that is produced by all green plants. Starch is a soft, white, tasteless powder that is insoluble in alcohol, cold water, or other solvents. The basic chemical formula of the starch molecule is (C6H10O5)n. Starch is a polysaccharide comprising of glucosemonomers that are joined in α 1,4 linkages. The simplest form of starch is the linear polymer amylose; amylopectin is the branched form.Starch is manufactured in the green leaves of plants from the excess glucose produced during process of photosynthesis and serves as a reserve food supply for the plant. Starch is stored in chloroplasts of the cell in the form of granules and in others as storage organs in the roots of the cassava plant; the tuber of the potato; the seeds of corn, wheat, and rice and the stem pith of sago. According to the requirement, starch is broken down, in the presence of certain enzymes and water, into its constituent monomer glucose units, which diffuse from the cell to nourish the plant tissues. In humans and other animals, starch from plants is broken down into its constituent sugar molecules, which then supply energy to the tissues.