UNIT 2
Number system
1. Difference between Computer Architecture VS Computer Organization
Computer Architecture | Computer Organization |
Computer Architecture is concerned with the way hardware components are connected together to form a computer system. | Computer Organization is concerned with the structure and behaviour of a computer system as seen by the user. |
It acts as the interface between hardware and software. | It deals with the components of a connection in a system. |
Computer Architecture helps us to understand the functionalities of a system. | Computer Organization tells us how exactly all the units in the system are arranged and interconnected. |
A programmer can view architecture in terms of instructions, addressing modes and registers. | Whereas Organization expresses the realization of architecture. |
While designing a computer system architecture is considered first. | An organization is done on the basis of architecture. |
Computer Architecture deals with high-level design issues. | Computer Organization deals with low-level design issues. |
Architecture involves Logic (Instruction sets, Addressing modes, Data types, Cache optimization) | Organization involves Physical Components (Circuit design, Adders, Signals, Peripherals) |
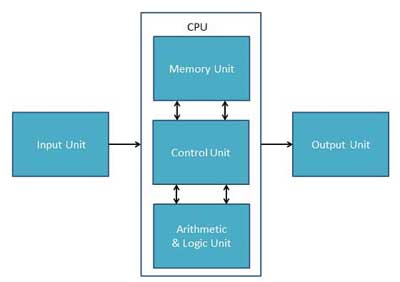
2. Explain Central Processing Unit (CPU).
- CPU is considered as the brain of the computer.
- CPU performs all types of data processing operations.
- It stores data, intermediate results, and instructions (program).
- It controls the operation of all parts of the computer.

CPU itself has following three components.
- Memory or Storage Unit
- Control Unit
- ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
Memory or Storage Unit
This unit can store instructions, data, and intermediate results. This unit supplies information to other units of the computer when needed. It is also known as internal storage unit or the main memory or the primary storage or Random Access Memory (RAM).
Its size affects speed, power, and capability. Primary memory and secondary memory are two types of memories in the computer. Functions of the memory unit are −
- It stores all the data and the instructions required for processing.
- It stores intermediate results of processing.
- It stores the final results of processing before these results are released to an output device.
- All inputs and outputs are transmitted through the main memory.
Control Unit
This unit controls the operations of all parts of the computer but does not carry out any actual data processing operations.
Functions of this unit are −
- It is responsible for controlling the transfer of data and instructions among other units of a computer.
- It manages and coordinates all the units of the computer.
- It obtains the instructions from the memory, interprets them, and directs the operation of the computer.
- It communicates with Input/Output devices for transfer of data or results from storage.
- It does not process or store data.
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
This unit consists of two subsections namely,
- Arithmetic Section
- Logic Section
Arithmetic Section
Function of arithmetic section is to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. All complex operations are done by making repetitive use of the above operations.
Logic Section
Function of logic section is to perform logic operations such as comparing, selecting, matching, and merging of data.
3. Explain memory and its types
A memory is just like a human brain. It is used to store data and instructions. Computer memory is the storage space in the computer, where data is to be processed and instructions required for processing are stored. The memory is divided into large number of small parts called cells. Each location or cell has a unique address, which varies from zero to memory size minus one. For example, if the computer has 64k words, then this memory unit has 64 * 1024 = 65536 memory locations. The address of these locations varies from 0 to 65535.
Memory is primarily of three types −
- Cache Memory
- Primary Memory/Main Memory
- Secondary Memory
Cache Memory
Cache memory is a very high speed semiconductor memory which can speed up the CPU. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory. It is used to hold those parts of data and program which are most frequently used by the CPU. The parts of data and programs are transferred from the disk to cache memory by the operating system, from where the CPU can access them.

Advantages
The advantages of cache memory are as follows −
- Cache memory is faster than main memory.
- It consumes less access time as compared to main memory.
- It stores the program that can be executed within a short period of time.
- It stores data for temporary use.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of cache memory are as follows −
- Cache memory has limited capacity.
- It is very expensive.
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary memory holds only those data and instructions on which the computer is currently working. It has a limited capacity and data is lost when power is switched off. It is generally made up of semiconductor device. These memories are not as fast as registers. The data and instruction required to be processed resides in the main memory. It is divided into two subcategories RAM and ROM.

Characteristics of Main Memory
- These are semiconductor memories.
- It is known as the main memory.
- Usually volatile memory.
- Data is lost in case power is switched off.
- It is the working memory of the computer.
- Faster than secondary memories.
- A computer cannot run without the primary memory.
Secondary Memory
This type of memory is also known as external memory or non-volatile. It is slower than the main memory. These are used for storing data/information permanently. CPU directly does not access these memories, instead they are accessed via input-output routines. The contents of secondary memories are first transferred to the main memory, and then the CPU can access it. For example, disk, CD-ROM, DVD, etc.

Characteristics of Secondary Memory
- These are magnetic and optical memories.
- It is known as the backup memory.
- It is a non-volatile memory.
- Data is permanently stored even if power is switched off.
- It is used for storage of data in a computer.
- Computer may run without the secondary memory.
- Slower than primary memories.
4. Explain input devices with example
Input Devices
Following are some of the important input devices which are used in a computer
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Joy Stick
- Light pen
- Track Ball
- Scanner
- Graphic Tablet
- Microphone
- Magnetic Ink Card Reader(MICR)
- Optical Character Reader(OCR)
- Bar Code Reader
- Optical Mark Reader(OMR)
Keyboard
Keyboard is the most common and very popular input device which helps to input data to the computer. The layout of the keyboard is like that of traditional typewriter, although there are some additional keys provided for performing additional functions.

Keyboards are of two sizes 84 keys or 101/102 keys, but now keyboards with 104 keys or 108 keys are also available for Windows and Internet.
The keys on the keyboard are as follows −
S.No | Keys & Description |
1 | Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and digit keys (09) which generally give the same layout as that of typewriters. |
2 | Numeric Keypad It is used to enter the numeric data or cursor movement. Generally, it consists of a set of 17 keys that are laid out in the same configuration used by most adding machines and calculators. |
3 | Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the keyboard which are arranged in a row at the top of the keyboard. Each function key has a unique meaning and is used for some specific purpose. |
4 | Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen control. It includes four directional arrow keys. Control keys also include Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc). |
5 | Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen. |
Mouse
Mouse is the most popular pointing device. It is a very famous cursor-control device having a small palm size box with a round ball at its base, which senses the movement of the mouse and sends corresponding signals to the CPU when the mouse buttons are pressed.
Generally, it has two buttons called the left and the right button and a wheel is present between the buttons. A mouse can be used to control the position of the cursor on the screen, but it cannot be used to enter text into the computer.

Advantages
- Easy to use
- Not very expensive
- Moves the cursor faster than the arrow keys of the keyboard.
Joystick
Joystick is also a pointing device, which is used to move the cursor position on a monitor screen. It is a stick having a spherical ball at its both lower and upper ends. The lower spherical ball moves in a socket. The joystick can be moved in all four directions.

The function of the joystick is similar to that of a mouse. It is mainly used in Computer Aided Designing (CAD) and playing computer games.
Light Pen
Light pen is a pointing device similar to a pen. It is used to select a displayed menu item or draw pictures on the monitor screen. It consists of a photocell and an optical system placed in a small tube.

When the tip of a light pen is moved over the monitor screen and the pen button is pressed, its photocell sensing element detects the screen location and sends the corresponding signal to the CPU.
Track Ball
Track ball is an input device that is mostly used in notebook or laptop computer, instead of a mouse. This is a ball which is half inserted and by moving fingers on the ball, the pointer can be moved.

Since the whole device is not moved, a track ball requires less space than a mouse. A track ball comes in various shapes like a ball, a button, or a square.
Scanner
Scanner is an input device, which works more like a photocopy machine. It is used when some information is available on paper and it is to be transferred to the hard disk of the computer for further manipulation.

Scanner captures images from the source which are then converted into a digital form that can be stored on the disk. These images can be edited before they are printed.
Digitizer
Digitizer is an input device which converts analog information into digital form. Digitizer can convert a signal from the television or camera into a series of numbers that could be stored in a computer. They can be used by the computer to create a picture of whatever the camera had been pointed at.

Digitizer is also known as Tablet or Graphics Tablet as it converts graphics and pictorial data into binary inputs. A graphic tablet as digitizer is used for fine works of drawing and image manipulation applications.
Microphone
Microphone is an input device to input sound that is then stored in a digital form.

The microphone is used for various applications such as adding sound to a multimedia presentation or for mixing music.
Magnetic Ink Card Reader (MICR)
MICR input device is generally used in banks as there are large number of cheques to be processed every day. The bank's code number and cheque number are printed on the cheques with a special type of ink that contains particles of magnetic material that are machine readable.

This reading process is called Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR). The main advantages of MICR is that it is fast and less error prone.
Optical Character Reader (OCR)
OCR is an input device used to read a printed text.

OCR scans the text optically, character by character, converts them into a machine readable code, and stores the text on the system memory.
Bar Code Readers
Bar Code Reader is a device used for reading bar coded data (data in the form of light and dark lines). Bar coded data is generally used in labelling goods, numbering the books, etc. It may be a handheld scanner or may be embedded in a stationary scanner.

Bar Code Reader scans a bar code image, converts it into an alphanumeric value, which is then fed to the computer that the bar code reader is connected to.
Optical Mark Reader (OMR)
OMR is a special type of optical scanner used to recognize the type of mark made by pen or pencil. It is used where one out of a few alternatives is to be selected and marked.

It is specially used for checking the answer sheets of examinations having multiple choice questions.
5. Explain output devices with example
Following are some of the important output devices used in a computer.
- Monitors
- Graphic Plotter
- Printer
Monitors
Monitors, commonly called as Visual Display Unit (VDU), are the main output device of a computer. It forms images from tiny dots, called pixels that are arranged in a rectangular form. The sharpness of the image depends upon the number of pixels.
There are two kinds of viewing screen used for monitors.
- Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT)
- Flat-Panel Display
Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Monitor
The CRT display is made up of small picture elements called pixels. The smaller the pixels, the better the image clarity or resolution. It takes more than one illuminated pixel to form a whole character, such as the letter ‘e’ in the word help.

A finite number of characters can be displayed on a screen at once. The screen can be divided into a series of character boxes - fixed location on the screen where a standard character can be placed. Most screens are capable of displaying 80 characters of data horizontally and 25 lines vertically.
There are some disadvantages of CRT −
- Large in Size
- High power consumption
Flat-Panel Display Monitor
The flat-panel display refers to a class of video devices that have reduced volume, weight and power requirement in comparison to the CRT. You can hang them on walls or wear them on your wrists. Current uses of flat-panel displays include calculators, video games, monitors, laptop computer, and graphics display.

The flat-panel display is divided into two categories −
- Emissive Displays − Emissive displays are devices that convert electrical energy into light. For example, plasma panel and LED (Light-Emitting Diodes).
- Non-Emissive Displays − Non-emissive displays use optical effects to convert sunlight or light from some other source into graphics patterns. For example, LCD (Liquid-Crystal Device).
Printers
Printer is an output device, which is used to print information on paper.
There are two types of printers −
- Impact Printers
- Non-Impact Printers
Impact Printers
Impact printers print the characters by striking them on the ribbon, which is then pressed on the paper.
Characteristics of Impact Printers are the following −
- Very low consumable costs
- Very noisy
- Useful for bulk printing due to low cost
- There is physical contact with the paper to produce an image
These printers are of two types −
- Character printers
- Line printers
Character Printers
Character printers are the printers which print one character at a time.
These are further divided into two types:
- Dot Matrix Printer(DMP)
- Daisy Wheel
Dot Matrix Printer
In the market, one of the most popular printers is Dot Matrix Printer. These printers are popular because of their ease of printing and economical price. Each character printed is in the form of pattern of dots and head consists of a Matrix of Pins of size (5*7, 7*9, 9*7 or 9*9) which come out to form a character which is why it is called Dot Matrix Printer.

Advantages
- Inexpensive
- Widely Used
- Other language characters can be printed
Disadvantages
- Slow Speed
- Poor Quality
Daisy Wheel
Head is lying on a wheel and pins corresponding to characters are like petals of Daisy (flower) which is why it is called Daisy Wheel Printer. These printers are generally used for word-processing in offices that require a few letters to be sent here and there with very nice quality.

Advantages
- More reliable than DMP
- Better quality
- Fonts of character can be easily changed
Disadvantages
- Slower than DMP
- Noisy
- More expensive than DMP
Line Printers
Line printers are the printers which print one line at a time.

These are of two types −
- Drum Printer
- Chain Printer
Drum Printer
This printer is like a drum in shape hence it is called drum printer. The surface of the drum is divided into a number of tracks. Total tracks are equal to the size of the paper, i.e. for a paper width of 132 characters, drum will have 132 tracks. A character set is embossed on the track. Different character sets available in the market are 48 character set, 64 and 96 characters set. One rotation of drum prints one line. Drum printers are fast in speed and can print 300 to 2000 lines per minute.
Advantages
- Very high speed
Disadvantages
- Very expensive
- Characters fonts cannot be changed
Chain Printer
In this printer, a chain of character sets is used, hence it is called Chain Printer. A standard character set may have 48, 64, or 96 characters.
Advantages
- Character fonts can easily be changed.
- Different languages can be used with the same printer.
Disadvantages
- Noisy
Non-impact Printers
Non-impact printers print the characters without using the ribbon. These printers print a complete page at a time, thus they are also called as Page Printers.
These printers are of two types −
- Laser Printers
- Inkjet Printers
Characteristics of Non-impact Printers
- Faster than impact printers
- They are not noisy
- High quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Laser Printers
These are non-impact page printers. They use laser lights to produce the dots needed to form the characters to be printed on a page.

Advantages
- Very high speed
- Very high quality output
- Good graphics quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Cannot be used to produce multiple copies of a document in a single printing
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers are non-impact character printers based on a relatively new technology. They print characters by spraying small drops of ink onto paper. Inkjet printers produce high quality output with presentable features.

They make less noise because no hammering is done and these have many styles of printing modes available. Color printing is also possible. Some models of Inkjet printers can produce multiple copies of printing also.
Advantages
- High quality printing
- More reliable
Disadvantages
- Expensive as the cost per page is high
- Slow as compared to laser printer
6. Explain number system and its types
When we type some letters or words, the computer translates them in numbers as computers can understand only numbers. A computer can understand the positional number system where there are only a few symbols called digits and these symbols represent different values depending on the position they occupy in the number.
The value of each digit in a number can be determined using −
- The digit
- The position of the digit in the number
- The base of the number system (where the base is defined as the total number of digits available in the number system)
Decimal Number System
The number system that we use in our day-to-day life is the decimal number system. Decimal number system has base 10 as it uses 10 digits from 0 to 9. In decimal number system, the successive positions to the left of the decimal point represent units, tens, hundreds, thousands, and so on.
Each position represents a specific power of the base (10). For example, the decimal number 1234 consists of the digit 4 in the units position, 3 in the tens position, 2 in the hundreds position, and 1 in the thousands position. Its value can be written as
(1 x 1000)+ (2 x 100)+ (3 x 10)+ (4 x l)
(1 x 103)+ (2 x 102)+ (3 x 101)+ (4 x l00)
1000 + 200 + 30 + 4
1234
As a computer programmer or an IT professional, you should understand the following number systems which are frequently used in computers.
S.No. | Number System and Description |
1 | Binary Number System Base 2. Digits used : 0, 1 |
2 | Octal Number System Base 8. Digits used : 0 to 7 |
3 | Hexa Decimal Number System Base 16. Digits used: 0 to 9, Letters used : A- F |
Binary Number System
Characteristics of the binary number system are as follows −
- Uses two digits, 0 and 1
- Also called as base 2 number system
- Each position in a binary number represents a 0 power of the base (2). Example 20
- Last position in a binary number represents a x power of the base (2). Example 2x where x represents the last position - 1.
Example
Binary Number: 101012
Calculating Decimal Equivalent −
Step | Binary Number | Decimal Number |
Step 1 | 101012 | ((1 x 24) + (0 x 23) + (1 x 22) + (0 x 21) + (1 x 20))10 |
Step 2 | 101012 | (16 + 0 + 4 + 0 + 1)10 |
Step 3 | 101012 | 2110 |
Note − 101012 is normally written as 10101.
Octal Number System
Characteristics of the octal number system are as follows −
- Uses eight digits, 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
- Also called as base 8 number system
- Each position in an octal number represents a 0 power of the base (8). Example 80
- Last position in an octal number represents a x power of the base (8). Example 8x where x represents the last position - 1
Example
Octal Number: 125708
Calculating Decimal Equivalent −
Step | Octal Number | Decimal Number |
Step 1 | 125708 | ((1 x 84) + (2 x 83) + (5 x 82) + (7 x 81) + (0 x 80))10 |
Step 2 | 125708 | (4096 + 1024 + 320 + 56 + 0)10 |
Step 3 | 125708 | 549610 |
Note − 125708 is normally written as 12570.
Hexadecimal Number System
Characteristics of hexadecimal number system are as follows −
- Uses 10 digits and 6 letters, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F
- Letters represent the numbers starting from 10. A = 10. B = 11, C = 12, D = 13, E = 14, F = 15
- Also called as base 16 number system
- Each position in a hexadecimal number represents a 0 power of the base (16). Example, 160
- Last position in a hexadecimal number represents a x power of the base (16). Example 16x where x represents the last position - 1
Example
Hexadecimal Number: 19FDE16
Calculating Decimal Equivalent −
Step | Binary Number | Decimal Number |
Step 1 | 19FDE16 | ((1 x 164) + (9 x 163) + (F x 162) + (D x 161) + (E x 160))10 |
Step 2 | 19FDE16 | ((1 x 164) + (9 x 163) + (15 x 162) + (13 x 161) + (14 x 160))10 |
Step 3 | 19FDE16 | (65536+ 36864 + 3840 + 208 + 14)10 |
Step 4 | 19FDE16 | 10646210 |
Note − 19FDE16 is normally written as 19FDE.
7. Why we use Structured Programming?
We use structured programming because it allows the programmer to understand the program easily. If a program consists of thousands of instructions and an error occurs then it is complicated to find that error in the whole program, but in structured programming, we can easily detect the error and then go to that location and correct it. This saves a lot of time.
These are the following rules in structured programming:
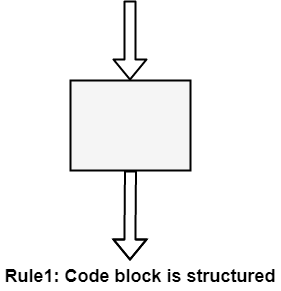
Structured Rule One: Code Block
If the entry conditions are correct, but the exit conditions are wrong, the error must be in the block. This is not true if the execution is allowed to jump into a block. The error might be anywhere in the program. Debugging under these circumstances is much harder.
Rule 1 of Structured Programming: A code block is structured, as shown in the figure. In flow-charting condition, a box with a single entry point and single exit point are structured. Structured programming is a method of making it evident that the program is correct.
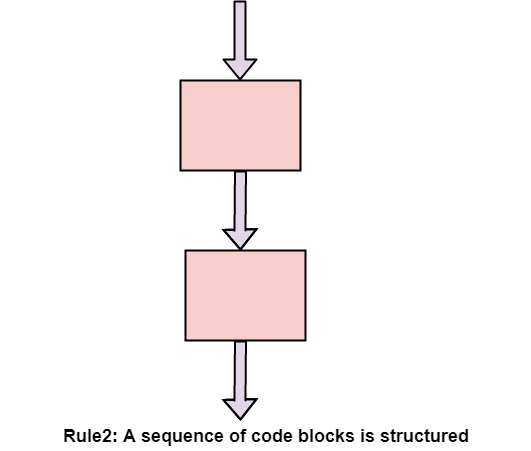
Structure Rule Two: Sequence
A sequence of blocks is correct if the exit conditions of each block match the entry conditions of the following block. Execution enters each block at the block's entry point and leaves through the block's exit point. The whole series can be regarded as a single block, with an entry point and an exit point.
Rule 2 of Structured Programming: Two or more code blocks in the sequence are structured, as shown in the figure.
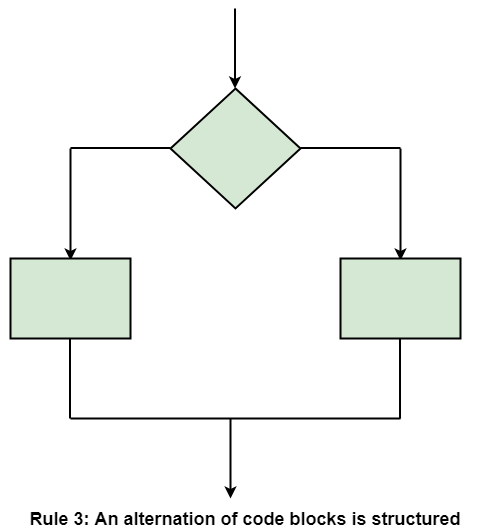
Structured Rule Three: Alternation
If-then-else is frequently called alternation (because there are alternative options). In structured programming, each choice is a code block. If alternation is organized as in the flowchart at right, then there is one entry point (at the top) and one exit point (at the bottom). The structure should be coded so that if the entry conditions are fulfilled, then the exit conditions are satisfied (just like a code block).
Rule 3 of Structured Programming: The alternation of two code blocks is structured, as shown in the figure.
An example of an entry condition for an alternation method is: register $8 includes a signed integer. The exit condition may be: register $8 includes the absolute value of the signed number. The branch structure is used to fulfill the exit condition.
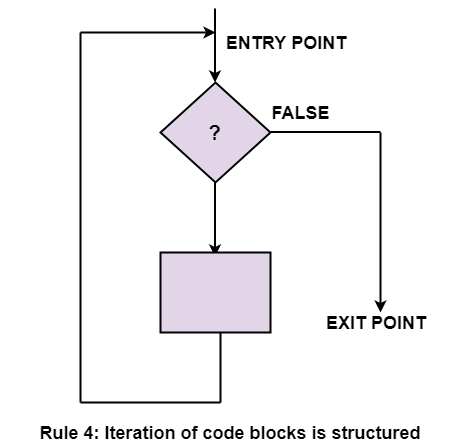
Structured Rule 4: Iteration
Iteration (while-loop) is organized as at right. It also has one entry point and one exit point. The entry point has conditions that must be satisfied, and the exit point has requirements that will be fulfilled. There are no jumps into the form from external points of the code.
Rule 4 of Structured Programming: The iteration of a code block is structured, as shown in the figure.
Structured Rule 5: Nested Structures
In flowcharting conditions, any code block can be spread into any of the structures. If there is a portion of the flowchart that has a single entry point and a single exit point, it can be summarized as a single code block.
Rule 5 of Structured Programming: A structure (of any size) that has a single entry point and a single exit point is equivalent to a code block. For example, we are designing a program to go through a list of signed integers calculating the absolute value of each one. We may (1) first regard the program as one block, then(2) sketch in the iteration required, and finally (3) put in the details of the loop body, as shown in the figure.
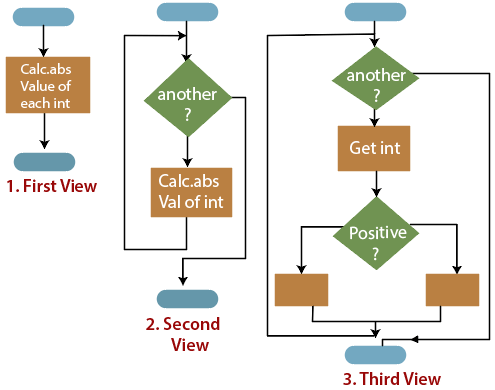
The other control structures are the case, do-until, do-while, and for are not needed. However, they are sometimes convenient and are usually regarded as part of structured programming. In assembly language, they add little convenience.
8. What is source code?
- Source code is the set of instructions and statements written by a programmer using a computer programming language. This code is later translated into machine language by a compiler. The translated code is referred to as object code.
- Source code is the source of a computer program. It contains declarations, instructions, functions, loops and other statements, which act as instructions for the program on how to function. Programs may contain one or more source code text files, which can be stored on a computer's hard disk, in a database, or be printed in books of code snippets.
- Programmers can add comments to their source code to help other developers understand it. Short scripts can also be run from source code using a scripting engine such as VBScript or the PHP engine.
- While large programs frequently reference hundreds or thousands of files, it is not uncommon for small programs to use just one source code. If there are many source files, the program may be organized into different sections. If a single file contains the entire program's variables and functions, it can be hard to locate specific sections of the code.
9. What is an Operating System and explain its function?
An Operating system (OS) is software which acts as an interface between the end user and computer hardware. Every computer must have at least one OS to run other programs. An application like Chrome, MS Word, Games, etc needs some environment in which it will run and perform its task. The OS helps you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer's language. It is not possible for the user to use any computer or mobile device without having an operating system.
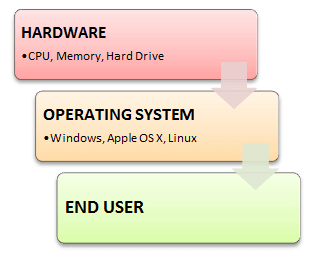
Features of Operating System
Here is a list commonly found important features of an Operating System:
- Protected and supervisor mode
- Allows disk access and file systems Device drivers Networking Security
- Program Execution
- Memory management Virtual Memory Multitasking
- Handling I/O operations
- Manipulation of the file system
- Error Detection and handling
- Resource allocation
- Information and Resource Protection
Functions of an Operating System
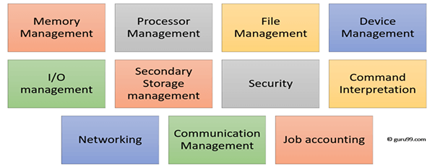
Function of an Operating System
In an operating system software performs each of the function:
- Process management:- Process management helps OS to create and delete processes. It also provides mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes.
2. Memory management:- Memory management module performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of memory space to programs in need of this resources.
3. File management:- It manages all the file-related activities such as organization storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
4. Device Management: Device management keeps tracks of all devices. This module also responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. It also performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of the devices.
5. I/O System Management: One of the main objects of any OS is to hide the peculiarities of that hardware devices from the user.
6. Secondary-Storage Management: Systems have several levels of storage which includes primary storage, secondary storage, and cache storage. Instructions and data must be stored in primary storage or cache so that a running program can reference it.
7. Security:- Security module protects the data and information of a computer system against malware threat and authorized access.
8. Command interpretation: This module is interpreting commands given by the and acting system resources to process that commands.
9. Networking: A distributed system is a group of processors which do not share memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors communicate with one another through the network.
10. Job accounting: Keeping track of time & resource used by various job and users.
11. Communication management: Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, and another software resource of the various users of the computer systems.
10. Explain operating system types its advantages and disadvantages
Types of Operating system
- Batch Operating System
- Multitasking/Time Sharing OS
- Multiprocessing OS
- Real Time OS
- Distributed OS
- Network OS
- Mobile OS
Batch Operating System
Some computer processes are very lengthy and time-consuming. To speed the same process, a job with a similar type of needs are batched together and run as a group.
The user of a batch operating system never directly interacts with the computer. In this type of OS, every user prepares his or her job on an offline device like a punch card and submit it to the computer operator.
Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
Time-sharing operating system enables people located at a different terminal(shell) to use a single computer system at the same time. The processor time (CPU) which is shared among multiple users is termed as time sharing.
Real time OS
A real time operating system time interval to process and respond to inputs is very small. Examples: Military Software Systems, Space Software Systems.
Distributed Operating System
Distributed systems use many processors located in different machines to provide very fast computation to its users.
Network Operating System
Network Operating System runs on a server. It provides the capability to serve to manage data, user, groups, security, application, and other networking functions.
Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems are those OS which is especially that are designed to power smartphones, tablets, and wearables devices.
Some most famous mobile operating systems are Android and iOS, but others include BlackBerry, Web, and watch OS.
The advantage of using Operating System
- Allows you to hide details of hardware by creating an abstraction
- Easy to use with a GUI
- Offers an environment in which a user may execute programs/applications
- The operating system must make sure that the computer system convenient to use
- Operating System acts as an intermediary among applications and the hardware components
- It provides the computer system resources with easy to use format
- Acts as an intermediator between all hardware's and software's of the system
Disadvantages of using Operating System
- If any issue occurs in OS, you may lose all the contents which have been stored in your system
- Operating system's software is quite expensive for small size organization which adds burden on them. Example Windows
- It is never entirely secure as a threat can occur at any time
Summary
- An operating system is a software which acts as an interface between the end user and computer hardware
- Operating systems were first developed in the late 1950s to manage tape storage
- The kernel is the central component of a computer operating systems. The only job performed by the kernel is to the manage the communication between the software and the hardware
- Two most popular kernels are Monolithic and Micro Kernels
- Process, Device, File, I/O, Secondary-Storage, Memory management are various functions of an Operating System
- Batch, Multitasking/Time Sharing, Multiprocessing, Real Time, Distributed, Network, Mobile are various types of Operating Systems