Unit 4
Organizational Processes
- What do you mean by Organization Structure?
Answer: Organization Structure refers to the system of interrelated relationships that defines the flow of activities in an organization. These activities may include roles, rules and responsibilities.
2. What are the different elements of Organization Structure?
Answer: Organization Structure refers to the system of interrelated relationships that defines the flow of activities in an organization. These activities may include roles, rules and responsibilities. The following are the different elements of organization structure:
i) Departmentalisation: The grouping of various tasks, teams’ roles and responsibilities is known as departmentalization. Similar activities are grouped together under one department.
Ii) Chain of Command: Chain of Command refers the flow of authority of authority from top to bottom through the pre-defined structure of relationships arranged in the range of hierarchy of positions.
Iii) Work Specialisation: Work specialization means every employee is assigned specific roles and responsibilities as per their qualification, skills and experience. This enables an employee to perform only those activities which they specialize in.
Iv) Span of Control: Span of control refers to the number of employees to be managed by manager within an organization. A tall structure of an organization will indication a small span of control since very few employees will be under control. But in flat structure, the span of control will be more.
v) Centralisation and Decentralisation: Centralisation refers to concentration of authority in the hands of top officials. They are Suppose, to take all decisions. The other employees will not participate in decision making and thus will only follow orders coming from the top officials. A Decentralised organization allows employees to give inputs on big decisions taken by the organization.
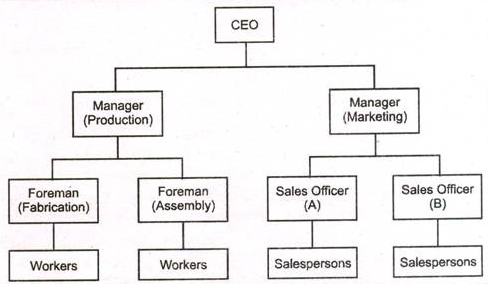
3. What is Line Organization? Give an example of Line organization.
Answer: Line organization has only direct, vertical relationships between different levels in the firm. There is only line departments which are directly involved in accomplishing the primary goal of the organization. This type of structure is evident in Military Organization.
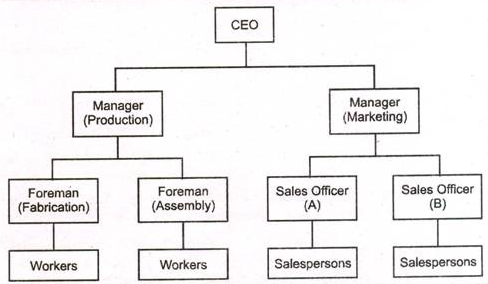
4. What do you mean by Staff Organization?
Answer: A position intended to provide expertise, advice and support for the line positions. The staff employees are employed only to assist the line members. They do not have any authority as regards decision making. They can only advice the line members, provide support as per their skills and knowledge.

5. Define Organization Culture.
Answer: Organizational culture refers to the common values, policies, practices observed by the organizational members as guidance in the organization activities.
6. What are the different types of Organization Culture?
Answer: Organizational culture refers to the common values, policies, practices observed by the organizational members as guidance in the organization activities. The different types of organizational culture that may be evident are:
- Normative Culture: In this, the norms and procedures of the organization are predefined and the rules and regulations are set as per the existing guidelines.
- Pragmatic Culture: In this, more emphasis is placed on the clients and the external parties. Customer satisfaction is the main motive of the employees in a pragmatic culture.
- Academy Culture: Here, organizations follow academy culture hire skilled individuals. The roles and responsibilities are delegated according to the back ground, educational qualification and work experience of the employees.
- Baseball team Culture: In this, the employees are considered as the most treasured possession of the organization. The employees are the true assets of the organization.
- Club Culture: Here, organizations follow a club culture and are very particular about the employees they recruit. The individuals are hired as per their specialization, educational qualification and interests.
- Fortress Culture: These are the organizations where the employees are not very sure about their career and longevity. Here, the employees are terminated if the organization is not performing well.
- Process Culture: In this, the employees adhere to the processes and procedures of the organization. Feedbacks and performance reviews do not matter much in such organizations.
7. What do you mean by Organization Change?
Answer: Organisational change means any change that occurs in the work environment. It may also refer to the alteration of structural relationships and roles of people in the organization. It is largely structural in nature. There are several ways to change an enterprise. Its technology can be changed; its people, its structure and other elements can be changed.
8. Discuss the process of Planned Change.
Answer: Organisational change means any change that occurs in the work environment. A common model for bringing change in people has three phase process:-
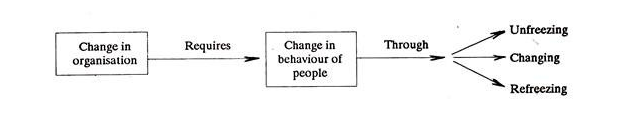
(1) Unfreezing:
The basic sense of unfreezing phase is that the individual is made to realize that his feelings, beliefs and behaviour are no longer relevant to the current situation in the organisation. Once convinced, people may change their behaviour. Reward for those willing to change and punishment for others may help in this matter.
(2) Changing:
Once an individual is convinced and ready to change then he learns to behave in new ways. He is initially provided with the model in which he is to recognise himself. Later he will accept the model and behave in the manner suggested by it. In another process (known as internalisation), the individual is placed in a situation where new behaviour is demanded of him if he is to operate successfully.
(3) Refreezing:
In this phase, an individual has to practice and experiment with the new method of behaviour and see that it effectively blends with his other behavioural attitudes.
9. Explain the factors involved in Organizational Change.
Answer: Organisational change means any change that occurs in the work environment. It may also refer to the alteration of structural relationships and roles of people in the organization. It is largely structural in nature.
Following are the factors in Organizational change are:
(A) External Pressures:
i. Change in Technology and Equipment:
Advancements in technology is the major cause (i.e., external pressure) of change. Each new technology results in the changes in the working of organization to meet and match the needs.
Ii. Market Situation:
A change in market situation refers to the rapidly changing of goals, needs and desires of consumers, suppliers, unions etc. If an organization has to survive, it has to cope with changes in market situations.
Iii. Social and Political Changes:
Organisational units literally have no control over social and political changes in the country. Relations between government and business or drive for social equality are some factors which may compel for organisational change.
(B) Internal Pressures (Pressures for Change from Within the Organisation):
i. Changes in the Managerial Personnel:
One of the most frequent reasons for major changes in the organisation is the change of executives at the top. No two managers have the same style, skills or managerial philosophies.
Ii. Deficiencies in the Existing Organization:
Many deficiencies are noticed in the organisations with the passage of time. A change is necessary to remove such deficiencies as lack of uniformity in the policies, obstacles in communication, any ambiguity etc.
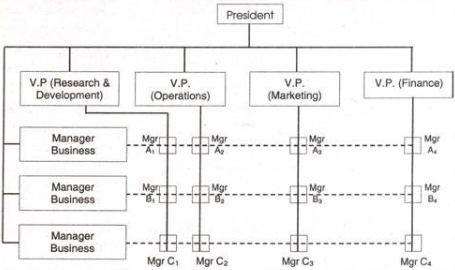
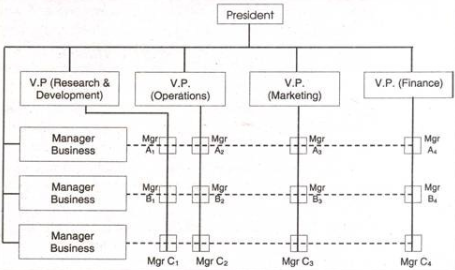
10. Explain the concept of Project Organization Structure.
Answer: A project organization structure facilitate establishment and distribution of authority for vertical coordination and control rather than horizontal relationships. Its work process may flow in any direction of work depending upon the distribution of talents and abilities in the organisation.
Project organisation is created when the project is big in size and subject to high standards of performance. A project organisation is solely responsive to the planning, design, development, production, evaluation, and support of a single system or product.
Conditions required for the creation of project organization are as follows:
(i) Project is of a technical nature, requiring utmost precision and accuracy e.g. Ship-building, designing and launching of satellites, aircraft manufacture etc.
(ii) Project completion requires huge cost.
(iii) Time factor is a critical factor; requiring project-completion within a limited prescribed time. Any delays in completion of project within time may tell upon the reputation of the organisation.
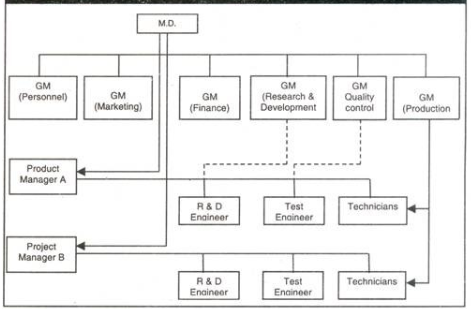
11. Explain the concept of Matrix Organization Culture.
Answer: Matrix Organization structure is a combination of two or more types of organization structure. It is designed to achieve specific results by using teams of specialists from different functional areas in the organisation.
The matrix organisation structure is complex but helps in achieving the ultimate goal i.e. reaching higher productivity. It has various benefits. This type of structure is used in organisations which have diverse product lines and services.
It breaks the monotony and gives more flexibility to the organisation. Employees work with colleagues of different departments who have their expertise in different functions.
When different people from diverse departments work together, it helps solve problems in a more efficient way. It does lead to overall development of employees as each one is exposed to different functions apart from their core job.
Here employees are assigned a job or a project outside their own department for a relatively temporary period. These teams are made up of people with diverse expertise who have come together and formed a team to attain a specific goal.
Unit 4
Organizational Processes
- What do you mean by Organization Structure?
Answer: Organization Structure refers to the system of interrelated relationships that defines the flow of activities in an organization. These activities may include roles, rules and responsibilities.
2. What are the different elements of Organization Structure?
Answer: Organization Structure refers to the system of interrelated relationships that defines the flow of activities in an organization. These activities may include roles, rules and responsibilities. The following are the different elements of organization structure:
i) Departmentalisation: The grouping of various tasks, teams’ roles and responsibilities is known as departmentalization. Similar activities are grouped together under one department.
Ii) Chain of Command: Chain of Command refers the flow of authority of authority from top to bottom through the pre-defined structure of relationships arranged in the range of hierarchy of positions.
Iii) Work Specialisation: Work specialization means every employee is assigned specific roles and responsibilities as per their qualification, skills and experience. This enables an employee to perform only those activities which they specialize in.
Iv) Span of Control: Span of control refers to the number of employees to be managed by manager within an organization. A tall structure of an organization will indication a small span of control since very few employees will be under control. But in flat structure, the span of control will be more.
v) Centralisation and Decentralisation: Centralisation refers to concentration of authority in the hands of top officials. They are Suppose, to take all decisions. The other employees will not participate in decision making and thus will only follow orders coming from the top officials. A Decentralised organization allows employees to give inputs on big decisions taken by the organization.
3. What is Line Organization? Give an example of Line organization.
Answer: Line organization has only direct, vertical relationships between different levels in the firm. There is only line departments which are directly involved in accomplishing the primary goal of the organization. This type of structure is evident in Military Organization.
4. What do you mean by Staff Organization?
Answer: A position intended to provide expertise, advice and support for the line positions. The staff employees are employed only to assist the line members. They do not have any authority as regards decision making. They can only advice the line members, provide support as per their skills and knowledge.

5. Define Organization Culture.
Answer: Organizational culture refers to the common values, policies, practices observed by the organizational members as guidance in the organization activities.
6. What are the different types of Organization Culture?
Answer: Organizational culture refers to the common values, policies, practices observed by the organizational members as guidance in the organization activities. The different types of organizational culture that may be evident are:
- Normative Culture: In this, the norms and procedures of the organization are predefined and the rules and regulations are set as per the existing guidelines.
- Pragmatic Culture: In this, more emphasis is placed on the clients and the external parties. Customer satisfaction is the main motive of the employees in a pragmatic culture.
- Academy Culture: Here, organizations follow academy culture hire skilled individuals. The roles and responsibilities are delegated according to the back ground, educational qualification and work experience of the employees.
- Baseball team Culture: In this, the employees are considered as the most treasured possession of the organization. The employees are the true assets of the organization.
- Club Culture: Here, organizations follow a club culture and are very particular about the employees they recruit. The individuals are hired as per their specialization, educational qualification and interests.
- Fortress Culture: These are the organizations where the employees are not very sure about their career and longevity. Here, the employees are terminated if the organization is not performing well.
- Process Culture: In this, the employees adhere to the processes and procedures of the organization. Feedbacks and performance reviews do not matter much in such organizations.
7. What do you mean by Organization Change?
Answer: Organisational change means any change that occurs in the work environment. It may also refer to the alteration of structural relationships and roles of people in the organization. It is largely structural in nature. There are several ways to change an enterprise. Its technology can be changed; its people, its structure and other elements can be changed.
8. Discuss the process of Planned Change.
Answer: Organisational change means any change that occurs in the work environment. A common model for bringing change in people has three phase process:-
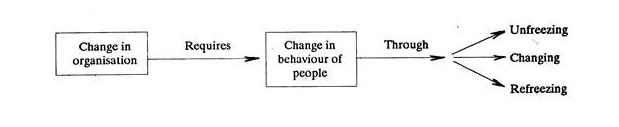
(1) Unfreezing:
The basic sense of unfreezing phase is that the individual is made to realize that his feelings, beliefs and behaviour are no longer relevant to the current situation in the organisation. Once convinced, people may change their behaviour. Reward for those willing to change and punishment for others may help in this matter.
(2) Changing:
Once an individual is convinced and ready to change then he learns to behave in new ways. He is initially provided with the model in which he is to recognise himself. Later he will accept the model and behave in the manner suggested by it. In another process (known as internalisation), the individual is placed in a situation where new behaviour is demanded of him if he is to operate successfully.
(3) Refreezing:
In this phase, an individual has to practice and experiment with the new method of behaviour and see that it effectively blends with his other behavioural attitudes.
9. Explain the factors involved in Organizational Change.
Answer: Organisational change means any change that occurs in the work environment. It may also refer to the alteration of structural relationships and roles of people in the organization. It is largely structural in nature.
Following are the factors in Organizational change are:
(A) External Pressures:
i. Change in Technology and Equipment:
Advancements in technology is the major cause (i.e., external pressure) of change. Each new technology results in the changes in the working of organization to meet and match the needs.
Ii. Market Situation:
A change in market situation refers to the rapidly changing of goals, needs and desires of consumers, suppliers, unions etc. If an organization has to survive, it has to cope with changes in market situations.
Iii. Social and Political Changes:
Organisational units literally have no control over social and political changes in the country. Relations between government and business or drive for social equality are some factors which may compel for organisational change.
(B) Internal Pressures (Pressures for Change from Within the Organisation):
i. Changes in the Managerial Personnel:
One of the most frequent reasons for major changes in the organisation is the change of executives at the top. No two managers have the same style, skills or managerial philosophies.
Ii. Deficiencies in the Existing Organization:
Many deficiencies are noticed in the organisations with the passage of time. A change is necessary to remove such deficiencies as lack of uniformity in the policies, obstacles in communication, any ambiguity etc.
10. Explain the concept of Project Organization Structure.
Answer: A project organization structure facilitate establishment and distribution of authority for vertical coordination and control rather than horizontal relationships. Its work process may flow in any direction of work depending upon the distribution of talents and abilities in the organisation.
Project organisation is created when the project is big in size and subject to high standards of performance. A project organisation is solely responsive to the planning, design, development, production, evaluation, and support of a single system or product.
Conditions required for the creation of project organization are as follows:
(i) Project is of a technical nature, requiring utmost precision and accuracy e.g. Ship-building, designing and launching of satellites, aircraft manufacture etc.
(ii) Project completion requires huge cost.
(iii) Time factor is a critical factor; requiring project-completion within a limited prescribed time. Any delays in completion of project within time may tell upon the reputation of the organisation.
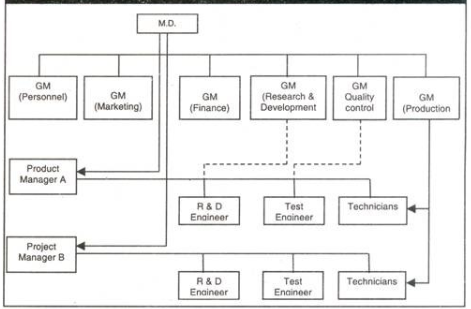
11. Explain the concept of Matrix Organization Culture.
Answer: Matrix Organization structure is a combination of two or more types of organization structure. It is designed to achieve specific results by using teams of specialists from different functional areas in the organisation.
The matrix organisation structure is complex but helps in achieving the ultimate goal i.e. reaching higher productivity. It has various benefits. This type of structure is used in organisations which have diverse product lines and services.
It breaks the monotony and gives more flexibility to the organisation. Employees work with colleagues of different departments who have their expertise in different functions.
When different people from diverse departments work together, it helps solve problems in a more efficient way. It does lead to overall development of employees as each one is exposed to different functions apart from their core job.
Here employees are assigned a job or a project outside their own department for a relatively temporary period. These teams are made up of people with diverse expertise who have come together and formed a team to attain a specific goal.