UNIT – 1
Introduction to Statistics
Q1) Define Statistics
A1) The term “statistics” is defined in two senses: - in singular and in Plural senses.
Firstly, in plural sense, statistics means systematic collection of numerical facts. Secondly in singular sense, the term statistics means the various methods used for collection, analysis and interpretation of numerical facts. It is described as statistical method. In our study we are more concerned with the second meaning of statistics.
Wallis and Roberts has defined Statistics as “Statistics is a body of methods for making wise decisions on the face of uncertainty.”
Edward N. Dubois has defined Statistics as “Statistics is a body of methods for obtaining and analyzing numerical data in order to make better decisions in an uncertain world.”
Q2) Discuss the scope of Statistics
A2) Statistics has become indispensable in every area today. There is hardly any field where statistics didn’t enter. Statistics is used right from the education till in aeronautical engineering. However, a few identified areas can be depicted as regards use of statistics:
Q3) State the functions of Statistics
A3) Statistics is a body of methods for obtaining and analyzing numerical data in order to make better decisions in an uncertain world The functions of statistics can be enumerated as under:
Q4) Explain the nature of Statistics.
A4) Statistics are numerical statements of facts capable of some meaningful analysis and interpretation, and in singular sense, it relates to the collection, classification, presentation and interpretation of numerical data. It is the science of data collection and analysis.
The nature of statistics can be enumerated as under:
Q5) Enumerate the advantages and disadvantages of Statistics.
A5) Statistics are numerical statements of facts capable of some meaningful analysis and interpretation, and in singular sense, it relates to the collection, classification, presentation and interpretation of numerical data. It is the science of data collection and analysis. The advantages or importance of Statistics can be identified as under:
Besides various advantages, certain disadvantages are also identified which are as under:
Q6) Write short note on distrust of statistics.
A6) The authenticity of statistical report fully depends on the statistical investigator who collects and compiles the data. It on his discretion how much with integrity he has done the survey without room for biasness. Many statisticians present the facts with wrong data due to not maintaining integrity. Hence the validity and reliability of statistical data completely depends on the honesty of the statistical investigator. The person who is the statistician might be inexperienced, lack of knowledge or liar. Hence the data may be mishandled and the result would be disastrous. The statisticians should be expert and experienced which can help in producing relevant and authentic information. Just for instance, if in case of medicines which are meant for curing people, but if they are handled by inefficient persons, they may prove fatal to the patients.
We cannot say that the medicine is bad; it is the person who did handle the research and presented wrong reports. Similarly, if a child gets burnt, it’s not the child to blame but the person who was not careful in keeping hot bowl in proper place.
Q7) What do you mean by census and sample survey?
A7) A well-organized procedure of gathering, recording and analyzing information regarding the members of the population is called a census. Under method census each and every unit of the universe is included in the collection of data. Huge amount of finance, time and labor are required for gathering information. This method is useful to find out the ratio of male to female, the ratio of literate to illiterate people, the ratio of people living in urban areas to the people in rural areas.
The sample is a small segment considered for study which represents the standard of entire population. The selection of sample should give justifiable conclusion about the whole population. When the population size is very large and it is difficult to consider all members then sampling method is used. Under this method selection of appropriate representative sample is utmost important. On the basis of data collected from sample, conclusion is drawn for the whole population.
Q8) What are the different types of data?
A8) Data are the raw facts and figures collected for investigation purposes either field survey or published sources. There are two types of sources of data: Primary Data and Secondary data.
Primary data is the information collected through original or first-hand research. Primary data is more reliable and authenticate as the data is nor changed or altered by any human beings. Also, the data is not published yet. Primary data is gathered by any authorized organization, investigator, and enumerator.
According to Horace Secrist “Data which are gathered originally for a certain purpose are known as primary data.”
Secondary data are public information that has been collected by others. The data collected from primary research and used by other is referred as secondary data. The secondary data may be obtained from various sources like industry surveys, database and information system, etc.
According to Blair, “The data which are used in an investigation, but which have been gathered originally by someone else for some other purpose are known as secondary data.”
Q9) What do you mean by classification? What are its types?
A9) Classification of data is the process of arranging the data into homogenous groups according to their common characteristics. Raw data cannot be easily understood and not fit for analysis and interpretation. Therefore, arrangement of data helps the user in comparison and analysis. Example- population of a state can be grouped according to sex, age, etc
According to Prof. Secrist, “Classification is the process of arranging data into sequences according to their common characteristics or separating them into different related parts.”
The different types of classification are:
Ex- production of food grains are classified in different states in India
S.No | Name of states | Total food grains (000’ tones) |
1 | Andhra Pradesh | 1093.00 |
2 | Bihar | 12899.09 |
3 | Karnataka | 1834.70 |
4 | Punjab | 41289.00 |
5 | Orissa | 3600 |
2. Chronological classification – classification of data on the basis of time (like months, years, etc) of their occurrence are called chronological classification. This type of classification is suitable for data which takes place in course of time such as population, production, sales, etc.
Ex – profit of a company from 2001 to 2005
S.No | Year | Profits (in 000 Rs) |
1 | 2001 | 77 |
2 | 2002 | 88 |
3 | 2003 | 89 |
4 | 2004 | 94 |
5 | 2005 | 99 |
3. Qualitative classification – under this classification, the data are classified on the basis of some attributes or quality such as sex, color, literacy, honesty, intelligence, religion, etc. In this the attributes cannot be measured. This sort of classification is known as descriptive classification.
For example, Population can be divided on the basis of marital status as married or unmarried etc.
4. Quantitative classification – quantitative classification states that classification of data according to some characteristics that can be measured such as height, weight, income, sales, profit, etc.
Ex – students are classified according to weights
S.No | weight | No. of students |
1 | 30-40 | 77 |
2 | 40-50 | 60 |
3 | 50-60 | 50 |
4 | 60 - 70 | 20 |
5. Alphabetical classification – when data are arranged according to alphabetical order is called alphabetical classification
Ex – state wise classification of population in alphabetical order
S.No | Name of states | Population |
1 | Andhra Pradesh | 157 |
2 | Bihar | 150 |
3 | Karnataka | 200 |
4 | Punjab | 700 |
5 | Orissa | 450 |
Q10) What is tabulation? Explain the different parts of tabulation.
A10) Tabulation is a systematic & logical presentation of numeric data in rows and columns, to facilitate comparison and statistical analysis. The method of placing organized data in tabular form is known as tabulation. Tabulation simplifies complex data and facilitates comparison.
According to Prof. L.R Connor, “Table involves the orderly and systematic presentation of numerical data in a form designed to elucidate the problem under consideration”
Q11) Discuss the various types of Sampling Techniques.
A11) The sample is a small segment considered for study which represents the standard of entire population. The selection of sample should give justifiable conclusion about the whole population. When the population size is very large and it is difficult to consider all members then sampling method is used. Under this method selection of appropriate representative sample is utmost important. On the basis of data collected from sample, conclusion is drawn for the whole population.
Types of sampling method
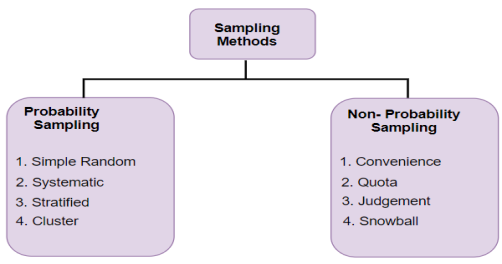
It is also called as random sampling. Random sampling is one of the simplest sampling techniques in which each sample have an equal chance of being chosen from the population. It is an unbiased representation of the population
Types of random sampling
2. Non random sampling
It is also called as non probability sampling. Non random sampling is one of the sampling techniques in which each sample does not have an equal chance of being chosen from the population. It is a biased representation of the population
Types of non-random sampling