Unit-5
BALANCING OF ROTATING MASSES
Q1) Explain Graphical method
A1) We can also use the graphical approach to obtain the position and the magnitude of the balancing mass as follows.
a) First of all, we have to draw the space diagram for the system as shown in figure 1.
b) Calculate the centrifugal force exerted by each mass on the rotating shaft.
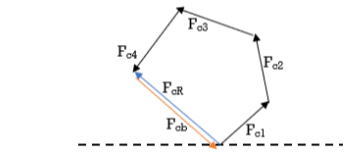
c) Now draw the vector diagram as shown in figure 5 with a suitable scale. Vector ab, bc, cd and de represents the force vectors due mass m1, m2, m3 and m4
d) Now use polygon law of vectors to find the resultant force, represented by vector ae.
e) The balancing force will be equal to this resultant force vector but acts in opposite direction.
|
Figure.1 Vector diagram for the unbalanced system
Q2) Balancing of single rotating mass by balancing masses in same plane and in different planes cannot take place.
A2) Balancing of single rotating mass by balancing masses in same plane and in different planes can be done with the help of both static balancing and dynamic balancing.
Q3) which of the following is true for centrifugal force causing unbalance?
A3)
Force acting radially outwards acts on the axis of rotation and is known as centrifugal force. This is a disturbing force on the axis of rotation, the magnitude of which is constant but the direction changes with the rotation of the mass.
Q4) In a revolving rotor, the centrifugal force remains balanced as long as the centre of the mass of the rotor lies?
A4) In a revolving rotor, the centrifugal force remains balanced as long as the centre of the mass of the rotor lies on the axis of shaft. In other cases, the system will be unbalanced.
Q5) If the unbalanced system is not set right then
A5) It is very essential that all the rotating and reciprocating parts should be completely balanced as far as possible otherwise the dynamic forces will be set up.
Q6) what is the effect of a rotating mass of a shaft on a system?
A6) Whenever an object containing mass is attached to a rotating shaft, it exerts some centrifugal force. This centrifugal force’s effect is to bend the shaft and to produce vibrations in it.
Q7) Balancing of reciprocating masses is the process of providing the second mass in order to counteract the effect of the centrifugal force of the first mass.
A7) The process of providing the second mass in order to counteract the effect of the centrifugal force of the first mass is called balancing of rotating masses. The main objective of balancing is to minimize the unbalanced forces.
Q8) Often an unbalance of forces is produced in rotary or reciprocating machinery due to?
A8) Often an unbalance of forces is produced in rotary or reciprocating machinery due to the inertia forces associated with the moving masses.
Q9) Define static balance
A9) A system of rotating masses is said to be in static balance if the centre of gravity of the system of masses lie on the axis of rotation.
Q10) Define dynamic balance
A10) A system of rotating masses is said to be in dynamic balance if any resultant centrifugal force or couple does not exist.
Q11) Define reference plane
A11) When several masses rotating in different planes are transferred to a single plane, then this single plane is known as the reference plane.