UNIT 1
Multidisciplinary nature of environmental studies
- Define environment?
Environment as a word covers the sum of extrinsic forces, factors and suitable conditions, which are essential for the origination and survival of all life forms. ‘Environment’ is composed of every external factor that has influenced all living organisms since birth.
Environment is the aggregate of physical, chemical, biological and social components on Earth which are capable of causing direct or indirect effects on the survival of living and non-living things and their interactions.
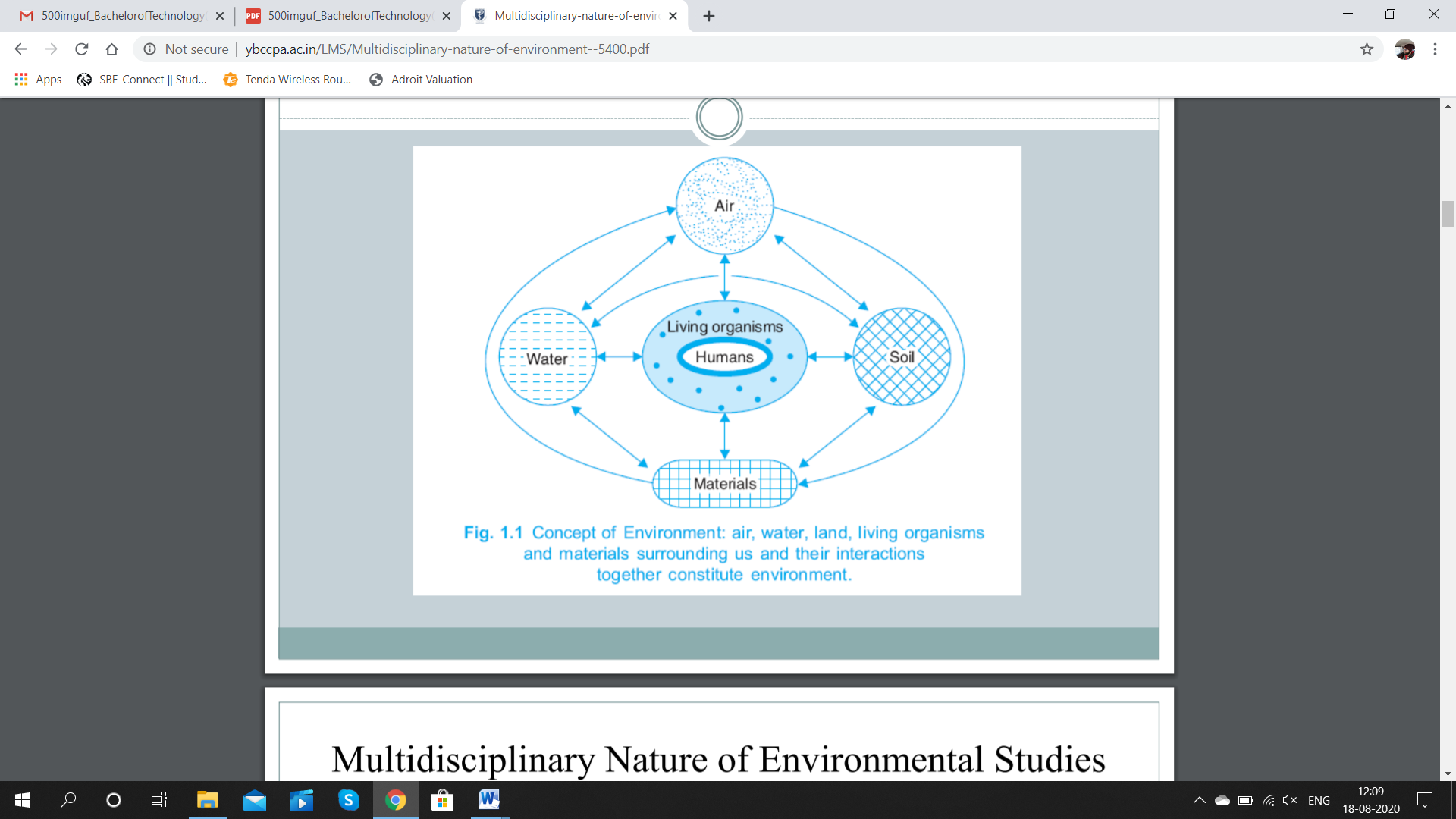
Interaction of Air, Water, Land (Soil), Resources (Materials) with Living Organisms constitutes Environment.
Study of environment & its components is a multidisciplinary field as it consists of Science, Arts, Commerce, Mathematics and other specialized fields such as Geography, Topography, Anthropology, etc.
Environmental studies provide us a platform for the thorough study of living organism and its surroundings.
- Environmental Studies as Applied Life Science: Life sciences including botany, zoology, microbiology, genetics, biochemistry, biotechnology, etc. help us in understanding the biotic components of environment and their interactions with each other and with abiotic components.
- Environmental Studies as Basic Physical Sciences: Core branches of physical sciences such as Chemistry, Physics, Geography, etc. give us an overview of chemical & physical structure of biotic components. Flow of energy transfer from one form to another also comes under this domain.
- Environmental Studies as Modeling Tool: It includes Mathematical Interpretations, Statistical Data Analysis, Computer Aided Analysis of Environment & its components.
- Environmental Studies as Technology: Branches of Civil Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Environmental Engineering, etc. have to deal with sustainable technological development without harming the environment in the form of Pollution Control, Waste Treatment and Reduction in overexploitation of natural resources.
- Environmental Studies as Management & Awareness: It covers all the rules regulations, laws and acts made in order to protect the environment and to create equilibrium between all life forms to sustain life and growth on earth.
2. Explain Scope for environment?
Like its multidisciplinary nature, scope of Environmental Studies is also wide as follows:
1. The study makes mindfulness among the individuals to think about different sustainable and non-renewable assets of the surroundings.
2. It gives the information about natural frameworks and circumstances related to human survival.
3. It gives fundamental idea about biodiversity and risks related to it.
4. The examination empowers one to create a cause & effect relationship of consequences caused by human activities of our natural surroundings.
5. It empowers one to choose most suitable alternative from available pool in order to reduce overuse of natural resources.
6. The awareness of Environmental Studies empowers ecologically educated residents by letting them know about the natural demonstrations, rights, rules, regulations, enactments, amendments in the existing environmental acts and so on to settle on proper decisions and choices for the insurance and improvement of the earth and its inhabitants.
7. The study reveals the social issues like over population, health, cleanliness and sanitation. It gives remedial measures to these issues in the most suitable manner.
8. The investigation attempts to recognize and create the eco-friendly skills and non-conventional technologies that would not create any hindrance in the pathway of development without putting an extra burden on environment.
9. It shows us the requirement for supportable usage of resources as these assets are acquired from our predecessors. Hence it is our responsibility to pass these on to our forthcoming generations without decaying their overall quality.
10. The scope of Environmental Studies is incomplete without its impact on employment opportunities in the form of Environmental-Journalism, Research & Development, Environmental Management, etc.
3. Explain importance for environment?
Importance:
1) Environmental studies help us to maintain ecological balance and equilibrium in the environment by providing a basic platform for interaction of environmental system and inter-related processes.
2) It gives information regarding the changes that takes place due to various factors and helps in gathering skills to analyze various environmental processes and the effect of human activities on them.
3) Environmental studies help to achieve sustainable development in order to achieve a state of optimum utilization of resources without affecting the needs of future generations. It ultimately makes us understand the relationship between development and the environment.
4) This field helps to educate people regarding their responsibilities and lawful duties towards the protection of environment.
5) Environmental study help us to analyze the impact of human activities on various processes occurring in water, air and land which leads to contamination and results in environmental pollution
6) It also deals with the most important issues like safe and clean potable water, health-hygiene and cleanliness of surroundings
7) The discipline provides knowledge of the environment and various environmental issues. It examines the scientific base for environmental, cultural and social concerns about our present energy needs, global climate changes, toxic emission and waste disposal.
8) Development and optimum utilization of energy resources is an important aspect of environmental studies.
9) Environmental acts, rules, regulations, law, amendments and fields like business administration, environmental engineering are emerging as new career opportunities under its domain.
10) To analyze the complex nature of vast bio-diversity on our planet, we need scientific approach of Environmental - Studies.
4. Explain Natural Resources?
Renewable natural resources are natural resources that, after exploitation, can return to their previous stock levels by natural processes of growth or replenishment. Conditionally renewable resources are those whose exploitation eventually reaches a level beyond which regeneration will become impossible.
A nonrenewable resource is a natural substance that is not replenished with the speed at which it is consumed. It is a finite resource. Fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas, and coal are examples of nonrenewable resources. ... Renewable resources are the opposite: Their supply replenishes naturally or can be sustained.
Natural resources
Any material which can be transformed in a way that it becomes more valuable and useful can be termed as resource. In other words, it is possible to obtain valuable items from any resources. Resource, therefore, are the means to attain given ends. The aspect of satisfaction is so important that we consider a thing or substance a resource, as so long it meets our needs. Life on this planet depends upon a large number of things and services provided by the nature, which are known as Natural Resources. Thus water, air, soil, minerals, coal, forests, crops and wild life are all examples of natural resources.
5. Explain Problems associated with natural resources?
1. The unequal consumption of natural resources
A major part of natural resources today are consumed in the technologically advanced or ‘developed’ world, usually termed ‘the west’. The ‘developing nations’ of ‘the east’, including India and China, also over use many resources because of their greater human population. However, the consumption of resources per capita (per individual) of the developed countries is up to 50 times greater than in most developing countries. Advanced countries produce over 75% of global industrial waste and greenhouse gases.
2. Planning land use
Land is a major resource, needed for not only for food production and animal husbandry, but also for industry and growing human settlements. These forms of intensive land use are frequently extended at the cost of ‘wild lands’, our remaining forests, grasslands, wetlands and deserts. This demands for a pragmatic policy that analyses the land allocation for different uses.
3. The need for sustainable lifestyles
Human standard of living and the health of the ecosystem are indicators of sustainable use of resources in any country or region. Ironically, both are not in concurrence with each other. Increasing the level of one, usually leads to degradation of other. Development policies should be formulated to strike a balance between the two.
6. Explain Forest resources: Use and over-exploitation?
Use and over exploitation
A forest is a biotic community predominantly of trees, shrubs and other woody vegetation, usually with a closed canopy. This invaluable renewable natural resource is beneficial to man in many ways.
The direct benefits from forests are:
(a) Fuel Wood:
Wood is used as a source of energy for cooking purpose and for keeping warm.
(b) Timber:
Wood is used for making furniture, tool-handles, railway sleepers, matches, ploughs, bridges, boats etc.
(c) Bamboos:
These are used for matting, flooring, baskets, ropes, rafts, cots etc.
(d) Food:
Fruits, leaves, roots and tubers of plants and meat of forest animals form the food of forest tribes.
(e) Shelter:
Mosses, ferns, insects, birds, reptiles, mammals and micro-organisms are provided shelter by forests.
(f) Paper:
Wood and Bamboo pulp are used for manufacturing paper (Newsprint, stationery, packing paper, sanitary paper)
(g) Rayon:
Bamboo and wood are used in the manufacture of rayon (yarns, artificial silk-fibres)
(h) Forest Products:
Tannins, gums, drugs, spices, insecticides, waxes, honey, horns, musk, ivory, hides etc. are all provided by the flora and fauna of forests.
Over exploitation of forests
Forests contribute substantially to the national economy. With increasing population increased demand of fuel wood, expansion of area under urban development and industries has lead to over exploitation of forest .At present international level we are losing forest at the rate of 1.7 crore hectares annually. Overexploitation also occurs due to overgrazing and conversion of forest to pastures for domestic use.
There has been unlimited exploitation of timber for commercial use. Due to increased industrial demand; timber extraction has significant effect on forest and tribal people.
Logging
- Poor logging results in degraded forest and may lead to soil erosion especially on slopes.
- New logging roads permit shifting cultivators and fuel wood gatherers to gain access to the logging area.
- Loss of long term forest productivity
- Species of plants and animals may be eliminated
- Exploitation of tribal people by contractor.
7. Explain Dams and other effects on forest and tribal people?
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru referred dam and valley projects as “Temples of modern India”. These big dams and rivers valley projects have multi-purpose uses. However, these dams are also responsible for the destruction of forests. They are responsible for degradation of catchment areas, loss of flora and fauna, increase of water borne diseases, disturbance in forest ecosystems, rehabilitation and resettlement of tribal peoples.
India has more than 1550 large dams, the maximum being in the state of Maharashtra (more than 600), followed by Gujarat (more than 250) and Madhya Pradesh (130).
The highest one is Tehri dam, on river Bhagirathi in Uttaranchal and the largest in terms of capacity is Bhakra dam on river Satluj in Himachal Pradesh. Big dams have been in sharp focus of various environmental groups all over the world, which is mainly because of several ecological problems including deforestation and socio-economic problems related to tribal or native people associated with them.
The Silent valley hydroelectric project was one of the first such projects situated in the tropical rain forest area of Western Ghats which attracted much concern of the people.
The crusade against the ecological damage and deforestation caused due to Tehri dam was led by Shri. Sunder Lal Bahaguna, the leader of Chipko Movement.
The cause of Sardar Sarovar Dam related issues have been taken up by the environmental activitist Medha Patkar, joined by Arundhati Ray and Baba Amte. For building big dams, large scale devastation of forests takes place which breaks the natural ecological balance of the region.
Floods, droughts and landslides become more prevalent in such areas. Forests are the repositories of invaluable gifts of nature in the form of biodiversity and by destroying them (particularly, the tropical rain forests), we are going to lose these species even before knowing them. These species could be having marvelous economic or medicinal value and deforestation results in loss of this storehouse of species which have evolved over millions of years in a single stroke.
8. Explain Use and over exploitation of surface and ground water?
Water resources are sources of water that are useful or potentially useful. • Uses of water include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities. • Virtually all of these human uses require fresh water
Water Resources-Use and Overutilization :
- The water Cycle through evaporation and precipitation, maintains hydrological systems .
- All aquatic ecosystems are used by a large number for their daily needs such as washing irrigation, cooking etc.
- One of the greatest challenges today is the management of these water resources.
- Due to increasing population there is an enormous supply for the available freshwater resources. India is likely to face water crisis by 2025.
- With growth of human population larger amounts of water will be required to fulfil basic needs Today in many areas this need cannot be met.
- Overutilization of water occurs at various levels:
- Most people use more water than required to carry out basic activities such as brushing, bathing, washing and cleaning etc.
- Farmers also sometimes use double the water required for irrigation.
- There are many ways in which the farmer can increase the yield by using less water for irrigation.
- With the growth of human population there is an increasing need for larger amounts of water to fulfil a variety of basic needs. Today in many areas this requirement cannot be met.
- Overutilization of water occurs at various levels. Most people use more water than really needed. Most of us waste water during a bath by using shower or during washing of clothes. Many agriculturists use more water than necessary to grow crops. There are many ways in which farmers can use less water without reducing the yields such as the use of drip irrigation systems.
- Agriculture also pollutes surface water and underground water stores by the excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Methods such as the use of biomass as fertilizers and non toxic pesticides such as neem products reduces the agricultural pollution of surface and ground water.
Industry tends to maximise short-term economic gains by not bothering about its liquid waste and releasing it into the streams, rivers, sea.
9. Define Floods, drought, conflicts over water?
Floods
Floods have been serious environmental hazards from centuries. Deforestation causes flood that kills people, damage crops and destroys homes. • Rivers changes its course during floods and tons of valuable soil is lost to the sea. As the forest are degraded, rain water no longer percolates slowly into the the sub-soil but runs off down the mountainside bearing large amount of top soil.
Droughts
In most arid regions of the world the rains are unpredictable. This leads to a periods when there is a serious scarcity of water to drink, use in farm, or provide for urban or industrial use. One of the factor that worsens the effect of droughts is deforestation. Drought is one of the major problem in our country, due to unpredictable climatic condition or due to the failure of one and more monsoon.
Conflicts over water
- Conflicts through use -Unequal distribution of water has often led to inter state or international disputes
- Constructions of dams -Hydroelectric power generation, dams are built across the rivers, which initiates conflict between the states.
10. Describe Environmental effects of extracting and using mineral resources?
Environmental Impacts of Mineral Extraction
Extracting and use of mineral resources can affect the environment adversely. Environmental affect may depend on factors such as mining procedures, ore quality, climate, size of operation, topography, etc. Some of major environmental impacts of mining and processing operations are as under
1. Degradation of land.
2. Pollution of surfaces and ground water resources.
3. Effect on growth of vegetation due to leaching out effect of minerals.
4. Surface water pollution and groundwater contamination lead to occupational health hazards etc.
5. Air pollution due to emission of gases.
6. Deforestation affects flora and fauna.
7. Rehabilitation of affected population.
11. Explain World food problems?
As per estimates of Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), about 840 million people remain chronically hungry and out of this 800 million are living in the developing world. In last decade, it is decreasing at the rate of 2.5 million per year, but at the same time world’s population is increasing. Target of cutting half the number of world’s chronically hungry and undernourished people by 2015 will difficult to meet, if the present trend continues. Due to inadequate purchasing power to buy food, it is difficult to fulfil minimum calorific requirement of human body per day. Large number of people are in India are poor which can be attribute to equitable distribution of income. Food insufficiency can be divided into two categories into under-nourishment and malnourishment. Both of these insufficiencies are global problems.
- Under-nourishment
The FAO estimates that the average minimum daily caloric intake over the whole world is about 2,500 calories per day. People who receive less than 90% of their minimum dietary intake on a long-term basis are considered undernourished. Those who receive less than 80% of their minimum daily caloric intake requirements are considered ‘seriously’ undernourished. Children in this category are likely to suffer from stunted growth, mental retardation, and other social and developmental disorders. Therefore, Under-nourishment means lack of sufficient calories in available food, resulting in little or no ability to move or work.
2. Malnourishment
Person may have excess food but still diet suffers from due to nutritional imbalance or inability to absorb or may have problem to utilize essential nutrients. If we compare diet of the developed countries with developing countries people in developed countries have processed food which may be deficient in fibre, vitamins and other components where as in the diet of developing countries, may be lack of specific nutrients because they consume less meat ,fruits and vegetables due to poor purchasing power .
Malnourishment can be defined as lack of specific components of food such as proteins, vitamins, or essential chemical elements.
The major problems of malnutrition are:
- Marasmus: a progressive emaciation caused by lack of protein and calories.
- Kwashiarkor: a lack of sufficient protein in the diet which leads to a failure of neural development and therefore learning disabilities.
- Anemia: it is caused by lack of iron in the diet or due to an inability to absorb iron from food.
- Pellagra: it occurs due to the deficiency of tryptophan and lysine, vitamins in the diet.
Every year, food problem kill as many people as were killed by the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima during World War II. This shows that there is drastic need to increase food production, equitably distribute it and also to control population growth. Although India is the third largest producer of staple crops, it is estimated that about 300 million Indians are still undernourished. India has only half as much land as USA, but it has nearly three times population to feed. Our food problems are directly related to population.
4. Balanced diet
Supply of adequate amount of different nutrient can help to improve malnutrition and its ill effects. Cereals like wheat and rice can supply only carbohydrate which are rich in energy supply, are only fraction of nutrition requirement. Cereal diet has to be supplemented with other food that can supply fat, protein and minor quantity of minerals and vitamins. Balanced diet will help to improve growth and health.