Unit 1
Unit 1
Concept of Double Entry System
Q1) Explain double entry system
Solution
For management to take future decision requires financial information. This is where accounting steps in that record, summaries, analyze all the business transaction.
Accounting is the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing, and interpreting the financial transactions and communicating the results to the persons interested in such information. Two methods for accounting are Single Entry System and Double Entry System. Mostly, we use Double Entry for better accounting purposes.
Double entry system
Double entry system of accounting deals with two aspects of every business transaction. In other words every transaction has two effects. For ex, a person buys a cold drink from a store and in return pays the money to shopkeeper for the cold drink. This transaction has two effects in terms of both buyer and seller. Buyer cash balance will decrease by the cost of purchase on the other hand he will acquire a cold drink. Seller will have one drink short but his cash balance will increase.
Accounting attempts to record both effect of transaction in the financial statement. This refers to double entry concept. Under this every transaction involves two parties , one party gives the benefit and other party receives it. It is also called dual entity of transaction.
Accounting records the two affects which are known as Debit (Dr) and Credit (Cr). Accounting system is based on the duality principal that for every Debit entry, there will always be an equal Credit entry.
Debit entries are ones that account for the following effects:
- Increase in assets
- Increase in expense
- Decrease in liability
- Decrease in equity
- Decrease in income
Credit entries are ones that account for the following effects:
- Decrease in assets
- Decrease in expense
- Increase in liability
- Increase in equity
- Increase in income
Accounting equation recorded in double entry are
Assets – Liabilities = Capital
Any increase in expense (Dr) will be offset by a decrease in assets (Cr) or increase in liability or equity (Cr) and vice-versa. The accounting equation will still be in equilibrium.
Examples of double entry
- Purchase of machine by cash
Machine account debited (increase in assets)
Cash account credited (decrease in assets)
2. Payment of utility bills
Utility expenses account debited (increase in expenses)
Cash account credited (decrease in assets)
3. Receipt of bank loans
Cash account credited (increase in assets)
Bank loan account credited (increase in liability)
Characteristic of double entry system
- Two parties – every business transaction involves two parties – debit and credit. According to the duality principal that for every Debit entry, there will always be an equal Credit entry.
2. Giver and receiver – every transaction must have giver and receiver. For ex, purchase a car, the buyer purchase a car from seller in return of cash – hence the buyer is the receiver and seller is the giver. When the seller receives the cash for the purchase made by buyer – the seller is the receiver of cash and buyer is the giver.
3. Exchange of equal amount – the amount of money of a transaction the party gives is equal to the amount the party receives.
4. Separate entity - the business enterprise and its owner are two separate independent entities. Thus, the business and personal transaction of its owner are separate.
5. Dual aspects – every transaction has two aspects – debit and credit. Debit is on the left side of account ledger and credit is on the right side of account ledger.
6. Result – under double entry system, total of debit is equal to total of credit.
7. Complete accounting system: Double entry system is a scientific and complete accounting system.
The process of keeping accounts under the double-entry system;
- Journal - It is called as daily book because transaction are recorded on day to day basis as and when takes place
2. Ledger - Ledger is the principal or primary book of accounts. The transactions are classified under appropriate heads, called accounts
3. Trial balance - Trial balance is a statement, prepared with debit and credit balances of ledger accounts to test the arithmetical accuracy of the books
4. Financial statement - The final accounts are prepared for ascertaining the operational results and financial position of the business. These are prepared with the help of trial balance.
Advantages of double entry system
- Through the trial balance, the system increase the accuracy of the accounting
- Profit and loss during the year can be calculated in detail
- The company keep accounting records which helps in controlling
- Using double entry system of accounting, current year can be compared with previous year to formulate the future course of action
- Under double entry system, the total amount of assets and liabilities can be ascertained
- Under the double-entry system, the accounts are maintained systematically thus it become easier to fix the price of the commodity
- The balance sheet ascertains the financial position of the business.
Q2)Explain accounting concepts and conventions
Accounting concepts defines the assumption on the basis of which financial statement of a business entity is prepared. Concepts are those basic assumption and condition which for the basis upon which the accountancy has been laid.
Accounting principles
- They should be based on real assumption
- They must be simple, understandable and explanatory
- They must be followed consistently
- They should be able to reflect future predictions
- They should be informational to users
Accounting convention emerges out of accounting practices, commonly known as accounting principle, adopted by various organizations over a period of time. Accounting bodies may change any of the convention to improve the quality of accounting information.
Accounting concepts
- Entity concept – Entity concept states that the business enterprise and its owner are two separate independent entities. Thus, the business and personal transaction of its owner are separate.
For example, when owner invests money in the business, it is recorded as liability of the business to the owner. Similarly, when owner takes money from business for personal use, it is not treated as business expenses.
2. Money measurement concept – This concept assumes that all business transaction must be in terms of money. Thus transactions expressed in terms of money are recorded in the books of account.
For example – sale of good, rent paid are expressed in money so recorded in books of account. Whereas sincerity, loyalty are not recorded in books of account because they cannot be measured in monetary terms.
3. Going concern concept - This concept states that a business firm will continue to carry on its activities for an indefinite period of time. It means every business entity has continuity of life and will not be resolved in the near future.
4. Accounting period concept –All transaction are recorded in the books of account on the assumption that profits on these transaction are to be ascertained for a specific period. Thus, this concept states that a balance sheet and profit and loss account should be prepared at regular interval
5. Accounting cost concept – It states that all assets are recorded in the books of account at their purchase price which include cost of acquisition, transportation and installation and not at its market price.
For example – fixed assets like building, machinery are recorded at purchase price
6. Dual aspect concept – dual aspect is the basic principle of accounting. It provides the basis of recording accounting transactions. For every credit, a corresponding debit is made. Therefore the transaction should be recorded in two places.
7. Matching concept – this concept states that revenue and expenses incurred to earn profit must belong to the same accounting period. So once the revenue is realized, the next step is to allocate it to the relevant accounting period. It is very helpful for the investors to know the exact amount of profit and loss in the business
8. Realization concept – the concept states that, revenue is realized at the time when goods and services are actually delivered. An advance or fee paid is not considered a profit until the goods or services are delivered to the buyer.
9. Accrual concept – accrual concept means the amount of money is yet to be paid or received at the end of the accounting period. It means cash received or not and expenses paid or not, both the transaction will be recorded in the books of account in that accounting period
Accounting convention
- Consistency – consistency means same accounting principles should be uses year after year, so that same standards are applied to calculate profit and loss. While comparing over a period of time a meaningful conclusion can be drawn. If a different accounting principles are used , then it cannot be comparable
2. Full disclosure – It includes all material and relevant facts concerning financial statements should be fully disclosed. Full disclosure means full, fair, adequate disclosure of accounting information. Parties like investor, lender, etc are interested in the financial information, so the business entity should disclose full and fair information.
3. Materiality – it means all material fact should be recorded in accounting. Accountant should record important data and leave insignificant data. Material fact influence the decision of the users.
4. Conservatism – the conservatism is based on the principle that “Anticipate no profit, but provide all the possible losses”. The main objective is to show minimum profit. Profit should not be over estimated. It is an unfair convention, it will lead to reduction in the capital of an enterprise
Q3)Explain Sub division of journal
Definition
In a large business concern a journal is divided into parts so that several clerk could work at the same time. This is known as subdivision of journal.
Objectives of subdivision
- To simplify the recording of business transaction in the book of original entry
- It enables the transaction are classified according to their name.
- To make it easier to locate any transaction recorded in the book of original entry
- Recording the transaction in the books of account result in reducing the chances of error and fraud
Advantages
- The transaction recorded in the sub division books is not bulky and hence there will be no difficulty in handling them.
- Accounting work is divided into large number of employees so the work is done nicely and promptly
- Because of division of labour, efficiency of employees increases
- The chances of fraud is minimised as the transaction are recorded in the books.
Types of subdivision of journals
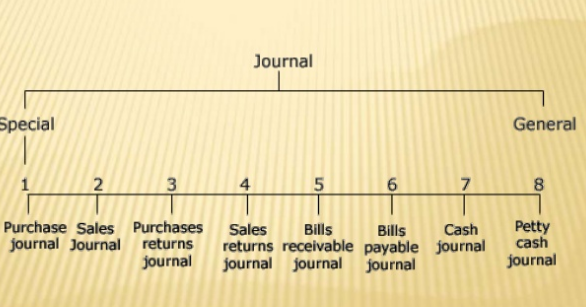
Special journal – special journal is popularly known as the subsidiary book. The transaction are recorded in regular basis and in chronological order. Special journal are divided into eight groups as follows
- Purchase book – purchase book is also called as purchase journal, invoice book, bought day book which records all credit purchase made by the organisation. Cash purchase of book are not recorded in the purchase book, they are recorded in cash books. Credit purchase other than goods such as stationary item are not recorded in the purchase book
Format
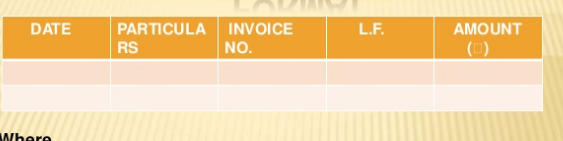
Where, data – represents when the transaction took place
Particulars- it includes the name of the seller and the particulars of goods purchased
Invoice no – reveals the serial number of the inward invoice
LF – This column represent the page number of supplier account in ledger books
Amount – amount column represent the price of the goods
2. Sales books – this book is also known as sales day book or sales journal. It records all credit sales of goods made by the organisation during a specified period of time.
Cash sales, cash and credit sales of assets are not recorded in the books. The entries are recorded on the basis of invoice issued to the customers
Format

Where,
Date – represents when the transaction took place
Particulars- it includes the name of the customer and the particulars of goods sold
Invoice no – reveals the serial number of the outward invoice
LF – This column represent the page number of supplier account in ledger books
Amount – amount column represent the price of the goods
3. Purchase return books – this books records all the return of goods to the supplier by the business. It is also called returns outward book or purchases returns day book. Goods may be returned due to many reasons such as not up to sample or because they are damaged etc. When good are returned to the supplier then an intimation is sent which is known as debit note
Format

Where,
Date – represents when the transaction took place
Particulars- it includes the name of the purchaser and the particulars of goods purchased
Debit note no – records the serial number of each debit note
LF – This column represent the page number of supplier account in ledger books
Amount – amount column represent the price of the goods
4. Sales returns books – this book records all the return of goods by the customers to the business. Sales returns book is also called returns inwards book. Customers who return goods should be sent a credit note by the business. This credit note means note sent by the business to another person showing the amount credited to the account of the later.

Format
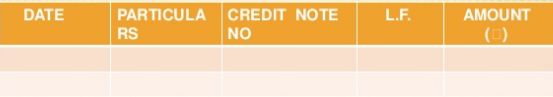
Where,
Date – represents when the transaction took place
Particulars- it includes the name of the purchaser and the particulars of goods purchased
Credit note no – records the serial number of each credit note
LF – This column represent the page number of supplier account in ledger books
Amount – amount column represent the price of the goods
5. Bills receivable book – bills receivable books is used to record the bills received from debtor. The details of the bill received from the debtors are recorded in the bills receivable books. The bills receivable are drawn when the seller makes credit sale to the business.
Format

Where,
Date – represents when the transaction took place
From whom received column - it includes the name of the person from whom the amount is to be recived.
Term column – how much time
Due date column – last date
LF – This column represent the page number of supplier account in ledger books
Amount – amount column represent the price of the goods
6. Bills payable book – bills payable book is used to record bill accepted by us and payable by the business. When a bill drawn by our creditor is accepted particulars of the same are recorded in this book. In the ledger the amount of each person whose bill has been accepted is debited with the bill amount. The total of bills accepted is credited to the bills payable account ledger.
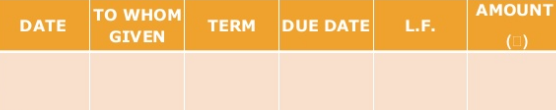
Where,
Date – represents when the transaction took place
To whom given - it includes the name of the person from whom the amount is to be paid.
Term column – how much time
Due date column – last date
LF – This column represent the page number of supplier account in ledger books
Amount – amount column represent the price of the goods
7. Cash book – a separate book is kept to record cash transaction refers to cashbook. The function of cash book is to keep records of all cash transaction.
Types of cash book
- Simple cash book - it record only cash transactions. All cash received are entered on the debit side, and all cash paid are entered on the credit side.
Format –
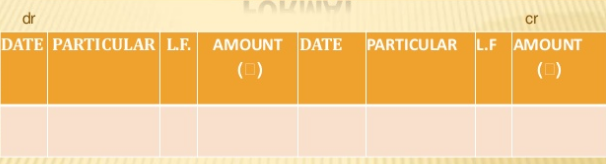
Where,
Date – represents when the transaction took place
Particulars- it includes cash transaction particulars
LF – This column represent the page number of supplier account in ledger books
Amount – amount column represent the price of the goods
b. Double cash book – it record cash as well as bank transactions. It is also called as two column cash book. The cash column is used to record all cash transactions and bank column used to record all receipts and payments made by checks and works as a bank account
Format
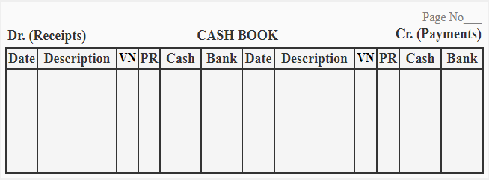
Where,
Date – represents when the transaction took place
Particulars- it includes cash and bank transaction particulars
Cash – records cash transaction
Bank – records transaction made on cheque or which are held via bank
c. Triple cash book – it record cash, bank and purchase discount and sales discount. It is also called as three column cash book
Format
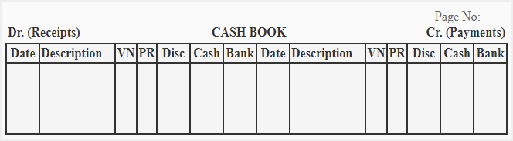
Where,
Date – represents when the transaction took place
Particulars- it includes cash and bank transaction particulars
Cash – records cash transaction
Bank – records transaction made on cheque or which are held via bank
Discount – shows discount allowed and received
d. Petty cash book - A petty cash book to record small day to day cash expenditures. For ex, stationary, cleaning charges, postages, etc
The petty cash book is defined as relatively small amount of cash kept at hand for making quick payments for miscellaneous small expenses in the business concern.
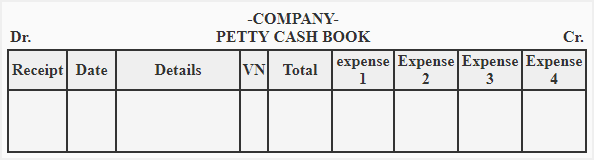
General journal
The transaction which do not fall within the scope of the above mentioned book are recorded in general journal. For ex, purchase of assets on credit, depreciation of assets, bad debts, etc. It is also known as modern journal, journal proper, principal journal.
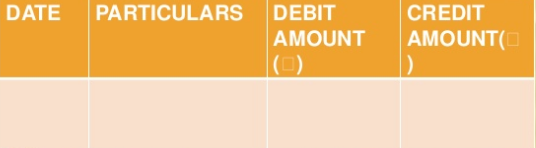
Where,
Date – represents when the transaction took place
Particulars- it includes all transaction particulars
Debit column – shows amount received
Credit column – shows amount paid
Q4)Explain preparation of ledger
Ledger
- Definition
“Ledger is the permanent storehouse of all the transactions” Field house Arther
- Ledger is the principal or primary book of accounts
- The transactions are classified under appropriate heads, called accounts
- The accounts contain the condensed and summarized record of all the related transactions
- It is the basis of preparing final account.
- Ledgers provide information of
- Debtors and creditors
- Purchase, sales and return
- Type of assets and value of assets
- Expenses and income
- Cash and bank balance
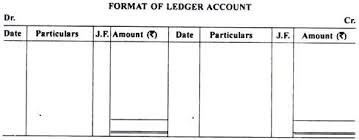
- Date on which the transaction taken place
- Particulars – on debit side, the account is written with prefix “To”. On the credit side, the account id written with prefix “By”.
- JF is the page number of journal provided for cross reference.
- The amount written in journal is written in ledger
Characteristics of ledger accounts
- The account has two sides left side of the account is debit and right side of the account is credit.
- Debit side record all the debit attitudes of transactions and credit side record all the credit attitudes of transactions
- Difference between the two sides are represented as balance. The debit balance shows excess of debit over credit side. The credit balance shows excess of credit over debit side.
- In the month/year end the excess balance is written over the closing balance at the end of the month date
- At the end, closing balance are forwarded as the beginning balance next year.
How double entry works in ledger
A ledger implemented in double entry book keeping method means each transaction make at least two account. Each transaction has debit and credit account. Left side shows debit entry and right side shows credit entry.
For better understanding lets use a n example of ledger accounts
Transaction
On jan1 2015, abc company sold to customers for cash 25,000.
The journal entry and ledger posting are as follows

In the above journal entry, the debit part is cash account and the credit part is sales account. All journal entries are similarly posted to accounts in general ledger.
Examples 2
Apple limited sell 20 kilos apple at rs. 100per kilo on 8 august 2020
Journal entry
Cash A/C Dr20000
To Sales A/C20000
Ledger account
Cash A/C | |||||
Dr. |
| Cr. | |||
Date | Description | Amount (Rs) | Date | Description | Amount (Rs) |
8.8.2020 | To Sales | 20000 |
|
|
|
Similarly, in Sales account, the entry will reflect as follows
Sales A/C | |||||
Dr. |
| Cr. | |||
Date | Description | Amount (Rs) | Date | Description | Amount (Rs) |
|
|
| 8.8.2020 | By Cash | 20000 |
Q5)Explain preparation of trial balance
Trial balance
- Definition
“Trial balance is a statement, prepared with debit and credit balances of ledger accounts to test the arithmetical accuracy of the books”. J.R. Batliboi
- It is the statement from which final accounts are prepared
- It is the list of balances of all the ledger accounts
- The total of debit and credit column of trial balance must tally
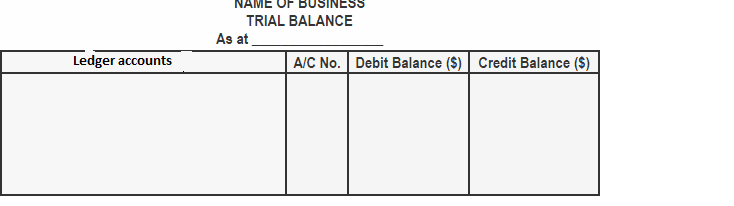
How does trial balance work?
The trial balance is the statement of all debits and credits. Business man prepares trial balance at the end of the reporting period regularly to ensure that the entries are mathematically correct in the books of account. The total of trial balance should be equal. In case the debit and credit does not match it means there is an error. For example, the accountant may have recorded an account or classified a transaction incorrectly.
Preparation of trial balance
- Before starting the trial balance all the ledger accounts should be closed. The ledger balance is provided by the difference between the sum of all the debit entries and the sum of all the credit entries
- Prepare trial balance worksheet. The column headers should be for the account number, account name and the corresponding columns for debit and credit balances.
- Every ledger account is transferred to the trial balance worksheet. The account name and number along with the account balance in the appropriate debit or credit column
- Add up the debit and credit column. In an error free trial balance the total should be same. Trial balance are closed when the total are same
- Accountants have to locate and rectify the errors, if there is a difference,
A trial balance looks like
All the account title are the closing balance of ledger account
ABC LTD - Trial Balance as at 31 December 2019 | ||
| Debit | Credit |
Account Title | Rs | Rs |
Share Capital | - | 15,000 |
Furniture & Fixture | 5,000 | - |
Building | 10,000 | - |
Creditor | - | 5,000 |
|
|
|
Debtors | 3,000 | - |
Cash | 2,000 | - |
Sales | - | 10,000 |
Cost of sales | 8,000 | - |
General and Administration Expense | 2,000 | - |
Total | 30,000 | 30,000 |
Q6)Explain preparation of trial balance and ledger
Ledger
- Definition
“Ledger is the permanent storehouse of all the transactions” Field house Arther
- Ledger is the principal or primary book of accounts
- The transactions are classified under appropriate heads, called accounts
- The accounts contain the condensed and summarized record of all the related transactions
- It is the basis of preparing final account.
- Ledgers provide information of
- Debtors and creditors
- Purchase, sales and return
- Type of assets and value of assets
- Expenses and income
- Cash and bank balance

- Date on which the transaction taken place
- Particulars – on debit side, the account is written with prefix “To”. On the credit side, the account id written with prefix “By”.
- JF is the page number of journal provided for cross reference.
- The amount written in journal is written in ledger
Characteristics of ledger accounts
- The account has two sides left side of the account is debit and right side of the account is credit.
- Debit side record all the debit attitudes of transactions and credit side record all the credit attitudes of transactions
- Difference between the two sides are represented as balance. The debit balance shows excess of debit over credit side. The credit balance shows excess of credit over debit side.
- In the month/year end the excess balance is written over the closing balance at the end of the month date
- At the end, closing balance are forwarded as the beginning balance next year.
How double entry works in ledger
A ledger implemented in double entry book keeping method means each transaction make at least two account. Each transaction has debit and credit account. Left side shows debit entry and right side shows credit entry.
For better understanding lets use a n example of ledger accounts
Transaction
On jan1 2015, abc company sold to customers for cash 25,000.
The journal entry and ledger posting are as follows
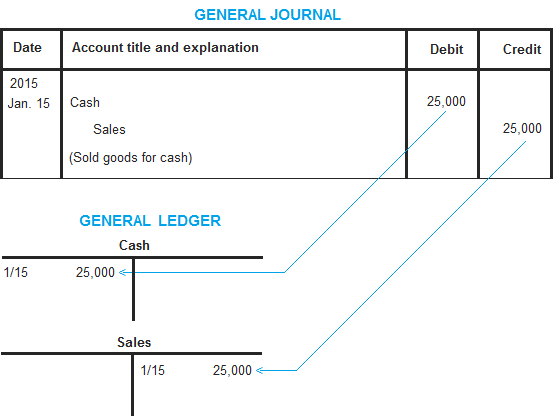
In the above journal entry, the debit part is cash account and the credit part is sales account. All journal entries are similarly posted to accounts in general ledger.
Examples 2
Apple limited sell 20 kilos apple at rs. 100per kilo on 8 august 2020
Journal entry
Cash A/C Dr20000
To Sales A/C20000
Ledger account
Cash A/C | |||||
Dr. |
| Cr. | |||
Date | Description | Amount (Rs) | Date | Description | Amount (Rs) |
8.8.2020 | To Sales | 20000 |
|
|
|
Similarly, in Sales account, the entry will reflect as follows
Sales A/C | |||||
Dr. |
| Cr. | |||
Date | Description | Amount (Rs) | Date | Description | Amount (Rs) |
|
|
| 8.8.2020 | By Cash | 20000 |
Trial balance
- Definition
“Trial balance is a statement, prepared with debit and credit balances of ledger accounts to test the arithmetical accuracy of the books”. J.R. Batliboi
- It is the statement from which final accounts are prepared
- It is the list of balances of all the ledger accounts
- The total of debit and credit column of trial balance must tally
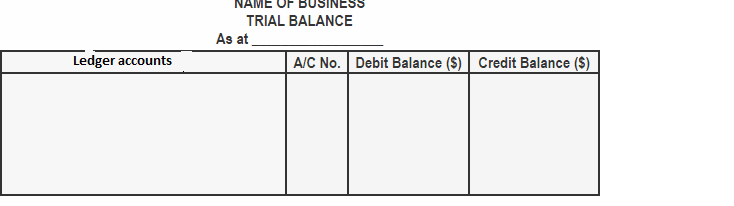
How does trial balance work?
The trial balance is the statement of all debits and credits. Business man prepares trial balance at the end of the reporting period regularly to ensure that the entries are mathematically correct in the books of account. The total of trial balance should be equal. In case the debit and credit does not match it means there is an error. For example, the accountant may have recorded an account or classified a transaction incorrectly.
Preparation of trial balance
- Before starting the trial balance all the ledger accounts should be closed. The ledger balance is provided by the difference between the sum of all the debit entries and the sum of all the credit entries
- Prepare trial balance worksheet. The column headers should be for the account number, account name and the corresponding columns for debit and credit balances.
- Every ledger account is transferred to the trial balance worksheet. The account name and number along with the account balance in the appropriate debit or credit column
- Add up the debit and credit column. In an error free trial balance the total should be same. Trial balance are closed when the total are same
- Accountants have to locate and rectify the errors, if there is a difference,
A trial balance looks like
All the account title are the closing balance of ledger account
ABC LTD - Trial Balance as at 31 December 2019 | ||
| Debit | Credit |
Account Title | Rs | Rs |
Share Capital | - | 15,000 |
Furniture & Fixture | 5,000 | - |
Building | 10,000 | - |
Creditor | - | 5,000 |
|
|
|
Debtors | 3,000 | - |
Cash | 2,000 | - |
Sales | - | 10,000 |
Cost of sales | 8,000 | - |
General and Administration Expense | 2,000 | - |
Total | 30,000 | 30,000 |
Q7) Explain revenue recognition
Meaning: - Revenue means gross inflow of cash, receivable or other consideration arising in the course of ordinary activities of an enterprise such as
a) Sale of goods.
b) Rendering of services.
c) Use of the enterprises resources by other, yielding interest, dividend and royalties.
Timing: - Revenue should be recognized at the time of sale of rendering of services.
Transaction Excluded: - AS 9 is not applicable to the following:
a) Revenue arising from construction contracts.
b) Revenue arising from hire, purchase, lease agreements.
c) Revenue arising from government grants and subsidies.
d) Revenues of insurance companies arising from insurance contracts.
Sale of Goods: - As per AS 9 revenue from sale of goods is recorded when
a) Seller has transferred the ownership of goods to the buyer for a price.
b) All significant risks and rewards of ownership have been transferred to the buyer.
c) Seller does not retain any effective control of ownership of the transferred goods.
d) There is no significant uncertainty in collection of amount of consideration.
Rendering of Services: - Revenue from service is recorded as the service is performed. It is measured by 2 methods.
a) Completer Service Contract Method: - Revenue is recorded on completion of the contract i.e. when rendering of service is complete.
b) Propionate Completion Method: - Revenue is recorded proportionately i.e. in proportion to the degree of completion of services under a contract.
Effect of Uncertainties: - Revenue is recorded only when there is no significant uncertainty in collection of amount of consideration. Revenue recognition is if the ultimate collection is uncertain.
When uncertainty of collection of revenue arises after the revenue recognition it is better to make provision for the uncertainty in collection.
Disclosure: - If revenue recognition is postponed, then the circumstances necessitating the postponement must be disclosed.
Q8)Explain accounting concepts
Accounting concepts defines the assumption on the basis of which financial statement of a business entity is prepared. Concepts are those basic assumption and condition which for the basis upon which the accountancy has been laid.
Accounting concepts
- Entity concept – Entity concept states that the business enterprise and its owner are two separate independent entities. Thus, the business and personal transaction of its owner are separate.
For example, when owner invests money in the business, it is recorded as liability of the business to the owner. Similarly, when owner takes money from business for personal use, it is not treated as business expenses.
2. Money measurement concept – This concept assumes that all business transaction must be in terms of money. Thus transactions expressed in terms of money are recorded in the books of account.
For example – sale of good, rent paid are expressed in money so recorded in books of account. Whereas sincerity, loyalty are not recorded in books of account because they cannot be measured in monetary terms.
3. Going concern concept - This concept states that a business firm will continue to carry on its activities for an indefinite period of time. It means every business entity has continuity of life and will not be resolved in the near future.
4. Accounting period concept –All transaction are recorded in the books of account on the assumption that profits on these transaction are to be ascertained for a specific period. Thus, this concept states that a balance sheet and profit and loss account should be prepared at regular interval
5. Accounting cost concept – It states that all assets are recorded in the books of account at their purchase price which include cost of acquisition, transportation and installation and not at its market price.
For example – fixed assets like building, machinery are recorded at purchase price
6. Dual aspect concept – dual aspect is the basic principle of accounting. It provides the basis of recording accounting transactions. For every credit, a corresponding debit is made. Therefore the transaction should be recorded in two places.
7. Matching concept – this concept states that revenue and expenses incurred to earn profit must belong to the same accounting period. So once the revenue is realized, the next step is to allocate it to the relevant accounting period. It is very helpful for the investors to know the exact amount of profit and loss in the business
8. Realization concept – the concept states that, revenue is realized at the time when goods and services are actually delivered. An advance or fee paid is not considered a profit until the goods or services are delivered to the buyer.
9. Accrual concept – accrual concept means the amount of money is yet to be paid or received at the end of the accounting period. It means cash received or not and expenses paid or not, both the transaction will be recorded in the books of account in that accounting period
Q9)Explain preparation of journal
- Definition
“The journal is a book of original entry in which transactions are recorded not provided for in specialized journals”
Eric L. Kohler
- The word journal has been derived from French word ‘Jour’ which means day. Thus, journal means daily record
- Entries in journal are recorded in chronological order, as and when the business transaction occurs
- It is called as daily book because transaction are recorded on day to day basis as and when takes place
- Entry in journal is followed with narration which describes briefly the true nature of transaction
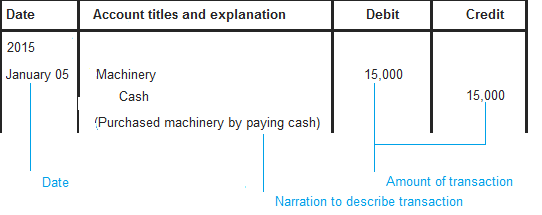
Proforma of a Journal

- Date/ S.No: date or serial number is the first column of Journal. The transaction record date or its serial number is updated in this column.
- Particulars: particulars are the second column of Journal. This column is updated with the particulars of business transactions that is related to the description of account type.
- Ledger Folio: The third column of Journal is Ledger Folio number where the journal entry is posted.
- Amount (Dr.) : The fourth column of Journal is used to update the debit amount of transaction.
- Amount (Cr.): The fifth column of Journal is used to update the credit amount of transaction.
Rules of double entry system
- Personal accounts – Account related to human beings and artificial person such as Anils account, accounts of firms, hospital, etc
RULE
Debit the receiver and credit the giver
2. Real accounts – accounts which can be touched, felt such as plant, building, cash, etc. It also includes account which cannot be touched but are measured in terms of rupee such as goodwill, etc
RULE
Debit what comes in and credit what goes out
3. Nominal account – account relate to business gains, loss, incomes and expenses such as wages account, interest account, etc
RULE
Debit all expenses and losses. Credit all incomes and gains
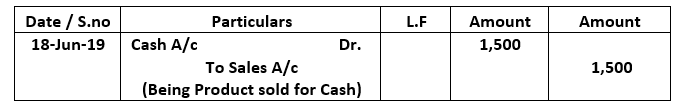
Examples of journal entry
A firm sold its product at 1500 and received full amount in cash
Q10)Explain advantages and process of double entry system
Double entry system of accounting deals with two aspects of every business transaction. In other words every transaction has two effects. For ex, a person buys a cold drink from a store and in return pays the money to shopkeeper for the cold drink. This transaction has two effects in terms of both buyer and seller. Buyer cash balance will decrease by the cost of purchase on the other hand he will acquire a cold drink. Seller will have one drink short but his cash balance will increase.
Accounting attempts to record both effect of transaction in the financial statement. This refers to double entry concept. Under this every transaction involves two parties , one party gives the benefit and other party receives it. It is also called dual entity of transaction.
Accounting records the two affects which are known as Debit (Dr) and Credit (Cr). Accounting system is based on the duality principal that for every Debit entry, there will always be an equal Credit entry.
Debit entries are ones that account for the following effects:
- Increase in assets
- Increase in expense
- Decrease in liability
- Decrease in equity
- Decrease in income
Credit entries are ones that account for the following effects:
- Decrease in assets
- Decrease in expense
- Increase in liability
- Increase in equity
- Increase in income
Accounting equation recorded in double entry are
Assets – Liabilities = Capital
Any increase in expense (Dr) will be offset by a decrease in assets (Cr) or increase in liability or equity (Cr) and vice-versa. The accounting equation will still be in equilibrium.
Examples of double entry
- Purchase of machine by cash
Machine account debited (increase in assets)
Cash account credited (decrease in assets)
2. Payment of utility bills
Utility expenses account debited (increase in expenses)
Cash account credited (decrease in assets)
3. Receipt of bank loans
Cash account credited (increase in assets)
Bank loan account credited (increase in liability)
Characteristic of double entry system
- Two parties – every business transaction involves two parties – debit and credit. According to the duality principal that for every Debit entry, there will always be an equal Credit entry.
2. Giver and receiver – every transaction must have giver and receiver. For ex, purchase a car, the buyer purchase a car from seller in return of cash – hence the buyer is the receiver and seller is the giver. When the seller receives the cash for the purchase made by buyer – the seller is the receiver of cash and buyer is the giver.
3. Exchange of equal amount – the amount of money of a transaction the party gives is equal to the amount the party receives.
4. Separate entity - the business enterprise and its owner are two separate independent entities. Thus, the business and personal transaction of its owner are separate.
5. Dual aspects – every transaction has two aspects – debit and credit. Debit is on the left side of account ledger and credit is on the right side of account ledger.
6. Result – under double entry system, total of debit is equal to total of credit.
7. Complete accounting system: Double entry system is a scientific and complete accounting system.
The process of keeping accounts under the double-entry system;
- Journal - It is called as daily book because transaction are recorded on day to day basis as and when takes place
2. Ledger - Ledger is the principal or primary book of accounts. The transactions are classified under appropriate heads, called accounts
3. Trial balance - Trial balance is a statement, prepared with debit and credit balances of ledger accounts to test the arithmetical accuracy of the books
4. Financial statement - The final accounts are prepared for ascertaining the operational results and financial position of the business. These are prepared with the help of trial balance.
Advantages of double entry system
- Through the trial balance, the system increase the accuracy of the accounting
- Profit and loss during the year can be calculated in detail
- The company keep accounting records which helps in controlling
- Using double entry system of accounting, current year can be compared with previous year to formulate the future course of action
- Under double entry system, the total amount of assets and liabilities can be ascertained
- Under the double-entry system, the accounts are maintained systematically thus it become easier to fix the price of the commodity
- The balance sheet ascertains the financial position of the business.