Unit-4
GEAR
Q1) What are the parameters we should consider in gear selection process?
A1) Gear Selection Considerations
Gears are employed in a variety of mechanical devices, and, consequently, several different types and designs are available. The suitability of each type of gear and its exact design for a motion or power transmission application is dependent on the specifications and requirements of the application. Some of the principal factors which may be considered when designing and choosing a gear include:
1) Operational and environmental conditions
2) Dimensional restrictions
3) Transmission requirements
4) Design standards
5) Costs
Q2) Explain Gear Terminology
A2) Gear Terminology
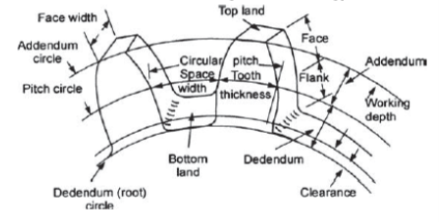
Gear terminology is the various terms to study the gear which is being discussed below and figure 1 show the various terms used in gear terminology.
|
Figure.1. Gear Terminology
Pitch Circle: It is an imaginary circle which transmits the same motion by pure rolling as the transmitted by the gears in mesh.
Pitch Circle Diameter: Diameter of pitch circle is known as the pitch circle diameter.
Circular pitch: Circular pitch is the distance of a point on one tooth to the corresponding point on the adjacent tooth along the pitch circle. It is denoted by the p.
t = number of teeth.
d = pitch circle diameter.
Diametric Pitch: Diametric pitch of a gear is the number of teeth per unit length of pitch circle diameter in inches. It is denoted by P.
Module: it is the ratio of pitch circle diameter in mm to the number of teeth on the gear. it is denoted by m.
Q3) Explain Velocity ratio
A3) Velocity ratio: It is the ratio of angular velocity of driven gear to the angular velocity of driving gear. It is denoted by VR.
Let N be the rpm, w be the angular velocity and T be the number of teeth on gear. While subscript 1 and 2 are used for the driving and driven gears respectively.
Q4) Explain Gear Ratio
A4) Gear ratio is the ratio of number of teeth on driven gear to the number of teeth on driving gear. it is denoted by G.
T= number of teeth on driven gear.
t = number of teeth on driving gear.
Q5) what is Involute Gear Profile
A5) Involute Gear Profile
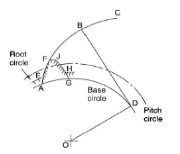
Involute profile is obtained by the locus of a point on a straight line when it rolls about a circumference of a circle without slipping. The circle about which the straight-line rolls is known as the base circle. Figure 2 shows the generation of involute profile in which the line BD is rolling about the base circle with center O and the path ABC shows the involute profile traced by the line.
|
Figure 2 Involute profile
Q6) what is Cycloidal Profile
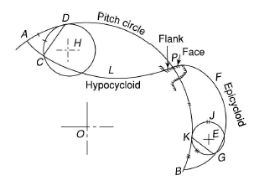
A6) Cycloidal profile is obtained by the locus of a point on the circumference of a circle when it rolls on a straight line without slipping. Gear tooth are made by two kind of cycloidal profiles. Face of gear tooth have epicycloid profile while flank have hypocycloid profile. Figure 3 shows the cycloidal profile of gear teeth.
Epicycloid profile is obtained by the locus of a point on the circumference of a circle when it rolls on the circumference of another circle without slipping, while hypocycloid profile is obtained by the locus of a point the circumference of a circle when it rolls inside the circumference of another circle.
|
Figure 3 Cycloidal Profile of gear teeth
Q7) Explain Path of contact?
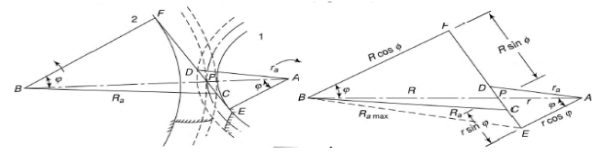
A7) In order to calculate the path of contact of gear considers the figure 4 which shows the two gears in contact. In which smaller gear is termed as the pinion while lager gear is known as the wheel.
|
Figure 4 Two gears in contact
Path of contact is given by the line CD shown in the figure 4. In the given figure:
R = radius of pitch circle for the wheel
r = radius of pitch circle for pinion
R a = radius of addendum circle for wheel
r a = radius of addendum circle for pinion
Q8) what are the different materials used to manufacture the gears?
A8) Materials used to manufacture gears:
Tempered steel is one of the most common materials for different types of gears, and aluminium is also common. Other materials used are:
Q9) what are the applications and utilities of gears?
A9) Applications & Utilities of Gears
The different types of gears are present in many sectors, such as:
Q10) Describe all the characteristics of gears?
A10) Characteristics of Gears by Type
“A” indicates advantageous characteristics and “D” indicates disadvantageous characteristics | |
Type of Gear | Characteristics |
Spur |
|
Helical |
|
Bevel |
|
Worm |
|
Rack and Pinion |
|