Unit – 3
Assembly practices
Q1) What do you mean by DFM and DFA.
A1)
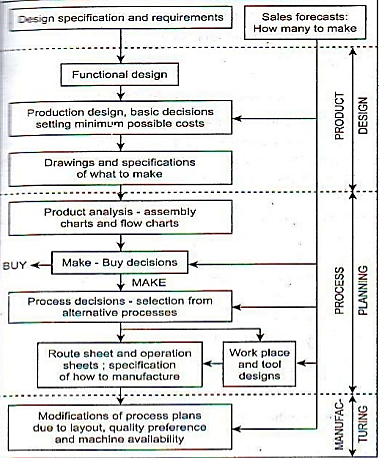
Q2) What is process planning and write its objective?
A2)
According to the American Society of Tool and Manufacturing Engineers “Process Planning is the systematic determination of the methods by which a product is to be manufactured economically and competitively”
Objectives:
Q3) What is selective assembly. Explain in detail.
A3)
The selective assembly can be referred to as a concept where the subcomponents are assembled to form a proper final assembly which will in return provide the highest tolerance specification.
Using selective assembly when the parts are being manufactured, the selective assembly resembles an old concept of inspection, in which the component is being identified as good or bad. If all the parts are correct and the component is good then it will be used for assembly or else it will be used for scrap purposes.
In selective assembly, if the components are divided into different categories, then the groups will be organized according to the sizes and dimensions. We have to make sure that all the parts are grouped together and all are ready for mating so that every component will match with the corresponding sized component to form an assembled part.
If a small shaft is mated with small holes, then large holes will be mated with large shafts. For clearance and interference fits in selective assembly, the minimum value increases and maximum value decreases, whereas for transition fit the maximum value of clearance and interference fit decreases
Q4) Define Material Handling and write the objectives of material handling.
A4)
Materials handling is the art and science of moving, packing and storing of substances in any form.
Importance of Material Handling:
Objective of Material Handling:
Q5) Define Material handling equipment and Write types of Material handling system.
A5)
Material handling equipment:
Material handling equipment (MHE) is used for the movement, storage, protection, consumption and disposal of materials within a facility or at a site.
Types of Material Handling System:
1. Equipment oriented systems: -
a) Convey or Systems
b) Tractor transfer system
c) Fork lift truck
d) Industrial truck system
e) Underground system
2. Material Oriented Systems:
a) Unit handling system
b) Bulk handling system
c) Liquid handling system
3. Methods oriented system:
a) Manual systems
b) Automated systems
c) Job shop handling system
d) Mass production system
4. Function oriented system
a) Transportation systems
b) Conveying systems
c) Transferring systems
d) Elevating systems
Q6) What do you understand by Material handling equipment write its types?
A6)
Material handling equipment:
Types of material handling equipment:
Q7) What do you mean by Design for manufacturability? What is the key principle in the DFMA Process?
A7)
Design for manufacturability (also sometimes known as design for manufacturing or DFM) is the general engineering art of designing products in such a way that they are easy to manufacture at the lowest possible cost.
Key Principles in the DFMA Process:
1. Minimize part count
2. Standardize parts and materials complexity
3. Create modular assemblies
4. Design for efficient joining
5. Minimize re-orientation of parts during assembly and/or machining
6. Simplify and reduce the number of manufacturing operations
7. Specify ‘acceptable’ surface finishes for functionality
Q8) Write the objective of process planning and its activities.
A8)
Objectives:
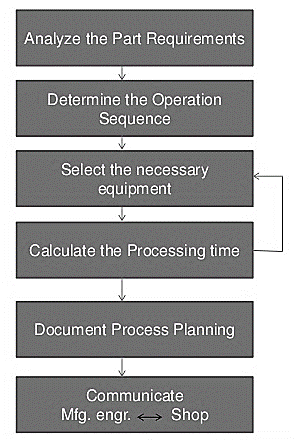
Fig. Process Planning Activities
Q9) What is the purpose of process planning?
A9)
Purpose.
Analysis of part requirement:
Q10) What is planning and write types of processes?
A10)
Planning in which the conditions necessary for transforming material from one state to another are determined.
It determines how a work is to be done.
It converts designs into workable instructions for manufacture, along with associated decisions on component purchase or fabrication and process and equipment selection.
Types of Processes: