Module 03
Operational Amplifiers
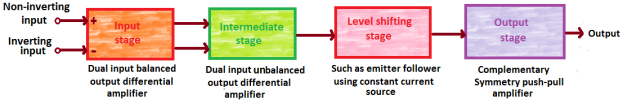
Fig : block diagram
The block diagram of op-amp consists of :
2. Write some characteristics of op-amp.
It has the following characteristics:
3. Draw and explain inverting amplifier.
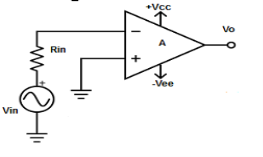
Fig : inverting op-amp
V1 = 0V and V2 = Vin
- Vout = A( - Vin )
- where, A is the voltage gain of op-amp.
4. Draw and explain summing amplifier.
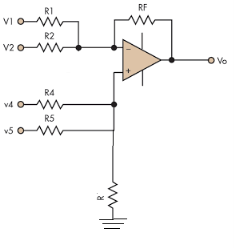
Fig. : Summing amplifier


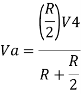
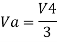
Hence,
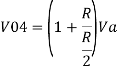
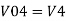
Similarly,
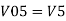
So, the resultant output voltage by all the 4 input voltages is given by,
Vo = V01 + V02 + V04 +V05
Vo = -V1 – V2 +V4 + V5
The output voltage Vo is equivalent to the sum all input voltages applied at both the terminals.
5. In a summing amplifier, if R = 1kΩ, Va = +3V, Vb = +8V, Vc = +9V, Vd = +5V and supply voltage is ±15V. Find the output voltage Vo.
Solution:
Vo = Sum of all input voltages applied at both the terminals
Vo = Va + Vb + Vc +Vd
Vo = -3 -8 +9 +5
Vo = +3V
6. Find the output voltage for the given circuit diagram if Rf = 5kΩ.
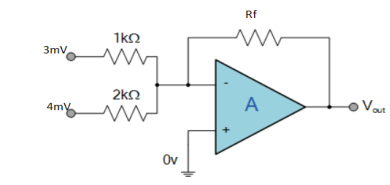
Solution :
We know,
Gain (Av) =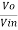 =
= 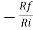
Hence,
Av1 = 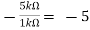
Av2 = 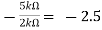
Now, Output voltage Vo = Sum of the two amplified input signals
Vo = Av1 x V1 + Av2 x V2
Vo =(-5 x 3) + ( -2.5x 4) mV
Vo = -25mV
As the above output voltage is negative hence it is an inverting amplifier.
7. Draw and explain Differentiator in detail.
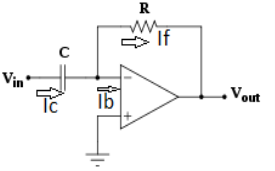
Fig. 7 : Differentiator
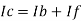
Since Ib = 0 then,
Ic ≈ If
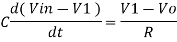
Since Gain A is very large hence, V1 = 0
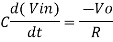
Or 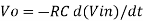
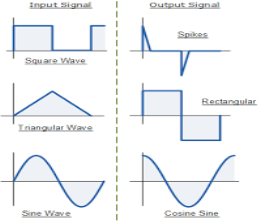
Fig.: Input and output waveform of differentiator
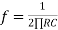 ( for 0 db gain)
( for 0 db gain)