Unit - 1
Unit - 1
Question Bank
- What are known the 7C’s of Communication?
The seven C’s of communication is a list of principles that you should ensure all of your communications adhere to. Their purpose is to help ensure that the person you’re communicating with hears what you’re trying to say. The seven C’s of communication include: clear, correct, complete, concrete, concise, considered and courteous.
1. Clear
There are several stages to clarity.
Firstly, it’s important to be clear about the purpose of the message you’re delivering. The recipient should be made aware of why they are receiving the message and what you’re trying to achieve by delivering it. If there are multiple goals, each should be laid out separately.
Secondly, it’s essential that the content of the communication is itself clear. The use of jargon must be avoided, use simple language and simple structures and always focus on the core points of your message.
2. Correct
It’s essential that both the factual information and the language and grammar you use are correct. If your audience spots errors in either, they will be distracted and your credibility will be greatly reduced. This will reduce the effectiveness of your communication.
3. Complete
Completeness is often one of the most important of the 7 Cs of communication.
When creating a message, it’s important to give the recipient all of the information they need to follow your line of reasoning and to reach the same conclusions you have. This level of detail will be different in different situations, and you should adjust your communications accordingly.
In addition, you should make things as easy as possible for the recipient. For example, if you are issuing a “call to action”, provide explicit guidance on that action. Increasingly it’s common to include things like hyperlinks in written communications or to attach FAQs, both of which help audiences access a complete set of information while also ensuring that core communications focus on core messages.
4. Concrete
When shaping your communication, you must ensure that you are specific and that the logic and messages that you’re using fit together, build on each other and support each other. Your arguments should be based on solid facts and opinions from credible sources and you should share irrefutable data to support your argument.
It may be important to help bring the solid nature of what you’ve created to life for your audience through examples that show the relevance of your messages for them as individuals.
5. Concise
When communicating messages of this nature it’s important to stick to the point and keep your messages short and simple. If a message can be given in five words, don't make it ten. Don’t repeat your messages.
The more you say, the more risk there is of confusion. Avoid that risk by focusing solely on the key points you need to deliver.
6. Courteous
Not everyone knows how to use the 7 Cs of communication.
You can increase the effectiveness of your communications by being polite and showing your audience that you respect them. Your messages should be friendly, professional, considerate, respectful, open and honest.
To help ensure you are courteous, you should always use some empathy and consider your messages from the point of view of the audience.
7. Coherent
The last of the 7 Cs of communication is coherence. If your communications are not coherent they will not be effective. To help make sure your communications are coherent you should have a logical flow and your style, tone and language should be consistent throughout.
In addition to making sure that each correspondence that is issued is coherent within itself, you should also ensure consistency of message when delivering multiple communications.
2. What is communication? Why is it important?
Communication is the process of transferring information by means of speaking, reading, listening and writing. Although the act of communication is heavily dependent on these four skills, it goes beyond these and also incorporate non-verbal elements such as body language, expressions, sign language, electronically transmitted codes (Morse code etc.) etc. It is both an art and a science.
Although every individual communicates simply by being in the world, learning effective communication skills requires hard work and determination. Developing good verbal and body language skills involves learning and consciously using your skills to improve.
One must be thoroughly familiar with all styles of correspondence in order to facilitate effective communication. The form of communication intrinsically depends upon the purpose and the central idea of the message to be conveyed. For example, it is feasible to acquire information or provide information using a formal phone call or an email whereas while conveying bad news to a particular individual a face-to-face conversation is considered rather apt.
Communication can be formal or informal
- Formal communication: Formal Communication is the exchange of official information that flows along the different levels of the organizational hierarchy and conforms to the prescribed professional rules, policy, standards, processes and regulations of the organization.
- Informal communication: Informal Communication is the casual and unofficial form of communication wherein the information is exchanged spontaneously between two or more persons without conforming the prescribed official rules, processes, system, formalities and chain of command.
Communication serves four major important functions within any group or organization. These are:
- Control
- Motivation
- Emotional expression
- Information
Control
Communication serves a controlling function in a hierarchical structure. When a teacher has to control her students or a manager has to control his employees and ask them to perform the required tasks, controlling words and tone has to be used. This function is mostly applicable in a formal setting however there may be some exceptions (Parents and children).
Motivation
Proper communication can be used to motivate employees to perform well. Motivational communication includes praising people for a well-done job, inspiring them to do even better and pointing out where they are going wrong and helping them rectify their mistakes. Motivational speakers also use communication as a tool to inspire and influence people.
Emotional Expression
Communication is useful tool for showing a whole range of emotions such as frustrations, happiness, anger. Therefore, it provides for the emotional expression of feelings which can be understood and provided with proper feedback.
Information
Communication facilitates decision-making, by passing information from one party to another. News channels, newspapers, current affairs all provide information regarding the daily events taking place in the word, this keeping one well informed.
3. Explain the process of communication with its various components?
The process of communication can be easily understood from the following flowchart:
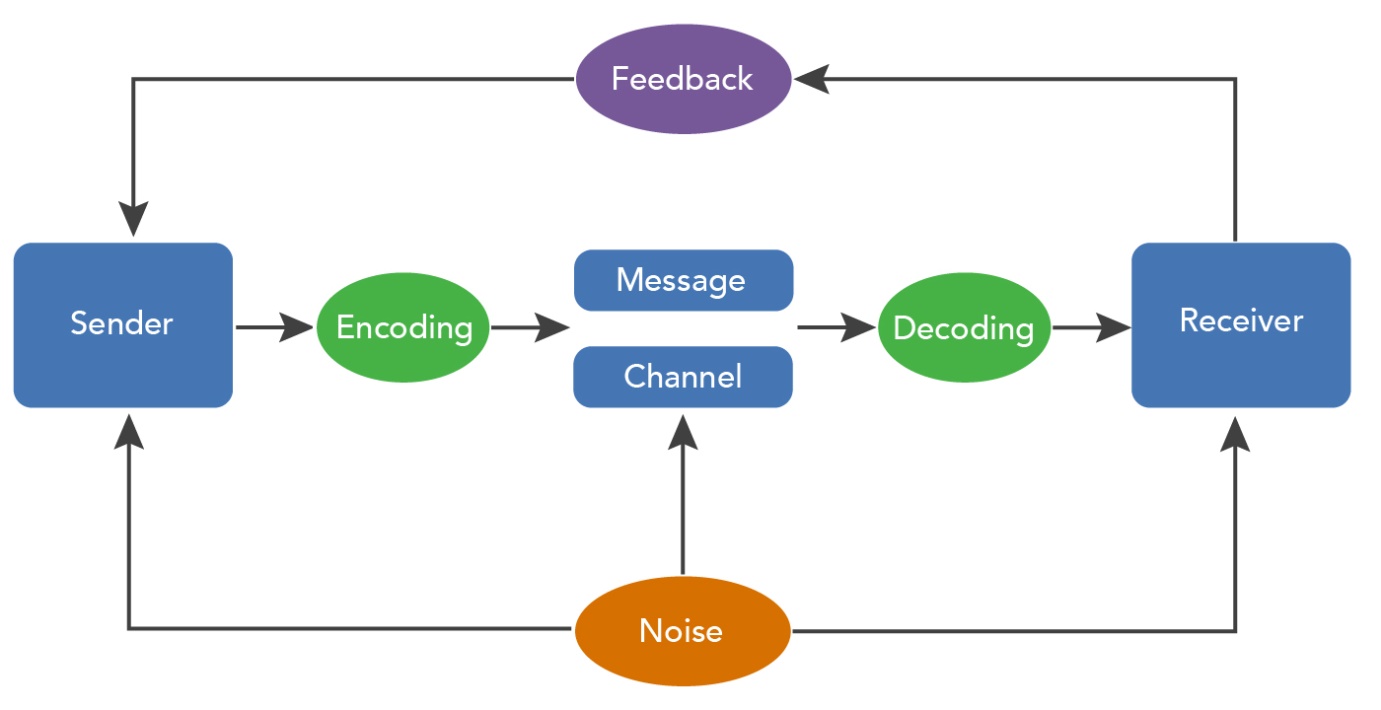
The communication process comprises of the following components:
- Sender: Sender is the individual who wants to send the message to the receiver. A sender makes effective use of words, symbols, pictures, graphs etc. available to him to construct the message. The views, background, approach, skills, competencies, and knowledge of the sender determine whether the message is approachable or not.
- Message: The message comprises of the information that is to be exchanged between the sender and the receiver. The central idea of the message must be clear and should be easily understood by the receiver.
- Channel: The medium of communication should be chosen with respect to the purpose of the message and the ability of the receiver to comprehend it. Hence, the sender must choose an appropriate medium for transmitting the message. The channel can be oral or written, the use of oral medium is preferred when the message is urgent and requires an immediate response, the written medium is preferred when the message is technical and there is a need for it to be documented.
- Receiver: The receiver is the individual to whom the message is addressed. The ability of the receiver to decode the message depends on the knowledge of the receiver, the reliance of the encoder, responsiveness of the receiver to the message.
- Feedback: After the receiver receives the message he tries to decode it, understand it and tried to provide a proper feedback to the sender, who then tries to interpret the feedback.
Communication requires the sender and the receiver to possess 4 basic skills, they are the main elements of the communication process, they include:
1-Listening
One should understand the main ideas of most speech in a standard dialect.
2-Speaking
One should be understood without difficulty by natives, and converse in a clear and participatory fashion.
One should be able to narrate and describe concrete and abstract topics using sustained, connected discourse.
3-Reading
One should easily follow the essential points of written text.
4-Writing
One should be able to address a variety of topics with significant precision and detail.
One should be able to organize writings with a sense of theoretical structure.
4. What is phonetic transcription? Give some examples.
Phonetic transcriptions are representations of the accurate pronunciation of a word. In the English language, phonetic transcriptions of words are essential, because the spelling of an English word may not necessarily tell you how you should pronounce it.
Phonetic transcriptions are typically written in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), in which each English sound has its own symbol.
For instance, the IPA-based phonetic transcription of the single syllable word HOME is hoʊm, and similarly the transcription of COME would be kʌm. It is noteworthy that even though in spelling, these words are similar as they both end in OME, their phonetic transcriptions are quite different, and therefore, they are pronounced differently.
In English the phonetic transcription of a word is usually written in between slashes, such as: /hoʊm/, /kʌm/.
Below are some examples of phonetic transcriptions of one and two syllable words:
That | ðæt | ||
You | Ju: | ||
Which | wɪtʃ | ||
Their | ðeəʳ | ||
About | əˈbaʊt | ||
Photo | ˈfoʊtoʊ | ||
Should | ʃʊd | ||
People | ˈpi:pəl | ||
Also | ˈɔ:lsoʊ | ||
Between | bɪˈtwi:n | ||
Many | ˈmeni | ||
Thicker | ˈθɪkəʳ | ||
Child | tʃaɪld | ||
Hear | hɪəʳ | ||
System | ˈsɪstəm | ||
Group | Gru:p | ||
Number | ˈnʌmbəʳ | ||
Again | əˈgen | ||
World | wɜ:ʳld | ||
Area | ˈeəriə | ||
Course | kɔ:ʳs | ||
Under | ˈʌndəʳ | ||
Problem | ˈprɒbləm | ||
Never | ˈnevəʳ | ||
Service | ˈsɜ:ʳvɪs | ||
Something | ˈsʌmθɪŋ | ||
Place | Pleɪs | ||
Point | pɔɪnt | ||
Provide | Prəˈvaɪd | ||
Large | lɑ:ʳdʒ | ||
Always | ˈɔ:lweɪz | ||
Next | Nekst | ||
Quick | Kwɪk | ||
Nervous | ˈnɜ:ʳvəs | ||
Local | ˈloʊkəl | ||
During | ˈdjʊərɪŋ | ||
Although | ɔ:lˈðoʊ | ||
Who | Hu: | ||
Rather | ˈræðəʳ | ||
Social | ˈsoʊʃəl | ||
Write | Raɪt | ||
Percent | pəʳ ˈsent | ||
Guest | Gest | ||
Both | Boʊθ | ||
Every | ˈevri | ||
Month | mʌnθ | ||
Head | Hed | ||
Question | ˈkwestʃən | ||
Power | ˈpaʊəʳ | ||
Change | tʃeɪndʒ | ||
Move | Mu:v | ||
Book | bʊk | ||
Young | jʌŋ | ||
National | ˈnæʃənəl | ||
Water | ˈwɔ:təʳ | ||
Yet | Jet | ||
Perhaps | pəʳ ˈhæps | ||
Until | ʌnˈtɪl | ||
Control | kənˈtroʊl | ||
Include | ɪnˈklu:d | ||
Believe | bɪˈli:v | ||
Allow | əˈlaʊ | ||
Stand | Stænd | ||
Idea | aɪˈdi:ə | ||
Result | rɪˈzʌlt | ||
Happen | ˈhæpən | ||
Friend | Frend | ||
Carry | ˈkæri | ||
Awful | ˈɔ:fəl | ||
Early | ˈɜ:ʳli | ||
View | Vju: | ||
Himself | hɪmˈself | ||
Xerox | ˈzɪərɒks | ||
Report | rɪˈpɔ:ʳt | ||
Law | lɔ: | ||
Ghost | Goʊst | ||
Modest | ˈmɒdɪst | ||
Person | ˈpɜ:ʳsən |
Once | wʌns |
Police | pəˈli:s |
Lose | Lu:z |
Major | ˈmeɪdʒəʳ |
Build | bɪld |
Language | ˈlæŋgwɪdʒ |
Else | Els |
Yeah | Jeə |
Centre | ˈsentəʳ |
Enough | ɪˈnʌf |
Calm | kɑ:m |
Colour | ˈkʌləʳ |
Lure | lʊəʳ |
Knife | Naɪf |
5. What is one-word substitution? Explain with help of examples.
Substitutions are useful to simplify sentences. Some phrases can easily be replaced by a single word containing the same meaning, thereby reducing the size of the structure of the sentence and simplifying it. They form an essential part of the vocabulary.
Some examples of one-word substitutes are listed below:
- To fall apart over time - Disintegrate
2. A copy of something that is identical - Facsimile
3. A smart and educated individual - Intellectual
4. Someone who is driven by passion to do crazy things - Zealot
5. Things to be done throughout the day - Schedule
6. To leave somewhere that is treacherous - Escape
7. A person who pushes an idea or belief system they do not believe – Hypocrite
8. Someone who sees everything negatively – Cynic
9. Something that is not understandable – Incomprehensible
10. A movie or play held during the daytime – Matinee
11. Time-frame between kids hitting puberty and being an adult – Adolescence
12. A person that is unknown – Anonymous
13. Someone that you work with – Colleague
Words for various fields of study:
Mapping of earth and its formation- Geography
Art related to ornate, good handwriting- Calligraphy
Scientific study of bodily diseases- Pathology
Study of birds- Ornithology
Study of celestial bodies- Astronomy
Study of collection of coins, tokens, paper money etc.- Numismatics
Study of earth and rocks- Geology
Study of election trends- Psephology
Study of flying aero planes- Aviation
Study of handwriting- Graphology
Study of hereditary, genes and variation in living organisms- Genetics
Study of human development- Anthropology
Study of languages - Philology
Study of living things- Biology
Study of religion- Theology
Study of science of insects- Entomology
Study of sound and sound waves - Acoustics
Study of the law of the flow of water and other liquids- Hydraulics
Study of the relation between the organism and their environment- Ecology
Study of various aspects of aging- Gerontology
The science of time order - Chronology
Study of religion- Theology
The science of human development- Anthropology
6. What are the major barriers to communication?
Communication is only complete if the message received by the recipient is interpreted in the same way as was intended by the sender. But due to the presence of a wide number of factors the message may be destroyed. These factors act as barriers to effective communication. It is essential to locate and eradicate these factors in order to allow free flowing communication.
Some of the barriers that block communication are listed below:
- Language Barriers – The linguistic ability of both the sender and receiver define their ability to effectively communicate. Especially when technical communication is concerned, the free flow of communication requires both parties to be sufficiently acquainted with the information that is being exchanged. For example, if two people from different backgrounds converse with the technical terminology of their own fields they are bound to misunderstand each other.
2. Psychological Barriers- The psychological state of the receiver plays a significant role when processing information. Factors such as personal issues, worries and stress might affect the receiver’s ability to decode information as they might be preoccupied with their own concerns.
Anger on the sender’s end is also an example of a psychological barrier, while angry one tends to convey thoughts one doesn’t mean only to regret later. Shyness, anxiety and depression may also act as barriers.
3. Physical Barriers- Physical barriers such as noise, physical distance between the speaker and receiver, conditions of the topography, poor lighting, speech impediment, hearing disability also affect effective communication.
4. Perceptual Barriers- The difference in how individuals perceive things also play a role in communication. People often find themselves unable to accept messages that go against their upbringing and values. Here even though the communication is effective, the feedback suffers. A similar situation might be perceived differently by different individuals and therefore might create disagreement.
5. Cultural Barriers- Different cultures possess different norms of social interactions and communication. Something deemed appropriate in one culture might not be the same in another. Body language and gestures play a vital role in non-verbal communication which might suffer due to cultural differences.
6. Inattention- One of the most common barriers towards effective communication is inattention, the receiver might simply be uninterested or might be daydreaming while the message is being conveyed to him.
7. How can communicational barriers be avoided?
Barriers can be easily avoided with a little effort and dedication. Below are some methods useful for avoiding these communication barriers:
- Clarity of words and purpose - Clarity is one of the most essential requirements of communication. While writing, it is necessary to write in good handwriting with proper grammar and sentence formation. While speaking one should use proper vocabulary and speak each word clearly and carefully along with proper inflections.
2. Active Listening- One should listen carefully what the speaker is saying in order to understand properly and provide feedback. One should be attentive while listening, ask open ended questions and should be able to summarize the information provided by the speaker.
3. Focus should be the other - While conversing one should maintain eye contact with the speaker as this shows the speaker that the message is being received by the listener. While speaking the focus should always be on the receiver.
4. Non-Verbal Communication- One’s body language often speaks as loud as his words. While communication one should show one’s reactions and interests through their body language.
5. Avoid Interruptions- It is essential to let the speaker finish talking before conveying one’s own thoughts. Interrupting is not only rude but also can be disadvantageous as one may not totally grasp the meaning of the speaker. If an interruption is absolutely necessary, one must use polite words like “pardon me” or “excuse me” instead of cutting the speaker in the middle of their thought process.
6. Controlling Emotions and Thinking before Speaking- It is said one must think twice before they speak. One must always consider the opinions and feelings of others before speaking their mind. One must also consider one’s own emotions and not speak out of anger or frustration. The process of communication should be logical rather than emotional.
7. The Message- The message one wishes to convey must always be clear and concise, there should be no doubts in one’s mind while speaking. The central idea of the message should always be conveyed completely and indubitably.
8. Eliminating Noise- One must eliminate all the outside forces that might disturb the conversation in order to maintain the flow of the communication process.
9. Feedback- One must pay attention to what the other person is saying and try to understand it as closely as possible to his intended meaning. This will allow him to provide proper responses.
8. What are International Phonetic Association (IPA) symbols in phonetics? What are the various phonetic symbols for vowels, consonants, and diphthongs?
Speech sounds, also known as Phonemes, is the smallest recurring sound in a sentence. Merriam Webster defines speech sound as “any one of the smallest recurrent recognizably same constituents of spoken language produced by movement or movement and configuration of a varying number of the organs of speech in an act of ear-directed communication.”
The English language consists of 26 alphabets but there are 44 speech sounds (Phonemes) in the English language consisting of 20 vowel sounds and 24 consonant sounds.
Phonemes (speech sounds) are represented in writing by placing the letters used to represent the sound between two slashes, for example, the sound that you say at the beginning of the word pot is represented by /p/.
Speech Sounds can be classified into three types, viz. Consonants, Vowels and diphthongs.
- Consonants:
A consonant is a sound accompanied by voice, in which there is either a complete or partial obstruction which prevents the air from freely issuing from the mouth.
In words such as base, maze, bathe, rouge, bake, path, long the sounds at the end of the words are distinctive. These twenty-four sounds may occur initially, medially and finally.
Consonants are perhaps more important than vowels because even if we pronounce the consonants only, most English words would be easy to understand. Consonant form the bones, the skeleton of English words and give them their basic shape. Moreover, differences of accent are mainly the result of differences in the sound of vowels; if the consonants are imperfect there will be a great risk of misunderstanding.
There are many types of consonants such as Fricatives (s,z,f,v), Plosives (stop) consonants (p and b; t and d; k and g). Nasal (m,n), Lateral and Gliding consonants.
Below are all the consonants comprised in the English phonetic script by the International Phonetics Association (IPA)
Unvoiced consonants
pfθts ʃ ʧ k
peafreethingtreeseesheep cheesecoin
Voiced consonants
bvðdzʒ ʤ g
boatvideothisdogzootelevisionjokego
m n ŋ h w l rj
mouse now thing hope we love runyou
2. Vowels:
In ordinary speech, a vowel is a voiced sound in the pronunciation of which the air passes through the mouth in a continuous stream, there being no obstruction and no narrowing such as would produce audible friction. All English vowels are voiced. Vowels like consonants can also occur initially or finally.
The following list consists of some words with vowel speech sounds:
Feel, fill, tall, bull, fool, mile, bat, toil, cart, pear, poor, butter, pier.
The qualities of vowels depend upon the position of the tongue and lips. It is convenient to classify them according to the position of the main part of the tongue. The position of the tip has no great effect on vowel quality. The tip of the tongue is supposed to be touching or near the lower teeth.
- Front vowels are the vowels which are produced with the front of the tongue raised in the direction of the hard palate. Ex. Feed.
- Back vowels are the vowels which are produced with the back of the tongue raises in the direction of the soft palate. Ex. Food.
- The vowels which are intermediate between the front and the back vowels are known as central vowels. Ex. Bird.
Below are the vowels comprised in the English Phonetic script by the International Phonetics Association (IPA)
ɪi:ʊu:
Shipsheepbookshoot
eɜ:əɔ:
leftherteacherdoor
æʌɒɑ:
hatuponfar
3. Diphthongs:
A diphthong is a deliberate glide where speech organs start in the position of one vowel and move towards another. A diphthong constitutes one syllable though the ear perceives two separate syllables.
Every diphthong may be said to have a first element (the starting point) and a second element (in the direction of which the glide is made). Most of the length and stress associated with the glide is concentrated on the first element. The second element is only lightly sounded. All English diphthongs are falling diphthongs (decrescendo).
The diphthongs are equivalent in length to the long pure vowels and are subject to the same variations of quantity. They also reflect variations in different regional and social types of speech.
Diphthongs are represented in phonetic transcription by a sequence of two letters, the first showing the position of the organs of speech at the beginning of the glide and the second showing their position at the end. In the case of ‘closing diphthongs’ the second letter indicates the point towards which the glide is made, but that point is not necessarily reached, and such diphthongs sound quite correct if the organs of speech perform only part of the maximum permissible movement.
Below are the diphthongs comprised in the English Phonetic script by the International Phonetics Association (IPA)
eɪɔɪaɪ
waitcoinlike
eəɪəʊə
hairheretourist
əʊaʊ
Showmouth
9. What is phonetics? What are the types of phonetics in English?
No two persons speak exactly alike and the pronunciations differ greatly depending upon the locality and geography of the speaker. So how should one decide on a model? The English spoken by the native speakers of in south-east England, also known as Received Pronunciation (R.P) is often considered acceptable. Language starts with the ear. Therefore, one must first “hear” English and pay close attention to how different words sound.
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that deals with the study and classification of how humans make and perceive sounds. In other words, It is the study of the physiological production of speech sounds and how different sounds are used to form syllables, words and sentences.
Phonetics can be classified into three main branches:
- Articulatory Phonetics
Articulatory Phonetics describes how the movement of different vocal organs are used to produce different speech sounds. It deals with the physical aspects of speech production. The organs of speech comprise of the Tongue, Nasal cavity, Lips, Epiglottis, Teeth, Uvula, Soft palate, Vocal chords, Windpipe, and the Pharyngeal Cavity.
2. Acoustic Phonetics
Acoustic Phonetics deal with the acoustic properties of speech sounds. The variations in air pressure while speaking form an essential component of how sounds are made. Speech sounds can be divided into two major classes, the first, sounds that consist of periodic wave form i.e the fluctuations in air pressure are in regular intervals, and the second, sounds that consist of a non-regular wave from,
3. Auditory Phonetics
Auditory Phonetics deal with the study of the variation between what is said by the speaker and what is heard by the receiver. In other words, it is the study of how humans perceive sounds.
Like the English language, Phonetics also consists of consonants and vowels. A consonant is a sound in which there is either a complete or partial obstruction which prevents the air from issuing freely from the mouth. On the other hand, a vowel is a voiced sound in the pronunciation of which the air passes through the mouth in a continuous stream, there being no obstruction such as would produce friction.
10. What are homonyms? Give examples.
Homonyms are words that sound the same or spelled the same but may have completely different meanings. Homonyms are rarer than Homophones but they are also ever present in the English language.
Below are some examples of Homonyms:
Band: A musical group/ a ring
Bat: A Flying Mammal/ An object used to play baseball, cricket.
Address: to speak to/a location
Rose: A type of flower/ to go up
Right: correct / direction opposite of left
Pound: unit of weight / to beat
Quarry - a site for mining stone / to extract or obtain slowly
Ream - a pile of paper / to juice a citrus fruit
Ring - a band on a finger / something circular in shape
Right - correct / direction opposite of left
Rock - a genre of music / a stone
Rose - to have gotten up / a flower
Spring - a season / coiled metal
Stalk - a part of a plant / to follow or harass someone
Tender - gentle / offer of money
Tire - to grow fatigued / a part of a wheel
Well - in good health / a source for water in the ground
11. Explain the meaning of term Homophones with the help of examples.
Homophones can be defined as pairs of words which sound alike but have different meanings and different spellings. Homophones can be frequently found in the English language and although they might sound similar but their meanings can be completely different or even opposite.
Below are some examples of homophones:
Sell/cell: The former means to deliver something for money while the latter means a small compartment.
Hear/here: The former means to listen to something or someone will the latter describes a place.
Cent/Scent: The former is a unit of currency while the latter is smell.
Hour/our: The former is a unit of time while the latter is a possessive adverb.
See/Sea: The former means to watch while the latter implies a large water body
Below are some commonly used homophones in the English language:
Air / heir
Aisle / isle
Ante- / anti-
Eye / I
Bare / bear
Be / bee
Brake / break
Buy / by
Cereal / serial
Coarse /course
Dam / damn
Dear / deer
Die / dye
Fair / fare
Fir/ fur
Flour/ flower
For/ four
Hair/ hare
Heal/ heel
Hear/ here
Him/ hymn
Hole/ whole
Hour/ our
Idle/ idol
In/ inn
Knight / night
Knot/ not
Know/ no
Made/ maid
Mail/ male
Meat/ meet
Morning / mourning
None / nun
Oar/ or
One/ won
Pair/ pear
Peace / piece
Plain/ plane
Poor/ pour
Pray/ prey
Principal / principle
Profit/ prophet
Real/ reel
Right/ write
Root/ route
Sail/ sale
Sea/ see
Seam/ seem
Sight/ site
Sew/ so
Shore/ sure
Sole/ soul
Some/ sum
Son/ sun
Stair/ stare
Stationary / stationery
Steal/ steel
Suite/ sweet
Tail / tale
Their/ there
To / too
Toe / tow
Waist / waste
Wait / weight
Way / weigh
Weak / week
Wear / where
12. Give some examples of Greek and Latin root words in the English language.
English is part of the German branch of the family of Indo-European language, so why is it so influenced in Latin and Greek? Although the origin of the English languages was introduced in England at the beginning of the 5th century by people from Denmark and Germany, the language was not entirely different from what we speak today.
When the Normans, a number of French Catholics, invaded the British islands in 1066, they came with their two languages: Latin and French. Because they were a ruling party long after the invasion, English became the language of the weak, effectively forcing English speakers to accept Latin and French words in their own language to match. Since the Renaissance began, nearly 500 years later, many Latin words, as well as those of the Greeks, were included to make English a more '' learned 'language because of the Renaissance's emphasis on classics.
- Abacus:
Abacus is derived from the Greek word - abax, meaning "sand tray."
- Allegory:
Allegory is derived from Greek - allos meaning "other" and agora meaning gathering place (especially the market). Eventually words join and are linked to the verb to speak of one thing and another to mean another.
- Apricot:
The term comes from the French - abricot - and it was a bit confusing until the fifteenth century - it does not have a single simple etymology, but rather a mixture of many theories under consideration. But all these roads lead to Rome, from where that name - and fruit - began to spread throughout Europe.
- Addictive:
Slaves agreed to allow Roman soldiers to pay for a concert in battle they were considered addicted to. Finally, a person who was addicted to anything called addiction.
- Alarm:
From Italian, "All'arme" - "To arms!"
- Alcohol:
Alcohol is taken from an Arabic al-kuhl, which has meant that there is a very good antimony powder used for eye makeup. It voiced the idea of something so elegant and smooth, so the Arabic alchemists give the name of al-khul which brings in any insubstantial powder obtained by slow release (a direct conversion of a solid base into a vapor, or process of return), and thus for all computers available through the sanitization process.
- Algebra:
The name means "the science of equations" in English comes from an article by one of al-Khowarizmi's (see "algorithm"), "Ab his AL-JAHR w'almuqaBAlah", meaning, "The Science of Transportation and Sanitation/ Cancellation."
- Algorithm:
The name means "rules of computing" in English, which is based on al-Khowarizmi (Try saying it soon), an Arabic mathematician who lives around A.D. 825 who completed the best known numerical work using Arabic numerals.
- Appendix:
In Latin it means "the hanging part." The human supplement hangs at the end of a large stomach; appendices given at the end of the book.
- Assassin:
Assassin from the old Arabic word "hashshshin," means "person who loves hash," that is, marijuana. Earlier it was referring to a group of heroes who would smoke before the war.
- Asthma:
Latin for asthma, "asthma," meaning "asthma" and "hypertension." The Latin word is derived from the Greek that feels the same.
- Avocado:
Avocado from "awaguatl," the original American testicle name. The Spaniards got the word and used to refer to what we now call avocado.
- Ballot:
Ballot, an Italian word meaning "small ball or pebble or stone." Italian citizens voted by placing a small stone or ball in one of the many boxes.
- Barbarian:
Barbarian from "barbaroi" in Greek, meaning "babblers”.
- Bead:
Bead from the Old English "gebed," which means, "prayer."
- Beserk:
Beserk mainly comes from the Old Icelandic "berserkr," meaning "bear shirt."
- Biscuit:
Biscuit from mediaeval French 'Bis + cuit' which means 'double cooked'
- Boulevard:
Boulevard from (French) Boulevard; and Bulwark
- Bucolic:
From the Greek "boukolos," meaning "shepherd," from "bous," meaning "ox."
- Bulimia:
Bulimia comes from the Greek "bous" meaning "ox" and "limos," which means "starvation," probably because a person with Bulimia is hungry for beef.
- Cab:
Old Italian terminology for goat (cabra in Spanish).
- Calculate:
The calculation comes from calculus, the Latin word pebble.
- Canter: (Spanish) Singing
From the Latin "Cantare," which means, "to sing often." Latin "Canere" simply means "to sing."
- Carnival:
Literal meaning: "Flesh, farewell." The end of "val" does not appear in the Latin "Vale." The modern Italian carnevale comes from the Old Italian "carnelevare"; levare = raise, place, remove. ) where people used to fast.
- Catharsis:
In Early Modern English, it is used in the sense of "cleaning." The concept of this name was still used as recently as 1803.
- Candidate:
From the Latin Candidus a word that means, "bright, shining, white, white." The ancient Roman members who were elected to this position wore bright white hats. The same name also spelled out the "firm", who are often not elected.
- Casarse: (Spanish, to marry)
From "casa," which means "house"; so is the English phrase, "to wrap."
- Cell:
Originally meant a monastery. It was Robert Hooke, who invented the first telescope. His first guess was the cork stem, which was made up of small columns. To him, the tiny fractions were like the little monasteries in which they lived, known as cells. Therefore, he called these microscopic building blocks "cells".
- Chapel:
From the Cape "Italian" Capella, since the original Chapel was where the cape ("capella") of the St. Martin of Tour was kept.
- Vulture and Chasm:
From the Greek "chainein," which means, "to soften"; So chaos was "just the beginning of the abyss" without the known universe we know.
- Champion; and Campus:
Check out Kampf
- Charlatan:
From the Spanish "charlar” for discussion /to chat.
- Cheers:
From the Greek "Kara" for "face," with Latin "Cara," and the French French "Chiere". So "Take courage," it means, "Put on a happy face."
- Chocolate:
It comes from the Spanish word for the same name, which came from the Nahuatl word (Aztecs language) "tchocoatl."
- Cider:
It comes from the Greek Greek sycamore, which came from an ancient Hebrew shekel, which means "any alcoholic beverage other than wine made to ferment fruit juice."
- Claim:
From the Latin "clamor", which is a judicial or public appeal raised on the discovery of sin.
- Conejo: (Spain) Rabbit
This Spanish word, meaning "rabbit," comes from the Latin word cuniculus, itself, which was taken in a letter from a previous Iberian name - according to Pliny the Elder - referring to both the animal and the scroll - and, by extension, any basement or trench. For its part, the name rabbit is a Flemish origin, and was originally used for small animals. The word used to refer to an old animal - in Flemish and Old English - was "cony" or "coney," which is derived from the cuniculus.
- Coward:
From Old French "coe" which means "tail." The OED adds, "The exact indication of the tail is uncertain: it may be an animal that 'turns tail' on a plane, or a practice in frightened animals to draw the tail between the hind legs: cf. The use of Heraldic in theory B 2. It is noteworthy that in the Old French version of Reynard the Fox , Coart is the name of a hare: this may be a descriptive adjective with regard to its zeal; it is closed, and that the word is then transferred to 'the heart of a hare.'
- Companion: Compañero (Spanish); Copain (French) Partner
From the Latin "Companionem," which was, "breadwinner" - "Con" (also) and "Pan" (bread) - your "partner" may have been someone to break bread with. "Look again to the Lord and take care of it.
- Cravate (French); Krawatte (German); Corbata (Spanish) Tie:
The names "Krawatte" (German), "cravate" (French) and "corbata" (Spanish), which all mean "human" tie, first appeared in the Napoleonic Wars when French troops entered the Crotia region, which, at that time, were part of the Holy Roman Empire. Evidently the Croatians were so capable of removing the German Habsburg yoke that they showed the victorious French troops a bouquet of flowers and ran to them and bound the scarlet threads in their uniforms as a gesture of goodwill. From them the name "Croat" or its variants appear to be attached to certain parts of Continental Europe.
- Cretin:
From the French "Crétin", which originally meant "Christian."
- The cup:
See Kopf
- Currant:
From the Corinthians
- Curfew:
From the French "couvrir feu," literally, "Cover the Fire."
- Daisy:
From "Eye of the Day." George Eddington writes, "Not special in itself, but Mata Hari also means" Eye of the day, "the young woman took the name because she lived in the Dutch East Indies and heard the natives so much in the sun. "
- Debonair:
French "good spirit." In the Middle Ages, people's lives were judged in part by the way they smiled. The person giving out “a good spirit” was viewed as a healthier and happier person.
- Deer:
From the Old English "deor," which means "animal."
- Demon: (German and English)
From the Greek "Daimon" this supernatural force is somewhere between humans and gods, without undesirable touch. An example would be the daimon of Socrates. The daimonans had a genius that did not conform to our modern ideas of good or evil: it was a natural force that could give clues about the circumstances and the critical actions.
- Denim:
The heavy cloth used for jeans was originally made in Nimes, France, as well as in Genoa, Italy (see jean). It was renamed Serge di Nimes - later reduced to di Nimes, which became denim.
- Derive:
From the Latin "De Rivus," "From the broadcast."
- Deutsch: (German by German)
"Deutsch" comes from the Old German word "diutisc" which means "human language" (as opposed to Latin). There are uncertain hints of the "Germanic" origins as the Celtic "Angry Men" or Old High German "Greedy Men"!
- Dexterity:
From the Latin "dexter," meaning "right" (in the left sense).
- Dibbs:
It is suggested that this phrase is based on an old children's play called dibstones. The game, which was played with sheep knuckle-bones or gemstones, dates back to at least the 17th century (that's right, that's when the name started being written). The goal was to catch his opponent's stones, and when a stone was hit, the winner would call "Dibbs!" with the meaning "I want [stone]". It was recently used out of the game but with the same meaning, and there you have it. Interestingly, the use of this outside of the game was not recorded until 1932 in the US. (Lee Quinn)
- Elite:
From the Latin Latin, which means "to choose," from which we find a modern Spanish word that means the same, elegir.
- Escape:
In Latin, escape means "out of the cape." The ancient Romans often avoided arresting the runaway population.
- Essay:
The English noun phrase comes from the French verb "story", to try. The earliest scholars believed that their papers were a modest attempt to present their papers.
- Exchequer:
The Moors introduced Abacus in Europe to expand the Europeans, and monks distributed the device throughout Europe. In Britain, it was used but in its simplicity: they used a checkbox and letters such as checks (instead of using standard rods and beads) - and this gave the British version an "exchequer" to the "Chancellor" of the Exchequer.
- Faro: (Spanish) Lighthouse
An ancient island from Egypt, the Paroah Island, had a lighthouse.
Feo: (Spanish) Ugly
From the Latin "Foedus," "disgusting.”
13. What are some English words derived for Latin prefixes and suffixes?
English speakers today--or even people trying to find out English--can enjoy understanding a number of the derivatives, or parts of a word taken from other languages, like Latin and Greek. Since there are over 1,000,000 words within the English, it's impossible to memorize all of them. However, understanding some basic components of words and customary ones that are derivatives of the classical languages can assist you determine their meaning.
In some ways, a word is simply sort of a cake, made from different ingredients. You'll find out what a word means by watching its three parts. The root, or the foremost basic sort of the word that also has meaning, is what makes up the bottom of the word. Frequently something is going to be attached the start of a word to feature meaning, which is named a prefix. Suffixes are almost like prefixes, but instead come at the top of the word. For instance, if you study the word ''microbiology,'' you'll see it's composed of those three parts, all of Greek origin: a prefix, ''micro-'' (meaning ''small''); a root, ''bio'' (meaning ''life''); and a suffix, ''logy'' (meaning ''study of''). Understanding these parts can assist you determine that microbiology is that the ''study of small life forms.''
Many English words and word parts are often traced back to Latin and Greek. The subsequent table lists some common Latin roots.
Latin root Basic meaning Example words:
Latin root | Basic meaning | Example words |
-dict- | To say | Contradict, dictate, diction, edict, predict |
-duc- | To lead, bring, take | Deduce, produce, reduce |
-gress- | To walk | Digress, progress, transgress |
-ject- | To throw | Eject, inject, interject, project, reject, subject |
-pel- | To drive | Compel, dispel, impel, repel |
-pend- | To hang | Append, depend, impend, pendant, pendulum |
-port- | To carry | Comport, deport, export, import, report, support |
-scrib-, -script- | To write | Describe, description, prescribe, prescription, subscribe, subscription, transcribe, transcription |
-tract- | To pull, drag, draw | Attract, contract, detract, extract, protract, retract, traction |
-vert- | To turn | Convert, divert, invert, revert |
From the instance words within the above table, it's easy to ascertain how roots combine with prefixes to make new words. For instance , the basis -tract-, meaning “to pull,” can combine with variety of prefixes, including de- and re-. Detract means literally “to pull away” (de-, “away, off”) and retract means literally “to pull back” (re-, “again, back”). The subsequent table gives an inventory of Latin prefixes and their basic meanings.
Latin prefix | Basic meaning | Example words |
Co- | Together | Coauthor, coedit, coheir |
De- | Away, off; generally indicates reversal or removal in English | Deactivate, debone, defrost, decompress, deplane |
Dis- | Not, not any | Disbelief, discomfort, discredit, disrepair, disrespect |
Inter- | Between, among | International, interfaith, intertwine, intercellular, interject |
Non- | Not | Nonessential, nonmetallic, nonresident, nonviolence, nonskid, nonstop |
Post- | After | Postdate, postwar, postnasal, postnatal |
Pre- | Before | Preconceive, preexist, premeditate, predispose, prepossess, prepay |
Re- | Again; back, backward | Rearrange, rebuild, recall, remake, rerun, rewrite |
Sub- | Under | Submarine, subsoil, subway, subhuman, substandard |
Trans- | Across, beyond, through | Transatlantic, transpolar |
Words and word roots may also combine with suffixes. Here are examples/ instances of some important English suffixes that come from Latin:
Latin suffix | Basic meaning | Example words |
-able, -ible | Forms adjectives and means “capable or worthy of” | Likable, flexible |
-ation | Forms nouns from verbs | Creation, civilization, automation, speculation, information |
-fy, -ify | Forms verbs and means “to make or cause to become” | Purify, acidify, humidify |
-ment | Forms nouns from verbs | Entertainment, amazement, statement, banishment |
-ty, -ity | Forms nouns from adjectives | Subtlety, certainty, cruelty, frailty, loyalty, royalty; eccentricity, electricity, peculiarity, similarity, technicality |
14. Give some examples of words derived in English from Greek and Latin prefixes and suffixes.
Most of these combining/ interactive forms can be used as either prefixes or suffixes. Examples are presented to illustrate current usage.
Prefixes | Derived From: | Meaning | Example |
a-, ab- | Latin | Off, from, down, away | Abduct, avert |
a-, an- | Greek | Not, without, less | Abiotic, anaerobic |
Actin- | G. Aktis | a ray, beam, spoke | Actinomycete |
Ad- | Latin | To, attached to, | Adsorption |
Aer- | Greek | Air | Aerobic |
Amphi- | Greek | Both, about, around | Amphibian |
Ana- | Latin | Away, through, again | Analysis |
Andro- | Greek | Man, male | Androgens |
Angio- | Greek | a vessel, closed container | Angiospermae |
Anthropo- | Greek | Referring to man | Anthropology |
Ant-, anti- | Greek | Against, away, opposite | Antibiosis |
Ante- | Latin | Before | Anteroom |
Ap-, aph-, apo- | Latin | From, off, separate | Apogee |
Aqua- | Latin | Water | Aquatic |
Arche-, archeo- | Greek | Ancient, primitive | Archeology |
Arthri-, arthro- | G. Arthron | Joint, jointed | Arthritis |
Asco- | G. Askos | Bag, sack, bladder | Ascospore |
Aureo- | L. Aureus | Gold colored | Aureomycin |
Auto- | G. Autos | Self | Autoimmune |
Bi- | Latin | Two, twice, double | Bipolar, binocular |
Bio-, bios- | Greek | Related to life | Biology, biocidal |
Blasto- | G. Blastos | An embryonic layer or cell | Blastomere |
Brachy- | Greek | Short | Brachycephalic |
Brad-, brady- | Greek | Slow, slowness | Bradycardia |
Bry-, bryo- | G. Bryon | Moss, mossy | Bryophyte |
Calic-, calix- | Latin | Cuplike | Calyx |
Cani-, canis- | Latin | Dog | Canine |
Cardia- | G. Kardia | Heart | Cardiac |
Carn- | L. Carnis | Flesh | Carnivore |
Carp- | L. Carpalis | Wrist, bones | Carpel |
Cata- | Greek | Decomposition, degradation | Catabolism |
Cell- | L. Cella | Small room | Cellular |
Cephal- | Latin | Head | Cephalic |
Chloro- | G. Chloros | Green, containing chloride | Chlorophyll |
Chroma-, chromo- | Greek | Colored | Chromosome |
Chron-, chrono- | G. Chronos | Time | Chronometer |
Circum- | Latin | Around, near, about | Circumnavigate |
Coel- | G. Koilos | Hollow cavity, belly | Coelom |
Col-, com-, con- | Latin | With, together | Combine, collide |
Contra- | Latin | Against | Contradict |
Crypto- | G. Kryptos | Hidden | Cryptogamic |
Cyano- | G. Kyanos | Dark blue, blue-green | Cyanobacteria |
Cyst- | G. Kystis | Bladder | Cystitis |
Cyt-,cyte-,cyto- | G. Kytos | Cell, a hollow vessel | Cytology |
De- | Latin | Undoing, removal of, from | Dehydration |
Den-, dent- | L. Dens | Tooth | Dentition |
Dendro- | Greek | Tree | Dendrochronology |
Derm-, derma- | Greek | Skin, hide | Dermatitis |
Deut-, deutero- | Greek | Second, secondary | Deuterium |
Di- | Greek | Double, twice, two | Disaccharide |
Dia- | Greek | Through, across | Diameter |
Diplo- | Greek | Twofold, double | Diploid |
Dis- | Latin | Apart, away | Dissolve |
Dorm- | Latin | To sleep | Dormant, dormitory |
Drom-, drome- | Greek | a running, racing | Dromendary |
e-, ec- | Latin | Out, out of | Efferent |
Eco- | G. Oikos | House, environment | Ecology |
Ecto- | G. Ektos | Outside | Ectoderm |
En-, endo- | G. Endon | Within, internal | Endoskeleton |
Entero- | G. Enteron | Intestine | Enterocolitis |
Entomo- | G. Entoma | Insect | Entomology |
Eo-, eos- | Greek | The dawn | Eocene, Eohippus |
Epi- | Greek | Upon, above, top | Epidermis |
Erythro- | Greek | Red | Erythrocyte |
Eu- | Greek | Proper, true, good | Eukaryotic |
Ex- | Latin | Out, from | Excise |
Exo- | Greek | Outer, external | Exoskeleton |
Extra- | L. Exter | Outside of, beyond | Extracellular |
Flagell- | L. Flagrum | Whip, whiplike | Flagellum |
Fuc-, fuco- | G. Phyktos | Seaweed, algae, lichen | Fucoxanthin |
Gamo- | G. Gamos | Sexual union | Gamogenesis |
Gastero-,gastro- | G. Gaster | Stomach, belly | Gastroenteritis |
Geno- | L.gene | Origin, development | Genotype |
Ge-, geo- | Greek | Earth | Geology |
Glu-, glyco- | Greek | Sweet, sugar | Glucose, glycogen |
Gon-,goni-,gono- | Greek | Reproductive, sexual | Gonorrhea |
Gymn-, gymno- | G. Gymnos | Naked, bare | Gymnosperm |
Gyn-,gyne-,gyno- | Greek | Woman, female | Gynecology |
Halo- | G. Hals | Salt | Halophile |
Haplo- | G. Haploos | Single | Haploid |
Heme-, hemo- | G. Haimo | Blood | Hematologist |
Hemi- | Greek | Half | Hemisphere |
Hepta- | Greek | Seven | Heptanes |
Herb- | L. Herba | Pertaining to plants | Herbicide |
Hetero- | Greek | Different, other, unlike | Heterozygous |
Hex-, hexa- | Greek | Six | Hexagonal |
Hipp-, hippo- | G. Hippos | Horse | Hippodrome |
Histo- | G. Histos | Tissue | Histology |
Holo- | G. Holos | Whole, entire | Holoblastic |
Homeo, homo- | Greek | Same, similar, like | Homogeneous |
Hyal-, hyalo- | G. Hyalos | Glassy, transparent | Hyaloids |
Hydr-, hydro- | Greek | Pertaining to water | Hydrolysis |
Hyper- | Greek | Above, more, over | Hyperactive |
Hypo- | Greek | Below, less, under | Hypodermic |
Ichthy-,ichthyo- | Greek | Referring to fish | Ichthyology |
Inter- | Latin | Between | Intercellular |
Intra- | Latin | Within, inside | Intracellular |
Intro- | Latin | Inward, within | Introvert |
Iso- | Greek | Equal, same | Isotonic |
Kine- | Greek | Movement, moving | Kinetics |
Leuc-, leuk- | Greek | White | Leucocyte |
Lycan- | G. Lykos | Wolf | Lycanthropy |
Macro- | Greek | Large, big, long | Macromolecule |
Man-, manu- | Latin | Hand | Manual |
Mastig- | G. Mastigos | Whip | Mastigophora |
Meg-, mega- | Greek | Great, large | Megabyte |
Melan-,melano- | Greek | Black, dark | Melanin |
Mero- | G. Merus | Part, piece | Meroblast |
Mes-, meso- | G. Mesos | Middle, in between | Mesoderm |
Met-, meta- | Greek | Later, following, changed in position or form | Metamorphosis |
Micro- | G. Mikros | Small | Microbiology |
Milli- | Latin | a thousandth part | Millimeter |
Mio- | G. Meion | Less, smaller | Miocene |
Mito- | G. Mitos | Thread | Mitosis |
Mon-, mono- | Greek | One, single | Monocular |
Morph- | Greek | Shape, form | Morphology |
Mor-, mort- | Latin | Die, death, | Mortality |
Muc-, muco- | Latin | Consisting of many units | Multicellular |
Mus- | Latin | Mouse, as one running | Muscle |
Myco-, mykos- | Greek | Fungus, mushroom | Mycology |
Myo- | G. Mys | Muscle | Myoglobin |
Myxo- | Greek | Slime, mucus | Myxomycetes |
Nemato- | Greek | Thread, threadlike | Nematode |
Neuro- | Greek | Name | Nomenclature |
Ob- | Latin | Against | Obtuse |
Octa- | Greek | Eight | Octopus |
Olig-, oligo- | Greek | Few, small, less | Oligarchy |
Omni- | Latin | All, everywhere | Omnipotent |
Oo- | Greek | Pertaining to an egg | Oocyte |
Ophthalmo- | Greek | Referring to the eye | Ophthalmologist |
Opisth-,opistho- | Greek | Behind, backwards, back | Opisthobranchia |
Orni-, ornitho- | Greek | Bird | Ornithology |
Orth-, ortho- | Greek | Straight | Orthodontist |
Osteo- | Greek | Bone | Osteocyte |
Oto- | Greek | Referring to the ear | Otology |
Ova-,ovi-,ovul- | Latin | Egg | Ovary, oviduct |
Paleo- | Greek | Old, ancient | Paleontology |
Para- | Greek | Beside, near, beyond | Parasitism |
Path-, patho- | Greek | Disease, suffer | Pathogenic |
Ped-, pedi- | Latin | Foot | Pedicure |
Penna-, pinna- | Latin | Feather, feathery | Pinnate |
Pent-, penta- | Greek | Five | Pentagon |
Per- | Latin | Through | Pervade, peruse |
Peri- | Greek | Around, surrounding | Perimeter |
Pher- | Greek | Bearing, carrying, support | Pheromone |
Phil- philo- | Greek | Loving, attracted to | Philanthropy |
Phob- | Greek | Fear, fearing | Phobic |
Photo- | Greek | Pertaining to light | Photosynthesis |
Phyco- | Greek | Seaweed, algae | Phycology |
Phylo- | Greek | Tribe, race, related group | Phylogeny |
Phyto- | Greek | Pertaining to plants | Phytohormone |
Plasm-, plasma- | Greek | Formative substance | Plasmablasts |
Plati-, platy- | Greek | Flat | Platypus |
Pleio- pleo- | Greek | More, many | Pleiomorphic |
Pod-,poda-,podi- | Greek | Foot | Podiatrist |
Poly- | Greek | Many | Polyhedron |
Post- | Latin | After | Postnatal |
Pre- | Latin | Before | Prenatal |
Preter- | Latin | Beyond | Preterhuman |
Prim- | Latin | First | Primary |
Pro- | Greek | Before, on behalf of | Proboscis |
Pro- | Latin | Forward | Progressive |
Proto- | Greek | First, primary | Protozoa |
Pseudo- | Greek | False | Pseudopod |
Psilo- | Greek | Bare, mere | Psilopsida |
Pteri-, ptero- | Greek | Fern, feather | Pteridophyte |
Quadr-, quadri- | Latin | Four | Quadruped |
Radi- | Latin | Ray, spoke of wheel | Radial |
Re- | Latin | Back, again | Repeat |
Retro- | Latin | Backward | Retroactive |
Rhiz-, rhizo- | Greek | Pertaining to roots | Rhizoids |
Rhod-, rhodo- | Greek | a rose, red | Rhodopsin |
Rota- | Latin | Wheel | Rotate |
Sapr-, sapro- | Greek | Rotten, putrid, dead | Saprobe |
Sarc-, sarco- | Greek | Flesh, fleshy | Sarcoma |
Schiz-, schizo- | Greek | Split, splitting | Schizocoel |
Se- | Latin | Apart | Secede |
Semi- | Latin | Half | Semicircle |
Soma-, somato- | Greek | Body | Somatic |
Sperma-,spermato- | Greek | Seed | Spermatozoa |
Sporo- | Greek | Spore | Sporophyte |
Staphylo- | Greek | Bunch of grapes | Staphylococcus |
Stoma- | Greek | Mouth | Stomata |
Strepto- | Greek | Twisted, string of | Streptococcus |
Sub- | Latin | Below, under, smaller | Subapical |
Supra-, super- | Latin | Above, over | Supernova |
Sym-, syn- | Greek | Together, with | Synthesis |
Taxi-, taxo- | Greek | To make order, arrangement | Taxonomy |
Tel-,tele-,telo- | Greek | Distant, end | Telophase |
Terra-, terre- | Latin | Land, earth | Terrestrial |
Tetra- | Greek | Four | Tetrapod |
Therm-, thermo- | Greek | Heat | Thermometer |
Thigmo- | Greek | Touch | Thigmotaxis |
Trans- | Latin | Across, through, over | Transfer |
Tri- | Latin | Three | Triangle |
Tricho- | Greek | Hair | Trichocyst |
Triplo- | Latin | Triple | Triploid |
Troche-, trocho- | Greek | Wheel, hoop | Trochophore |
Tropho- | Greek | Nourishment | Trophoblast |
Ultra- | Latin | Beyond, exceedingly | Ultraconservative |
Uni- | Latin | Consisting of one | Unicellular |
Vice- | Latin | In place of | Vice-president |
Vid-, vis- | Latin | See | Vision |
Xen-, xeno- | Greek | Dry, desert | Xerophytes |
Zoo- | Greek | Animal, life | Zoology |
Zyg-, zygo- | Greek | To join together | Zygote |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Suffixes | Derived From: | Meaning | Example |
-biosis | Greek | Mode of living, way of life | Symbiosis |
-blast | Greek | Formative, embryonic | Mesoblast |
-chaeta-, -chete | Greek | a bristle | Polychaeta |
-chrome | Greek | Color | Mercurochrome |
-cidal, -cide | Latin | Killer, a killing | Insecticide |
-cocci, -coccus | Greek | Round, seed, kernel | Streptococcus |
-cyst | Greek | Pouch, sac | Trichocyst |
-dactyl | Greek | Finger | Pentadactyl |
-derm, -dermis | Greek | Skin, layer | Epidermis |
-elle, -ule, -la, -le, -let, -ole | Latin | Small, diminutive endings | Globule, piglet |
-emia | Greek | Blood disease | Anemia |
-fer | Latin | Bearer, producer, carry | Conifer, transfer |
-gamous, -gamy | Greek | Marriage, sexual fusion | Polygamy |
-gen, -geny | Greek | Origin, production | Progeny, hydrogen |
-genesis | Latin | Origin, development of | Embryogenesis |
-gony | Latin | Something produced | Cosmogony |
-graph | Greek | Drawing, writing | Chromatograph |
-hedral, -hedron | Greek | Side | Polyhedral |
-hydrate | Greek | Compound formed by union of water with other substance | Carbohydrate |
-ism | Greek | Act, practice or result of | Terrorism |
-ite | Latin | a division or part | Somite |
-itis | Greek | Inflammation or infection | Appendicitis |
-jugal, -jugate | Latin | To yoke, join together | Conjugate |
-logy | G. Logos | Science or study of | Biology |
-lysis, -lytic | Greek | Loosening, separation, splitting into smaller units | Photolysis |
-mer, -merous | G. Meros | a part, piece | Polymer |
-meter | G. Metron | a measurement | Diameter |
-morph | Greek | Form | Endomorph |
-mycin | Greek | Derived from a fungus | Aureomycin |
-nomy | Greek | Systematized knowledge of | Astronomy |
-oma | Greek | Timorous | Carcinoma |
-osis, -otic | Greek | Abnormal condition, disease | Neurosis |
-phage | Greek | Eater | Bacteriophage |
-phase | Greek | a stage or condition | Metaphase |
-phil, -phile | Greek | Fear, fearing | Hydrophobia |
-phor, -phore | Greek | Bearing, carrying, supporting | Sporangiophore |
-phyll | Greek | Leaf | Chlorophyll |
-phyta, -phyte | Greek | Plant | Epiphyte |
-plasm | Greek | Formative substance | Cytoplasm |
-plast | Greek | Organized particle, granule | Chloroplast |
-pod, -poda | Greek | Foot | Arthropod |
-some | Greek | Body | Chromosome |
-stasis | Greek | a stationary position | Homeostasis |
-stat, -static | Greek | Stationary, still | Hemostat |
-stomy | Greek | Opening into | Colostomy |
-therm | Greek | Heat | Homeotherm |
-thes, -thesis | Greek | Arrangement, in order | Hypothesis |
-tom, -tomy | Greek | Dividing, surgery | Lobotomy |
-trope, -tropic | Greek | Turning | Phototropic |
-vor, -vore | L. Vorare | Feeding | Carnivore |
15. What are synonyms? Explain with the help of examples.
Synonyms are words that carry a similar or same meaning to another word. Sometimes even though the synonym of a word has an identical meaning the word and the synonym may not be interchangeable. For example, "blow up" and "explode" have the same meaning, but "blow up" is informal (used more in speech) and "explode" is more formal (used more in writing and careful speech). Synonyms also provide variety to speech and writing.
Many words in the English language contain more than one synonym. Some examples of Synonyms:
Shallow - superficial
Stop – cease
Spontaneous - capricious
Gloomy – sad - unhappy
House - home - abode
Evil - bad - wicked
Garbage - trash - junk - waste
Present – gift – reward – award
Sniff – smell – inhale
Little – small – tiny
Under – below – beneath
Short list of synonyms in English, listed by the part of speech:
Nouns:
- Belly / stomach
- Children / kids
- Disaster / catastrophe
- Earth / soil
- Father / dad
- Happiness / joy
- Instinct / intuition/ understanding
- Mother / mom
- Present / gift
- Sunrise / dawn
Verbs:
- Answer / reply
- Beat / defeat
- Behave / act
- Begin / start
- Close / shut/ turn on/turn off
- Leave / exit
- Provide / supply/ distribution
- Select / choose
- Shout / yell
- Speak / talk
Adjectives:
- Big / large
- Complete / total/number
- Correct / right
- Crazy / mad
- Foolish / silly /fool/ stupid
- Happy / glad
- Hard / difficult
- Ill / sick
- Last / final
- Near / close
- Sad / unhappy
- Stable / steady/ strong
Adverbs:
- Abroad / overseas
- Almost / nearly/ about / approx.
- Bad / poorly
- Fast / quickly
- Intentionally / purposefully
- Out / outside
- Rarely / seldom/ not common
- Sometimes / occasionally/ periodically
- Surely / for sure/ definetly
- Very / highly / extremely/too much
Prepositions:
- Above / over/ more
- About / regarding / concerning
- Against / versus
- Below / beneath / under
- By / via
- Despite / in spite of
- In / into/ to
- Off / away
- Until / till
- With / including
Conjunctions:
- And / plus
- Because / since
- But / yet/for now
- If / provided
- Once / as soon as possible/ and
Interjections:
- Hello / hi
- Gee / gosh
- Goodness / goodness me / my goodness
- No / nope
- Oh Lord / oh good Lord
- Thanks / thank you
- Whoopee / yahoo / hooray
- Yes / yeah
16. What are antonyms? Give examples.
Antonyms are words that carry the opposite meaning to another word. They can be used to show contrast between two things or emphasize a point. Antonyms can be totally different words from their counterparts or can also be formed by adding prefixes to some words.
Below are some examples of antonyms that are commonly used in the English language:
Antonyms formed by changing entire words
Love – hate
Beginning – ending
Ugly – beautiful
Wild – tame
Extrovert – introvert
Antonyms formed by adding prefix –un
Acceptable - unacceptable
Able - unable
Do - undo
Certain – uncertain
Seen – Unseen
Antonyms formed by adding the prefix –in
Decent – indecent
Tolerant – intolerant
Human – inhuman
Curable – incurable
Expressible – inexpressible
Antonyms formed by adding the prefix –non
Sense – nonsense
Essential – nonessential
Flammable – non-flammable
Renewable – non-renewable
Entity – nonentity
Other prefixes used to form antonyms of words are –anti (Thesis - Antithesis), -ill (Literate – Illiterate), -mis (Informed – Misinformed), -dis (Assemble – Disassemble) etc.
Short list of antonyms in English, listed by the part of speech:
Nouns
- Day / night
- East / west
- The enemy / friend
- Failure / success
- Guest / host
- Health / disease
- Question / answer
- Speaker / listener
- Summer / winter
- Top / bottom/ up / down
Verbs
- Agree / disagree/accept
- Arrive / leave/ come / go
- Begin / end/ start
- Fall asleep / wakefulness/sleep
- Find / lose/ gain
- Lend / borrowing
- Love / hate
- Open / close/turn on /turn off
- Remember / forget
- Start / stop
Adjectives
- Is asleep / awake
- Beautiful / ugly /good/ bad
- Big / small
- Black / white
- Cheap / expensive
- Dead / alive
- It is dry / wet
- Easy / difficult
- Full / empty
- Good / bad
- Hot / cold
- Intelligent / stupid/you are smart
- Sad / happy/ exciting
- Sick / living healthy
- Thin / fat
Adverbs
- Always / never
- With anger / happily/ excitement
- Fast / slowly
- Here / there
- Inside / outside/ indoors/ outdoors
- Likely / unlikely/possible/ impossible
- Near / far
- Partly / fully
- Seemingly / actually/ visually
- Yesterday / tomorrow
Prepositions
- Above / below
- Against / for / because
- Before / after
- In / out/ indoors/ outdoors
- Like / unlike/ love / contrast
- On / off
- Plus / minus
- To / from
- Towards / away/remote
- With / without
Conjunctions
- And / or
- Therefore / nevertheless /or so
Interjections
- Bravo / boo
- Hello / goodbye
- Holy cow / duh
- Phew / oops
- Thanks / no thanks
- Yes / no
- Yippee / oh my/ oh
Unit - 1
Question Bank
- What are known the 7C’s of Communication?
The seven C’s of communication is a list of principles that you should ensure all of your communications adhere to. Their purpose is to help ensure that the person you’re communicating with hears what you’re trying to say. The seven C’s of communication include: clear, correct, complete, concrete, concise, considered and courteous.
1. Clear
There are several stages to clarity.
Firstly, it’s important to be clear about the purpose of the message you’re delivering. The recipient should be made aware of why they are receiving the message and what you’re trying to achieve by delivering it. If there are multiple goals, each should be laid out separately.
Secondly, it’s essential that the content of the communication is itself clear. The use of jargon must be avoided, use simple language and simple structures and always focus on the core points of your message.
2. Correct
It’s essential that both the factual information and the language and grammar you use are correct. If your audience spots errors in either, they will be distracted and your credibility will be greatly reduced. This will reduce the effectiveness of your communication.
3. Complete
Completeness is often one of the most important of the 7 Cs of communication.
When creating a message, it’s important to give the recipient all of the information they need to follow your line of reasoning and to reach the same conclusions you have. This level of detail will be different in different situations, and you should adjust your communications accordingly.
In addition, you should make things as easy as possible for the recipient. For example, if you are issuing a “call to action”, provide explicit guidance on that action. Increasingly it’s common to include things like hyperlinks in written communications or to attach FAQs, both of which help audiences access a complete set of information while also ensuring that core communications focus on core messages.
4. Concrete
When shaping your communication, you must ensure that you are specific and that the logic and messages that you’re using fit together, build on each other and support each other. Your arguments should be based on solid facts and opinions from credible sources and you should share irrefutable data to support your argument.
It may be important to help bring the solid nature of what you’ve created to life for your audience through examples that show the relevance of your messages for them as individuals.
5. Concise
When communicating messages of this nature it’s important to stick to the point and keep your messages short and simple. If a message can be given in five words, don't make it ten. Don’t repeat your messages.
The more you say, the more risk there is of confusion. Avoid that risk by focusing solely on the key points you need to deliver.
6. Courteous
Not everyone knows how to use the 7 Cs of communication.
You can increase the effectiveness of your communications by being polite and showing your audience that you respect them. Your messages should be friendly, professional, considerate, respectful, open and honest.
To help ensure you are courteous, you should always use some empathy and consider your messages from the point of view of the audience.
7. Coherent
The last of the 7 Cs of communication is coherence. If your communications are not coherent they will not be effective. To help make sure your communications are coherent you should have a logical flow and your style, tone and language should be consistent throughout.
In addition to making sure that each correspondence that is issued is coherent within itself, you should also ensure consistency of message when delivering multiple communications.
2. What is communication? Why is it important?
Communication is the process of transferring information by means of speaking, reading, listening and writing. Although the act of communication is heavily dependent on these four skills, it goes beyond these and also incorporate non-verbal elements such as body language, expressions, sign language, electronically transmitted codes (Morse code etc.) etc. It is both an art and a science.
Although every individual communicates simply by being in the world, learning effective communication skills requires hard work and determination. Developing good verbal and body language skills involves learning and consciously using your skills to improve.
One must be thoroughly familiar with all styles of correspondence in order to facilitate effective communication. The form of communication intrinsically depends upon the purpose and the central idea of the message to be conveyed. For example, it is feasible to acquire information or provide information using a formal phone call or an email whereas while conveying bad news to a particular individual a face-to-face conversation is considered rather apt.
Communication can be formal or informal
- Formal communication: Formal Communication is the exchange of official information that flows along the different levels of the organizational hierarchy and conforms to the prescribed professional rules, policy, standards, processes and regulations of the organization.
- Informal communication: Informal Communication is the casual and unofficial form of communication wherein the information is exchanged spontaneously between two or more persons without conforming the prescribed official rules, processes, system, formalities and chain of command.
Communication serves four major important functions within any group or organization. These are:
- Control
- Motivation
- Emotional expression
- Information
Control
Communication serves a controlling function in a hierarchical structure. When a teacher has to control her students or a manager has to control his employees and ask them to perform the required tasks, controlling words and tone has to be used. This function is mostly applicable in a formal setting however there may be some exceptions (Parents and children).
Motivation
Proper communication can be used to motivate employees to perform well. Motivational communication includes praising people for a well-done job, inspiring them to do even better and pointing out where they are going wrong and helping them rectify their mistakes. Motivational speakers also use communication as a tool to inspire and influence people.
Emotional Expression
Communication is useful tool for showing a whole range of emotions such as frustrations, happiness, anger. Therefore, it provides for the emotional expression of feelings which can be understood and provided with proper feedback.
Information
Communication facilitates decision-making, by passing information from one party to another. News channels, newspapers, current affairs all provide information regarding the daily events taking place in the word, this keeping one well informed.
3. Explain the process of communication with its various components?
The process of communication can be easily understood from the following flowchart:
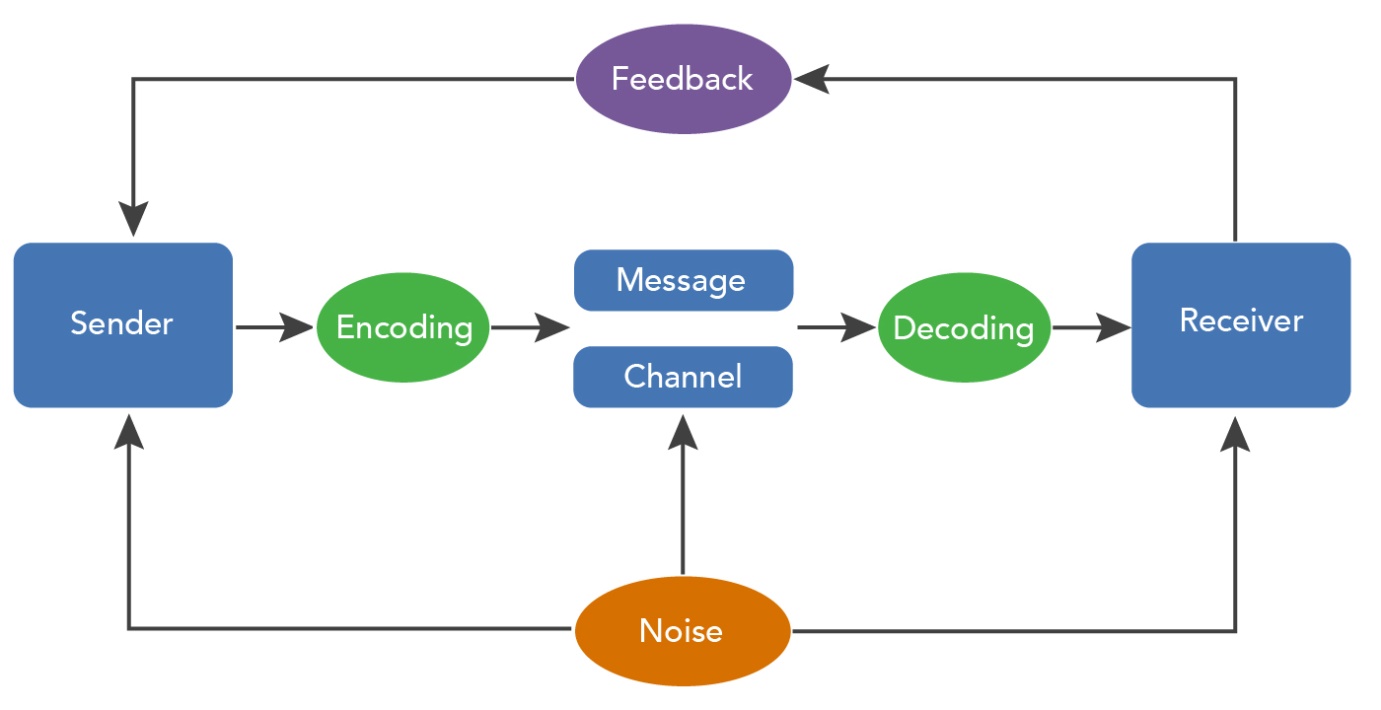
The communication process comprises of the following components:
- Sender: Sender is the individual who wants to send the message to the receiver. A sender makes effective use of words, symbols, pictures, graphs etc. available to him to construct the message. The views, background, approach, skills, competencies, and knowledge of the sender determine whether the message is approachable or not.
- Message: The message comprises of the information that is to be exchanged between the sender and the receiver. The central idea of the message must be clear and should be easily understood by the receiver.
- Channel: The medium of communication should be chosen with respect to the purpose of the message and the ability of the receiver to comprehend it. Hence, the sender must choose an appropriate medium for transmitting the message. The channel can be oral or written, the use of oral medium is preferred when the message is urgent and requires an immediate response, the written medium is preferred when the message is technical and there is a need for it to be documented.
- Receiver: The receiver is the individual to whom the message is addressed. The ability of the receiver to decode the message depends on the knowledge of the receiver, the reliance of the encoder, responsiveness of the receiver to the message.
- Feedback: After the receiver receives the message he tries to decode it, understand it and tried to provide a proper feedback to the sender, who then tries to interpret the feedback.
Communication requires the sender and the receiver to possess 4 basic skills, they are the main elements of the communication process, they include:
1-Listening
One should understand the main ideas of most speech in a standard dialect.
2-Speaking
One should be understood without difficulty by natives, and converse in a clear and participatory fashion.
One should be able to narrate and describe concrete and abstract topics using sustained, connected discourse.
3-Reading
One should easily follow the essential points of written text.
4-Writing
One should be able to address a variety of topics with significant precision and detail.
One should be able to organize writings with a sense of theoretical structure.
4. What is phonetic transcription? Give some examples.
Phonetic transcriptions are representations of the accurate pronunciation of a word. In the English language, phonetic transcriptions of words are essential, because the spelling of an English word may not necessarily tell you how you should pronounce it.
Phonetic transcriptions are typically written in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), in which each English sound has its own symbol.
For instance, the IPA-based phonetic transcription of the single syllable word HOME is hoʊm, and similarly the transcription of COME would be kʌm. It is noteworthy that even though in spelling, these words are similar as they both end in OME, their phonetic transcriptions are quite different, and therefore, they are pronounced differently.
In English the phonetic transcription of a word is usually written in between slashes, such as: /hoʊm/, /kʌm/.
Below are some examples of phonetic transcriptions of one and two syllable words:
That | ðæt | ||
You | Ju: | ||
Which | wɪtʃ | ||
Their | ðeəʳ | ||
About | əˈbaʊt | ||
Photo | ˈfoʊtoʊ | ||
Should | ʃʊd | ||
People | ˈpi:pəl | ||
Also | ˈɔ:lsoʊ | ||
Between | bɪˈtwi:n | ||
Many | ˈmeni | ||
Thicker | ˈθɪkəʳ | ||
Child | tʃaɪld | ||
Hear | hɪəʳ | ||
System | ˈsɪstəm | ||
Group | Gru:p | ||
Number | ˈnʌmbəʳ | ||
Again | əˈgen | ||
World | wɜ:ʳld | ||
Area | ˈeəriə | ||
Course | kɔ:ʳs | ||
Under | ˈʌndəʳ | ||
Problem | ˈprɒbləm | ||
Never | ˈnevəʳ | ||
Service | ˈsɜ:ʳvɪs | ||
Something | ˈsʌmθɪŋ | ||
Place | Pleɪs | ||
Point | pɔɪnt | ||
Provide | Prəˈvaɪd | ||
Large | lɑ:ʳdʒ | ||
Always | ˈɔ:lweɪz | ||
Next | Nekst | ||
Quick | Kwɪk | ||
Nervous | ˈnɜ:ʳvəs | ||
Local | ˈloʊkəl | ||
During | ˈdjʊərɪŋ | ||
Although | ɔ:lˈðoʊ | ||
Who | Hu: | ||
Rather | ˈræðəʳ | ||
Social | ˈsoʊʃəl | ||
Write | Raɪt | ||
Percent | pəʳ ˈsent | ||
Guest | Gest | ||
Both | Boʊθ | ||
Every | ˈevri | ||
Month | mʌnθ | ||
Head | Hed | ||
Question | ˈkwestʃən | ||
Power | ˈpaʊəʳ | ||
Change | tʃeɪndʒ | ||
Move | Mu:v | ||
Book | bʊk | ||
Young | jʌŋ | ||
National | ˈnæʃənəl | ||
Water | ˈwɔ:təʳ | ||
Yet | Jet | ||
Perhaps | pəʳ ˈhæps | ||
Until | ʌnˈtɪl | ||
Control | kənˈtroʊl | ||
Include | ɪnˈklu:d | ||
Believe | bɪˈli:v | ||
Allow | əˈlaʊ | ||
Stand | Stænd | ||
Idea | aɪˈdi:ə | ||
Result | rɪˈzʌlt | ||
Happen | ˈhæpən | ||
Friend | Frend | ||
Carry | ˈkæri | ||
Awful | ˈɔ:fəl | ||
Early | ˈɜ:ʳli | ||
View | Vju: | ||
Himself | hɪmˈself | ||
Xerox | ˈzɪərɒks | ||
Report | rɪˈpɔ:ʳt | ||
Law | lɔ: | ||
Ghost | Goʊst | ||
Modest | ˈmɒdɪst | ||
Person | ˈpɜ:ʳsən |
Once | wʌns |
Police | pəˈli:s |
Lose | Lu:z |
Major | ˈmeɪdʒəʳ |
Build | bɪld |
Language | ˈlæŋgwɪdʒ |
Else | Els |
Yeah | Jeə |
Centre | ˈsentəʳ |
Enough | ɪˈnʌf |
Calm | kɑ:m |
Colour | ˈkʌləʳ |
Lure | lʊəʳ |
Knife | Naɪf |
5. What is one-word substitution? Explain with help of examples.
Substitutions are useful to simplify sentences. Some phrases can easily be replaced by a single word containing the same meaning, thereby reducing the size of the structure of the sentence and simplifying it. They form an essential part of the vocabulary.
Some examples of one-word substitutes are listed below:
- To fall apart over time - Disintegrate
2. A copy of something that is identical - Facsimile
3. A smart and educated individual - Intellectual
4. Someone who is driven by passion to do crazy things - Zealot
5. Things to be done throughout the day - Schedule
6. To leave somewhere that is treacherous - Escape
7. A person who pushes an idea or belief system they do not believe – Hypocrite
8. Someone who sees everything negatively – Cynic
9. Something that is not understandable – Incomprehensible
10. A movie or play held during the daytime – Matinee
11. Time-frame between kids hitting puberty and being an adult – Adolescence
12. A person that is unknown – Anonymous
13. Someone that you work with – Colleague
Words for various fields of study:
Mapping of earth and its formation- Geography
Art related to ornate, good handwriting- Calligraphy
Scientific study of bodily diseases- Pathology
Study of birds- Ornithology
Study of celestial bodies- Astronomy
Study of collection of coins, tokens, paper money etc.- Numismatics
Study of earth and rocks- Geology
Study of election trends- Psephology
Study of flying aero planes- Aviation
Study of handwriting- Graphology
Study of hereditary, genes and variation in living organisms- Genetics
Study of human development- Anthropology
Study of languages - Philology
Study of living things- Biology
Study of religion- Theology
Study of science of insects- Entomology
Study of sound and sound waves - Acoustics
Study of the law of the flow of water and other liquids- Hydraulics
Study of the relation between the organism and their environment- Ecology
Study of various aspects of aging- Gerontology
The science of time order - Chronology
Study of religion- Theology
The science of human development- Anthropology
6. What are the major barriers to communication?
Communication is only complete if the message received by the recipient is interpreted in the same way as was intended by the sender. But due to the presence of a wide number of factors the message may be destroyed. These factors act as barriers to effective communication. It is essential to locate and eradicate these factors in order to allow free flowing communication.
Some of the barriers that block communication are listed below:
- Language Barriers – The linguistic ability of both the sender and receiver define their ability to effectively communicate. Especially when technical communication is concerned, the free flow of communication requires both parties to be sufficiently acquainted with the information that is being exchanged. For example, if two people from different backgrounds converse with the technical terminology of their own fields they are bound to misunderstand each other.
2. Psychological Barriers- The psychological state of the receiver plays a significant role when processing information. Factors such as personal issues, worries and stress might affect the receiver’s ability to decode information as they might be preoccupied with their own concerns.
Anger on the sender’s end is also an example of a psychological barrier, while angry one tends to convey thoughts one doesn’t mean only to regret later. Shyness, anxiety and depression may also act as barriers.
3. Physical Barriers- Physical barriers such as noise, physical distance between the speaker and receiver, conditions of the topography, poor lighting, speech impediment, hearing disability also affect effective communication.
4. Perceptual Barriers- The difference in how individuals perceive things also play a role in communication. People often find themselves unable to accept messages that go against their upbringing and values. Here even though the communication is effective, the feedback suffers. A similar situation might be perceived differently by different individuals and therefore might create disagreement.
5. Cultural Barriers- Different cultures possess different norms of social interactions and communication. Something deemed appropriate in one culture might not be the same in another. Body language and gestures play a vital role in non-verbal communication which might suffer due to cultural differences.
6. Inattention- One of the most common barriers towards effective communication is inattention, the receiver might simply be uninterested or might be daydreaming while the message is being conveyed to him.
7. How can communicational barriers be avoided?
Barriers can be easily avoided with a little effort and dedication. Below are some methods useful for avoiding these communication barriers:
- Clarity of words and purpose - Clarity is one of the most essential requirements of communication. While writing, it is necessary to write in good handwriting with proper grammar and sentence formation. While speaking one should use proper vocabulary and speak each word clearly and carefully along with proper inflections.
2. Active Listening- One should listen carefully what the speaker is saying in order to understand properly and provide feedback. One should be attentive while listening, ask open ended questions and should be able to summarize the information provided by the speaker.
3. Focus should be the other - While conversing one should maintain eye contact with the speaker as this shows the speaker that the message is being received by the listener. While speaking the focus should always be on the receiver.
4. Non-Verbal Communication- One’s body language often speaks as loud as his words. While communication one should show one’s reactions and interests through their body language.
5. Avoid Interruptions- It is essential to let the speaker finish talking before conveying one’s own thoughts. Interrupting is not only rude but also can be disadvantageous as one may not totally grasp the meaning of the speaker. If an interruption is absolutely necessary, one must use polite words like “pardon me” or “excuse me” instead of cutting the speaker in the middle of their thought process.
6. Controlling Emotions and Thinking before Speaking- It is said one must think twice before they speak. One must always consider the opinions and feelings of others before speaking their mind. One must also consider one’s own emotions and not speak out of anger or frustration. The process of communication should be logical rather than emotional.
7. The Message- The message one wishes to convey must always be clear and concise, there should be no doubts in one’s mind while speaking. The central idea of the message should always be conveyed completely and indubitably.
8. Eliminating Noise- One must eliminate all the outside forces that might disturb the conversation in order to maintain the flow of the communication process.
9. Feedback- One must pay attention to what the other person is saying and try to understand it as closely as possible to his intended meaning. This will allow him to provide proper responses.
8. What are International Phonetic Association (IPA) symbols in phonetics? What are the various phonetic symbols for vowels, consonants, and diphthongs?
Speech sounds, also known as Phonemes, is the smallest recurring sound in a sentence. Merriam Webster defines speech sound as “any one of the smallest recurrent recognizably same constituents of spoken language produced by movement or movement and configuration of a varying number of the organs of speech in an act of ear-directed communication.”
The English language consists of 26 alphabets but there are 44 speech sounds (Phonemes) in the English language consisting of 20 vowel sounds and 24 consonant sounds.
Phonemes (speech sounds) are represented in writing by placing the letters used to represent the sound between two slashes, for example, the sound that you say at the beginning of the word pot is represented by /p/.
Speech Sounds can be classified into three types, viz. Consonants, Vowels and diphthongs.
- Consonants:
A consonant is a sound accompanied by voice, in which there is either a complete or partial obstruction which prevents the air from freely issuing from the mouth.
In words such as base, maze, bathe, rouge, bake, path, long the sounds at the end of the words are distinctive. These twenty-four sounds may occur initially, medially and finally.
Consonants are perhaps more important than vowels because even if we pronounce the consonants only, most English words would be easy to understand. Consonant form the bones, the skeleton of English words and give them their basic shape. Moreover, differences of accent are mainly the result of differences in the sound of vowels; if the consonants are imperfect there will be a great risk of misunderstanding.
There are many types of consonants such as Fricatives (s,z,f,v), Plosives (stop) consonants (p and b; t and d; k and g). Nasal (m,n), Lateral and Gliding consonants.
Below are all the consonants comprised in the English phonetic script by the International Phonetics Association (IPA)
Unvoiced consonants
pfθts ʃ ʧ k
peafreethingtreeseesheep cheesecoin
Voiced consonants
bvðdzʒ ʤ g
boatvideothisdogzootelevisionjokego
m n ŋ h w l rj
mouse now thing hope we love runyou
2. Vowels:
In ordinary speech, a vowel is a voiced sound in the pronunciation of which the air passes through the mouth in a continuous stream, there being no obstruction and no narrowing such as would produce audible friction. All English vowels are voiced. Vowels like consonants can also occur initially or finally.
The following list consists of some words with vowel speech sounds:
Feel, fill, tall, bull, fool, mile, bat, toil, cart, pear, poor, butter, pier.
The qualities of vowels depend upon the position of the tongue and lips. It is convenient to classify them according to the position of the main part of the tongue. The position of the tip has no great effect on vowel quality. The tip of the tongue is supposed to be touching or near the lower teeth.
- Front vowels are the vowels which are produced with the front of the tongue raised in the direction of the hard palate. Ex. Feed.
- Back vowels are the vowels which are produced with the back of the tongue raises in the direction of the soft palate. Ex. Food.
- The vowels which are intermediate between the front and the back vowels are known as central vowels. Ex. Bird.
Below are the vowels comprised in the English Phonetic script by the International Phonetics Association (IPA)
ɪi:ʊu:
Shipsheepbookshoot
eɜ:əɔ:
leftherteacherdoor
æʌɒɑ:
hatuponfar
3. Diphthongs:
A diphthong is a deliberate glide where speech organs start in the position of one vowel and move towards another. A diphthong constitutes one syllable though the ear perceives two separate syllables.
Every diphthong may be said to have a first element (the starting point) and a second element (in the direction of which the glide is made). Most of the length and stress associated with the glide is concentrated on the first element. The second element is only lightly sounded. All English diphthongs are falling diphthongs (decrescendo).
The diphthongs are equivalent in length to the long pure vowels and are subject to the same variations of quantity. They also reflect variations in different regional and social types of speech.
Diphthongs are represented in phonetic transcription by a sequence of two letters, the first showing the position of the organs of speech at the beginning of the glide and the second showing their position at the end. In the case of ‘closing diphthongs’ the second letter indicates the point towards which the glide is made, but that point is not necessarily reached, and such diphthongs sound quite correct if the organs of speech perform only part of the maximum permissible movement.
Below are the diphthongs comprised in the English Phonetic script by the International Phonetics Association (IPA)
eɪɔɪaɪ
waitcoinlike
eəɪəʊə
hairheretourist
əʊaʊ
Showmouth
9. What is phonetics? What are the types of phonetics in English?
No two persons speak exactly alike and the pronunciations differ greatly depending upon the locality and geography of the speaker. So how should one decide on a model? The English spoken by the native speakers of in south-east England, also known as Received Pronunciation (R.P) is often considered acceptable. Language starts with the ear. Therefore, one must first “hear” English and pay close attention to how different words sound.
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that deals with the study and classification of how humans make and perceive sounds. In other words, It is the study of the physiological production of speech sounds and how different sounds are used to form syllables, words and sentences.
Phonetics can be classified into three main branches:
- Articulatory Phonetics
Articulatory Phonetics describes how the movement of different vocal organs are used to produce different speech sounds. It deals with the physical aspects of speech production. The organs of speech comprise of the Tongue, Nasal cavity, Lips, Epiglottis, Teeth, Uvula, Soft palate, Vocal chords, Windpipe, and the Pharyngeal Cavity.
2. Acoustic Phonetics
Acoustic Phonetics deal with the acoustic properties of speech sounds. The variations in air pressure while speaking form an essential component of how sounds are made. Speech sounds can be divided into two major classes, the first, sounds that consist of periodic wave form i.e the fluctuations in air pressure are in regular intervals, and the second, sounds that consist of a non-regular wave from,
3. Auditory Phonetics
Auditory Phonetics deal with the study of the variation between what is said by the speaker and what is heard by the receiver. In other words, it is the study of how humans perceive sounds.
Like the English language, Phonetics also consists of consonants and vowels. A consonant is a sound in which there is either a complete or partial obstruction which prevents the air from issuing freely from the mouth. On the other hand, a vowel is a voiced sound in the pronunciation of which the air passes through the mouth in a continuous stream, there being no obstruction such as would produce friction.
10. What are homonyms? Give examples.
Homonyms are words that sound the same or spelled the same but may have completely different meanings. Homonyms are rarer than Homophones but they are also ever present in the English language.
Below are some examples of Homonyms:
Band: A musical group/ a ring
Bat: A Flying Mammal/ An object used to play baseball, cricket.
Address: to speak to/a location
Rose: A type of flower/ to go up
Right: correct / direction opposite of left
Pound: unit of weight / to beat
Quarry - a site for mining stone / to extract or obtain slowly
Ream - a pile of paper / to juice a citrus fruit
Ring - a band on a finger / something circular in shape
Right - correct / direction opposite of left
Rock - a genre of music / a stone
Rose - to have gotten up / a flower
Spring - a season / coiled metal
Stalk - a part of a plant / to follow or harass someone
Tender - gentle / offer of money
Tire - to grow fatigued / a part of a wheel
Well - in good health / a source for water in the ground
11. Explain the meaning of term Homophones with the help of examples.
Homophones can be defined as pairs of words which sound alike but have different meanings and different spellings. Homophones can be frequently found in the English language and although they might sound similar but their meanings can be completely different or even opposite.
Below are some examples of homophones:
Sell/cell: The former means to deliver something for money while the latter means a small compartment.
Hear/here: The former means to listen to something or someone will the latter describes a place.
Cent/Scent: The former is a unit of currency while the latter is smell.
Hour/our: The former is a unit of time while the latter is a possessive adverb.
See/Sea: The former means to watch while the latter implies a large water body
Below are some commonly used homophones in the English language:
Air / heir
Aisle / isle
Ante- / anti-
Eye / I
Bare / bear
Be / bee
Brake / break
Buy / by
Cereal / serial
Coarse /course
Dam / damn
Dear / deer
Die / dye
Fair / fare
Fir/ fur
Flour/ flower
For/ four
Hair/ hare
Heal/ heel
Hear/ here
Him/ hymn
Hole/ whole
Hour/ our
Idle/ idol
In/ inn
Knight / night
Knot/ not
Know/ no
Made/ maid
Mail/ male
Meat/ meet
Morning / mourning
None / nun
Oar/ or
One/ won
Pair/ pear
Peace / piece
Plain/ plane
Poor/ pour
Pray/ prey
Principal / principle
Profit/ prophet
Real/ reel
Right/ write
Root/ route
Sail/ sale
Sea/ see
Seam/ seem
Sight/ site
Sew/ so
Shore/ sure
Sole/ soul
Some/ sum
Son/ sun
Stair/ stare
Stationary / stationery
Steal/ steel
Suite/ sweet
Tail / tale
Their/ there
To / too
Toe / tow
Waist / waste
Wait / weight
Way / weigh
Weak / week
Wear / where
12. Give some examples of Greek and Latin root words in the English language.
English is part of the German branch of the family of Indo-European language, so why is it so influenced in Latin and Greek? Although the origin of the English languages was introduced in England at the beginning of the 5th century by people from Denmark and Germany, the language was not entirely different from what we speak today.
When the Normans, a number of French Catholics, invaded the British islands in 1066, they came with their two languages: Latin and French. Because they were a ruling party long after the invasion, English became the language of the weak, effectively forcing English speakers to accept Latin and French words in their own language to match. Since the Renaissance began, nearly 500 years later, many Latin words, as well as those of the Greeks, were included to make English a more '' learned 'language because of the Renaissance's emphasis on classics.
- Abacus:
Abacus is derived from the Greek word - abax, meaning "sand tray."
- Allegory:
Allegory is derived from Greek - allos meaning "other" and agora meaning gathering place (especially the market). Eventually words join and are linked to the verb to speak of one thing and another to mean another.
- Apricot:
The term comes from the French - abricot - and it was a bit confusing until the fifteenth century - it does not have a single simple etymology, but rather a mixture of many theories under consideration. But all these roads lead to Rome, from where that name - and fruit - began to spread throughout Europe.
- Addictive:
Slaves agreed to allow Roman soldiers to pay for a concert in battle they were considered addicted to. Finally, a person who was addicted to anything called addiction.
- Alarm:
From Italian, "All'arme" - "To arms!"
- Alcohol:
Alcohol is taken from an Arabic al-kuhl, which has meant that there is a very good antimony powder used for eye makeup. It voiced the idea of something so elegant and smooth, so the Arabic alchemists give the name of al-khul which brings in any insubstantial powder obtained by slow release (a direct conversion of a solid base into a vapor, or process of return), and thus for all computers available through the sanitization process.
- Algebra:
The name means "the science of equations" in English comes from an article by one of al-Khowarizmi's (see "algorithm"), "Ab his AL-JAHR w'almuqaBAlah", meaning, "The Science of Transportation and Sanitation/ Cancellation."
- Algorithm:
The name means "rules of computing" in English, which is based on al-Khowarizmi (Try saying it soon), an Arabic mathematician who lives around A.D. 825 who completed the best known numerical work using Arabic numerals.
- Appendix:
In Latin it means "the hanging part." The human supplement hangs at the end of a large stomach; appendices given at the end of the book.
- Assassin:
Assassin from the old Arabic word "hashshshin," means "person who loves hash," that is, marijuana. Earlier it was referring to a group of heroes who would smoke before the war.
- Asthma:
Latin for asthma, "asthma," meaning "asthma" and "hypertension." The Latin word is derived from the Greek that feels the same.
- Avocado:
Avocado from "awaguatl," the original American testicle name. The Spaniards got the word and used to refer to what we now call avocado.
- Ballot:
Ballot, an Italian word meaning "small ball or pebble or stone." Italian citizens voted by placing a small stone or ball in one of the many boxes.
- Barbarian:
Barbarian from "barbaroi" in Greek, meaning "babblers”.
- Bead:
Bead from the Old English "gebed," which means, "prayer."
- Beserk:
Beserk mainly comes from the Old Icelandic "berserkr," meaning "bear shirt."
- Biscuit:
Biscuit from mediaeval French 'Bis + cuit' which means 'double cooked'
- Boulevard:
Boulevard from (French) Boulevard; and Bulwark
- Bucolic:
From the Greek "boukolos," meaning "shepherd," from "bous," meaning "ox."
- Bulimia:
Bulimia comes from the Greek "bous" meaning "ox" and "limos," which means "starvation," probably because a person with Bulimia is hungry for beef.
- Cab:
Old Italian terminology for goat (cabra in Spanish).
- Calculate:
The calculation comes from calculus, the Latin word pebble.
- Canter: (Spanish) Singing
From the Latin "Cantare," which means, "to sing often." Latin "Canere" simply means "to sing."
- Carnival:
Literal meaning: "Flesh, farewell." The end of "val" does not appear in the Latin "Vale." The modern Italian carnevale comes from the Old Italian "carnelevare"; levare = raise, place, remove. ) where people used to fast.
- Catharsis:
In Early Modern English, it is used in the sense of "cleaning." The concept of this name was still used as recently as 1803.
- Candidate:
From the Latin Candidus a word that means, "bright, shining, white, white." The ancient Roman members who were elected to this position wore bright white hats. The same name also spelled out the "firm", who are often not elected.
- Casarse: (Spanish, to marry)
From "casa," which means "house"; so is the English phrase, "to wrap."
- Cell:
Originally meant a monastery. It was Robert Hooke, who invented the first telescope. His first guess was the cork stem, which was made up of small columns. To him, the tiny fractions were like the little monasteries in which they lived, known as cells. Therefore, he called these microscopic building blocks "cells".
- Chapel:
From the Cape "Italian" Capella, since the original Chapel was where the cape ("capella") of the St. Martin of Tour was kept.
- Vulture and Chasm:
From the Greek "chainein," which means, "to soften"; So chaos was "just the beginning of the abyss" without the known universe we know.
- Champion; and Campus:
Check out Kampf
- Charlatan:
From the Spanish "charlar” for discussion /to chat.
- Cheers:
From the Greek "Kara" for "face," with Latin "Cara," and the French French "Chiere". So "Take courage," it means, "Put on a happy face."
- Chocolate:
It comes from the Spanish word for the same name, which came from the Nahuatl word (Aztecs language) "tchocoatl."
- Cider:
It comes from the Greek Greek sycamore, which came from an ancient Hebrew shekel, which means "any alcoholic beverage other than wine made to ferment fruit juice."
- Claim:
From the Latin "clamor", which is a judicial or public appeal raised on the discovery of sin.
- Conejo: (Spain) Rabbit
This Spanish word, meaning "rabbit," comes from the Latin word cuniculus, itself, which was taken in a letter from a previous Iberian name - according to Pliny the Elder - referring to both the animal and the scroll - and, by extension, any basement or trench. For its part, the name rabbit is a Flemish origin, and was originally used for small animals. The word used to refer to an old animal - in Flemish and Old English - was "cony" or "coney," which is derived from the cuniculus.
- Coward:
From Old French "coe" which means "tail." The OED adds, "The exact indication of the tail is uncertain: it may be an animal that 'turns tail' on a plane, or a practice in frightened animals to draw the tail between the hind legs: cf. The use of Heraldic in theory B 2. It is noteworthy that in the Old French version of Reynard the Fox , Coart is the name of a hare: this may be a descriptive adjective with regard to its zeal; it is closed, and that the word is then transferred to 'the heart of a hare.'
- Companion: Compañero (Spanish); Copain (French) Partner
From the Latin "Companionem," which was, "breadwinner" - "Con" (also) and "Pan" (bread) - your "partner" may have been someone to break bread with. "Look again to the Lord and take care of it.
- Cravate (French); Krawatte (German); Corbata (Spanish) Tie:
The names "Krawatte" (German), "cravate" (French) and "corbata" (Spanish), which all mean "human" tie, first appeared in the Napoleonic Wars when French troops entered the Crotia region, which, at that time, were part of the Holy Roman Empire. Evidently the Croatians were so capable of removing the German Habsburg yoke that they showed the victorious French troops a bouquet of flowers and ran to them and bound the scarlet threads in their uniforms as a gesture of goodwill. From them the name "Croat" or its variants appear to be attached to certain parts of Continental Europe.
- Cretin:
From the French "Crétin", which originally meant "Christian."
- The cup:
See Kopf
- Currant:
From the Corinthians
- Curfew:
From the French "couvrir feu," literally, "Cover the Fire."
- Daisy:
From "Eye of the Day." George Eddington writes, "Not special in itself, but Mata Hari also means" Eye of the day, "the young woman took the name because she lived in the Dutch East Indies and heard the natives so much in the sun. "
- Debonair:
French "good spirit." In the Middle Ages, people's lives were judged in part by the way they smiled. The person giving out “a good spirit” was viewed as a healthier and happier person.
- Deer:
From the Old English "deor," which means "animal."
- Demon: (German and English)
From the Greek "Daimon" this supernatural force is somewhere between humans and gods, without undesirable touch. An example would be the daimon of Socrates. The daimonans had a genius that did not conform to our modern ideas of good or evil: it was a natural force that could give clues about the circumstances and the critical actions.
- Denim:
The heavy cloth used for jeans was originally made in Nimes, France, as well as in Genoa, Italy (see jean). It was renamed Serge di Nimes - later reduced to di Nimes, which became denim.
- Derive:
From the Latin "De Rivus," "From the broadcast."
- Deutsch: (German by German)
"Deutsch" comes from the Old German word "diutisc" which means "human language" (as opposed to Latin). There are uncertain hints of the "Germanic" origins as the Celtic "Angry Men" or Old High German "Greedy Men"!
- Dexterity:
From the Latin "dexter," meaning "right" (in the left sense).
- Dibbs:
It is suggested that this phrase is based on an old children's play called dibstones. The game, which was played with sheep knuckle-bones or gemstones, dates back to at least the 17th century (that's right, that's when the name started being written). The goal was to catch his opponent's stones, and when a stone was hit, the winner would call "Dibbs!" with the meaning "I want [stone]". It was recently used out of the game but with the same meaning, and there you have it. Interestingly, the use of this outside of the game was not recorded until 1932 in the US. (Lee Quinn)
- Elite:
From the Latin Latin, which means "to choose," from which we find a modern Spanish word that means the same, elegir.
- Escape:
In Latin, escape means "out of the cape." The ancient Romans often avoided arresting the runaway population.
- Essay:
The English noun phrase comes from the French verb "story", to try. The earliest scholars believed that their papers were a modest attempt to present their papers.
- Exchequer:
The Moors introduced Abacus in Europe to expand the Europeans, and monks distributed the device throughout Europe. In Britain, it was used but in its simplicity: they used a checkbox and letters such as checks (instead of using standard rods and beads) - and this gave the British version an "exchequer" to the "Chancellor" of the Exchequer.
- Faro: (Spanish) Lighthouse
An ancient island from Egypt, the Paroah Island, had a lighthouse.
Feo: (Spanish) Ugly
From the Latin "Foedus," "disgusting.”
13. What are some English words derived for Latin prefixes and suffixes?
English speakers today--or even people trying to find out English--can enjoy understanding a number of the derivatives, or parts of a word taken from other languages, like Latin and Greek. Since there are over 1,000,000 words within the English, it's impossible to memorize all of them. However, understanding some basic components of words and customary ones that are derivatives of the classical languages can assist you determine their meaning.
In some ways, a word is simply sort of a cake, made from different ingredients. You'll find out what a word means by watching its three parts. The root, or the foremost basic sort of the word that also has meaning, is what makes up the bottom of the word. Frequently something is going to be attached the start of a word to feature meaning, which is named a prefix. Suffixes are almost like prefixes, but instead come at the top of the word. For instance, if you study the word ''microbiology,'' you'll see it's composed of those three parts, all of Greek origin: a prefix, ''micro-'' (meaning ''small''); a root, ''bio'' (meaning ''life''); and a suffix, ''logy'' (meaning ''study of''). Understanding these parts can assist you determine that microbiology is that the ''study of small life forms.''
Many English words and word parts are often traced back to Latin and Greek. The subsequent table lists some common Latin roots.
Latin root Basic meaning Example words:
Latin root | Basic meaning | Example words |
-dict- | To say | Contradict, dictate, diction, edict, predict |
-duc- | To lead, bring, take | Deduce, produce, reduce |
-gress- | To walk | Digress, progress, transgress |
-ject- | To throw | Eject, inject, interject, project, reject, subject |
-pel- | To drive | Compel, dispel, impel, repel |
-pend- | To hang | Append, depend, impend, pendant, pendulum |
-port- | To carry | Comport, deport, export, import, report, support |
-scrib-, -script- | To write | Describe, description, prescribe, prescription, subscribe, subscription, transcribe, transcription |
-tract- | To pull, drag, draw | Attract, contract, detract, extract, protract, retract, traction |
-vert- | To turn | Convert, divert, invert, revert |
From the instance words within the above table, it's easy to ascertain how roots combine with prefixes to make new words. For instance , the basis -tract-, meaning “to pull,” can combine with variety of prefixes, including de- and re-. Detract means literally “to pull away” (de-, “away, off”) and retract means literally “to pull back” (re-, “again, back”). The subsequent table gives an inventory of Latin prefixes and their basic meanings.
Latin prefix | Basic meaning | Example words |
Co- | Together | Coauthor, coedit, coheir |
De- | Away, off; generally indicates reversal or removal in English | Deactivate, debone, defrost, decompress, deplane |
Dis- | Not, not any | Disbelief, discomfort, discredit, disrepair, disrespect |
Inter- | Between, among | International, interfaith, intertwine, intercellular, interject |
Non- | Not | Nonessential, nonmetallic, nonresident, nonviolence, nonskid, nonstop |
Post- | After | Postdate, postwar, postnasal, postnatal |
Pre- | Before | Preconceive, preexist, premeditate, predispose, prepossess, prepay |
Re- | Again; back, backward | Rearrange, rebuild, recall, remake, rerun, rewrite |
Sub- | Under | Submarine, subsoil, subway, subhuman, substandard |
Trans- | Across, beyond, through | Transatlantic, transpolar |
Words and word roots may also combine with suffixes. Here are examples/ instances of some important English suffixes that come from Latin:
Latin suffix | Basic meaning | Example words |
-able, -ible | Forms adjectives and means “capable or worthy of” | Likable, flexible |
-ation | Forms nouns from verbs | Creation, civilization, automation, speculation, information |
-fy, -ify | Forms verbs and means “to make or cause to become” | Purify, acidify, humidify |
-ment | Forms nouns from verbs | Entertainment, amazement, statement, banishment |
-ty, -ity | Forms nouns from adjectives | Subtlety, certainty, cruelty, frailty, loyalty, royalty; eccentricity, electricity, peculiarity, similarity, technicality |
14. Give some examples of words derived in English from Greek and Latin prefixes and suffixes.
Most of these combining/ interactive forms can be used as either prefixes or suffixes. Examples are presented to illustrate current usage.
Prefixes | Derived From: | Meaning | Example |
a-, ab- | Latin | Off, from, down, away | Abduct, avert |
a-, an- | Greek | Not, without, less | Abiotic, anaerobic |
Actin- | G. Aktis | a ray, beam, spoke | Actinomycete |
Ad- | Latin | To, attached to, | Adsorption |
Aer- | Greek | Air | Aerobic |
Amphi- | Greek | Both, about, around | Amphibian |
Ana- | Latin | Away, through, again | Analysis |
Andro- | Greek | Man, male | Androgens |
Angio- | Greek | a vessel, closed container | Angiospermae |
Anthropo- | Greek | Referring to man | Anthropology |
Ant-, anti- | Greek | Against, away, opposite | Antibiosis |
Ante- | Latin | Before | Anteroom |
Ap-, aph-, apo- | Latin | From, off, separate | Apogee |
Aqua- | Latin | Water | Aquatic |
Arche-, archeo- | Greek | Ancient, primitive | Archeology |
Arthri-, arthro- | G. Arthron | Joint, jointed | Arthritis |
Asco- | G. Askos | Bag, sack, bladder | Ascospore |
Aureo- | L. Aureus | Gold colored | Aureomycin |
Auto- | G. Autos | Self | Autoimmune |
Bi- | Latin | Two, twice, double | Bipolar, binocular |
Bio-, bios- | Greek | Related to life | Biology, biocidal |
Blasto- | G. Blastos | An embryonic layer or cell | Blastomere |
Brachy- | Greek | Short | Brachycephalic |
Brad-, brady- | Greek | Slow, slowness | Bradycardia |
Bry-, bryo- | G. Bryon | Moss, mossy | Bryophyte |
Calic-, calix- | Latin | Cuplike | Calyx |
Cani-, canis- | Latin | Dog | Canine |
Cardia- | G. Kardia | Heart | Cardiac |
Carn- | L. Carnis | Flesh | Carnivore |
Carp- | L. Carpalis | Wrist, bones | Carpel |
Cata- | Greek | Decomposition, degradation | Catabolism |
Cell- | L. Cella | Small room | Cellular |
Cephal- | Latin | Head | Cephalic |
Chloro- | G. Chloros | Green, containing chloride | Chlorophyll |
Chroma-, chromo- | Greek | Colored | Chromosome |
Chron-, chrono- | G. Chronos | Time | Chronometer |
Circum- | Latin | Around, near, about | Circumnavigate |
Coel- | G. Koilos | Hollow cavity, belly | Coelom |
Col-, com-, con- | Latin | With, together | Combine, collide |
Contra- | Latin | Against | Contradict |
Crypto- | G. Kryptos | Hidden | Cryptogamic |
Cyano- | G. Kyanos | Dark blue, blue-green | Cyanobacteria |
Cyst- | G. Kystis | Bladder | Cystitis |
Cyt-,cyte-,cyto- | G. Kytos | Cell, a hollow vessel | Cytology |
De- | Latin | Undoing, removal of, from | Dehydration |
Den-, dent- | L. Dens | Tooth | Dentition |
Dendro- | Greek | Tree | Dendrochronology |
Derm-, derma- | Greek | Skin, hide | Dermatitis |
Deut-, deutero- | Greek | Second, secondary | Deuterium |
Di- | Greek | Double, twice, two | Disaccharide |
Dia- | Greek | Through, across | Diameter |
Diplo- | Greek | Twofold, double | Diploid |
Dis- | Latin | Apart, away | Dissolve |
Dorm- | Latin | To sleep | Dormant, dormitory |
Drom-, drome- | Greek | a running, racing | Dromendary |
e-, ec- | Latin | Out, out of | Efferent |
Eco- | G. Oikos | House, environment | Ecology |
Ecto- | G. Ektos | Outside | Ectoderm |
En-, endo- | G. Endon | Within, internal | Endoskeleton |
Entero- | G. Enteron | Intestine | Enterocolitis |
Entomo- | G. Entoma | Insect | Entomology |
Eo-, eos- | Greek | The dawn | Eocene, Eohippus |
Epi- | Greek | Upon, above, top | Epidermis |
Erythro- | Greek | Red | Erythrocyte |
Eu- | Greek | Proper, true, good | Eukaryotic |
Ex- | Latin | Out, from | Excise |
Exo- | Greek | Outer, external | Exoskeleton |
Extra- | L. Exter | Outside of, beyond | Extracellular |
Flagell- | L. Flagrum | Whip, whiplike | Flagellum |
Fuc-, fuco- | G. Phyktos | Seaweed, algae, lichen | Fucoxanthin |
Gamo- | G. Gamos | Sexual union | Gamogenesis |
Gastero-,gastro- | G. Gaster | Stomach, belly | Gastroenteritis |
Geno- | L.gene | Origin, development | Genotype |
Ge-, geo- | Greek | Earth | Geology |
Glu-, glyco- | Greek | Sweet, sugar | Glucose, glycogen |
Gon-,goni-,gono- | Greek | Reproductive, sexual | Gonorrhea |
Gymn-, gymno- | G. Gymnos | Naked, bare | Gymnosperm |
Gyn-,gyne-,gyno- | Greek | Woman, female | Gynecology |
Halo- | G. Hals | Salt | Halophile |
Haplo- | G. Haploos | Single | Haploid |
Heme-, hemo- | G. Haimo | Blood | Hematologist |
Hemi- | Greek | Half | Hemisphere |
Hepta- | Greek | Seven | Heptanes |
Herb- | L. Herba | Pertaining to plants | Herbicide |
Hetero- | Greek | Different, other, unlike | Heterozygous |
Hex-, hexa- | Greek | Six | Hexagonal |
Hipp-, hippo- | G. Hippos | Horse | Hippodrome |
Histo- | G. Histos | Tissue | Histology |
Holo- | G. Holos | Whole, entire | Holoblastic |
Homeo, homo- | Greek | Same, similar, like | Homogeneous |
Hyal-, hyalo- | G. Hyalos | Glassy, transparent | Hyaloids |
Hydr-, hydro- | Greek | Pertaining to water | Hydrolysis |
Hyper- | Greek | Above, more, over | Hyperactive |
Hypo- | Greek | Below, less, under | Hypodermic |
Ichthy-,ichthyo- | Greek | Referring to fish | Ichthyology |
Inter- | Latin | Between | Intercellular |
Intra- | Latin | Within, inside | Intracellular |
Intro- | Latin | Inward, within | Introvert |
Iso- | Greek | Equal, same | Isotonic |
Kine- | Greek | Movement, moving | Kinetics |
Leuc-, leuk- | Greek | White | Leucocyte |
Lycan- | G. Lykos | Wolf | Lycanthropy |
Macro- | Greek | Large, big, long | Macromolecule |
Man-, manu- | Latin | Hand | Manual |
Mastig- | G. Mastigos | Whip | Mastigophora |
Meg-, mega- | Greek | Great, large | Megabyte |
Melan-,melano- | Greek | Black, dark | Melanin |
Mero- | G. Merus | Part, piece | Meroblast |
Mes-, meso- | G. Mesos | Middle, in between | Mesoderm |
Met-, meta- | Greek | Later, following, changed in position or form | Metamorphosis |
Micro- | G. Mikros | Small | Microbiology |
Milli- | Latin | a thousandth part | Millimeter |
Mio- | G. Meion | Less, smaller | Miocene |
Mito- | G. Mitos | Thread | Mitosis |
Mon-, mono- | Greek | One, single | Monocular |
Morph- | Greek | Shape, form | Morphology |
Mor-, mort- | Latin | Die, death, | Mortality |
Muc-, muco- | Latin | Consisting of many units | Multicellular |
Mus- | Latin | Mouse, as one running | Muscle |
Myco-, mykos- | Greek | Fungus, mushroom | Mycology |
Myo- | G. Mys | Muscle | Myoglobin |
Myxo- | Greek | Slime, mucus | Myxomycetes |
Nemato- | Greek | Thread, threadlike | Nematode |
Neuro- | Greek | Name | Nomenclature |
Ob- | Latin | Against | Obtuse |
Octa- | Greek | Eight | Octopus |
Olig-, oligo- | Greek | Few, small, less | Oligarchy |
Omni- | Latin | All, everywhere | Omnipotent |
Oo- | Greek | Pertaining to an egg | Oocyte |
Ophthalmo- | Greek | Referring to the eye | Ophthalmologist |
Opisth-,opistho- | Greek | Behind, backwards, back | Opisthobranchia |
Orni-, ornitho- | Greek | Bird | Ornithology |
Orth-, ortho- | Greek | Straight | Orthodontist |
Osteo- | Greek | Bone | Osteocyte |
Oto- | Greek | Referring to the ear | Otology |
Ova-,ovi-,ovul- | Latin | Egg | Ovary, oviduct |
Paleo- | Greek | Old, ancient | Paleontology |
Para- | Greek | Beside, near, beyond | Parasitism |
Path-, patho- | Greek | Disease, suffer | Pathogenic |
Ped-, pedi- | Latin | Foot | Pedicure |
Penna-, pinna- | Latin | Feather, feathery | Pinnate |
Pent-, penta- | Greek | Five | Pentagon |
Per- | Latin | Through | Pervade, peruse |
Peri- | Greek | Around, surrounding | Perimeter |
Pher- | Greek | Bearing, carrying, support | Pheromone |
Phil- philo- | Greek | Loving, attracted to | Philanthropy |
Phob- | Greek | Fear, fearing | Phobic |
Photo- | Greek | Pertaining to light | Photosynthesis |
Phyco- | Greek | Seaweed, algae | Phycology |
Phylo- | Greek | Tribe, race, related group | Phylogeny |
Phyto- | Greek | Pertaining to plants | Phytohormone |
Plasm-, plasma- | Greek | Formative substance | Plasmablasts |
Plati-, platy- | Greek | Flat | Platypus |
Pleio- pleo- | Greek | More, many | Pleiomorphic |
Pod-,poda-,podi- | Greek | Foot | Podiatrist |
Poly- | Greek | Many | Polyhedron |
Post- | Latin | After | Postnatal |
Pre- | Latin | Before | Prenatal |
Preter- | Latin | Beyond | Preterhuman |
Prim- | Latin | First | Primary |
Pro- | Greek | Before, on behalf of | Proboscis |
Pro- | Latin | Forward | Progressive |
Proto- | Greek | First, primary | Protozoa |
Pseudo- | Greek | False | Pseudopod |
Psilo- | Greek | Bare, mere | Psilopsida |
Pteri-, ptero- | Greek | Fern, feather | Pteridophyte |
Quadr-, quadri- | Latin | Four | Quadruped |
Radi- | Latin | Ray, spoke of wheel | Radial |
Re- | Latin | Back, again | Repeat |
Retro- | Latin | Backward | Retroactive |
Rhiz-, rhizo- | Greek | Pertaining to roots | Rhizoids |
Rhod-, rhodo- | Greek | a rose, red | Rhodopsin |
Rota- | Latin | Wheel | Rotate |
Sapr-, sapro- | Greek | Rotten, putrid, dead | Saprobe |
Sarc-, sarco- | Greek | Flesh, fleshy | Sarcoma |
Schiz-, schizo- | Greek | Split, splitting | Schizocoel |
Se- | Latin | Apart | Secede |
Semi- | Latin | Half | Semicircle |
Soma-, somato- | Greek | Body | Somatic |
Sperma-,spermato- | Greek | Seed | Spermatozoa |
Sporo- | Greek | Spore | Sporophyte |
Staphylo- | Greek | Bunch of grapes | Staphylococcus |
Stoma- | Greek | Mouth | Stomata |
Strepto- | Greek | Twisted, string of | Streptococcus |
Sub- | Latin | Below, under, smaller | Subapical |
Supra-, super- | Latin | Above, over | Supernova |
Sym-, syn- | Greek | Together, with | Synthesis |
Taxi-, taxo- | Greek | To make order, arrangement | Taxonomy |
Tel-,tele-,telo- | Greek | Distant, end | Telophase |
Terra-, terre- | Latin | Land, earth | Terrestrial |
Tetra- | Greek | Four | Tetrapod |
Therm-, thermo- | Greek | Heat | Thermometer |
Thigmo- | Greek | Touch | Thigmotaxis |
Trans- | Latin | Across, through, over | Transfer |
Tri- | Latin | Three | Triangle |
Tricho- | Greek | Hair | Trichocyst |
Triplo- | Latin | Triple | Triploid |
Troche-, trocho- | Greek | Wheel, hoop | Trochophore |
Tropho- | Greek | Nourishment | Trophoblast |
Ultra- | Latin | Beyond, exceedingly | Ultraconservative |
Uni- | Latin | Consisting of one | Unicellular |
Vice- | Latin | In place of | Vice-president |
Vid-, vis- | Latin | See | Vision |
Xen-, xeno- | Greek | Dry, desert | Xerophytes |
Zoo- | Greek | Animal, life | Zoology |
Zyg-, zygo- | Greek | To join together | Zygote |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Suffixes | Derived From: | Meaning | Example |
-biosis | Greek | Mode of living, way of life | Symbiosis |
-blast | Greek | Formative, embryonic | Mesoblast |
-chaeta-, -chete | Greek | a bristle | Polychaeta |
-chrome | Greek | Color | Mercurochrome |
-cidal, -cide | Latin | Killer, a killing | Insecticide |
-cocci, -coccus | Greek | Round, seed, kernel | Streptococcus |
-cyst | Greek | Pouch, sac | Trichocyst |
-dactyl | Greek | Finger | Pentadactyl |
-derm, -dermis | Greek | Skin, layer | Epidermis |
-elle, -ule, -la, -le, -let, -ole | Latin | Small, diminutive endings | Globule, piglet |
-emia | Greek | Blood disease | Anemia |
-fer | Latin | Bearer, producer, carry | Conifer, transfer |
-gamous, -gamy | Greek | Marriage, sexual fusion | Polygamy |
-gen, -geny | Greek | Origin, production | Progeny, hydrogen |
-genesis | Latin | Origin, development of | Embryogenesis |
-gony | Latin | Something produced | Cosmogony |
-graph | Greek | Drawing, writing | Chromatograph |
-hedral, -hedron | Greek | Side | Polyhedral |
-hydrate | Greek | Compound formed by union of water with other substance | Carbohydrate |
-ism | Greek | Act, practice or result of | Terrorism |
-ite | Latin | a division or part | Somite |
-itis | Greek | Inflammation or infection | Appendicitis |
-jugal, -jugate | Latin | To yoke, join together | Conjugate |
-logy | G. Logos | Science or study of | Biology |
-lysis, -lytic | Greek | Loosening, separation, splitting into smaller units | Photolysis |
-mer, -merous | G. Meros | a part, piece | Polymer |
-meter | G. Metron | a measurement | Diameter |
-morph | Greek | Form | Endomorph |
-mycin | Greek | Derived from a fungus | Aureomycin |
-nomy | Greek | Systematized knowledge of | Astronomy |
-oma | Greek | Timorous | Carcinoma |
-osis, -otic | Greek | Abnormal condition, disease | Neurosis |
-phage | Greek | Eater | Bacteriophage |
-phase | Greek | a stage or condition | Metaphase |
-phil, -phile | Greek | Fear, fearing | Hydrophobia |
-phor, -phore | Greek | Bearing, carrying, supporting | Sporangiophore |
-phyll | Greek | Leaf | Chlorophyll |
-phyta, -phyte | Greek | Plant | Epiphyte |
-plasm | Greek | Formative substance | Cytoplasm |
-plast | Greek | Organized particle, granule | Chloroplast |
-pod, -poda | Greek | Foot | Arthropod |
-some | Greek | Body | Chromosome |
-stasis | Greek | a stationary position | Homeostasis |
-stat, -static | Greek | Stationary, still | Hemostat |
-stomy | Greek | Opening into | Colostomy |
-therm | Greek | Heat | Homeotherm |
-thes, -thesis | Greek | Arrangement, in order | Hypothesis |
-tom, -tomy | Greek | Dividing, surgery | Lobotomy |
-trope, -tropic | Greek | Turning | Phototropic |
-vor, -vore | L. Vorare | Feeding | Carnivore |
15. What are synonyms? Explain with the help of examples.
Synonyms are words that carry a similar or same meaning to another word. Sometimes even though the synonym of a word has an identical meaning the word and the synonym may not be interchangeable. For example, "blow up" and "explode" have the same meaning, but "blow up" is informal (used more in speech) and "explode" is more formal (used more in writing and careful speech). Synonyms also provide variety to speech and writing.
Many words in the English language contain more than one synonym. Some examples of Synonyms:
Shallow - superficial
Stop – cease
Spontaneous - capricious
Gloomy – sad - unhappy
House - home - abode
Evil - bad - wicked
Garbage - trash - junk - waste
Present – gift – reward – award
Sniff – smell – inhale
Little – small – tiny
Under – below – beneath
Short list of synonyms in English, listed by the part of speech:
Nouns:
- Belly / stomach
- Children / kids
- Disaster / catastrophe
- Earth / soil
- Father / dad
- Happiness / joy
- Instinct / intuition/ understanding
- Mother / mom
- Present / gift
- Sunrise / dawn
Verbs:
- Answer / reply
- Beat / defeat
- Behave / act
- Begin / start
- Close / shut/ turn on/turn off
- Leave / exit
- Provide / supply/ distribution
- Select / choose
- Shout / yell
- Speak / talk
Adjectives:
- Big / large
- Complete / total/number
- Correct / right
- Crazy / mad
- Foolish / silly /fool/ stupid
- Happy / glad
- Hard / difficult
- Ill / sick
- Last / final
- Near / close
- Sad / unhappy
- Stable / steady/ strong
Adverbs:
- Abroad / overseas
- Almost / nearly/ about / approx.
- Bad / poorly
- Fast / quickly
- Intentionally / purposefully
- Out / outside
- Rarely / seldom/ not common
- Sometimes / occasionally/ periodically
- Surely / for sure/ definetly
- Very / highly / extremely/too much
Prepositions:
- Above / over/ more
- About / regarding / concerning
- Against / versus
- Below / beneath / under
- By / via
- Despite / in spite of
- In / into/ to
- Off / away
- Until / till
- With / including
Conjunctions:
- And / plus
- Because / since
- But / yet/for now
- If / provided
- Once / as soon as possible/ and
Interjections:
- Hello / hi
- Gee / gosh
- Goodness / goodness me / my goodness
- No / nope
- Oh Lord / oh good Lord
- Thanks / thank you
- Whoopee / yahoo / hooray
- Yes / yeah
16. What are antonyms? Give examples.
Antonyms are words that carry the opposite meaning to another word. They can be used to show contrast between two things or emphasize a point. Antonyms can be totally different words from their counterparts or can also be formed by adding prefixes to some words.
Below are some examples of antonyms that are commonly used in the English language:
Antonyms formed by changing entire words
Love – hate
Beginning – ending
Ugly – beautiful
Wild – tame
Extrovert – introvert
Antonyms formed by adding prefix –un
Acceptable - unacceptable
Able - unable
Do - undo
Certain – uncertain
Seen – Unseen
Antonyms formed by adding the prefix –in
Decent – indecent
Tolerant – intolerant
Human – inhuman
Curable – incurable
Expressible – inexpressible
Antonyms formed by adding the prefix –non
Sense – nonsense
Essential – nonessential
Flammable – non-flammable
Renewable – non-renewable
Entity – nonentity
Other prefixes used to form antonyms of words are –anti (Thesis - Antithesis), -ill (Literate – Illiterate), -mis (Informed – Misinformed), -dis (Assemble – Disassemble) etc.
Short list of antonyms in English, listed by the part of speech:
Nouns
- Day / night
- East / west
- The enemy / friend
- Failure / success
- Guest / host
- Health / disease
- Question / answer
- Speaker / listener
- Summer / winter
- Top / bottom/ up / down
Verbs
- Agree / disagree/accept
- Arrive / leave/ come / go
- Begin / end/ start
- Fall asleep / wakefulness/sleep
- Find / lose/ gain
- Lend / borrowing
- Love / hate
- Open / close/turn on /turn off
- Remember / forget
- Start / stop
Adjectives
- Is asleep / awake
- Beautiful / ugly /good/ bad
- Big / small
- Black / white
- Cheap / expensive
- Dead / alive
- It is dry / wet
- Easy / difficult
- Full / empty
- Good / bad
- Hot / cold
- Intelligent / stupid/you are smart
- Sad / happy/ exciting
- Sick / living healthy
- Thin / fat
Adverbs
- Always / never
- With anger / happily/ excitement
- Fast / slowly
- Here / there
- Inside / outside/ indoors/ outdoors
- Likely / unlikely/possible/ impossible
- Near / far
- Partly / fully
- Seemingly / actually/ visually
- Yesterday / tomorrow
Prepositions
- Above / below
- Against / for / because
- Before / after
- In / out/ indoors/ outdoors
- Like / unlike/ love / contrast
- On / off
- Plus / minus
- To / from
- Towards / away/remote
- With / without
Conjunctions
- And / or
- Therefore / nevertheless /or so
Interjections
- Bravo / boo
- Hello / goodbye
- Holy cow / duh
- Phew / oops
- Thanks / no thanks
- Yes / no
- Yippee / oh my/ oh