Network Theorems
Q1) Find the current through 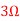 resistance.
resistance.
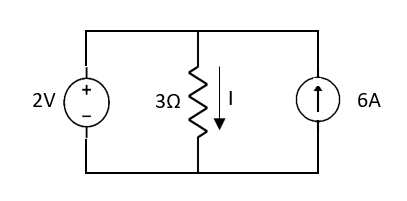
Fig 1 Circuit Diagram
A1)
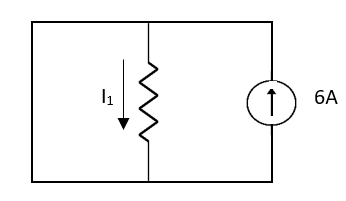
Fig 2 Short circuit 2V
 1 = 0
1 = 0
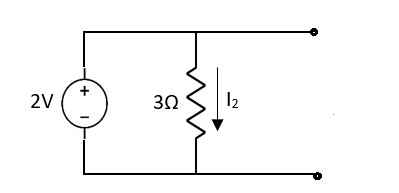
Fig 3 Open circuit 6A
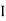 2 =
2 =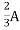
 1 +
1 +  2
2 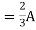
Q2) Find Value of current I
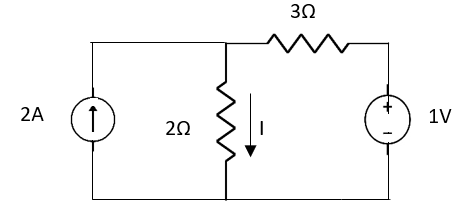
Fig 4 Circuit Diagram
A2) Applying Superposition Theorem
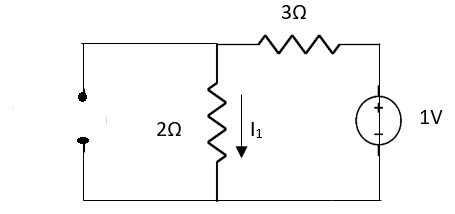
Fig 5 Circuit with 2A open circuit

Fig 6 Circuit with 1V short circuit
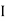 1 =
1 = 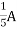
 2 =
2 = 
=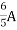
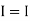 1 +
1 + 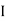 2
2
= 
Q3) Find Vth and Rth for the circuit shown below?
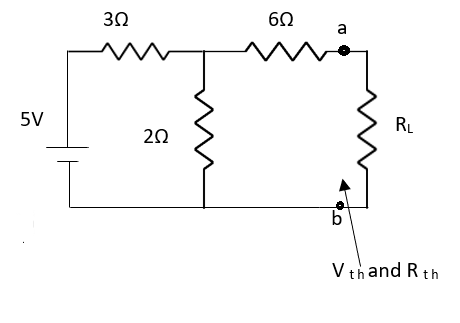
Fig 7 Circuit Diagram
A3)
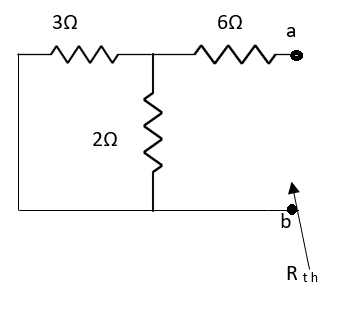
Fig 8 Circuit for finding Rth
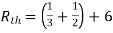
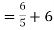
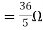
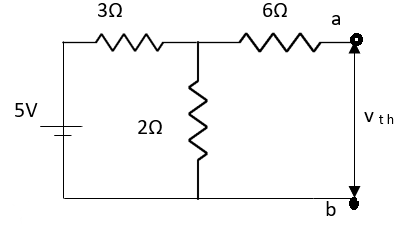
Fig 9 Finding Vth across a and b
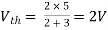
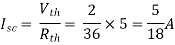
Finding Isc from circuit directly:
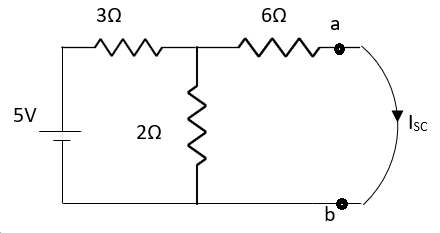
Fig 10 Finding Isc
By KCL,
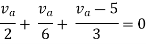
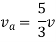
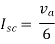
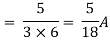
Q4) Find Vth and Rth across a and b?
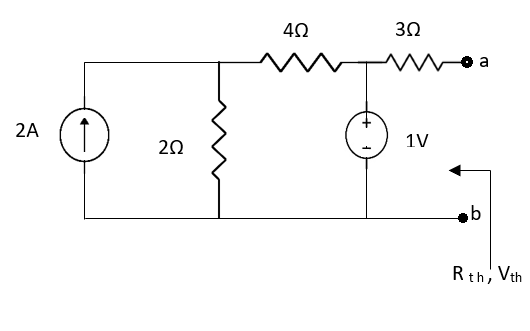
Fig 11 Circuit Diagram
A4) Finding Rth
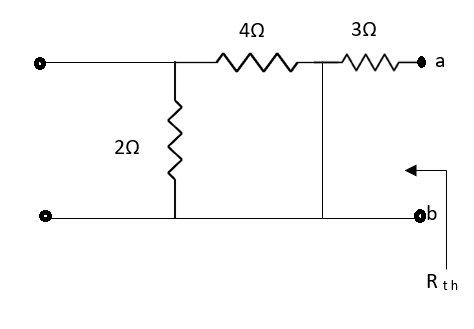
Fig 12 Circuit for Rth

Also, clear from circuit that Vth = 1V.

Fig 13 Circuit for Isc
By applying KVL we get,
1-3Isc=0
Isc= A
A
Q5) Find Isc and Rth across terminal a and b?
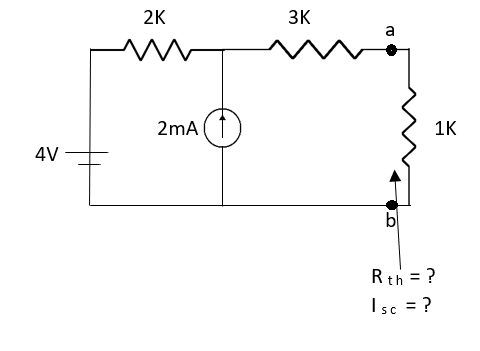
Fig 14 Circuit Diagram
A5)
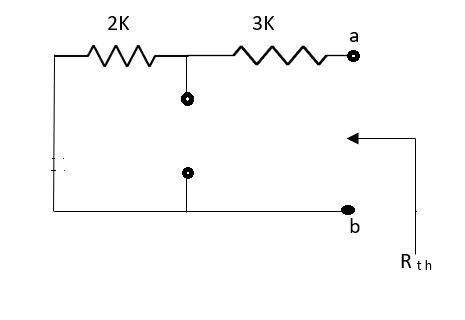
Fig 15 Circuit for finding RTh
Rth=3k+2k=5k
By applying KVL we get
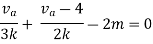


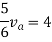
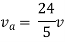
Therefore, 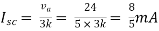
Q6) Find the value of voltage Vx?

Fig 16 Circuit Diagram
A6) For Rth
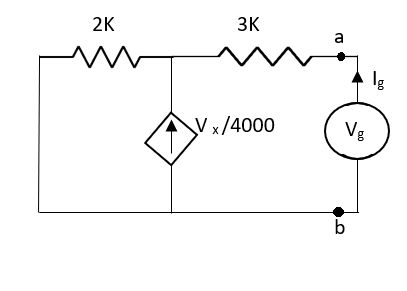
Fig 17 Circuit for finding Rth
By KCL,
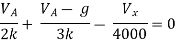
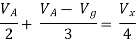
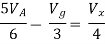
But, 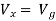
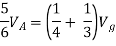


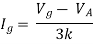

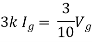
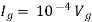

By KVL,


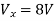
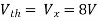
Q7) Find value of current I in the circuit?
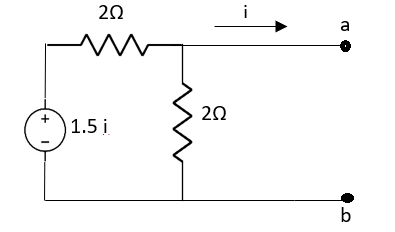
Fig 18 Circuit diagram
A7)
Since, no independent source is present so,
Isc = 0
And we know that,
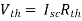

Since Rth cannot be zero
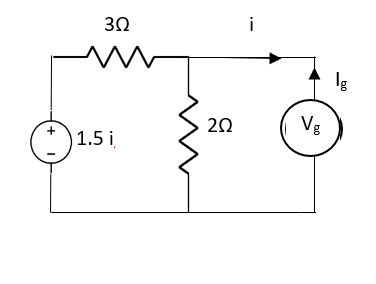
Fig 19 Circuit for finding Rth

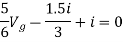
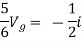
But 
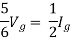

Q8) Find out the Norton’s equivalent
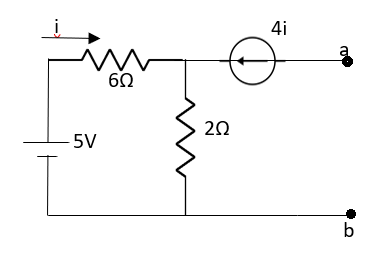
Fig 20 Circuit diagram
A8)
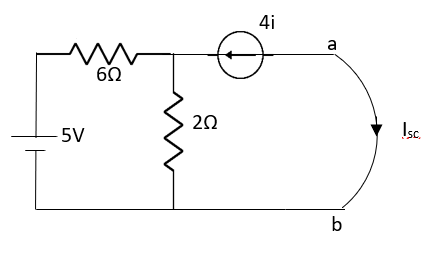
Fig 21 Circuit for finding Isc
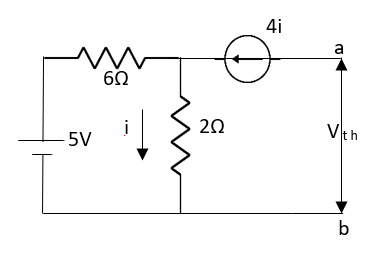
Fig 22 Circuit for finding Vth

Since, there is no significance of current source
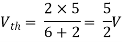
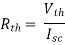

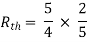
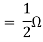
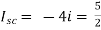 A
A
Q9) Find out the value of load resistance if power absorbed is maximum.
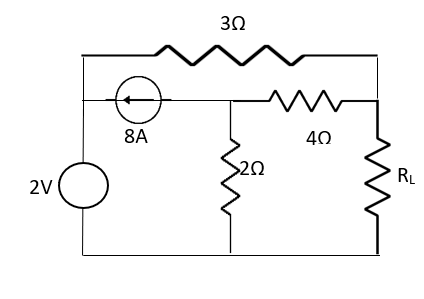
Fig 23 Circuit Diagram
A9) find Thevenin’s equation

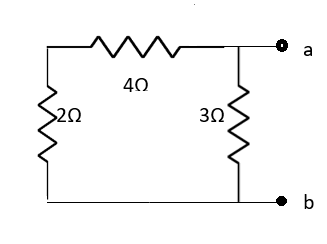
Fig 24 Finding Rth


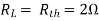
Q10) Find maximum power delivered is RL if its value is
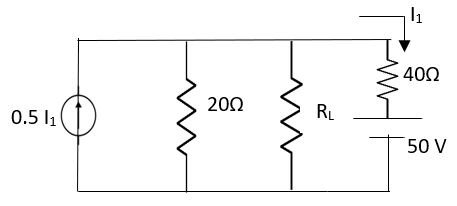
A10)
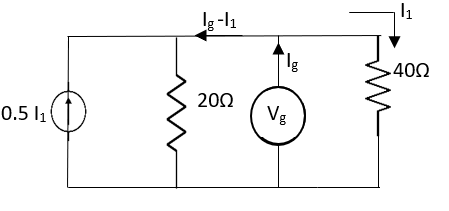
Fig 25 Circuit for finding Rth
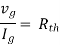
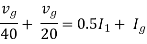
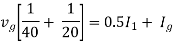
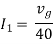
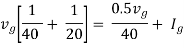
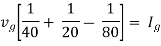
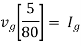
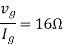
Therefore, 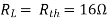
Q11) Verify the Reciprocity theorem for the given network?

Fig 26 Circuit Diagram
A11) The value of current Ix flowing due to 20V source is
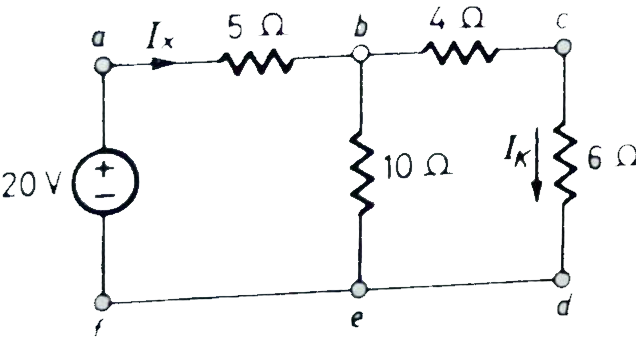
Fig 27 When 20V is at its place
Ix = 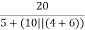 = 2A
= 2A
By current Division
Ik = Ix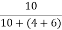 = 1A
= 1A
Now the voltage source of 20V is connected to branch cd. The current source now will be given as

Fig 28 When 20V is connected to the cd
Iy= 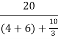 = 3/2 A
= 3/2 A
Then Ij = Iy  = 1A
= 1A
From above we see that Ik = Ij = 1A
The reciprocity theorem is verified.
Q12) Using nodal analysis find the voltage across 5resistor.
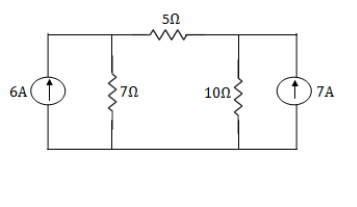
A12)
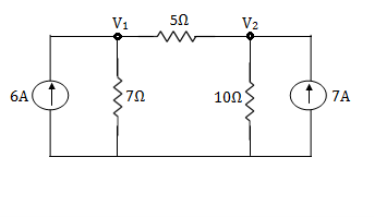
For V1

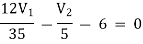
 ………….. 1
………….. 1
For V2
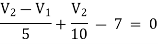
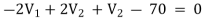
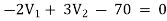 …………… 2
…………… 2
Solving 1 and 2:
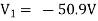
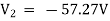
For 5 voltage = 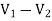
= -50.9 + 57.27
= 6.37V