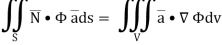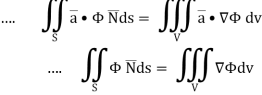Unit-4
Vector integral calculus
Q1: Evaluate  where F= cos y.i-x siny j and C is the curve y=
where F= cos y.i-x siny j and C is the curve y=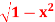 in the xy plae from (1,0) to (0,1)
in the xy plae from (1,0) to (0,1)
A1:
The curve y=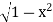 i.e x2+y2 =1. Is a circle with centre at the origin and radius unity.
i.e x2+y2 =1. Is a circle with centre at the origin and radius unity.
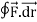 =
= 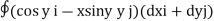
= 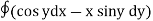
=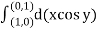 =-1
=-1
Q2: Evaluate 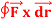 where
where  = (2xy +z2) I +x2j +3xz2 k along the curve x=t, y=t2, z= t3 from (0,0,0) to (1,1,1).
= (2xy +z2) I +x2j +3xz2 k along the curve x=t, y=t2, z= t3 from (0,0,0) to (1,1,1).
A2:
F x dr = 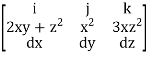
Put x=t, y=t2, z= t3
Dx=dt ,dy=2tdt, dz=3t2dt.
F x dr = 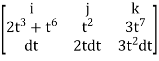
=(3t4-6t8) dti – ( 6t5+3t8 -3t7) dt j +( 4t4+2t7-t2)dt k
=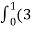 t4-6t3)dti –(6t5+3t8-3t7)dt j+(4t4 + 2t7 – t2)dt k
t4-6t3)dti –(6t5+3t8-3t7)dt j+(4t4 + 2t7 – t2)dt k
=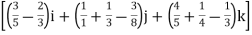
=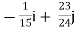 +
+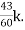
Q3: Prove that ͞͞͞F = [y2cos x +z3] i+(2y sin x – 4) j +(3xz2 + 2) k is a conservative field. Find (i) scalar potential for͞͞͞F (ii) the work done in moving an object in this field from (0, 1, -1) to ( / 2,-1, 2)
/ 2,-1, 2)
 A3:
A3:
(a) The fleld is conservative if cur͞͞͞͞͞͞F = 0.
 Now, curl͞͞͞F =
Now, curl͞͞͞F = 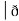 ̷̷
̷̷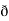 X
X 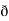 /
/ 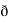 y
y 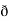 /
/ 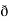 z
z
Y2COS X +Z3 2y sin x-4 3xz2 + 2
; Cur 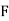 = (0-0) – (3z2 – 3z2) j + (2y cos x- 2y cos x) k = 0
= (0-0) – (3z2 – 3z2) j + (2y cos x- 2y cos x) k = 0
; F is conservative.
(b) Since F is conservative there exists a scalar potential ȸ such that
F = ȸ
 (y2cos x=z3) i + (2y sin x-4) j + (3xz2 + 2) k =
(y2cos x=z3) i + (2y sin x-4) j + (3xz2 + 2) k = 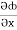 i +
i + 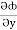 j +
j + 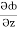 k
k
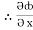 = y2cos x + z3,
= y2cos x + z3, 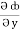 = 2y sin x – 4,
= 2y sin x – 4, 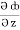 = 3xz2 + 2
= 3xz2 + 2
Now, 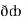 =
= 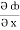 dx +
dx + 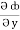 dy +
dy + 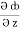 dz
dz
= (y2cos x + z3) dx +(2y sin x – 4)dy + (3xz2 + 2)dz
= (y2cos x dx + 2y sin x dy) +(z3dx +3xz2dz) +(- 4 dy) + (2 dz)
=d(y2 sin x + z3x – 4y -2z)
 ȸ = y2 sin x +z3x – 4y -2z
ȸ = y2 sin x +z3x – 4y -2z
(c) now, work done =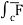 .d ͞r
.d ͞r
= 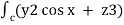 dx + (2y sin x – 4) dy + ( 3xz2 + 2) dz
dx + (2y sin x – 4) dy + ( 3xz2 + 2) dz
= 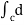 (y2 sin x + z3x – 4y + 2z) (as shown above)
(y2 sin x + z3x – 4y + 2z) (as shown above)
= [ y2 sin x + z3x – 4y + 2z ]( 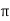 /2, -1, 2)
/2, -1, 2)
= [ 1 +8  + 4 + 4 ] – { - 4 – 2} =4
+ 4 + 4 ] – { - 4 – 2} =4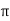 + 15
+ 15
Q4: Find the circulation of  around the curve C where
around the curve C where  =yi+zj+xk and C is circle
=yi+zj+xk and C is circle 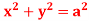 .
.
A4:
Parametric eqn of circle are:
x=a cos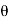
y=a sin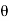
z=0
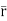 =xi+yj+zk = a cos
=xi+yj+zk = a cos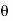 i + b cos
i + b cos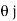 + 0 k
+ 0 k
d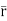 =(-a sin
=(-a sin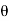 i + a cos
i + a cos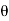 j)d
j)d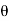
Circulation =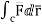 =
=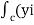 +zj+xk). d
+zj+xk). d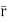
=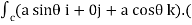 -a sin
-a sin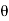 i + a cos
i + a cos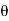 j)d
j)d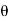
=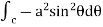 =
= 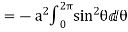
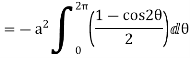
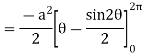
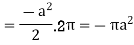
Q5: Apply Green’s theorem to evaluate 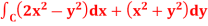 where C is the boundary of the area enclosed by the x-axis and the upper half of circle
where C is the boundary of the area enclosed by the x-axis and the upper half of circle 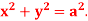
A5:
We know that by Green’s theorem-
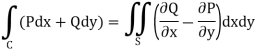
And it it given that-
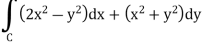
Now comparing the given integral-
P = 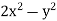 and Q =
and Q = 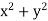
Now-
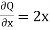 and
and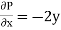
So that by Green’s theorem, we have the following integral-
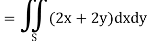
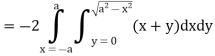
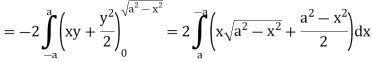
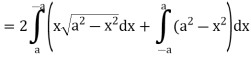
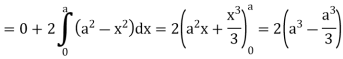
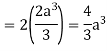
Q6: Verify green’s theorem in xy-plane for  where C is the boundary of the region enclosed by
where C is the boundary of the region enclosed by 
A6:
On comparing with green’s theorem,
We get-
P = 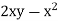 and Q =
and Q = 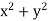
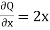 and
and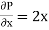
By using Green’s theorem-
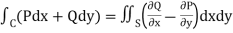 ………….. (1)
………….. (1)
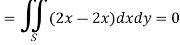
And left hand side= 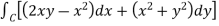
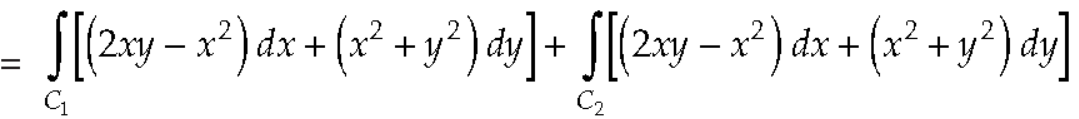 ………….. (2)
………….. (2)
Now,
Along 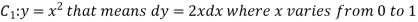
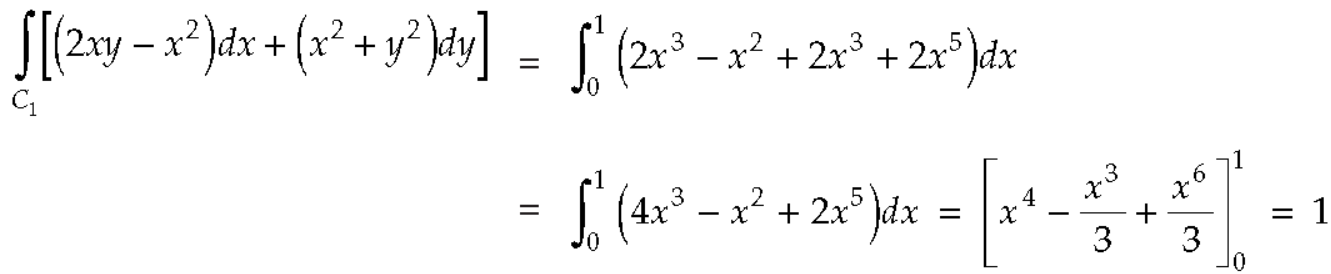
Along 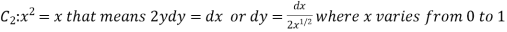
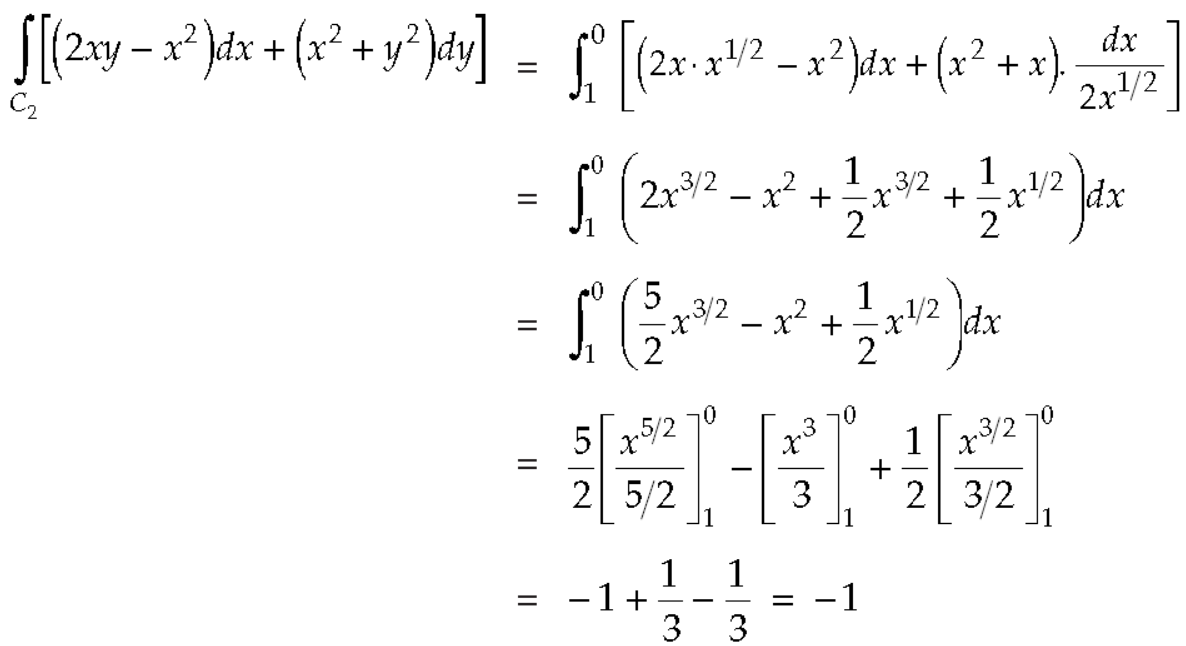
Put these values in (2), we get-
L.H.S. = 1 – 1 = 0
So that the Green’s theorem is verified.
Q7: Evaluate 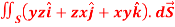 , where S is the surface of the sphere
, where S is the surface of the sphere 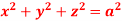 in the first octant.
in the first octant.
A7:
Here-
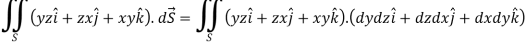
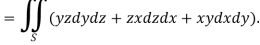
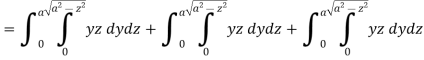
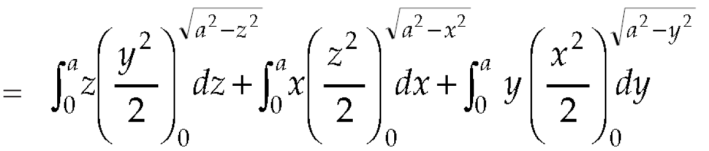
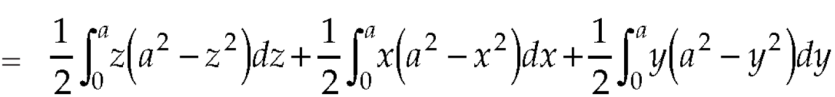
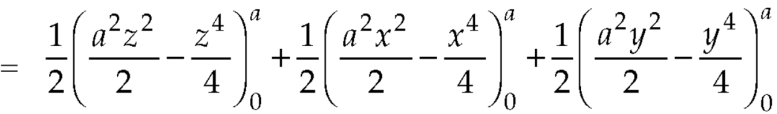
Which becomes-
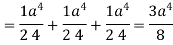
Q8: Evaluate 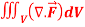 if V is the region in the first octant bounded by
if V is the region in the first octant bounded by 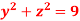 and the plane x = 2 and
and the plane x = 2 and 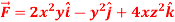 .
.
A8:
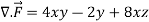
x varies from 0 to 2
The volume will be-
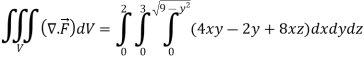
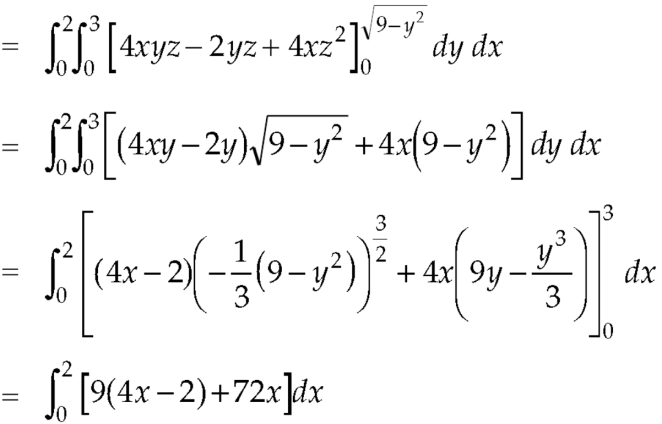
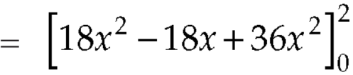
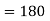
Q9: If 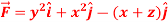 and C is the boundary of the triangle with vertices at (0, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0) and (1, 1, 0), then evaluate
and C is the boundary of the triangle with vertices at (0, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0) and (1, 1, 0), then evaluate 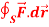 by using Stoke’s theorem.
by using Stoke’s theorem.
A9:
here we see that z-coordinates of each vertex of the triangle is zero, so that the triangle lies in the xy-plane and 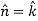
Now,
Curl 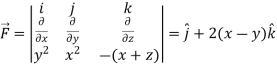
Curl 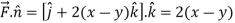
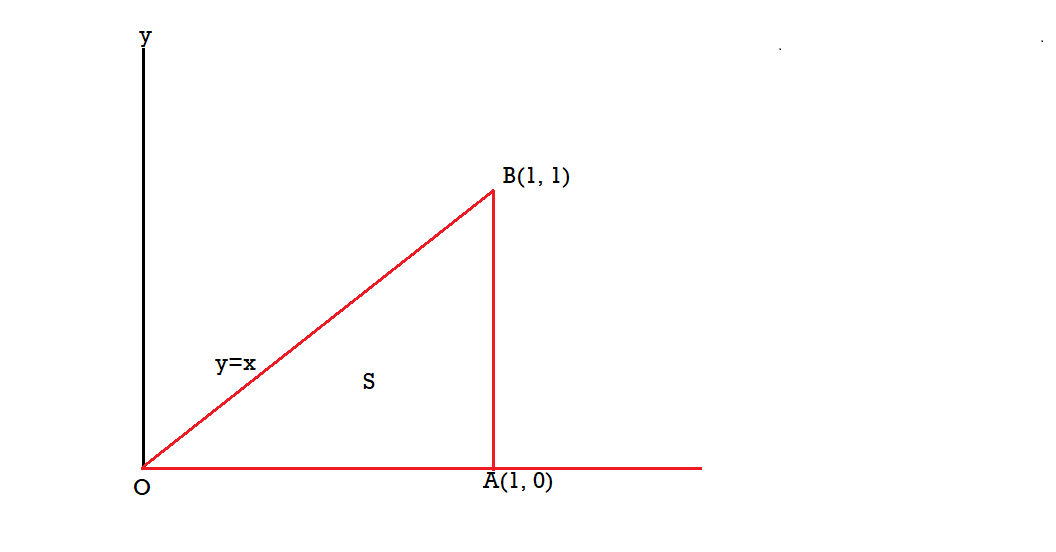
The equation of the line OB is y = x
Now by stoke’s theorem,
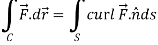
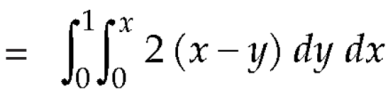
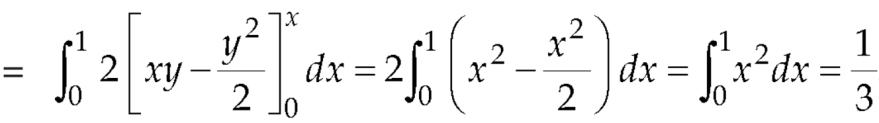
Q10: Show that 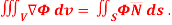
A10:
By divergence theorem, 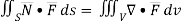 ..…(1)
..…(1)
Comparing this with the given problem let 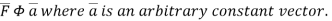
Hence, by (1)
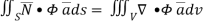 ………….(2)
………….(2)
Now ,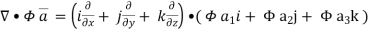
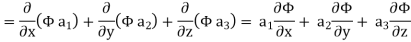
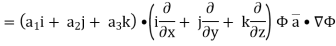
Hence,from (2), Weget,