Unit-1
Basic Semiconductor and PN Junction Theory
Q1) Difference between drift and diffusion current?
Sol: 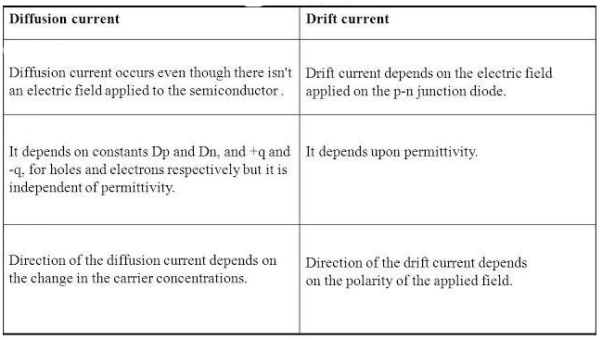
Q2) Explain how the temperature effects the semiconductor parameters?
Sol: The effect of temperature on the semiconductors parameters is listed below
i) Intrinsic concentration: The intrinsic carrier concentration depends upon the temperature. For N-type semiconductors the number of holes changes with change in temperature and electrons are not much affected. For P-type semiconductor the number of electrons increases with increase in temperature and hole are not much affected.
Ii) Forbidden energy gap: The energy required to break the covalent bond is called forbidden energy. This is the difference between energy level of CB and VB. This gap decreases with increase in temperature.
Iii) Mobility: the mobility decreases in intrinsic semiconductor with temperature. As the temperature increases there are a greater number of charge carriers with high energy, this results in collision of the charge carriers decreasing their mobility. The mobility for Extrinsic semiconductors decreases with increase in temperature.
Iv) Conductivity: The conductivity increases in intrinsic semiconductors with increase in temperature as there are a greater number of charge carriers at high temperature. For extrinsic semiconductor the conductivity decreases with temperature because the majority carrier concentration is almost constant, but mobility decreases.
Q3) List difference between N-type and P-type semiconductors?
Sol:

Q4) Explain energy band theory of crystals?
Sol: According to Neil Bohr’s theory of atomic structure all atoms have different energy levels. When two or more atoms are placed near to each other their energy levels get transformed to energy band structure. These energy bands are formed due to mutual interaction between the atoms caused by the electromagnetic force between them.
The below figure shows the energy bands of various energy levels. The electrons nearer to nucleus of interacting atom are having energy band 1 and those in outer orbit have E2, E3 so no.
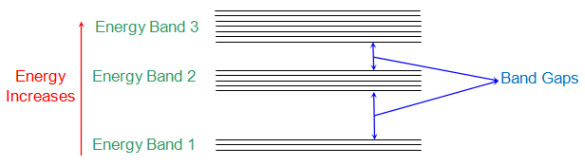
Fig: Energy band in crystal
Energy band in crystals can of different types which are
i) Valence Band: The electrons in the outer most orbit of an atom is present in this energy band. This is the highest energy band at room temperature. This band can be completely or partially filled.
Ii) Conduction Band: This is the lowest energy band containing electrons which are free from the attractive force of atom’s nucleus.
The Valence band has low energy level than conduction band. This is the reason that CB is above the VB separated by energy gap.
Q5) For a p-type Ge ni = 2.1x1019m-3 density of boron =3.2x1023 atoms m-3. The electron and hole mobility are 0.4 and 0.2 m2V-1s-1. Calculate conductivity before and after addition of boron?
Sol: Before adding boron
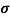 = q (p
= q (p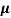 p+n
p+n n)
n)
= ni q (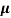 p+
p+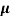 n) = 2.1x1019x1.6x10-19x(0.4+0.2)=2.016 S/m-1
n) = 2.1x1019x1.6x10-19x(0.4+0.2)=2.016 S/m-1
After adding boron
 = q p
= q p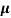 p
p
= 3.2x1023x1.6x10-19x0.2=10.24x103S/m-1
Q6) Determine the density of the donor atoms which have been added to the intrinsic Ge to make it a n-type material of resistivity 0.1x10-2ohm-m. Mobility of electron in n-type semiconductor is 0.5m2V-1s-1.
Sol: 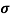 = q (n
= q (n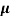 n)
n)
n= 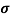 /q
/q n
n
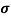 = 1/
= 1/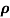
n= 1/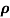 q
q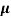 n = 1/(0.1x10-2x0.5x1.6x10-19) = 1.25x1022m-3
n = 1/(0.1x10-2x0.5x1.6x10-19) = 1.25x1022m-3
Q7) The intrinsic carrier density at room temperature in Ge is 3.4x1019m-3. If electron and hole mobilities are 0.4 and 0.2 m2V-1s-1 respectively. Calculate its resistivity?
Sol: 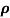 = 1/
= 1/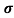
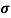 =ni q (
=ni q ( p+
p+ n) = 3.4x1019x 1.6x10-19(0.4+0.2) = 3.264S/m-1
n) = 3.4x1019x 1.6x10-19(0.4+0.2) = 3.264S/m-1
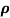 = 1/
= 1/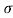 = 1/3.264 = 0.31ohm-m
= 1/3.264 = 0.31ohm-m
Q8) The electron and hole mobilities in In-Sb are 6 and 0.2 m2V-1s-1 respectively. At room temperature resistivity of In-Sb is 2x10-4ohm-m. Find intrinsic carrier concentration assuming the material to be intrinsic?
Sol: 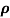 = 1/
= 1/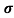
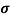 =ni q (
=ni q (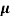 p+
p+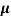 n)
n)
ni = 1/ 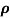 q (
q (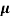 p+
p+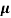 n) = 1/2x10-4x1.6x10-19(6+0.2) = 5.04x1021m-3
n) = 1/2x10-4x1.6x10-19(6+0.2) = 5.04x1021m-3
Q9) An electric field of 90Vm-1 is applied to n-type semiconductor. Determine the current density in sample given electron mobility 0.4 m2V-1s-1, n=5.9x1020m-3?
Sol: J=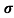 E
E
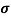 = nq
= nq n = 5.9x1020x1.6x10-19x0.4=37.36S/m-1
n = 5.9x1020x1.6x10-19x0.4=37.36S/m-1
J=3.39x103
Q10) Determine the density of the donor atoms which have been added to the intrinsic Ge to make it a n-type material of resistivity 0.5x10-2ohm-m. Mobility of electron in n-type semiconductor is 0.8m2V-1s-1.
Sol: 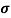 = q (n
= q (n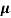 n)
n)
n= 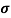 /q
/q n
n
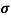 = 1/
= 1/
n= 1/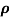 q
q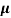 n = 1/(0.5x10-2x0.8x1.6x10-19) = 1.56x1021m-3
n = 1/(0.5x10-2x0.8x1.6x10-19) = 1.56x1021m-3