Question Bank
Unit - 7
- What is use of CAD software in Engineering Drawing?
Ans:
Manufacturing of a product is the main activity in engineering profession. The design of a product may start with trial designs in the form of sketches on paper. As the design improves and undergoes changes, the final form of design must be the scaled manufacturing drawings with finer details included. These drawings are two-dimensional representations of three dimensional objects designed.
During the process of design, the designer may have to carry out a large amount of computations so that an optimum design is obtained. A computer with good graphic capabilities helps the designer to,
(i) realize his ideas.
(ii) carry out complex computations.
(iii) present the results of computations in a useful form for decision making and possible improvement.
(iv) present the improved model for evaluation. Interactive Computer Graphics (ICG) is the tool of the designer.
2. What is Computer aided drawing?
Ans:
A part to be manufactured is defined first in terms of its geometry which also includes dimensions, tolerances, surface finish, and in some cases the type of fit between two mating parts. The two-dimensional representation of a part, called an engineering drawing or a blueprint, shows three orthogonal views of the part. Sometimes, when three views are not enough to define the part, additional sectional views, auxiliary views may have to be added for conveying the right information.
Any design is finally represented in the form of orthographic views and auxiliary views so that production can be carried out. Hence, the computer aided drafting is an important tool for Computer Aided Design. The Computer Aided Drafting (CAD) system is the computerization of technical, production, electronics and architectural drawings.
CAD is the product of computer era. Its development originated from early computer graphics systems. CAD can find its roots to the development of Interactive Computer Graphics (ICG). A system called Sketchpad was developed at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, U.S.A., in 1963 by Ivan Sutherland.
In the beginning, CAD systems were no more than graphics editors with some built-in design symbols. The geometry available to the user was limited to lines, circular arcs, and a combination of the two. The development of free-form curves and surfaces such as Coon's patch, Ferguson's patch, Bezier's curve, and 8-splines enabled a CAD system to be used for more sophisticated work. A 30 CAD system allows a user to do very sophisticated design and analysis work.
Computer aided drawing and drafting system uses the computer to assist in generation of blueprint data. CAD systems are essential in design and many computers-based systems are commercially available. 20 drawing systems correspond directly to traditional engineering drawings, and they are developed to substitute manual drafting.
3. List out advantages of computer aided drawing.
Ans:
The advantages offered by computerized drafting systems can be summarized as:
(a) It increases the accuracy and productivity of designer.
(b) It allows design alterations to be made easily.
(c) It offers better drawing visualization through colours.
(d) It improves the quality of drawings produced.
(e) Drawings are easier to store and retrieve.
(f) Storage space required is less.
(g) Transfer of drawings is faster and cheaper.
(h) It permits the use of library of standard symbols for more productive CAD work.
4. What are graphic output devices?
Ans:
A hard copy i.e. copy on paper of what is displayed on a graphics terminal can be obtained by a variety of graphics printers and plotters. The computer graphic output device may be thought of as paper and a pen or a pencil.
(1) Dot Matrix Printers (DMP) and laser Printers: Dot Matrix Printer is the most commonly used printer for text printing. The characters are formed by printing dots in a specific manner. The dot matrix printer [fig. 2(vi)] can also be used for printing of drawings, but the quality of output is poor.
(2) Pen Plotters [fig. 2(v)]: Pen plotters are the simplest output devices for CAD. A pen plotter consists of a device to hold the paper. Usually two orthogonal motorized carriages hold a pen and move it under computer control. There are three inputs to the pen plotter: (i) an X coordinate, (ii) a Y coordinate and (iii) a pen variable. The pen variable can specify the pen colour by pen number, the pen to be up (non-drawing position) or down (in contact with paper in drawing position).
The two varieties of plotters are flat-bed and drum plotters. The flat-bed plotter is limited by the paper size it can handle. The drum plotter utilizes a continuous roll of paper which rolls over the top of the drum. The capacity and capabilities of a plotter are evaluated by the size of paper it can handle, resolution, speed of plotting, number of pens it can handle, etc.
(3) Ink-Jet printers/plotters: These are dot matrix printers. The drawing which is made up of lines, arcs, characters and symbols is converted into dot form. Then the rows of dots are printed across the width of the paper by impelling a tiny jet of ink on the surface of paper. The jets are switched on and off at high frequency to create multicolor plots.
Typically, the resolution is 600 to 900 dots per inch, and each dot is arranged to overlap the adjacent ones. This provides a high-quality photo-realistic picture. These plotters are quiet during operation. These plotters are used for colour plots of drawings, shaded images, contour plots and artistic work.
(4) laser printers: A laser printer rapidly produces high quality text and graphics on plain paper. The fastest colour laser printers can print over 100 pages per minute. It can write with much greater speed than an ink jet and can draw more precisely, without spilling any excess ink. The toner powder of laser printer is cheap and lasts a long time compared to expensive ink cartridges.
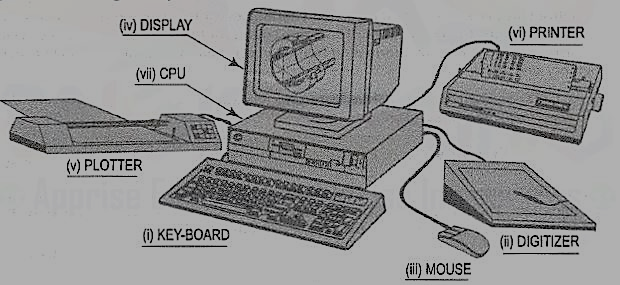
Figure 2 CAD system hardware
5. What is the use of CAD software?
Ans:
The major functions to be performed by a computer aided drafting system are:
(a) Basic set-up of a drawing
(b) Drawing the objects
(c) Changing the object properties
(d) Translating the objects
(e) Scaling the objects
(f) Clipping the objects to fit the image to the screen
(g) Creating symbol libraries for frequently used objects
(h) Text insertion
(i) Dimensioning
(j) Creates various layers (Transparent sheets)
(k) Allows zoom-in and zoom-out of any components drawing
(I) Creates different numbers of print/plot layouts.
6. List out function keys in AutoCAD.
Ans:
F1Online Help
F2Toggles between Drawing screen to text screen
F3Toggles between OSNAP- On and Off
F4Toggles between Tablet- On and Off
F5Switches among lso planes Top, Right and Left
F6Toggles between Coordinates- On and Off
F7Toggles between Grid- On and Off
F8Toggles between Ortho Mode- On and Off
F9Toggles between Snap Mode- On and Off
F10 Toggles between Polar Tracking- On and Off
F11 Toggles between Objects Snap Tracking- On and Off
7. What are various drawing entities in AutoCAD?
Ans:
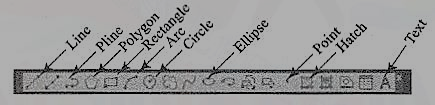
Figure 4
(1) Line: A line is specified by giving its two endpoints. The LINE command can be used to draw a single line or a series of lines with the end-point of one being the start point of the next. When a series of such lines is created, each line is treated as a separate entity. To create a closed polygon, the user has to type in C (close option) for the To point: prompt. This causes the last and the first points to be joined by a line and thus creating a closed boundary.
(2) Pline: Polylines are interesting drawing entities. Polylines can include both lines and arcs connected at end-points. Thus, a polyline is a single entity with multiple segments. The polylines can be straight or curved, can be wide (like a TRACE) or tapered. Fillets and chamfers can be added where needed on a polyline. Curve fitting and hatching can easily be performed on a polyline.
(3) Polygon (fig. 5): A polygon also a polyline with equal length of sides. The regular polygon can either be inscribed in a circle or circumscribed about the circle. The polygon may also be constructed by specifying the length of one side and the number of sides of polygon (called edges). In this method a polygon is constructed in anti-clockwise direction from the two-edge end-points that have been specified.
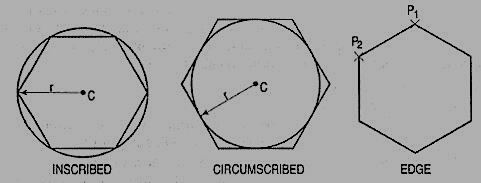
Figure 5 Polygon
(5) Arc (fig. 6): This command is used to draw an arc accurately. Usually there are three parameters required for drawing an arc.
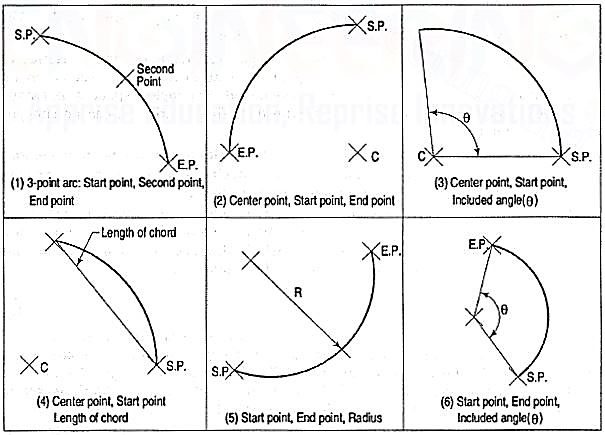
Figure 6 Arcs
8. What are commands used to edit a drawing?
Ans:
(1) Move [fig. 9 (i)]: Moves selected objects to another location about a base point.
(2) Rotate [fig. 9 (ii)]: Rotates selected objects through a specified angle about a base point.
(3) Copy [fig. 9 (iii)]: Creates one or more copies of selected objects at another location. The function of COPY command is like the MOVE command except that it preserves a copy of the objects selected at the original location.
(4) Mirror [fig. 9 (iv)]: Creates a mirror image of the selected objects about a specified line.
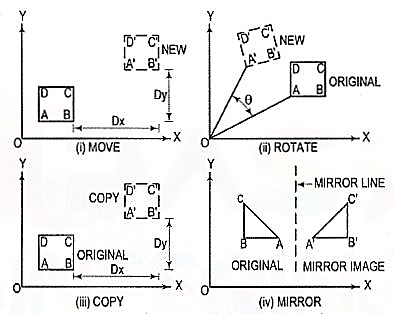
Figure 9
(5) Array: This command creates multiple copies of selected objects in rectangular or polar form. This is a form of COPY command.
(6) Erase: This command deletes the selected entities. A record of entities erased is always maintained. The most recent entity can be unerased by OOPS command.
(7) Oops: This command retrieves all objects erased by the last Erase and after executing Block or Wblock command.
(8) Break: This command erases a portion of line, arc, circle or a 20 polyline between two selected points.
(9) fillet : This command is used to create around corner between two lines. The lines are shortened or extended to fit a tangent arc of specified radius. FILLET works on any combination of two lines, arcs, circles, non-parallel lines, or a single polyline