Unit – 1
An introduction to programming and Introduction to Java
Q1) What are the differences between C++ and Java?
A1)
Index | C++ | Java |
Platform-independent | C++ is platform-dependent. | Java is platform-independent. |
Mainly used for | C++ is mainly used for system programming. | Java is mainly used for application programming. It is widely used in window, web-based, enterprise and mobile applications. |
Design Goal | C++ was designed for systems and applications programming. It was an extension of C programming language. | Java was designed and created as an interpreter for printing systems but later extended as a support network computing. It was designed with a goal of being easy to use and accessible to a broader audience. |
Goto | C++ supports the goto statement. | Java doesn't support the goto statement. |
Multiple inheritance | C++ supports multiple inheritance. | Java doesn't support multiple inheritance through class. It can be achieved by interfaces in java. |
Operator Overloading | C++ supports operator overloading. | Java doesn't support operator overloading. |
Pointers | C++ supports pointers. You can write pointer program in C++. | Java supports pointer internally. However, you can't write the pointer program in java. It means java has restricted pointer support in Java. |
Hardware | C++ is nearer to hardware. | Java is not so interactive with hardware. |
Structure and Union | C++ supports structures and unions. | Java doesn't support structures and unions. |
Compiler and Interpreter | C++ uses compiler only. C++ is compiled and run using the compiler which converts source code into machine code so, C++ is platform dependent. | Java uses compiler and interpreter both. Java source code is converted into bytecode at compilation time. The interpreter executes this bytecode at runtime and produces output. Java is interpreted that is why it is platform independent. |
Call by Value and Call by reference | C++ supports both call by value and call by reference. | Java supports call by value only. There is no call by reference in java. |
Thread Support | C++ doesn't have built-in support for threads. It relies on third-party libraries for thread support. | Java has built-in thread support. |
Documentation comment | C++ doesn't support documentation comment. | Java supports documentation comment (/** ... */) to create documentation for java source code. |
Virtual Keyword | C++ supports virtual keyword so that we can decide whether or not override a function. | Java has no virtual keyword. We can override all non-static methods by default. In other words, non-static methods are virtual by default. |
Unsigned right shift >>> | C++ doesn't support >>> operator. | Java supports unsigned right shift >>> operator that fills zero at the top for the negative numbers. For positive numbers, it works same like >> operator. |
Inheritance Tree | C++ creates a new inheritance tree always. | Java uses a single inheritance tree always because all classes are the child of Object class in java. The object class is the root of the inheritance tree in java. |
Object-oriented | C++ is an object-oriented language. However, in C language, single root hierarchy is not possible. | Java is also an object-oriented language. However, everything (except fundamental types) is an object in Java. It is a single root hierarchy as everything gets derived from java.lang.Object. |
Q2) What are the main differences between the Java platform and other platforms?
A2)
There are the following differences between the Java platform and other platforms
Java is the software-based platform whereas other platforms may be the hardware platforms or software-based platforms.
Java is executed on the top of other hardware platforms whereas other platforms can only have the hardware components.
Q3) What is the platform?
A3)
A platform is the hardware or software environment in which a piece of software is executed. There are two types of platforms, software-based and hardware-based. Java provides the software-based platform.
Q4) List the features of Java Programming language.
A4)
There are the following features in Java Programming Language.
- Simple: Java is easy to learn. The syntax of Java is based on C++ which makes easier to write the program in it.
- Object-Oriented: Java follows the object-oriented paradigm which allows us to maintain our code as the combination of different type of objects that incorporates both data and behavior.
- Portable: Java supports read-once-write-anywhere approach. We can execute the Java program on every machine. Java program (.java) is converted to bytecode (.class) which can be easily run on every machine.
- Platform Independent: Java is a platform independent programming language. It is different from other programming languages like C and C++ which needs a platform to be executed. Java comes with its platform on which its code is executed. Java doesn't depend upon the operating system to be executed.
- Interpreted: Java uses the Just-in-time (JIT) interpreter along with the compiler for the program execution.
- Secured: Java is secured because it doesn't use explicit pointers. Java also provides the concept of ByteCode and Exception handling which makes it more secured.
- Robust: Java is a strong programming language as it uses strong memory management. The concepts like Automatic garbage collection, Exception handling, etc. make it more robust.
- Architecture Neutral: Java is architectural neutral as it is not dependent on the architecture. In C, the size of data types may vary according to the architecture (32 bit or 64 bit) which doesn't exist in Java.
- High Performance: Java is faster than other traditional interpreted programming languages because Java bytecode is "close" to native code. It is still a little bit slower than a compiled language (e.g., C++).
- Multithreaded: We can write Java programs that deal with many tasks at once by defining multiple threads. The main advantage of multi-threading is that it doesn't occupy memory for each thread. It shares a common memory area. Threads are important for multi-media, Web applications, etc.
- Distributed: Java is distributed because it facilitates users to create distributed applications in Java. RMI and EJB are used for creating distributed applications. This feature of Java makes us able to access files by calling the methods from any machine on the internet.
- Dynamic: Java is a dynamic language. It supports dynamic loading of classes. It means classes are loaded on demand. It also supports functions from its native languages, i.e., C and C++.
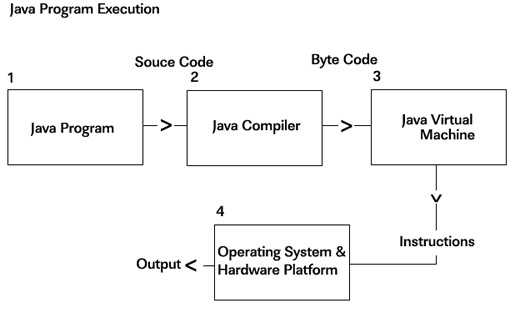
Q5) What is JVM?
A5)
Java virtual Machine (JVM) is a virtual Machine that provides runtime environment to execute java byte code.
The JVM doesn't understand Java typo, that's why you compile your *.java files to obtain *.class files that contain the bytecodes understandable by the JVM.
JVM control execution of every Java program.
It enables features such as automated exception handling, Garbage-collected heap.
JVM Architecture
Q6) What is Bytecode?
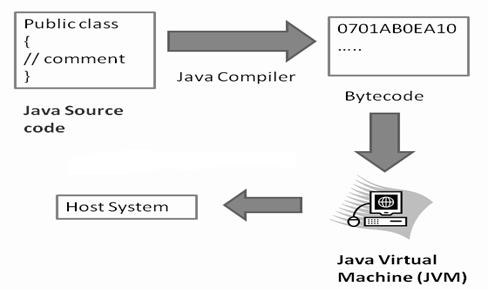
A6)
Bytecode is nothing but the intermediate representation of Java source code which is produced by the Java compiler by compiling that source code.
This byte code is a machine independent code.
It is not a completely a compiled code but it is an intermediate code somewhere in the middle which is later interpreted and executed by JVM. Bytecode is a machine code for JVM.
Q7) What are Basic Parameters used in Java Program?
A7)
Class Simple{
Public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello Java");
}
}
Save the above file as Simple.java.
To compile: javac Simple.java
To execute: java Simple
OutPut:
Hello Java
There are some basic parameters are used as follows:
1) class keyword is used to declare a class in Java.
2) public keyword is an access modifier that represents visibility. It means it is visible to all.
3) static is a keyword. If we declare any method as static, it is known as the static method. The core advantage of the static method is that there is no need to create an object to invoke the static method. The main () method is executed by the JVM, so it doesn't require creating an object to invoke the main () method. So, it saves memory.
4) void is the return type of the method. It means it doesn't return any value.
5) main represents the starting point of the program.
6) String[] args or String args[] is used for command line argument.
7) System.out.println() is used to print statement. Here, System is a class, out is an object of the Print Stream class, println() is a method of the Print Stream class.
Q8) How many types of memory areas are allocated by JVM?
A8)
- Class (Method) Area: Class Area stores per-class structures such as the runtime constant pool, field, method data, and the code for methods.
- Heap: It is the runtime data area in which the memory is allocated to the objects
- Stack: Java Stack stores frames. It holds local variables and partial results, and plays a part in method invocation and return. Each thread has a private JVM stack, created at the same time as the thread. A new frame is created each time a method is invoked. A frame is destroyed when its method invocation completes.
- Program Counter Register: PC (program counter) register contains the address of the Java virtual machine instruction currently being executed.
- Native Method Stack: It contains all the native methods used in the application.
Q9) What are the various access specifiers in Java?
A9)
In Java, there are four access specifiers given below.
a) Public: The classes, methods, or variables which are defined as public, can be accessed by any class or method.
b) Protected: Protected can be accessed by the class of the same package, or by the sub-class of this class, or within the same class.
c) Default: Default are accessible within the package only. By default, all the classes, methods, and variables are of default scope.
d) Private: The private class, methods, or variables defined as private can be accessed within the class only.
Q10) What is class loader?
A10)
Class loader is a subsystem of JVM which is used to load class files. Whenever we run the java program, it is loaded first by the class loader. There are three built-in class loaders in Java.
- Bootstrap Class Loader: This is the first-class loader which is the superclass of Extension class loader. It loads the rt.jar file which contains all class files of Java Standard Edition like java.lang package classes, java.net package classes, java.util package classes, java.io package classes, java.sql package classes, etc.
- Extension Class Loader: This is the child class loader of Bootstrap and parent class loader of System class loader. It loads the jar files located inside $JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/ext directory.
- System/Application Class Loader: This is the child class loader of Extension class loader. It loads the class files from the class path. By default, the class path is set to the current directory. You can change the class path using "-cp" or "-classpath" switch. It is also known as Application class loader.
Q11) What are Operators? Different types of operators used in java?
A11)
Operator in Java is a symbol that is used to perform operations. For example: +, -, *, / etc.
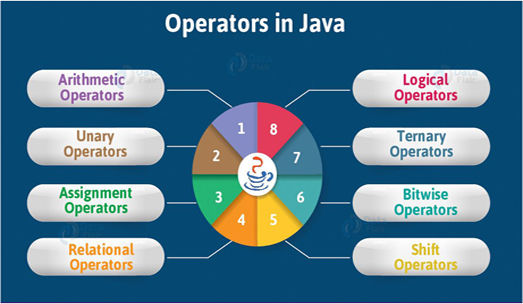
Operator Type | Category | Precedence |
Unary | Postfix | Expr++ expr-- |
Prefix | ++expr --expr +expr -expr ~! | |
Arithmetic | Multiplicative | * / % |
Additive | + - | |
Shift | Shift | << >> >>> |
Relational | Comparison | < > <= >= instance of |
Equality | == != | |
Bitwise | Bitwise AND | & |
Bitwise exclusive OR | ^ | |
Bitwise inclusive OR | | | |
Logical | Logical AND | && |
Logical OR | || | |
Ternary | Ternary | ? : |
Assignment | Assignment | = += -= *= /= %= &= ^= |= <<= >>= >>>= |
Q12) What is the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM?
A12)
JVM
JVM is an acronym for Java Virtual Machine; it is an abstract machine which provides the runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed. It is a specification which specifies the working of Java Virtual Machine. Its implementation has been provided by Oracle and other companies. Its implementation is known as JRE.
JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms (so JVM is platform dependent). It is a runtime instance which is created when we run the Java class. There are three notions of the JVM: specification, implementation, and instance.
JRE
JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment. It is the implementation of JVM. The Java Runtime Environment is a set of software tools which are used for developing Java applications. It is used to provide the runtime environment. It is the implementation of JVM. It physically exists. It contains a set of libraries + other files that JVM uses at runtime.
JDK
JDK is an acronym for Java Development Kit. It is a software development environment which is used to develop Java applications and applets. It physically exists. It contains JRE + development tools. JDK is an implementation of any one of the below given Java Platforms released by Oracle Corporation:
- Standard Edition Java Platform
- Enterprise Edition Java Platform
- Micro Edition Java Platform
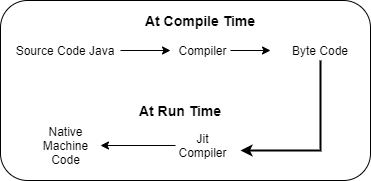
Q13) What is JIT compiler?
A13)
Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler: It is used to improve the performance. JIT compiles parts of the bytecode that have similar functionality at the same time, and hence reduces the amount of time needed for compilation. Here the term “compiler” refers to a translator from the instruction set of a Java virtual machine (JVM) to the instruction set of a specific CPU.
Q14) What is the output of the following Java program?
Class Test
{
Public static void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println(10 * 20 + "Javamy");
System.out.println("Javamy" + 10 * 20);
}
}
A14)
The output of the above code will be
200Javamy
Javamy200
Explanation
In the first case, the numbers 10 and 20 will be multiplied first and then the result 200 is treated as the string and concatenated with the string Javamy to produce the output 200Javamy.
In the second case, the numbers 10 and 20 will be multiplied first to be 200 because the precedence of the multiplication is higher than addition. The result 200 will be treated as the string and concatenated with the string Javamy to produce the output as Javamy
Q15) What is an object?
A15)
The Object is the real-time entity having some state and behavior. In Java, Object is an instance of the class having the instance variables as the state of the object and the methods as the behavior of the object. The object of a class can be created by using the new keyword.
Q16) What is the difference between an object-oriented programming language and object-based programming language?
A16)
There are the following basic differences between the object-oriented language and object-based language.
a) Object-oriented languages follow all the concepts of OOPs whereas, the object-based language doesn't follow all the concepts of OOPs like inheritance and polymorphism.
b) Object-oriented languages do not have the inbuilt objects whereas Object-based languages have the inbuilt objects, for example, JavaScript has window object.
Examples of object-oriented programming are Java, C#, Smalltalk, etc. whereas the examples of object-based languages are JavaScript, VBScript, etc.
Q17) What is the purpose of static methods and variables?
A17)
The methods or variables defined as static are shared among all the objects of the class.
The static is the part of the class and not of the object. The static variables are stored in the class area, and we do not need to create the object to access such variables.
Therefore, static is used in the case, where we need to define variables or methods which are common to all the objects of the class.
For example, In the class simulating the collection of the students in a college, the name of the college is the common attribute to all the students. Therefore, the college name will be defined as static.
Q18) What are variables? Different types of variables used in java?
A18)
A variable is the name of a reserved area allocated in memory. In other words, it is a name of the memory location.
1)Local Variable
A variable declared inside the body of the method is called local variable. You can use this variable only within that method and the other methods in the class aren't even aware that the variable exists.
A local variable cannot be defined with "static" keyword.
2) Instance Variable
A variable declared inside the class but outside the body of the method, is called an instance variable. It is not declared as static.
It is called an instance variable because its value is instance-specific and is not shared among instances.
3) Static variable
A variable that is declared as static is called a static variable. It cannot be local. You can create a single copy of the static variable and share it among all the instances of the class. Memory allocation for static variables happens only once when the class is loaded in the memory.
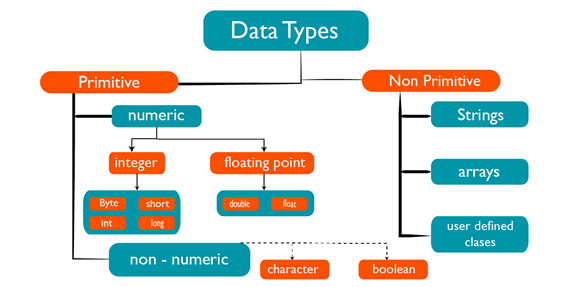
Q19) How many data types are used in java?
A19)
Data types specify the different sizes and values that can be stored in the variable. There are two types of data types in Java:
- Primitive data types: The primitive data types include boolean, char, byte, short, int, long, float and double.
- Non-primitive data types: The non-primitive data types include Classes, Interfaces, and Arrays.
Data Type | Default Value | Default size |
Boolean | False | 1 bit |
Char | '\u0000' | 2 byte |
Byte | 0 | 1 byte |
Short | 0 | 2 byte |
Int | 0 | 4 byte |
Long | 0L | 8 byte |
Float | 0.0f | 4 byte |
Q20) Why java uses Unicode System?
A20)
Unicode is a universal international standard character encoding that is capable of representing most of the world's written languages.
- ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) for the United States.
- ISO 8859-1 for Western European Language.
- KOI-8 for Russian.
- GB18030 and BIG-5 for Chinese, and so on.
This caused two problems:
1. A particular code value corresponds to different letters in the various language standards.
2. The encodings for languages with large character sets have variable length. Some common characters are encoded as single bytes, other require two or more byte.
To solve these problems, a new language standard was developed i.e., Unicode System.
In Unicode, character holds 2 bytes, so java also uses 2 bytes for characters.
Lowest value:\u0000 highest value:\uFFFF