|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
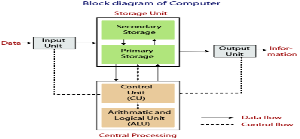
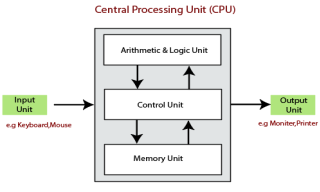
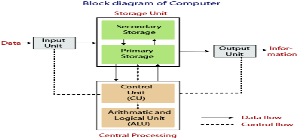
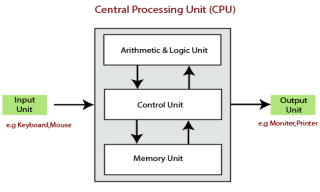
Arithmetic and logic unit ::
ALU perform all the arithmetic and logic calculation provided to computer systems that are addition,substraction,multiplication,division,comparison,greater,less.
Control Unit ::
This unit controls and facilitates all the activities and operations performed in the PC system. It gets programs from the main memory of the computer system to interpret or translate them and control other units to get the desired result.
Cache ::
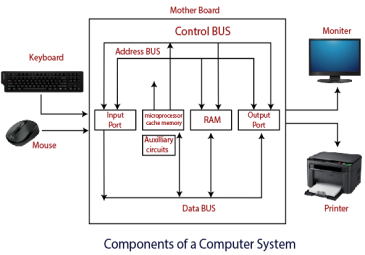
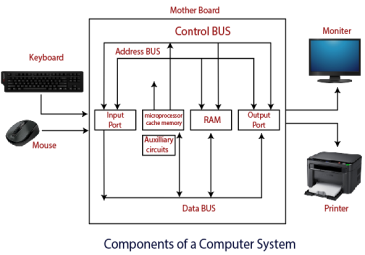
Cache memory dwells between the main memory and processor. The rate of exchanging data and information is substantially higher compared to other memory of computer system. The cache memory saves and holds the data or set of information that is about to process immediately by the system.
The cache memory is not available to users they cannot delete, update, refresh the programs inside the memory, the manufacturer, or the computer programmers can erase or update the data which is stored inside the cache memory.
They are quite expensive therefore they were first introduced or installed in a large computer only in small numbers however as the technology developed the small computer, or desktop computer used cache memory and we usually call them as l1 cache and l2 cache. CPU [Central Processing Unit] | Processor SpeedThe speed of the microprocessor is the essential ingredient as the software technology has developed to the extreme use of large programs and application are made available to users to execute this application high speed of processors are required. The processor speed can be defined and characterized as the speed at which it executes the instructions and directions. The speed of the processor is measured in MHz (Millions of Pulses for each second) and GHz (Billion of pulses for each second)The speed of mini and mainframe computers are measured in MIPS (Millions of instruction per second) and BIPS (Billions of instructions per second). Functions of CPU in ComputerThe CPU Is considered as the brain or heart of the computer as it is responsible for each and every operation performed in a computer system. It controls and organizes every section and unit of a Personal computer. Every instruction passed to a computer system is firstly converted into binary numbers that consist of 0s 1s which is in machine-readable form later this instruction which has been changed over are send to the registry and eventually they are transferred and exchanged to CPU for further and additional processing and preparing as processor have ALU which stands for Arithmetic and logical operation with the help of ALU computer performs every mathematical and logical operation.There are Four Primary Functions of Processor
Decode:: All the program or instruction are translated from assembly language or low level to binary language which helps the computer system to deliver the output in human-readable or intelligent form. This process of conversion and transformation from one language to another is called as DECODING
Execute :: The processor recovers the instructions and data from memory and processes them to get wanted output with the assistance of ALU (Arithmetic and coherent unit).
Store :: After the procedure is finished in ALU. The output is put away in memory for additionally processing. The speed of PC altogether relies on the CPU. The fundamental usefulness of PC can be made fast by introducing present-day processors. Q5) What is VDU?A5) Stands for "Visual Display Unit." A VDU displays images generated by a computer or other electronic device. The term VDU is often used synonymously with "monitor," but it can also refer to another type of display, such as a digital projector. Visual display units may be peripheral devices or may be integrated with the other components. For example, the Apple iMac uses an all-in-one design, in which the screen and computer are built into a single unit.Early VDUs were primarily cathode ray tube (CRT) displays and typically had a diagonal size of 13 inches or less. During the 1990s, 15" and 17" displays became standard, and some manufacturers began producing displays over 20" in size. At the turn of the century, flat panel displays became more common, and by 2006, CRT displays were hard to find.Today, it is common for computers to come with VDUs that are 20" to 30" in size. Thanks to the recent growth in LCD, plasma, and LED technology, manufacturing large screens is much more cost effective than before. Q6) Explain Keyboard and MouseA6) KeyboardKeyboard is the most common and very popular input device which helps to input data to the computer. The layout of the keyboard is like that of traditional typewriter, although there are some additional keys provided for performing additional functions.
|
S.No | Keys & Description |
1 | Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and digit keys (09) which generally give the same layout as that of typewriters. |
2 | Numeric Keypad It is used to enter the numeric data or cursor movement. Generally, it consists of a set of 17 keys that are laid out in the same configuration used by most adding machines and calculators. |
3 | Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the keyboard which are arranged in a row at the top of the keyboard. Each function key has a unique meaning and is used for some specific purpose. |
4 | Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen control. It includes four directional arrow keys. Control keys also include Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc). |
5 | Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen. |
|
|
S.No | Keys & Description |
1 | Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and digit keys (09) which generally give the same layout as that of typewriters. |
2 | Numeric Keypad It is used to enter the numeric data or cursor movement. Generally, it consists of a set of 17 keys that are laid out in the same configuration used by most adding machines and calculators. |
3 | Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the keyboard which are arranged in a row at the top of the keyboard. Each function key has a unique meaning and is used for some specific purpose. |
4 | Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen control. It includes four directional arrow keys. Control keys also include Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc). |
5 | Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arithmetic and logic unit ::
ALU perform all the arithmetic and logic calculation provided to computer systems that are addition,substraction,multiplication,division,comparison,greater,less.
Control Unit ::
This unit controls and facilitates all the activities and operations performed in the PC system. It gets programs from the main memory of the computer system to interpret or translate them and control other units to get the desired result.
Cache ::
Cache memory dwells between the main memory and processor. The rate of exchanging data and information is substantially higher compared to other memory of computer system. The cache memory saves and holds the data or set of information that is about to process immediately by the system.
The cache memory is not available to users they cannot delete, update, refresh the programs inside the memory, the manufacturer, or the computer programmers can erase or update the data which is stored inside the cache memory.
They are quite expensive therefore they were first introduced or installed in a large computer only in small numbers however as the technology developed the small computer, or desktop computer used cache memory and we usually call them as l1 cache and l2 cache. CPU [Central Processing Unit] | Processor SpeedThe speed of the microprocessor is the essential ingredient as the software technology has developed to the extreme use of large programs and application are made available to users to execute this application high speed of processors are required. The processor speed can be defined and characterized as the speed at which it executes the instructions and directions. The speed of the processor is measured in MHz (Millions of Pulses for each second) and GHz (Billion of pulses for each second)The speed of mini and mainframe computers are measured in MIPS (Millions of instruction per second) and BIPS (Billions of instructions per second). Functions of CPU in ComputerThe CPU Is considered as the brain or heart of the computer as it is responsible for each and every operation performed in a computer system. It controls and organizes every section and unit of a Personal computer. Every instruction passed to a computer system is firstly converted into binary numbers that consist of 0s 1s which is in machine-readable form later this instruction which has been changed over are send to the registry and eventually they are transferred and exchanged to CPU for further and additional processing and preparing as processor have ALU which stands for Arithmetic and logical operation with the help of ALU computer performs every mathematical and logical operation.There are Four Primary Functions of Processor
Decode:: All the program or instruction are translated from assembly language or low level to binary language which helps the computer system to deliver the output in human-readable or intelligent form. This process of conversion and transformation from one language to another is called as DECODING
Execute :: The processor recovers the instructions and data from memory and processes them to get wanted output with the assistance of ALU (Arithmetic and coherent unit).
Store :: After the procedure is finished in ALU. The output is put away in memory for additionally processing. The speed of PC altogether relies on the CPU. The fundamental usefulness of PC can be made fast by introducing present-day processors. Q5) What is VDU?A5) Stands for "Visual Display Unit." A VDU displays images generated by a computer or other electronic device. The term VDU is often used synonymously with "monitor," but it can also refer to another type of display, such as a digital projector. Visual display units may be peripheral devices or may be integrated with the other components. For example, the Apple iMac uses an all-in-one design, in which the screen and computer are built into a single unit.Early VDUs were primarily cathode ray tube (CRT) displays and typically had a diagonal size of 13 inches or less. During the 1990s, 15" and 17" displays became standard, and some manufacturers began producing displays over 20" in size. At the turn of the century, flat panel displays became more common, and by 2006, CRT displays were hard to find.Today, it is common for computers to come with VDUs that are 20" to 30" in size. Thanks to the recent growth in LCD, plasma, and LED technology, manufacturing large screens is much more cost effective than before. Q6) Explain Keyboard and MouseA6) KeyboardKeyboard is the most common and very popular input device which helps to input data to the computer. The layout of the keyboard is like that of traditional typewriter, although there are some additional keys provided for performing additional functions.
|
S.No | Keys & Description |
1 | Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and digit keys (09) which generally give the same layout as that of typewriters. |
2 | Numeric Keypad It is used to enter the numeric data or cursor movement. Generally, it consists of a set of 17 keys that are laid out in the same configuration used by most adding machines and calculators. |
3 | Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the keyboard which are arranged in a row at the top of the keyboard. Each function key has a unique meaning and is used for some specific purpose. |
4 | Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen control. It includes four directional arrow keys. Control keys also include Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc). |
5 | Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen. |
|
|
S.No | Keys & Description |
1 | Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and digit keys (09) which generally give the same layout as that of typewriters. |
2 | Numeric Keypad It is used to enter the numeric data or cursor movement. Generally, it consists of a set of 17 keys that are laid out in the same configuration used by most adding machines and calculators. |
3 | Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the keyboard which are arranged in a row at the top of the keyboard. Each function key has a unique meaning and is used for some specific purpose. |
4 | Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen control. It includes four directional arrow keys. Control keys also include Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc). |
5 | Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|