Unit 3
Basic Power transmission devices
Question 1) A compound gear consists of 4 gears A, B, C and D and they have 20, 30, 40 and 60 teeth respectively. A is fitted on the driver shaft, and D is fitted on the driven shaft, B and C are compound gears, B meshes with A, and C meshes with D. If A rotates at 180 rpm, find the rpm of D.?
Given:
TA= 20, TB= 30, TC= 40, TD= 60, N A=180 rpm
Find ND=?
Solution:
ND / NA = TA x TC / TB x TD
ND = NA x TA x TC / TB x TD
ND = 180 x 20 x 40 / 30 x 60
ND = 80 rpm
Question 2) two gear wheels having 80 teeth and 30 teeth mesh with each other. If the smaller gear wheel runs at 480rpm, find the speed of the larger wheel.
Given:
Larger Gear wheel T1 = 80, N1=?
Smaller Gear Wheel T2= 30, N2= 480 rpm
Velocity ratio of gear drive
N2 / N1 = T1 / T2
N1 = N2 x T2 / T1
N1 = 480 x 30 / 80
= 180 rpm
Question 3) in a simple train of gears, A has 30 teeth, B has 40 teeth, C has 60 teeth and D has 40 teeth. If A makes 36 rpm, find the rpm of the gear C and D.
Given: TA= 30, TB= 40, TC= 60, TD= 40, NA=36 rpm
Find NC=? ND=?
Solution =
NC / NA = TA / TC
NC = NA x TA / TC
= 36 x 30 / 60
= 18 rpm
ND / NA = TA / TD
ND = NA x TA / TD
= 36 x 30 / 40
= 27 rpm
Question 4) Explain Open Belt Drive?
Answer 4)
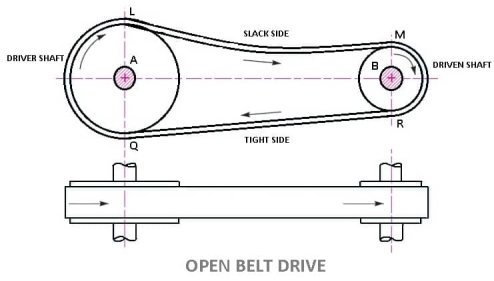
LENGTH OF OPEN BELT DRIVE FORMULA:
= π (r1 + r2) + 2x + (r1 – r2)2 /x ……………. (In terms of pulley radii)
= π/2 (d1 + d2) + 2x + (d1 – d2)2/ 4x ……….… (In terms of pulley diameters)
Question 5) Explain Cross Belt Drive?
Answer 5)
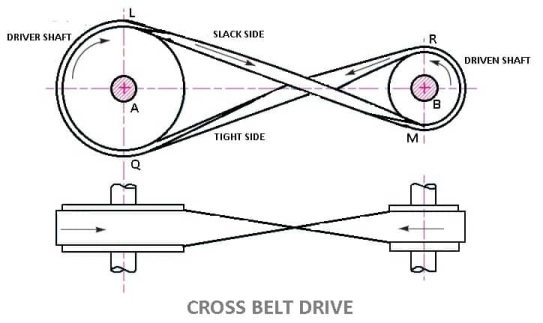
LENGTH OF CROSS BELT DRIVE
= π (r1+r2) + 2x + (r1+r2)2 /x …………… (In terms of pulley radii)
= π/2(d1+d2) +2x + (d1 + d2)2/ 4x …………(in terms of pulley diameters)
Question 6) Define Material of belts?
Answer 6)
The Materials used for belts and ropes must be strong, flexible, and durable. It must have high coefficient of friction: like
1- Leather belts
2- Cotton belts
3- Rubber belts
4- Balata belts
1. Leather belts :
The leather may be oak tanned or mineral salt tanned. Example chrome tanned. When the thickness of the belt required is more then, two or more strips are cemented together. Leather belts require periodic cleaning.
2. Cotton belts or Fabric belts :
Fabric belts are made by folding canvas or cotton ducks in layers and stitching together. The fabric belts are cheaper and best suited in warm climates, damp atmospheres. These are mostly used in Farm machinery, belt conveyor etc.
3. Rubber belts :
Rubber belts are made of Fabric with rubber layer. Rubber belts are used in sawmills, paper mills, etc.
4. Balata Belts:
Balata belts are similar to rubber belts except that balata gum is used in place of rubber. Balata belts are acid proof and water proof and it is not affected by animal oils or alkalies. The balata belts should not be at temperatures above 40° C because at this temperature the balata begins to soften and becomes sticky. The strength of balata belts is 25 percent higher than rubber belts.
Question 7)Explain type of belts?
Answer 7)
Different types of belt are as follows
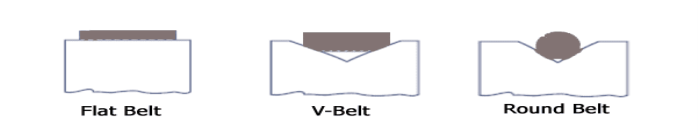
1. Flat Belt :
Flat belt has a rectangular cross section. Flat belts are capable of transmitting power over long distance between pulley centres. The efficiency of this drive is around 98 % and produces less noise.
This belt is mostly used in factories and workshops, where a moderate amount of power is to be transmitted, from one pulley to another when two pulleys are not more than 8 metres apart.
Flat belts drives are of following types:
2. V – Belt:
V-Belts also used with grooved pulleys, V-belts are trapezoidal in cross section. V-belts permit large speed ratios and can transmit higher power. Multiple drives are possible.
This belt is mostly used in factories and workshops, where a moderate amount of power is to be transmitted, from one pulley to another when two pulleys are very near to each other.
3. Circular Belt or Round Belt :
Circular Belt or Round belt has a circular cross section and is used with grooved pulleys, this belt is mostly used in factories and workshops, where a great amount of power is to be transmitted, from one pulley to another when two pulleys are more than 8 metres apart.
Question 8) Write advantage and disadvantage of rope drive?
Answer 8) Advantages of the rope drive
Disadvantages of the rope drive
Question 9) How is rope drive different from Belt drive and Chain drive?
Answer 9)
A Rope Drive uses a rope to transmit power from one system to another, for e.g in pulleys over a well. It is different from a belt drive because it does not use a belt to transmit power. A rope drive is expected to give a smoother operation and less noise than chain drive, but can have higher power losses
Question 10) Write types of gear?
Answer 10) A gear is a kind of machine element in which teeth are cut around cylindrical or cone shaped surfaces with equal spacing. By meshing a pair of these elements, they are used to transmit rotations and forces from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. Gears can be classified by shape as involute, cycloidal and trochoidal gears. Also, they can be classified by shaft positions as parallel shaft gears, intersecting shaft gears, and non-parallel and non-intersecting shaft gears.
Type of gear:
Following are the different types of gears:
- Spur Gears
- Helical Gears
- Double Helical or Herringbone Gears.
- Spiral gears
- Bevel Gears
- Worm Gears